Overview of Neurology, Endocrine, and Circulatory Systems
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
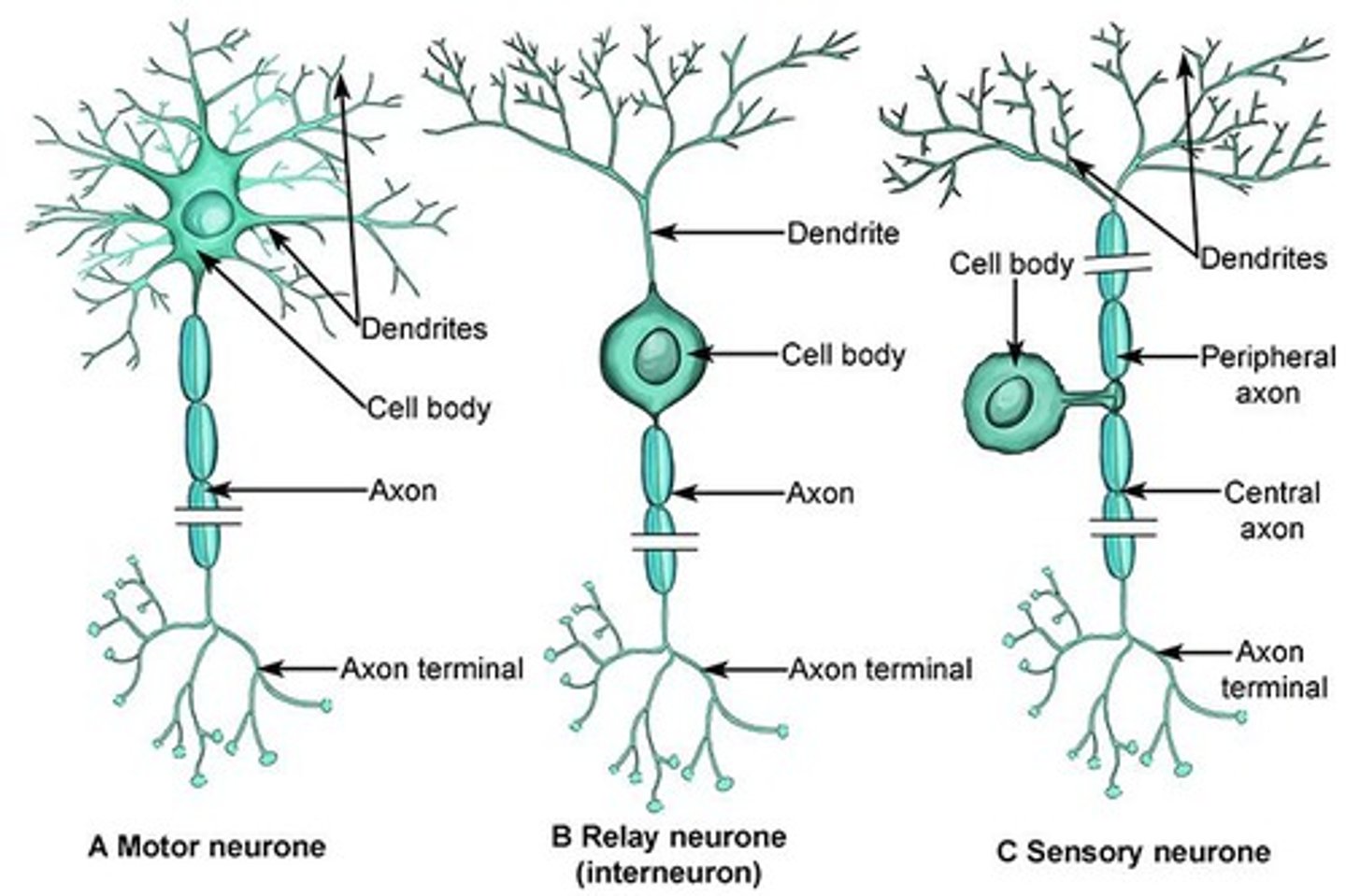
Motor Neuron
Carry signals from the CNS to muscles or glands to cause a response (movement, secretion, etc.).
Direction of Signal (Motor Neuron)
Away from the brain and spinal cord.
Examples (Motor Neuron)
Neurons that tell your leg to move or your heart to beat.
