1.2 - How markets work
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In the order of, 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, 2.6, 2.7, 2.3, 2.5, 2.8, 2.9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Consumers aim to maximise _____
utility
Firms/producers aim to maximise _____
profits
3 reasons why consumers may not behave rationally
the influence of other people’s behaviour
Habitual behaviour
Consumer weakness at computation
The movement along a demand curve is caused by
a change in price
a shift outwards/inwards of the demand curve is caused by
non-price factors
3 factors that may cause a shift in the demand curve:
Change in consumer’s income, tastes/preferences and the price of other goods
Explain the concept of the marginal utility theory
It examines the increase in satisfaction consumers gain from consuming an extra unit of a good (the benefit of consuming an extra good)
What is a normal good (in terms of demand)?
Where quantity demanded increases in response to an increase in income
What is an inferior good (in terms of demand)?
where quantity demanded decreases in response to an increase in income
A movement along the supply curve is caused by
a change in price
a shift of the supply curve is caused by
non-price factors
5 factors that cause a shift in supply
taxes and subsidies
a change in cost of raw materials
Improvements in technology
An increase in productivity
An increase in available workers
Why is the supply curve upwards sloping?
The profit motive - if prices are higher, it will become more profitable to sell the good/service
Market equilibrium price =
when a quantity of a good or service supplied = the quantity demanded
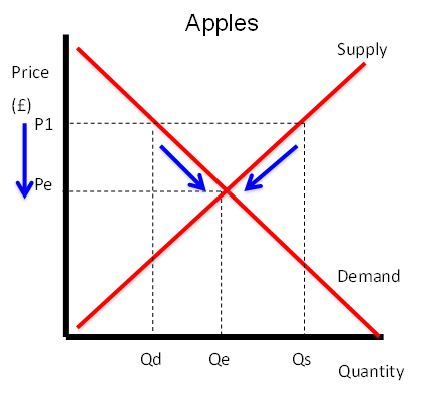
Does this diagram show excess demand or supply?
Supply
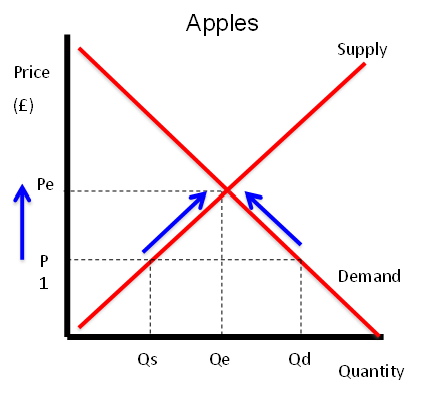
Does this diagram show excess demand or supply?
Demand
What happens in the market when there is excess demand?
Producers raise prices in order to generate more revenue, causing an extension in S and a contraction in D
What happens in the market when there is excess supply?
Producers gradually lower prices in order to generate more revenue, causing a contraction in S and an extension in D
What are the 3 functions in allocating scarce resources?
rationing
signalling
incentive
What is rationing function? (as a price mechanism)
When resources become scrcer the price will rise further and only those who can afford it receive it
What is the incentive function? (as a price mechanism)
When highers prices incentivse producers to increase the quantity supplied
Is the incentive function a short term or long term view?
short term
What is signalling function? (as a price mechanism)
Where prices carry information which is used by consumers and producers to make their market plans
Is the incentive function a short term or long term view?
Long-term
Price mechanisms work in ____, _______ and ____ market
local, national , global
When do markets form
A market is formed when producers and consumers meet to exchange goods and services
Markets allocate ____ ________ to produce goods and services required to meet ______ _____
scarce resources, consumer demands
What does PED measure?
PED measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price
If a good/service is elastic it is….
responsive with a change in price
If a good/service is inelastic it is…
unresponsive with a change in price
What is the formula for calculating PED?
(%change QD) / (%change in P)
What is the PED coefficient if it is elastic?
>1
What is the PED coefficient if it is inelastic?
<1
What is the PED coefficient if it is unitary/perfectly price inelastic?
=1
What is the PED coefficient if it is perfectly price elastic?
Infinity
Why is there a - sign infront of the PED?
because price and demand have an inverse relationship
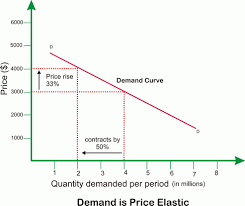
Is this product elastic/inelastic/perfectly inelasticor perfectly elastic?
Elastic
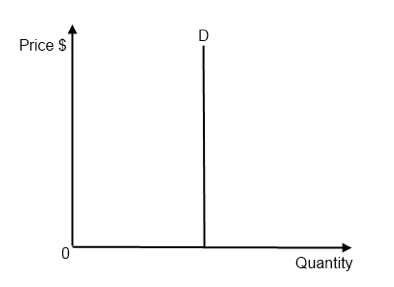
Is this product elastic/inelastic/perfectly inelastic or perfectly elastic?
perfectly inelastic
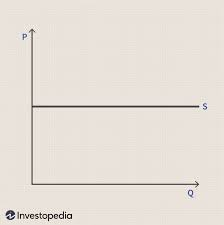
Is this product elastic/inelastic/perfectly inelastic or perfectly elastic? (it should say D not S)
perfectly elastic
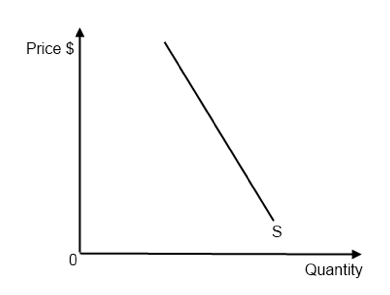
Is this product elastic/inelastic/perfectly inelastic or perfectly elastic? (it should say D not S)
inelastic
4 factors that influence PED
availability of substitutes
Addictiveness/habital behaviour
£ of product as proportion of income
Timeframe
How does the availability of substitutes affect PED?
the more substitutes the higher value of PED = more elastic
How does addictiveness/habitual behaviour affect PED?
addictiveness turns products into necessities and habitual consumption, resulting in a low value of PED = more inelastic
How does the price of a product as a proportion of one’s income affect PED?
the lower the proportion of income the price represents, the lower the PED value will be = relatively inelastic
consumers are ____ responsive to price changes on cheaper products
less
How does timeframe influence PED?
