Unit 13 - Genetics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Alleles
different forms of the same gene
how different? a little bit, maybe even one nucleotide, that’s why they’re considered the same gene just different versions of it
Dominant
trait that is seen as long as there is one dominant allele
Recessive
trait that is only seen in the presence of 2 recessive alleles
Homozygous
having 2 like alleles
Heterozygous
having 2 different alleles
Genotypes
actual gene makeup for a particular locus or trait
Phenotypes
visible trait
Law of Segregation
Alleles separate when gametes form
When the gametes form – each gamete receives only 1 of each pair of alleles.
Law of Independent Assortment
If genes aren’t on the same chromosome (linked) they will not have to remain together in the gamete
if they are linked, they will sometimes assort independently due to crossing over
When do you multiply?
when _ and _ have to happen.
When do you add?
When _ or - have to happen.
Incomplete dominance
Mix
white + red = pink
straight + curly = wavy
Codominance
Both exist together
white cow + red cow = red & white spotted cow
Multiple Alleles
More than two allele choices although there is always only have 2 alleles at each gene locus
Example: Human Blood Types
Alleles = A, B, & O (also an example of codominance)
What is the most common blood type?
O, even though it’s recessive.
X-inactivation
after embryonic development, 1 X is inactivated in each cell of females only
Barr Body
The inactivated X in a female that is is super-condensed
How does X-inactivation work?
In each cell, the X inactivated is random
~50% of the cells will express the gene on 1 chromosome
~50% will express the gene on the other
overall still expressing both alleles
What causes X-inactivation?
Why does it happen?
Methylation causes the condensation and turning off of the genes on the X
Need just one active copy once born (males only have one so if needed both then all males would be abnormal for those traits)
What are pedigrees used for?
Used to figure out genotypes of family members to see if someone is carrying a disease gene
Used to determine the mode of inheritance
Pleitropy
one gene affects many traits
Albinism – 1 mutation in 1 gene affects skin color, eye color, hair color, and eyesight
Polygenic
one trait determined by many genes – continuous pattern (like a gradient of variations)
Multifactorial
may be multiple genes and the environment
Epistasis
When one gene affects the expression of another
bb – brown coat color
Bb, BB – black coat color
C gene – dominant causes color to be deposited in coat so if no C gene then white coat color
Linkage
genes on the same chromosome
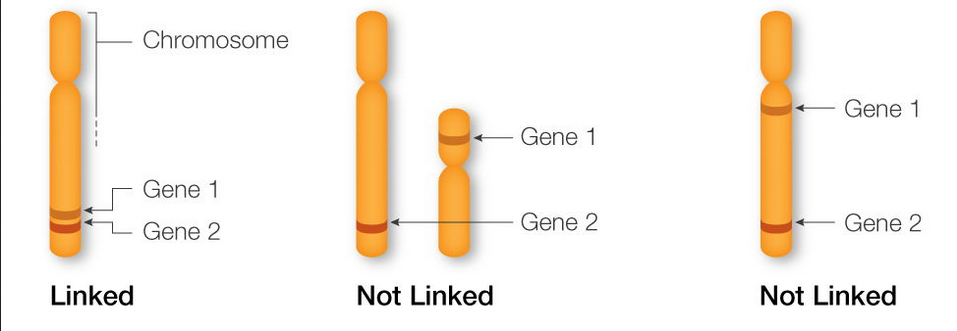
Linkage Mapping
If 2 genes are on the same chromosome, they will remain together in the gamete
if they don’t stay together it is due to crossing over
The closer two genes are on the same chromosome - the more likely they will stay together and not separate due to crossing over
How can you calculate the distance of linked genes?
Calculate % of the time crossing over occurs and separates the genes to tell relatively how far apart they are on the chromosome
(low % close, high % far)
Distance isn’t a real # - it’s just relative – called a map unit or Centimorgan.
How can you calculate the distance of linked genes (details)?
Take one parent that is heterozygous for both genes that you want to map and cross them with another parent that is homozygous recessive – any offspring that aren’t like either parent are due to crossing over
Take the # of offspring due to crossing over / # of total offspring = % crossing over = relative distance those gene are from each other
Example of Linkage Mapping
If no crossing over – Blonde Hair and Blue Eyed genes will always end up in the gamete together or Brown Hair and Brown Eyes.
If crossing over occurs you can get Blonde Hair and Brown eyes in the same gamete etc.
Aneuploidy
abnormal chromosome # (ex. Trisomy)
Polyploidy
3n, 4n (non-disjunction of all chromosomes)
More normal than aneuploid – some plants live fine but can only reproduce with other polyploid plants
What causes a polyploidy?
2n egg and 1n sperm = 3n
Or
Zygote replicates DNA but doesn’t divide = 4n
Sex Chromosomes and Chromosomal Inheritance
Non-disjuction of sex chromosomes
XXY – Klinefelter’s (small testes, sterile, breasts)
XYY – taller, more aggressive?? Males
XXX – normal female
XO – Turner’s Syndrome (no secondary sex characteristics, sterile, short)
Imprinting
genes that are expressed differently depending on whether they are from the mom or the dad
the same allele can lead to different traits depending on its parent of origin (sperm vs. egg).
In females, although their chromosomes are a mix of maternal and paternal origins, the imprinting on their eggs is reset. All imprinted genes in the egg are marked with a maternal imprinting pattern, even if the mother originally inherited that gene from her father.
Many times the methylation turns off the reading of a gene so only the other parent’s allele gets read in the offspring
Example of methylation
Deletion of a gene from chromosome 15
If inherited from the father:
Prader-Willi (retardation, short, obese, small hands and feet, insatiable appetite)
If inherited from the mother:
Angelman’s (uncontrollable laughter, jerky motions, loss of coordination)
What is Fragile X Syndrome and how does it happen?
Fragile X is a disorder where a piece of the X chromosome looks like it's hanging by a thread.
Caused by too many CGG repeats (normal = ~50, Fragile X = 200+).
It's the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability.
The number of repeats can grow over time in the egg, making it worse.
Worse when inherited from the mother, because the gene gets methylated and turned off.
What is Huntington’s disease, and how is it inherited?
Huntington’s is caused by too many CAG triplet repeats in a gene.
The number of repeats can get longer (worse) when passed down, especially from the father.
Note: Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother, not from the father.
What are some genetic diseases more common in certain groups, and why?
Cystic Fibrosis (mostly Caucasians):
1 in 25 are carriers; 1 in 2500 have it
Messed-up Cl⁻ channel protein → thick mucus, infections
Average lifespan ~27 years
Tay-Sachs (Ashkenazi Jews):
Causes seizures, blindness, poor coordination, intellectual disability
Sickle Cell Disease (African descent):
1 in 10 are carriers
Abnormal hemoglobin; gives malaria resistance
Inbreeding increases the chance of inheriting the same recessive genes, making these diseases more likely in close-knit groups.
What are examples of dominant diseases?
Achondroplasia (dwarfism):
1 in 10,000
Homozygous form is lethal (2 dwarf genes = death)
Must be a dwarf to pass it on
Two dwarfs can have a normal child
Huntington’s Disease:
Causes nervous system degeneration
What are examples of X-linked diseases?
Hemophilia
Color-Blindness
(More common in males)
What are examples of multifactorial diseases?
Heart disease
Diabetes
Cancer
Mental illness