Chapter 24: Urinary System Overview and Functions
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Urinary System
Organ system responsible for waste elimination.
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney for urine formation.
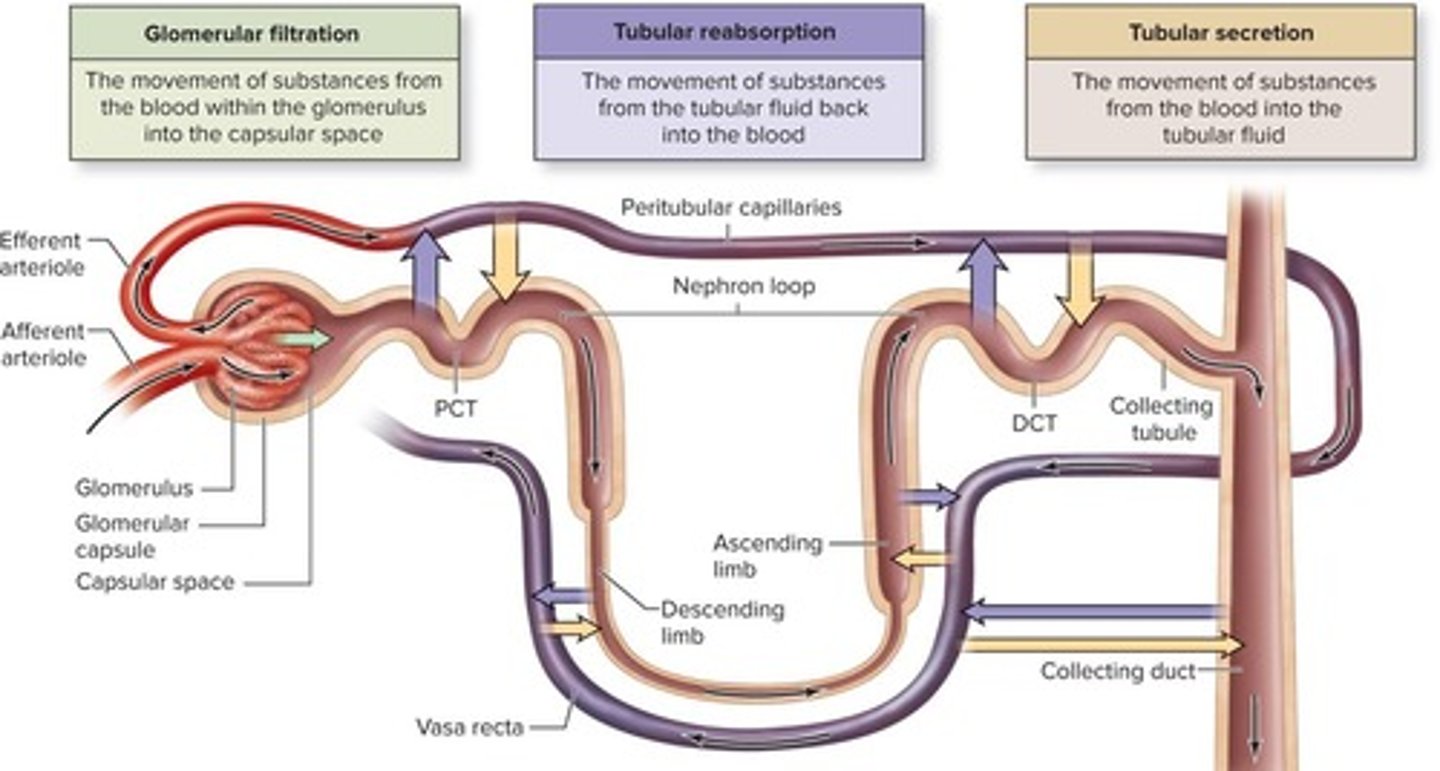
Micturition
The process of urination.
Urine Formation
Concentration of filtrate in the nephron.
Glomerular Filtration
First step in urine formation at glomerulus.
Glomerulus
Tuft of capillaries for blood filtration.
Afferent Arteriole
Supplies blood to the glomerulus.
Filtration Membrane
Thin structure filtering blood in glomerulus.
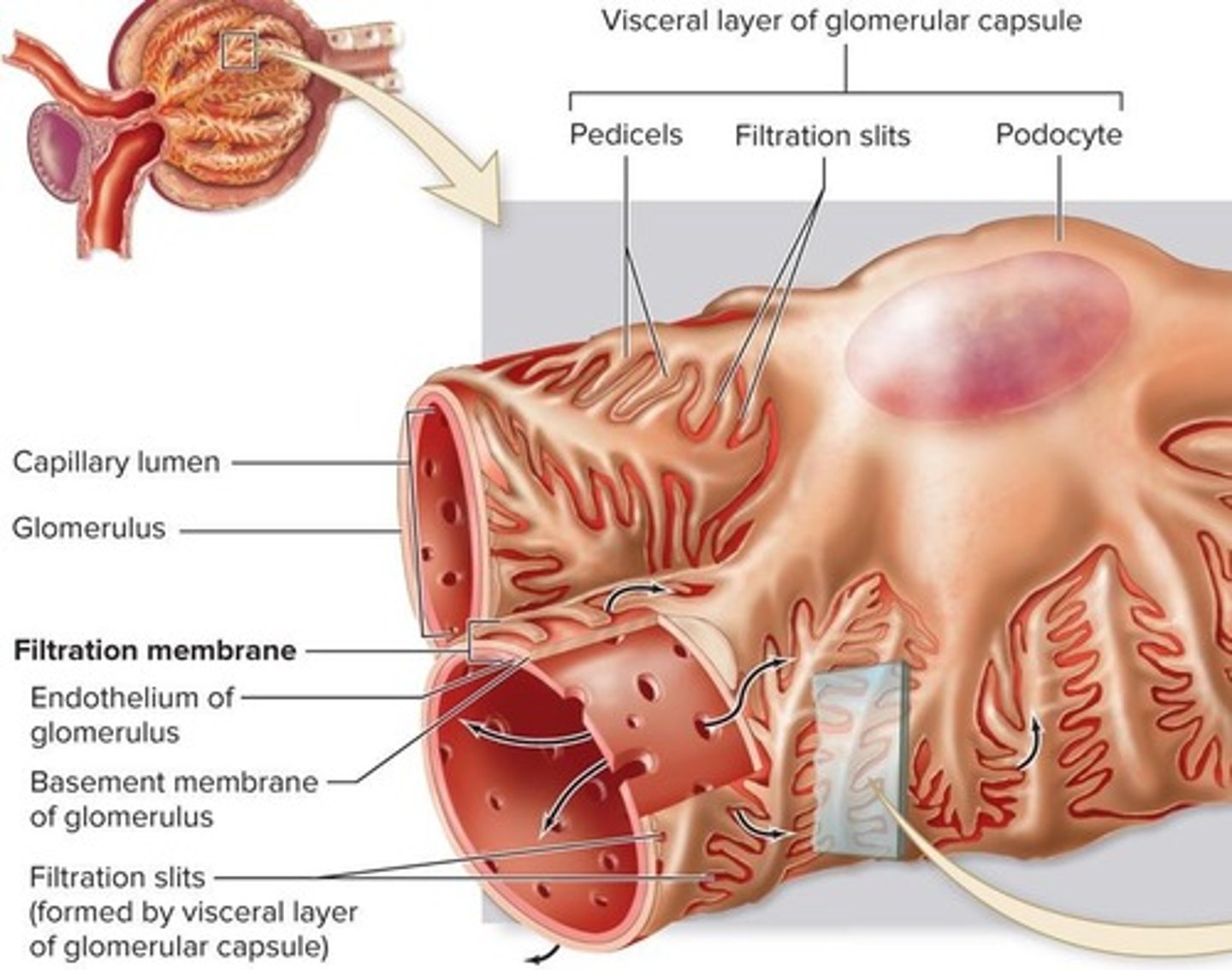
Endothelium
Inner layer of glomerular capillaries.