Location (Motor Neuron)
Found in the spinal cord and connected to muscles or glands in the PNS.
Multipolar
A type of neuron characterized by multiple extensions from the cell body. (motor neuron)
Sensory Neuron
Carry information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system (CNS).
Direction of Signal (Sensory Neuron)
Toward the brain and spinal cord.
Examples (Sensory Neuron)
Touch receptors in skin.
Location (Sensory Neuron)
Found in sensory organs and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Unipolar
A type of neuron characterized by a single extension from the cell body. (sensory neuron)
Interneuron
Connect sensory and motor neurons and process information within the CNS.
Direction of Signal (Interneuron)
Neither strictly afferent or efferent - they integrate and relay signals.
Examples (Interneuron)
Neurons in the brain or spinal cord that process stimuli and decide how to respond.
Location (Interneuron)
Entirely within the CNS (brain and spinal cord).
Bipolar
A type of neuron characterized by two extensions from the cell body. (interneuron)
Neuron
A specialized nerve cell that functions as the body's information messenger.
Resting State
The state of a neuron when the membrane potential is -70 mV.
Depolarization Phase
The phase where the membrane potential changes from -50 mV to +30 mV.
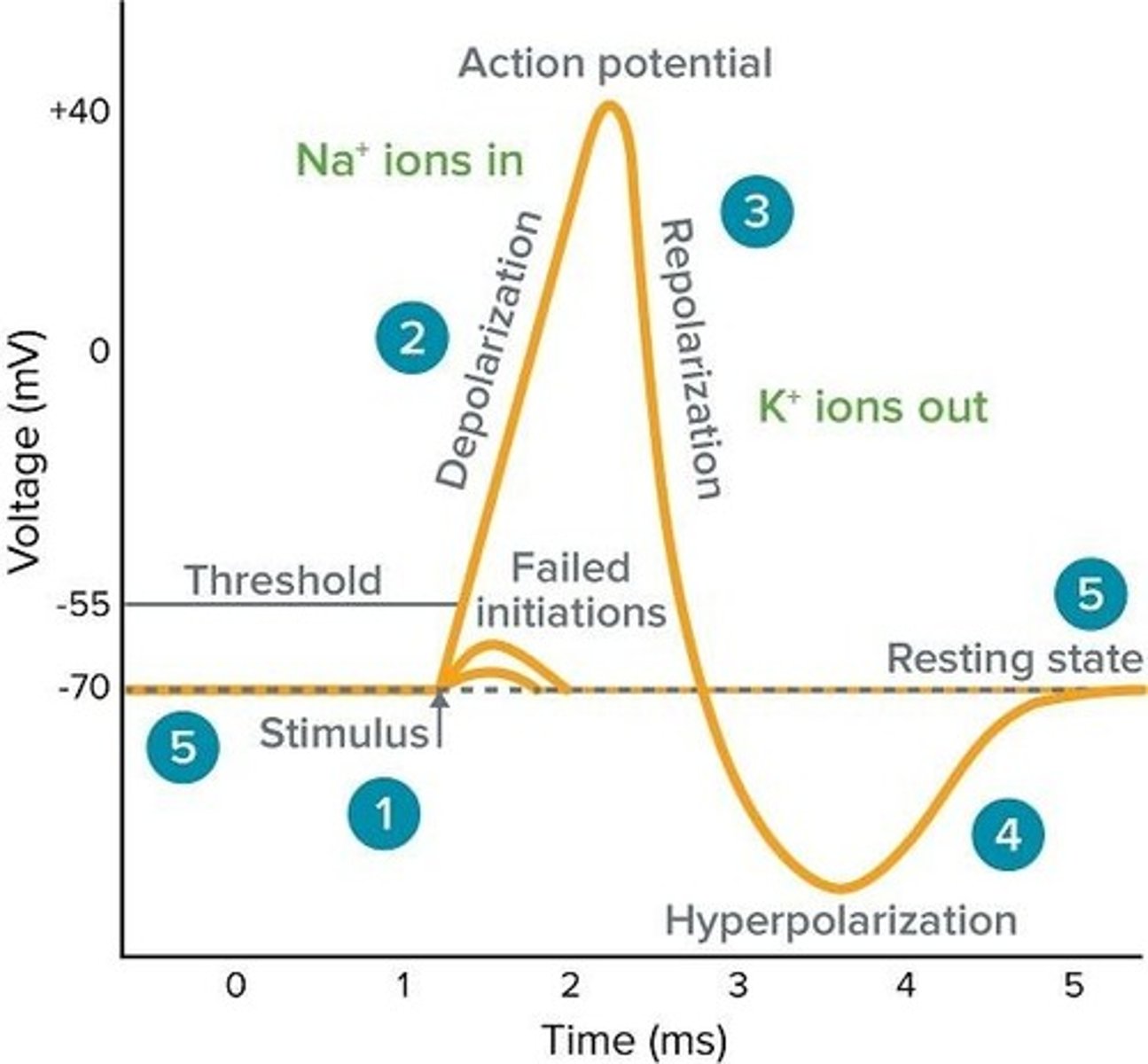
Threshold
The membrane potential level at approximately -50 mV where voltage-gated Na+ channels open rapidly.