In the short-term, consumrs are less responsive to price changes = inelastic, over the long-term consumers may look for substitutes (elastic)
YED measures:
the relationship between a change in QD for a good/service and a change in the consumers’ real income
What are the 4 different types of goods
Normal, Luxury, necessity, inferior
What is a normal good (YED)
a normal good is a good which when incomes are falling, demand for normal goods will fall e.g. name-branded food
what would the coefficient of a normal good be (YED)
+ (positive Y)
what is a luxury good
a luxury good is a good which will have a signficant decrease in demand with a drop in income e.g. designer clothes (luxury good classification is subjective)
what would the coefficient of a luxury good be (YED)
YED>+1 (high and positive)
what is a necessity good
a necessity good is where there wont be/will be a very little decrease in demand if incomes drop e.g. basic food
what would the coefficient of a necessity good be (YED)
YED is between 0<YED<1
what is an inferior good
if following an increase in real income, less of the good is purchased then it is an inferior good e.g. public transport
what coefficient would an inferior product have (YED)
(-) negative YED
What is the formula for YED
%change in QD / % change in income
Why is YED important for businesses
it helps firms to predict the effect of changes in the economic cycles on their sales
XED measures:
the responsiveness of the QD of one good to a change in the price of another related good
XED is useful in analysing the relationships between ______ and ___________ goods
substitute, complementary
what is the formula for XED
%change in QD of good A / %change in QD of good B
Substitutes have a _____ XED
positive
an ______ in the price of one product will lead to a rise in ______ for its substitute
increase, demand

do these substitutes have a strong or weak relationship
strong
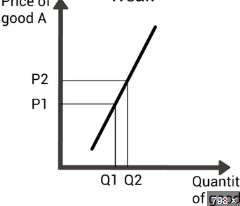
do these substitutes have a strif XED is _ong or weak relationship
weak
compliment goods have a ________ XED
negative
the ______ the coefficient for complementary goods, the closer the compliments are
higher
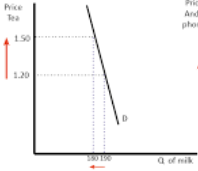
Does these compliment goods have a strong or weak relationship?
weak

Does these compliment goods have a strong or weak relationship?
strong
PED is important to firms in determining their ______ ________
pricing strategy
If demand is inelastic then an increase in price leads to an ______ in total revenue
increase
If demand is inelastic then an fall in price leads to an ______ in total revenue
fall
If PED is elastic then a rise in price ______ total revenue
reduces
If PED is elastic then a fall in price ______ total revenue
increases
PED is also important to governments in terms of understanding the burden of _______ on producers and consumers
taxation
The more price inelastic the good, a ______ proportion of the tax is paid by the consumer than the producer
greater
For subsidies, the more price inelastic the good, the greater the price ____ for consumers
fall
If YED shows demand for a firm’s product is income elastic and the economy experiences a recession, demand is likely to ____ significantly
fall
XED will tell a firm how demand for their own product will change following a _____ ______ by their __________
price change, competitiors
Calculation for total revenue (TR)
TR = P x Q
What is price elasticity of supply (PES)?
PES measures the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to a change in price
If supply is elastic producers can ______ their output without an ______ in cost or a time delay
increase, increase
If supply is inelastic, firms find it ____ to change their production in a given time period
hard
What is the formula for PES?
% change in QS / % change in P
What is the coefficient for price elastic PES?
>1
What is the coefficient for price inelastic PES?
<1
What is the coefficient for perfectly price elastic PES?
infinity
What is the coefficient for perfectly price inelastic PES?
0
4 factors that influence PES:
spare production capacity
stocks of finished products and components
Time period and production speed
ease and cost of factor substitution/ factor mobility
How does spare production capacity influence PES?
If there is plenty of spare capacity then a business can incrtease output without an increase in costs
How does stocks of finished products and components influence PES?
If stocks of raw materials and finished products are at a high level, then a firm is able to repsond to a change in demand (supply = elastic)
How does the time period and production speed influence PES?
supply is more elastic the longer the time that a firm is allowed to adjust its production levels
How does the ease and cost of factor substitution / factor mobility influence PES?
if capital and labour are occupationally mobuile then PES is likely to be higher as resources can be mobilized to supply the extra output
PES - In the short run it is _______ to adjust production
difficult
PES - Why is it difficuly for firms to adjust production in the short run?
because some factors are fixed
In the long run all factors of production can be _______
adjusted
In the long run firms can increase production, which makes supply ____ ______
more elastic
Consumer surplus is…
The difference between the price of consumer is willing to pay and the actual market price paid
Producer surplus is…
The difference between the price of firm is willing to supply for and the actual market price received
When the market is at equilibrium the consumer and producer surplus is _________
Maximised