Basement Membrane
Prevents large proteins from exiting capillaries.
Visceral Layer
Podocytes wrapping around glomerular capillaries.
Capsular Space
Area where filtrate accumulates before PCT.
Filtrate Composition
Includes water, glucose, ions, urea, vitamins.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Volume of filtrate formed per minute.
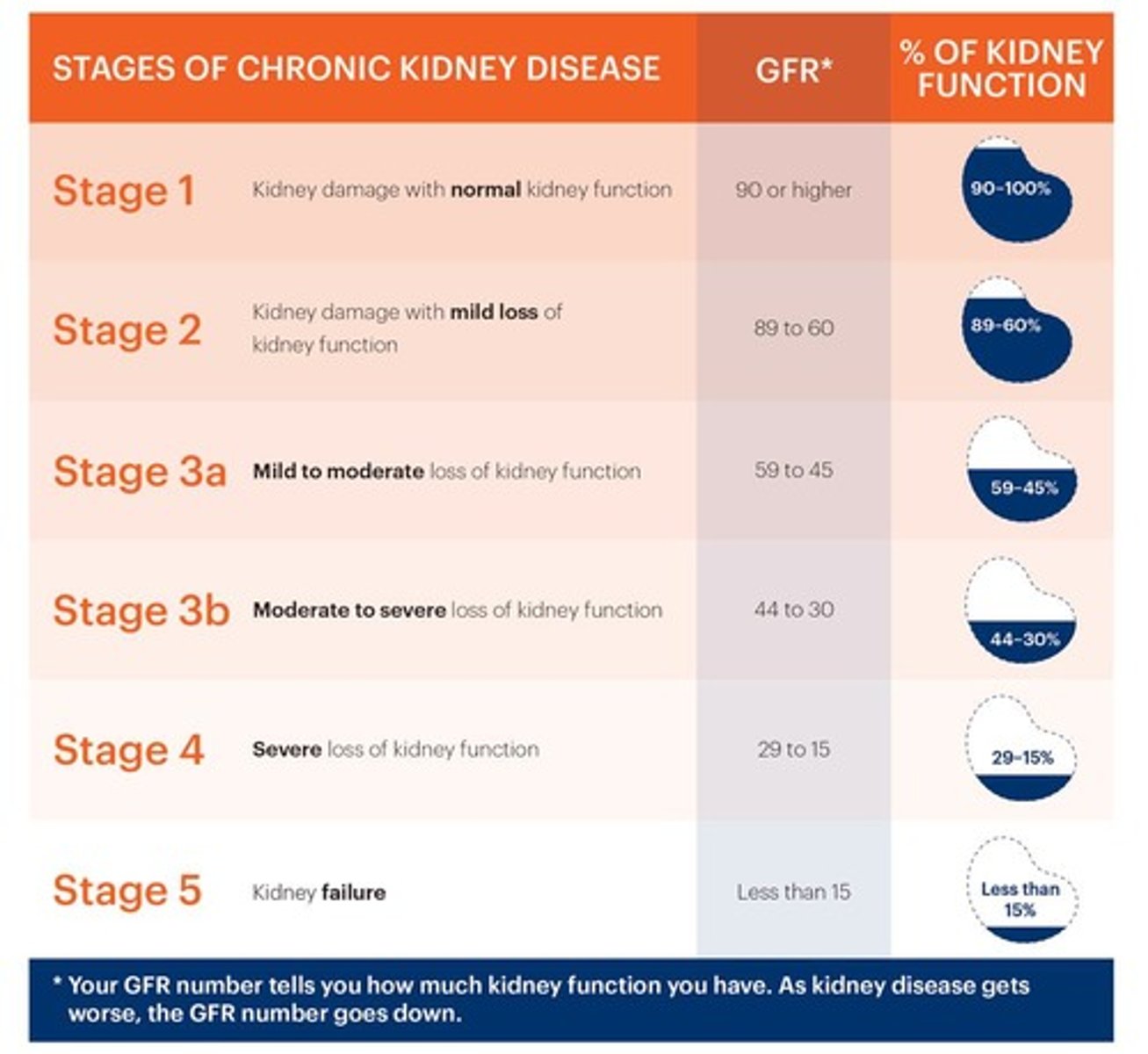
Normal GFR
Typically 120-125 mL/min in healthy kidneys.
Creatinine
By-product used to estimate GFR.
Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
Main factor regulating GFR.
Hydrostatic Pressure
Pushing force due to fluid presence.