Peak of Action Potential
The point where voltage-gated Na+ channels inactivate and voltage-gated K+ channels fully open.
Repolarization Phase
The phase where the membrane potential returns from +30 mV back down toward -70 mV.
Hyperpolarization Phase
The phase where the membrane potential reaches -80 mV due to prolonged opening of K+ channels.
Return to Resting State
The process where K+ channels close and the Na+/K+ pump restores and maintains resting membrane potential.
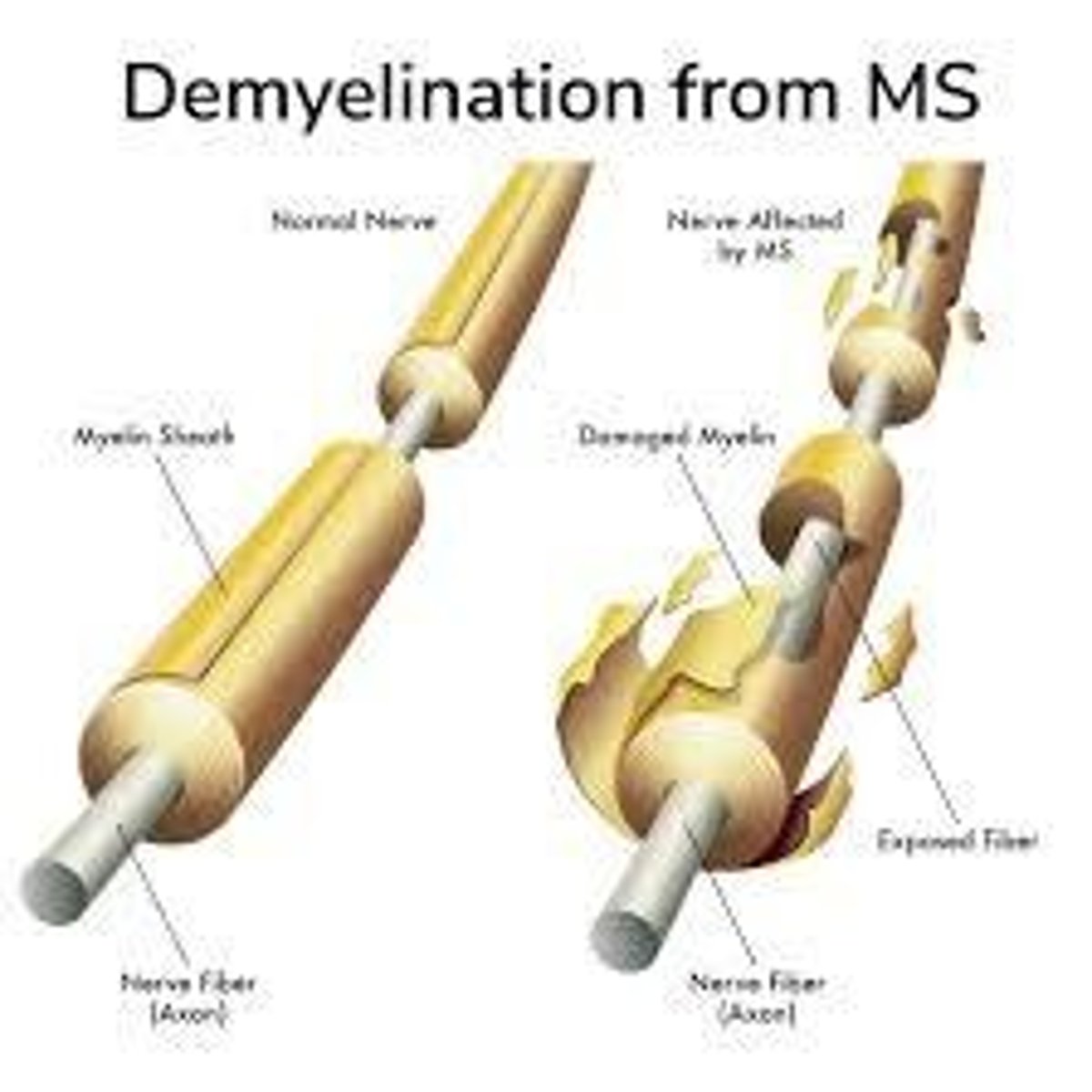
Multiple Sclerosis
A condition characterized by the loss of myelin sheath leading to weak muscles and paralysis.
