Communications final
1/472
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
473 Terms
Conflict
disagreement between people of groups
- may arise from different beliefs, values, and ideas about how the world ought to be
What does conflict evoke?
various emotions- often negative
Conflict from a positive perspective:
- Solving problems provides the opportunity for...
- Conflicts have the potential to stimulate....
- growth and learning
- creative thinking, provide feedback, and serve as a catalyst
The 3 primary types of conflict that occur in teams:
1. Relationship Conflict
2. Task Conflict
3. Process Conflict
Relationship Conflict
- Disagreement about what?
- Almost always detracts from...
- Is the type of conflict most people think of when...
- Often ____________, _________ to effectively resolve, distract from the _______________, and reduce ______________________
- about personal issues outside the task at hand
- team outcomes
- term "conflict" arises
- often emotional, difficult to effectively resolve, distract from the task at hand, and reduce collaborative problem solving
Task Conflict
- Disagreement about what?
- _________ destructive form of conflict
- Participants are able to separate _______ from _________________
- can remain ____________
- Have the highest potential to....
- about the content and/or outcomes of a task to be performed
- least destructive form of conflict
- able to separate tasks from relationship issues
- focused on the task at hand
- benefit team performance
Process Conflict
- Disagreement about what?
- Considered the....
- Issues of __________ in process conflicts are inherently __________ and _________________
- logistical issues of accomplishing a task (assigning duties, decision-making process)
- most negative form for team outcomes
- issues of contention in process conflicts are inherently personal and highly valuable (control of resources, role assignments)
Causes of conflict
- Lack of awareness
- Incompatible goals
- Scarce resources
- Dependence
- Values
Lack of awareness
- one or more involved parties does not have all the info needed
- awareness involves willingness to know, as well as knowing
- someone can try to make you aware of a fact or problem, but you can choose to ignore or avoid it