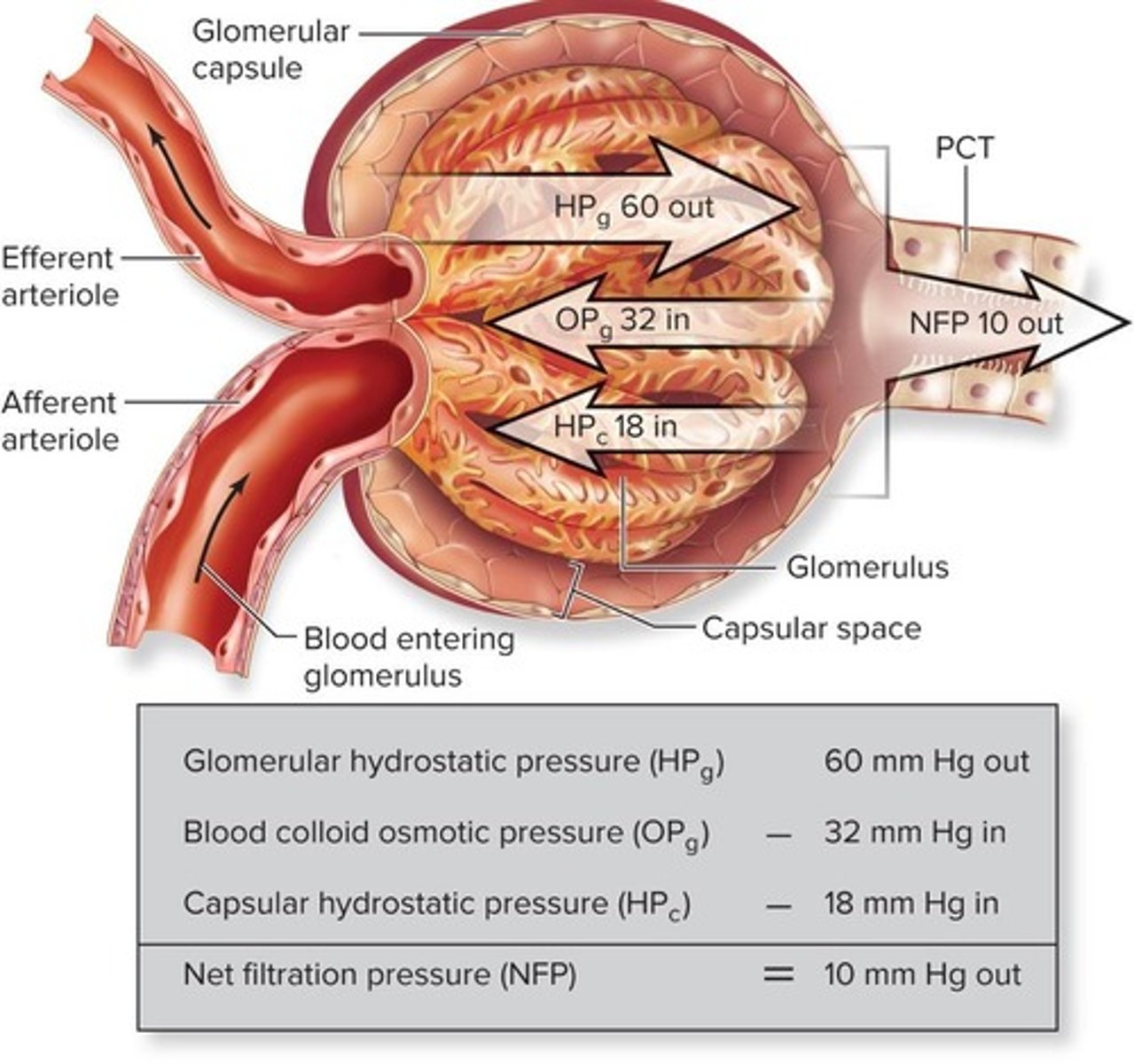
Osmotic Pressure
Pulling force due to solutes in solution.
NFP Equation
NFP = outward pressures - inward pressures.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of arterioles to regulate pressure.
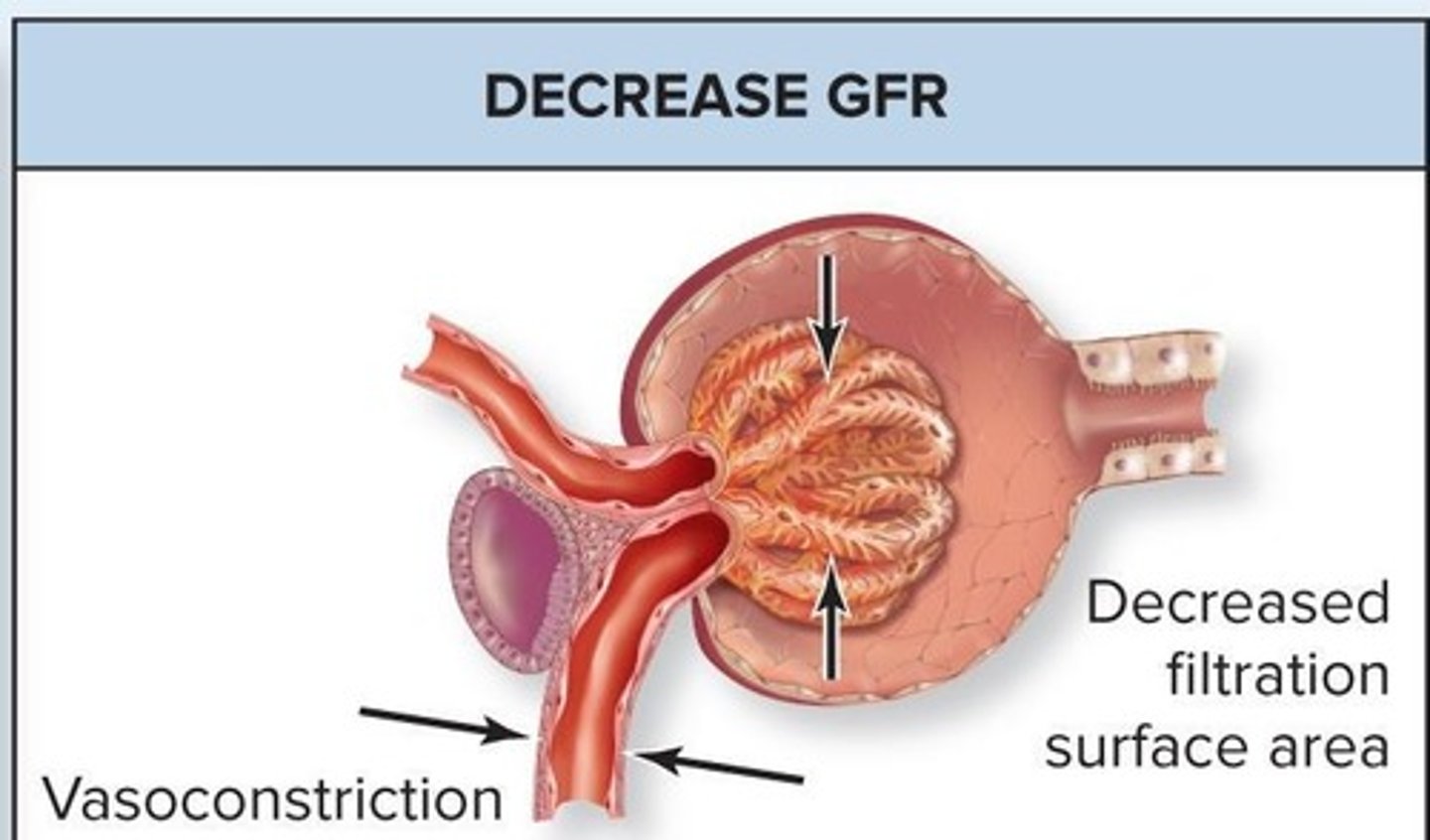
Vasodilation
Widening of arterioles to increase blood flow.