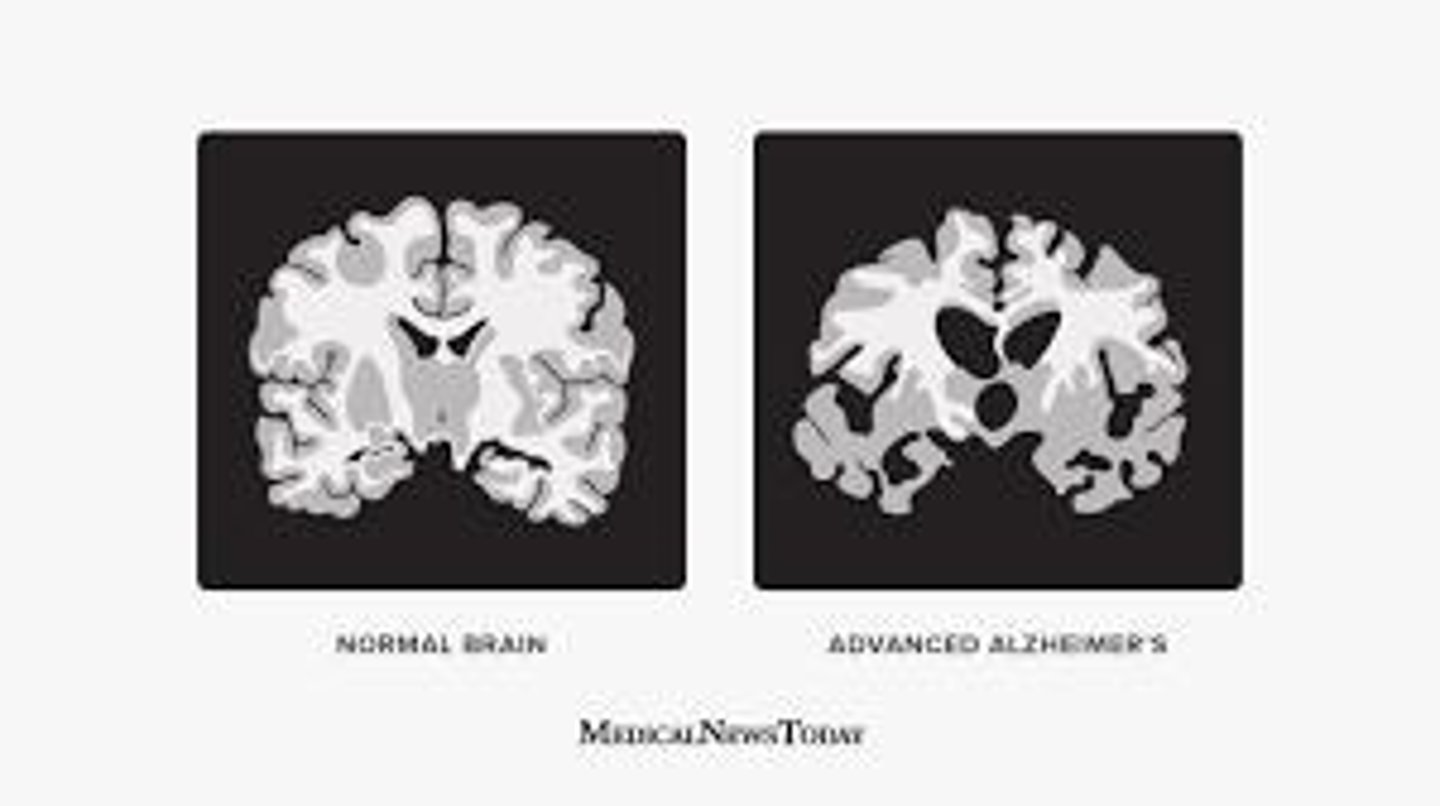
Alzheimer's
Loss of brain cells leading to severe memory loss.
Parkinson's
Loss of dopamine producing cells causing tremors, difficulty moving and speaking.
ALS
Death of motor neurons but doesn't affect sensory or mind.
Huntington's
Hereditary autosomal dominant gene causing death of brain cells.
Huntington's chorea
Uncontrollable movements associated with Huntington's disease.
Epilepsy
Uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain causing seizures or temporary unresponsiveness.
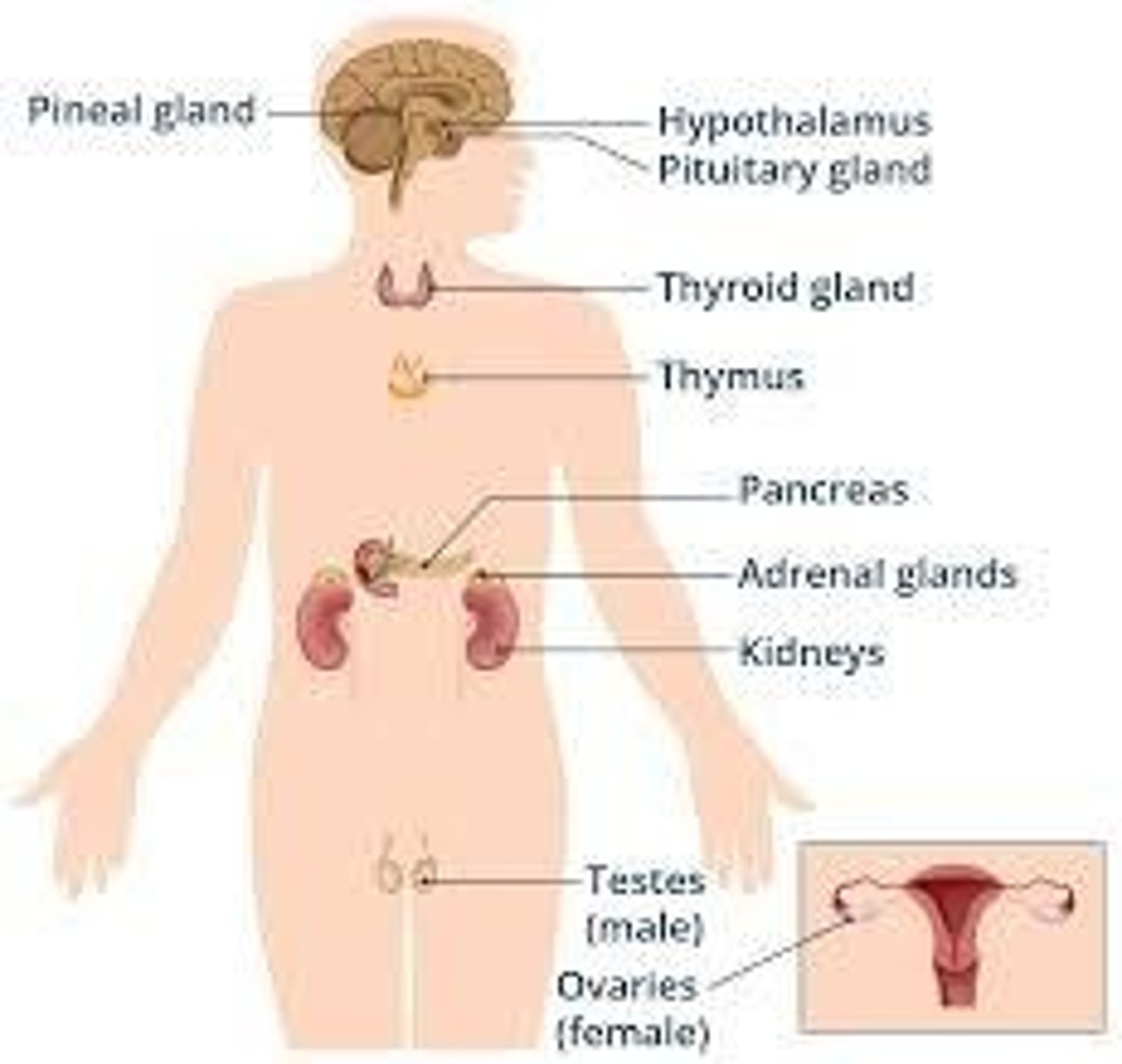
Endocrine Glands
Ductless glands that release hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Products made by Endocrine Glands
Hormones (chemical messengers).