Myogenic Response
Intrinsic control mechanism regulating blood flow in kidneys.
Afferent Arteriole Vasodilation
Increases blood flow into glomerulus, enhancing GFR.
Afferent Arteriole Vasoconstriction
Decreases blood flow into glomerulus, reducing GFR.
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Response to NaCl concentration changes in glomerulus.
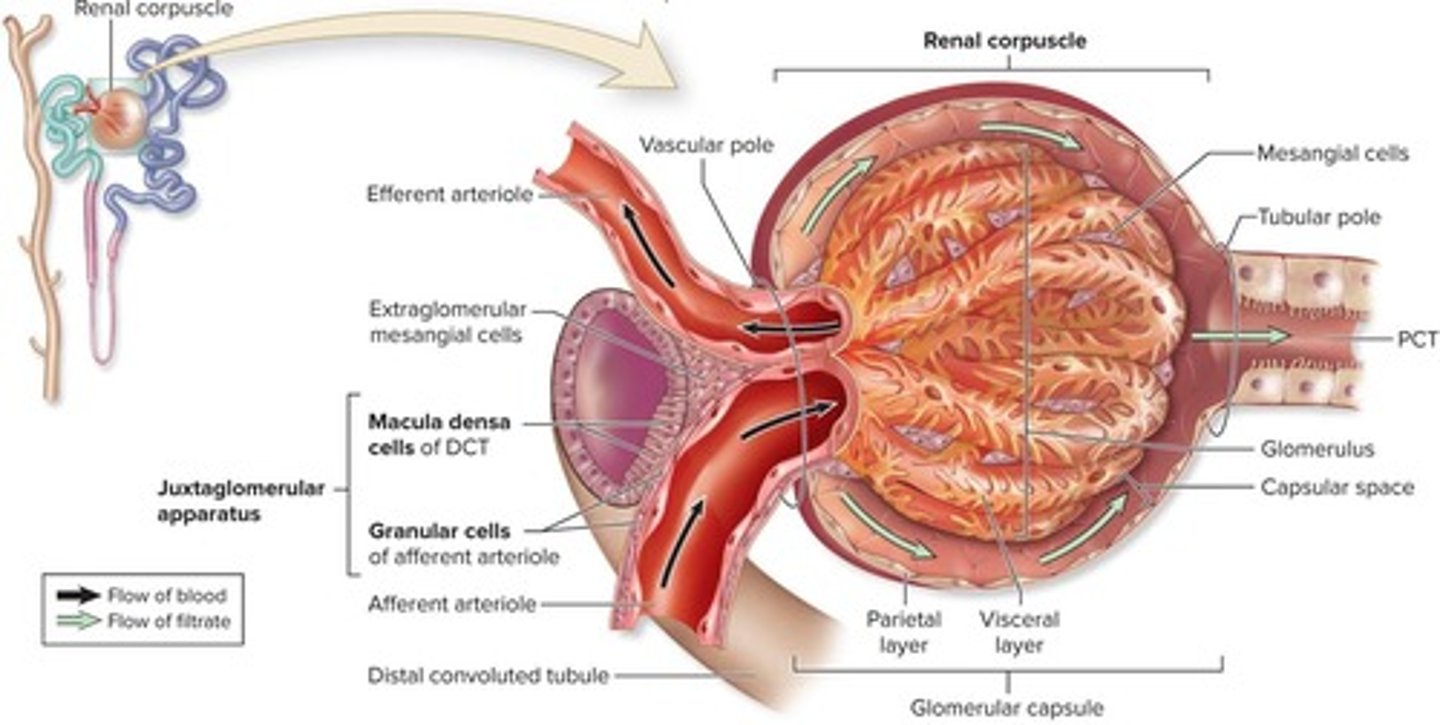
Macula Densa Cells
Detect sodium chloride levels, influencing JG cells.
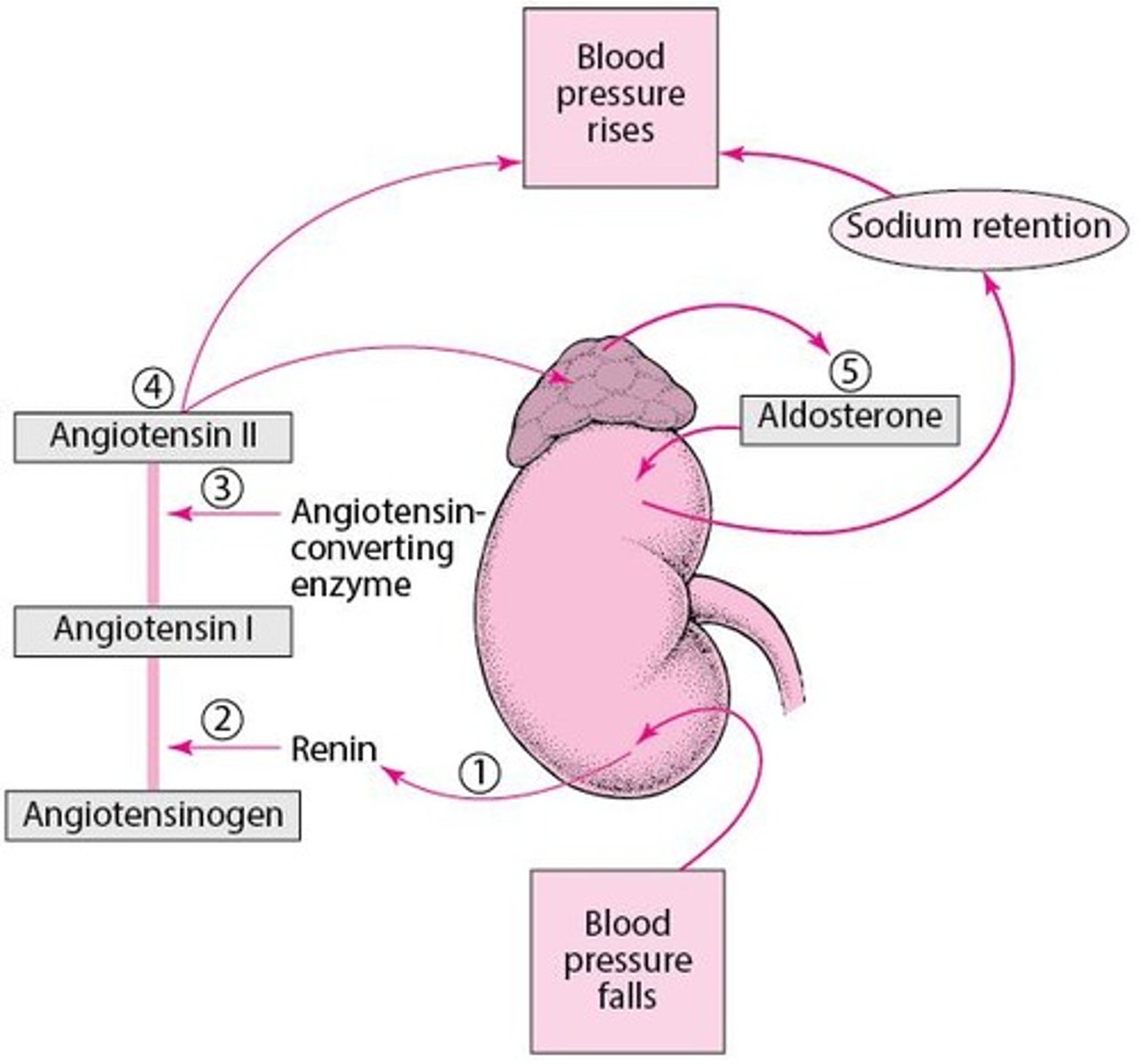
Juxtaglomerular Cells
Release renin affecting blood pressure and GFR.