Delivery Method of Endocrine Glands
Hormones are secreted into the blood, which carries them to distant target organs or tissues.
Examples of Endocrine Glands
Pituitary gland - growth hormone (GH), ACTH; Thyroid gland - thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3); Adrenal glands - cortisol, adrenaline; Pancreas (endocrine part) - insulin, glucagon; Ovaries/Testes - estrogen, testosterone.
Exocrine Glands
Glands that release their product through ducts to the outside of the body or into a body cavity.
Products made by Exocrine Glands
Enzymes, mucus, sweat, saliva, digestive juices, etc.
Delivery Method of Exocrine Glands
Secretions are transported via ducts directly to the target site (e.g., skin, mouth, digestive tract).
Examples of Exocrine Glands
Salivary glands - saliva; Sweat glands - sweat; Lacrimal glands - tears.
Hypothalamus
Has both endocrine and neurologic function and signals the pituitary gland.
Pituitary
Is the master gland that secretes to other glands (e.g., ACTH to adrenals, Prolactin to breast tissue).
Thyroid
Makes thyroxine, which controls metabolism.
Parathyroid
Makes parathormone which controls calcium.
Thymus
Involved in the immune system.
Adrenals
Makes cortisol, adrenaline, noradrenaline, and aldosterone.
Testes or ovaries
Makes testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone.
Pineal
Makes melatonin, which regulates sleep.
Pancreas
Makes insulin and glucagon for blood sugar control.
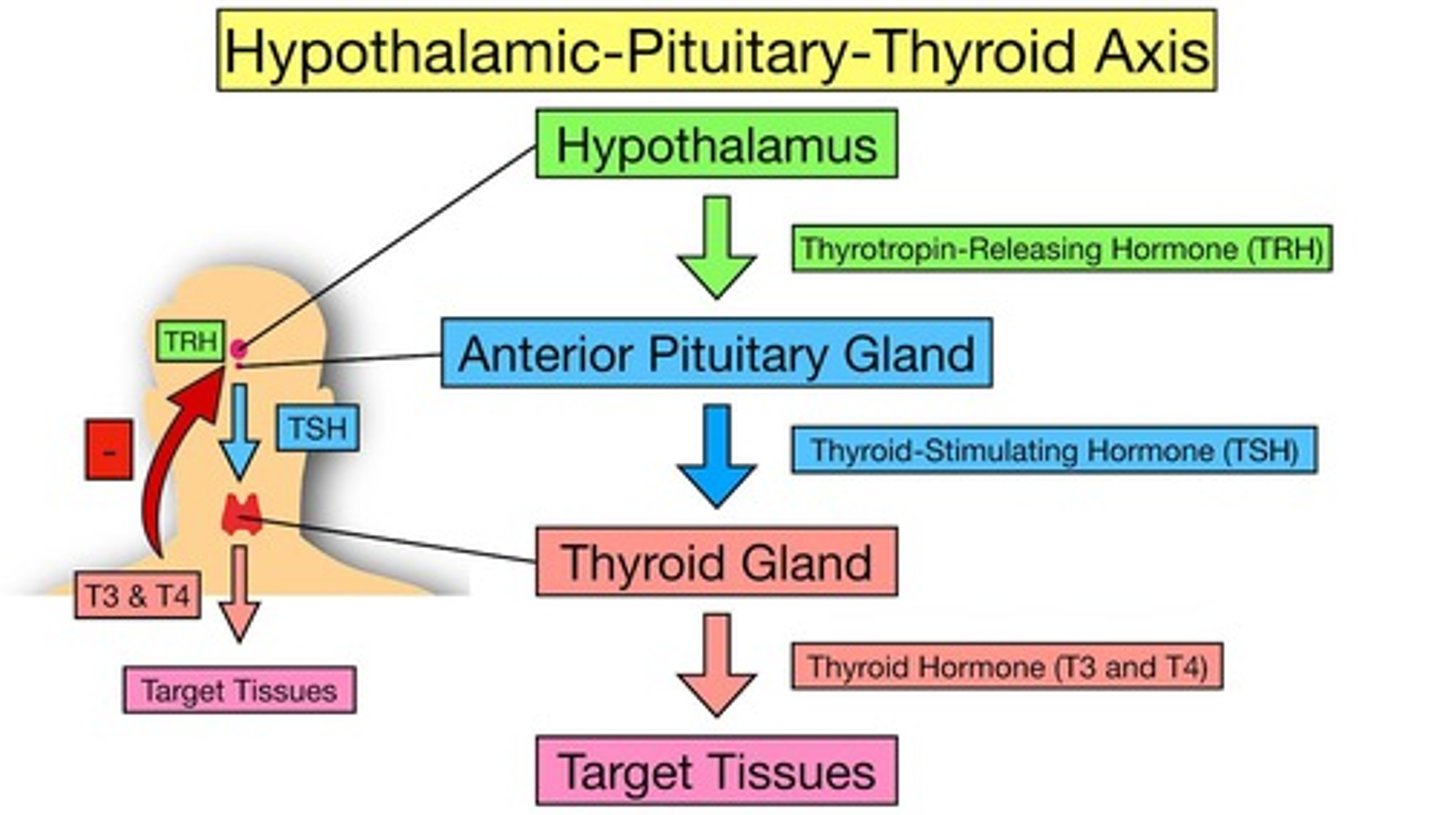
The levels of control for thyroxine
Hypothalamus releases TRH which acts on pituitary to release TSH, which acts on thyroid to release T3 and T4, increasing metabolic rate.
The Levels of control for glucose in blood
High glucose triggers insulin release from B cells in pancreas, increasing glucose uptake in cells; low glucose triggers glucagon release from alpha cells in pancreas, causing glycogen hydrolysis.
Type 1 Diabetes
Autoimmune condition where the immune system destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
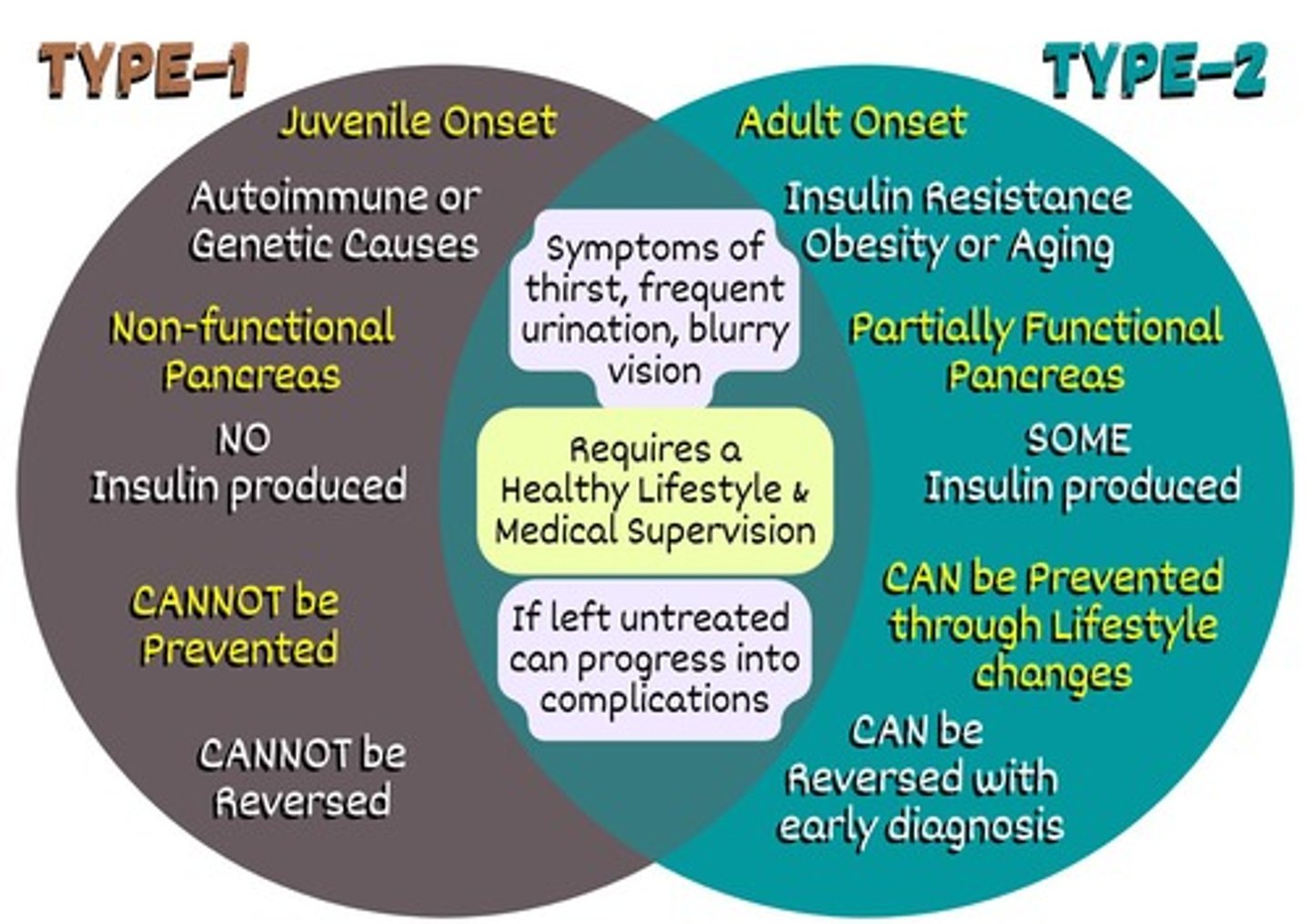
Type 2 Diabetes
Condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin.
Treatment
Managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
Prevention
Often preventable or delayed with healthy diet, exercise, and weight control.
GnRH
Hormone released by the hypothalamus that causes the pituitary to release FSH and LH.
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone that acts on the ovaries in females to produce estrogen and progesterone.
LH
Luteinizing hormone that acts on Leydig cells in males and ovaries in females.
Testosterone
Hormone released by the testes in response to LH.
Estrogen
Hormone produced by the ovaries in response to FSH.
Progesterone
Hormone produced by the ovaries in response to FSH.
SVC
Superior vena cava; brings deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.

IVC
Inferior vena cava; brings deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
Tricuspid Valve
Valve that allows blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
Right Ventricle
Chamber that pumps deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary valve to the lungs.
Pulmonary Valve
Valve that allows deoxygenated blood to flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary arteries.