Mesangial Cells
Regulate glomerular surface area for filtration.
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
Normal range for intrinsic controls: 80-180 mmHg.
Extrinsic Controls
Neural and hormonal regulation of GFR for homeostasis.
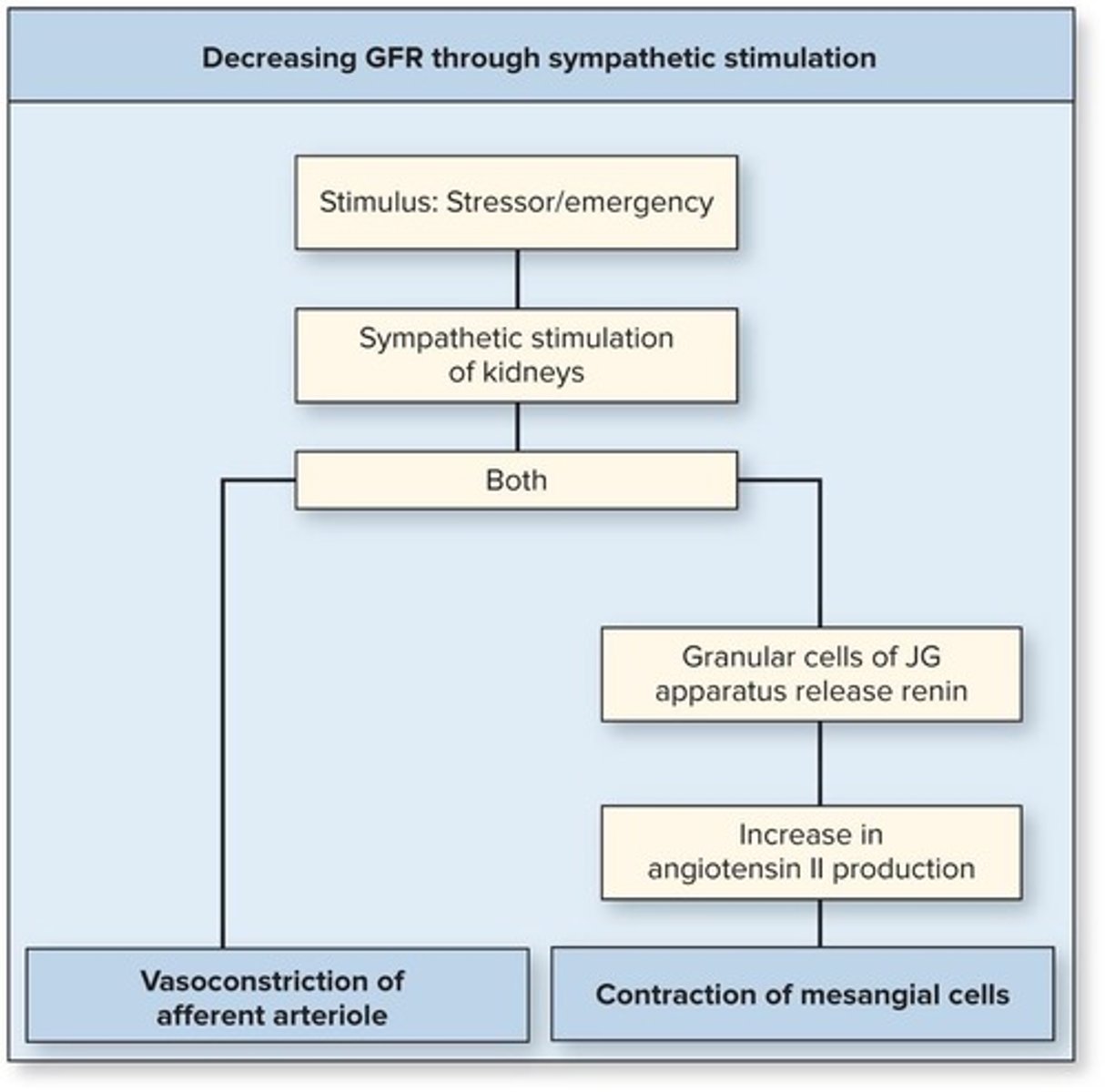
Sympathetic Nervous System
Stimulates renin release, decreasing GFR during low BP.