Pulmonary Arteries
Carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
Pulmonary Veins
Carry oxygenated blood back to the heart and enter the left atrium.
Left Atrium
Chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.
Bicuspid/Mitral Valve
Valve that allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
Left Ventricle
Chamber that pumps oxygenated blood through the aortic valve into the aorta.
Aortic Valve
Valve that allows oxygenated blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta.
Coronary Arteries
Supply the heart muscle with blood.
Angina
Chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Heart Attack (myocardial infarction)
Condition caused by blocked coronary arteries leading to heart muscle damage.
Varicose Veins
Damaged valves that cause blood to pool in vessels and can lead to blood clots.
Capillaries
Blood vessels that are one cell thick to allow for diffusion.
Pulse Rate
Normal is 60-100 beats per minute; athletes may have a lower rate.
Systolic Pressure
Higher pressure caused by blood being pushed out of the left ventricle into the aorta.
Diastolic Pressure
Lower pressure when the heart is relaxed and blood is not pushing against artery walls.
Cardiac Output
Calculated as pulse rate x stroke volume.
Echocardiogram
An ultrasound to check the heart's actions.
EKG
Test to check the electrical activity of the heart.
Arteriograms
Test to check the blood flow to the cardiac arteries.
Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
Test to check if blood pressure and blood are getting to the arms and legs.
Doppler Studies
Test to hear where the blockages are.