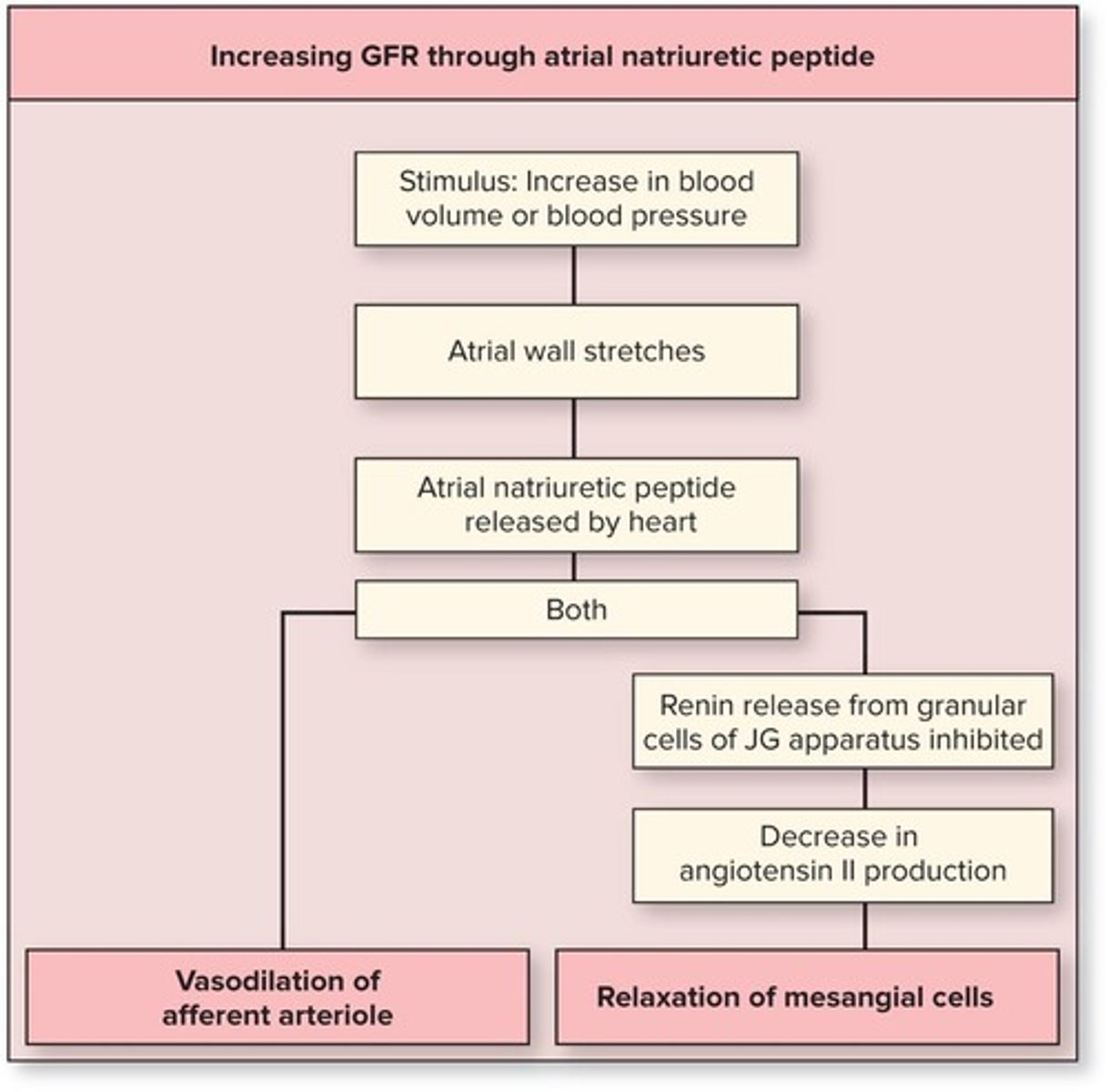
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Increases GFR by inducing vasodilation in high BP.
Net Filtration Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus affecting GFR.
Surface Area Regulation
Number of functional glomeruli impacts filtration rate.
Membrane Permeability
Fenestrated capillaries allow selective filtration in glomeruli.
Paracellular Route
Solutes move between cells during reabsorption.
Transcellular Route
Solutes move through cells during reabsorption.
Apical Surface
First membrane solutes cross in tubular cells.
Basal Surface
Second membrane solutes cross into interstitial space.
Filtration Membrane
Composed of fenestrated capillaries and podocytes.
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
Hormonal system regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
Filtration Slits
Openings formed by podocytes enhancing filtration.
Glomerular Capsule
Structure housing glomeruli, facilitating filtration process.
Transport Maximum
Limit on nutrient reabsorption by channel number.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Primary site for nutrient and water reabsorption.
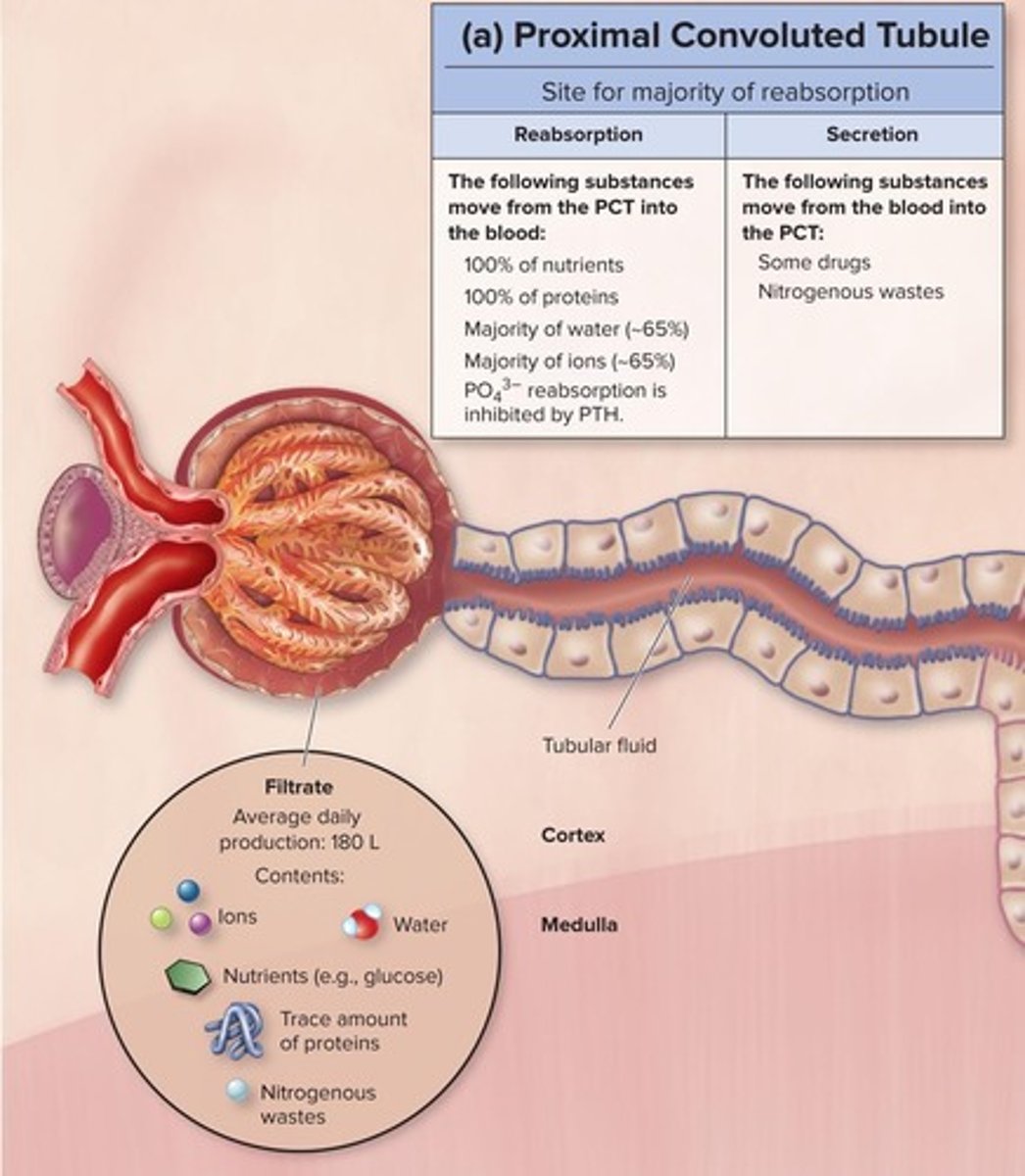
Reabsorption Percentage of Water in PCT
Approximately 85% of water reabsorbed here.
Reabsorption Percentage of Ions in PCT
About 65% of ions reabsorbed in PCT.
Nephron Loop
Site for additional water and ion reabsorption.
Countercurrent Mechanism
Process enhancing water and solute reabsorption.
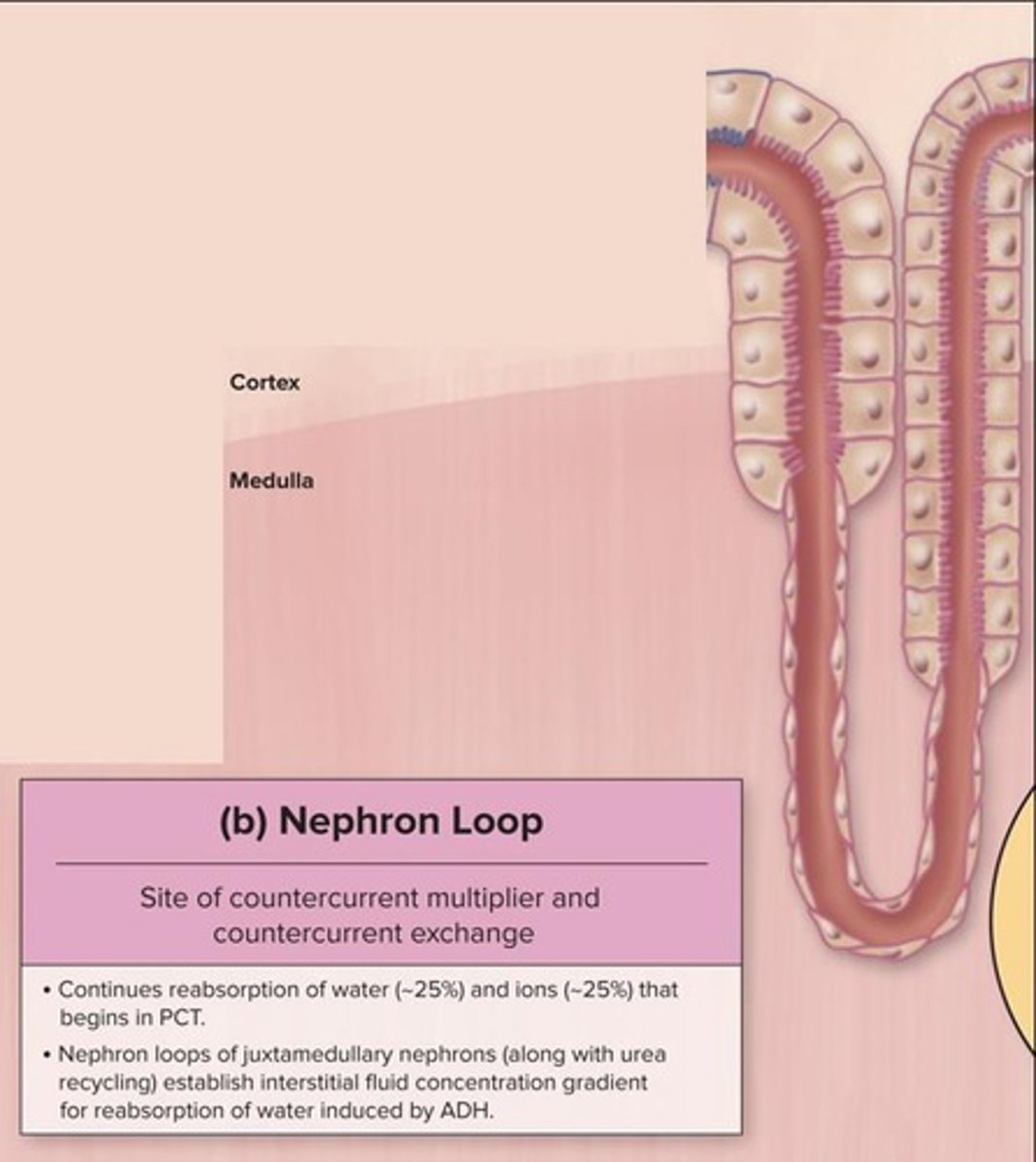
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Regulates water reabsorption in nephron loop.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Final regulation of urine composition occurs here.
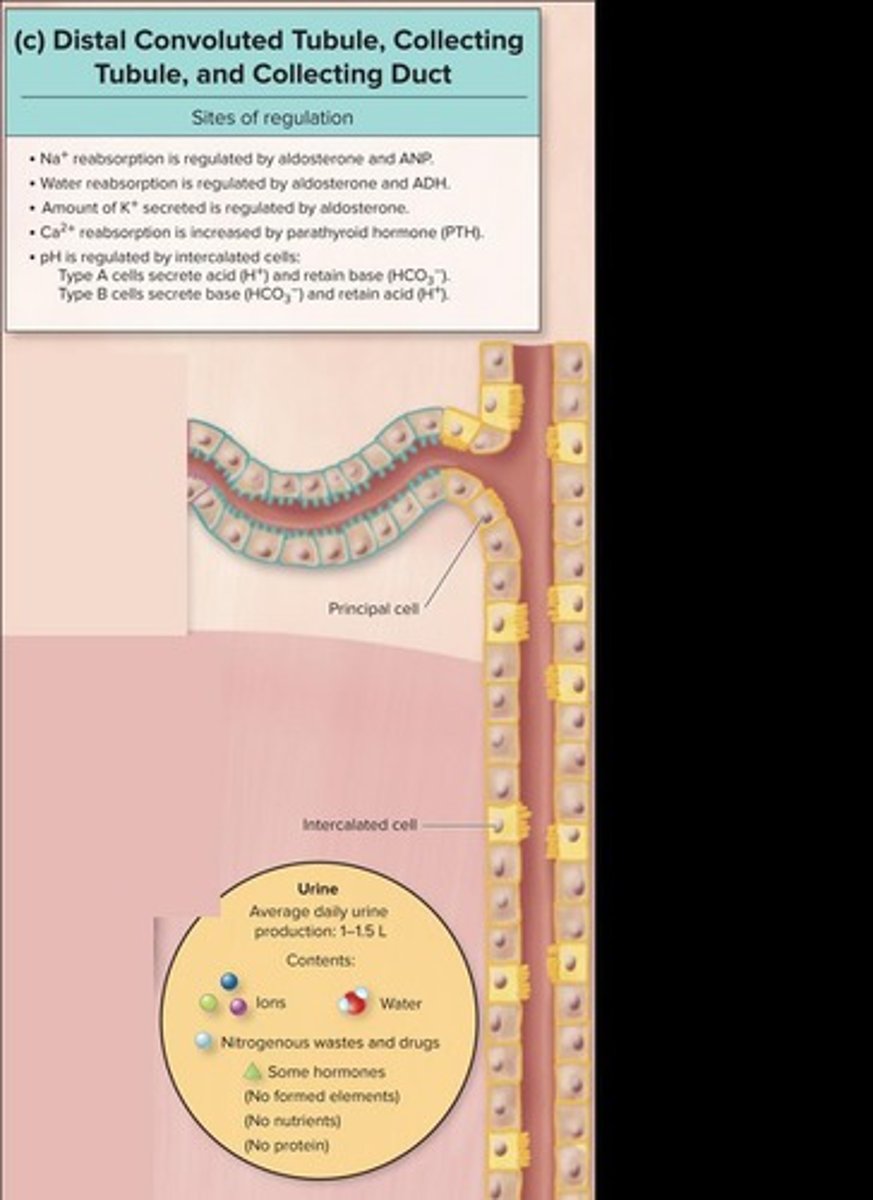
Aldosterone
Hormone regulating sodium and water reabsorption.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Inhibits sodium reabsorption, increasing urine output.
Intercalated Cells
Regulate pH and H+/HCO3- reabsorption.
Cotransporter Protein
Facilitates simultaneous transport of multiple substances.
Symporter Protein
Transports two substances in the same direction.
Antiporter Protein
Transports two substances in opposite directions.
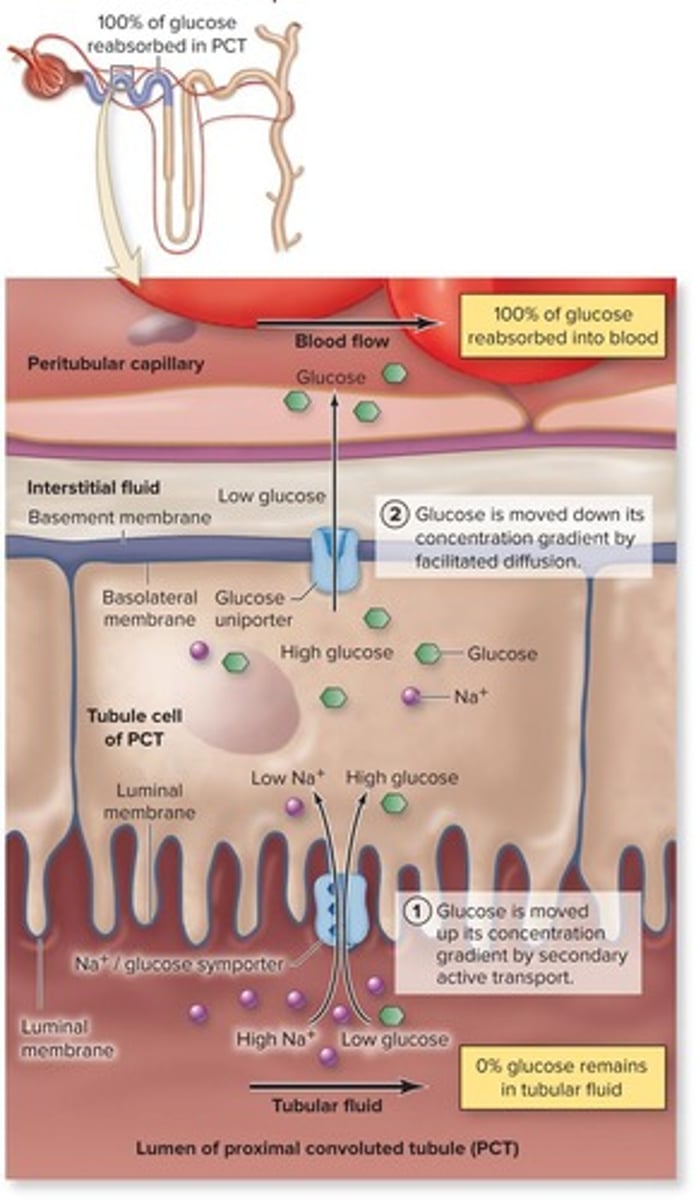
Glucose Reabsorption
Involves symporter and uniporter proteins in PCT.
Endocytosis of Proteins
Process to reclaim proteins in nephron.
Filtered Proteins
Includes insulin, angiotensin, and small albumin.
Sodium Reabsorption in PCT
Approximately 65% reabsorbed via active transport.
Sodium Reabsorption in Nephron Loop
About 25% reabsorbed as part of countercurrent.
Obligatory Water Reabsorption
Water reabsorption via always-present aquaporins.
Facultative Water Reabsorption
ADH increases aquaporins in collecting duct.
Potassium Handling
Potassium is both reabsorbed and secreted.
Type A cells
Always reabsorb potassium in kidneys.
Principal cells
Secrete potassium based on aldosterone levels.
Aldosterone
Hormone that regulates sodium and potassium balance.
Na+/K+ channels
Facilitate sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
Potassium secretion
Increased by aldosterone, more in urine.
Calcium phosphate
Main storage form of calcium and phosphate.
PTH
Hormone that regulates calcium and phosphate levels.
DCT cells
Distal convoluted tubule cells involved in calcium transport.
Bicarbonate reabsorption
90% occurs in proximal convoluted tubule.
Intercalated cells
Regulate urine pH in collecting duct.
Acidosis
Condition with low blood pH, Type A cells secrete H+.
Alkalosis
Condition with high blood pH, Type B cells reabsorb H+.
Nitrogenous wastes
Includes urea, uric acid, and creatinine.
Urea
Reabsorbed and secreted, from protein breakdown.
Uric acid
Reabsorbed and secreted, from nucleic acid breakdown.
Creatinine
Only secreted, from muscle metabolism.
Glucose in urine
Indicates diabetes mellitus when transport maximum exceeded.
Ketone bodies
Produced during fat metabolism in diabetes.
Erythrocytes in urine
Indicates bleeding or severe injury.
Leukocytes in urine
Indicates infection, often from bacteria.
Protein in urine
Normal levels are less than 150 mg/day.
Bile pigments
Indicate liver disease or bile duct obstruction.