- ex: if a pt is not aware of how to take a med properly, conflict may arise when the med does not work properly or causes harm
Incompatible goals
overall wants/needs of involved parties do not align
Ex: pt's goal may be getting med quickly. Pharmacist's goal may be accuracy and providing the pt with important info about his illness and drug therapy
Incompatible goals: when conflict arises, it is almost always because....
one party believes achievement of their goals being threatened
- threat can be true or perceived
Scarce resources
- parties in a conflict may find themselves competing for resources (rewards)
- resources may be tangible (raise or promotion) or intangible (respect, power, trust)
- Ex: drug info. is a scarce resource for pts. The time to provide that info. is a scarce resource for pharmacists
Dependence
- conflict occurs between 2 parties who cannot function independently
- both parties need to be aware of the extent to which they need each other
- when we depend on people, conflicts may arise because those people don't do things exactly the way we think they should be done
- Ex: pharmacists need techs to perform technical tasks so that the pharmacists can provide services to their pts that techs are not qualified to perform
Values
- people have different values, beliefs
- often see values as absolute "rights" and "wrongs"
- occurs when we are confronted with an opposing value or belief
- causes discomfort
- possibility exists that we believe something that may not have been true
Causes of conflict: Values- we should see this as an opportunity to...
question our own learning or to learn new truths, but many will simply defend their beliefs, even if the beliefs don't work. People resist change
The 5 conflict management styles
- Competing- dominating, forcing
- Collaborating- integrating, problem-solving
- Avoiding- withdrawing
- Accommodating- obliging, smoothing
- Compromising
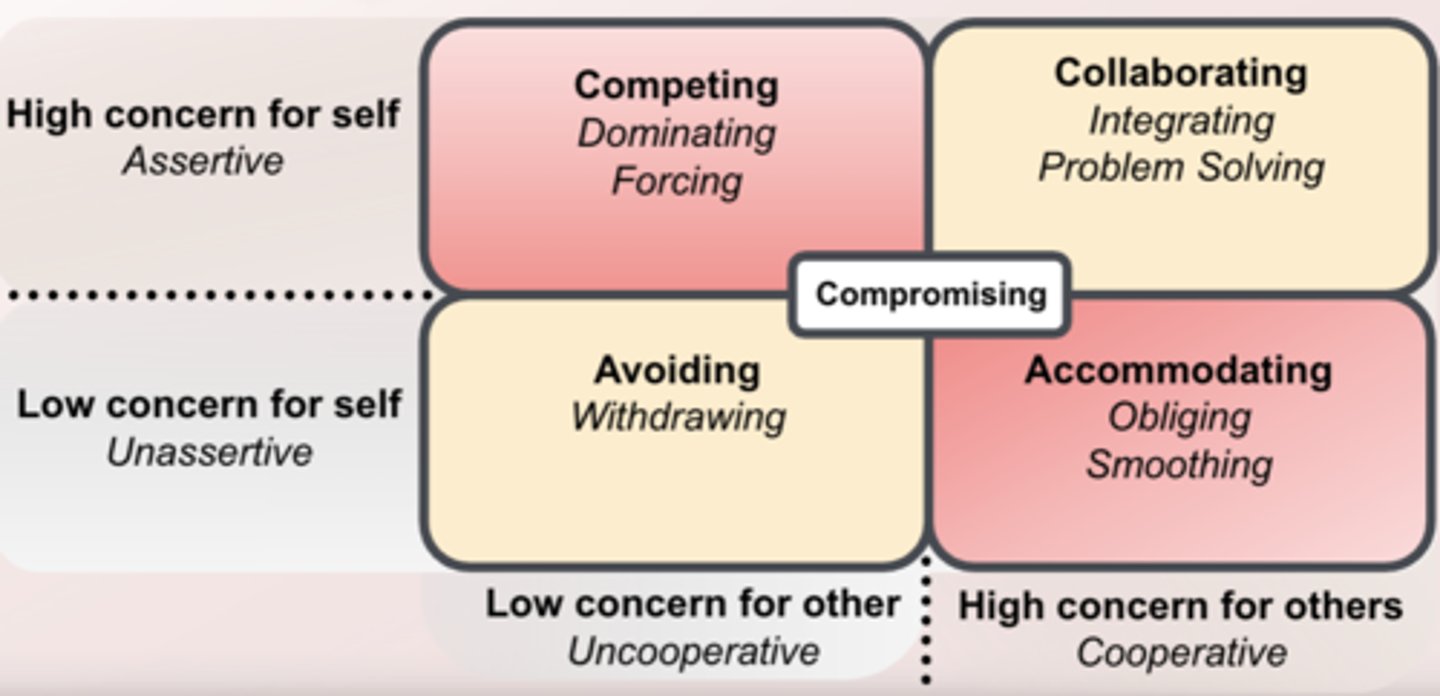
Avoiding
- Unassertive and uncooperative
- ignore conflict and avoid discussing the issue
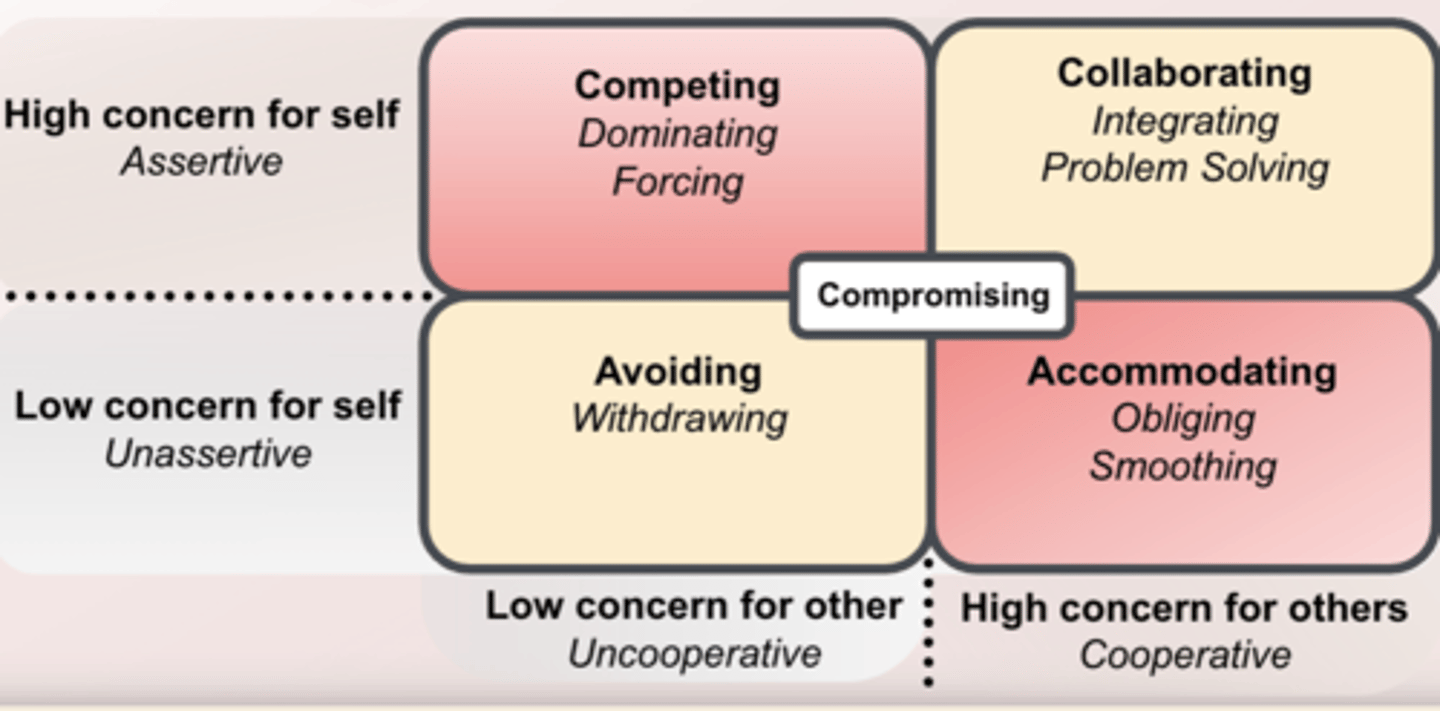
Competing
- Assertive and uncooperative
- dominate and impose one's views on others
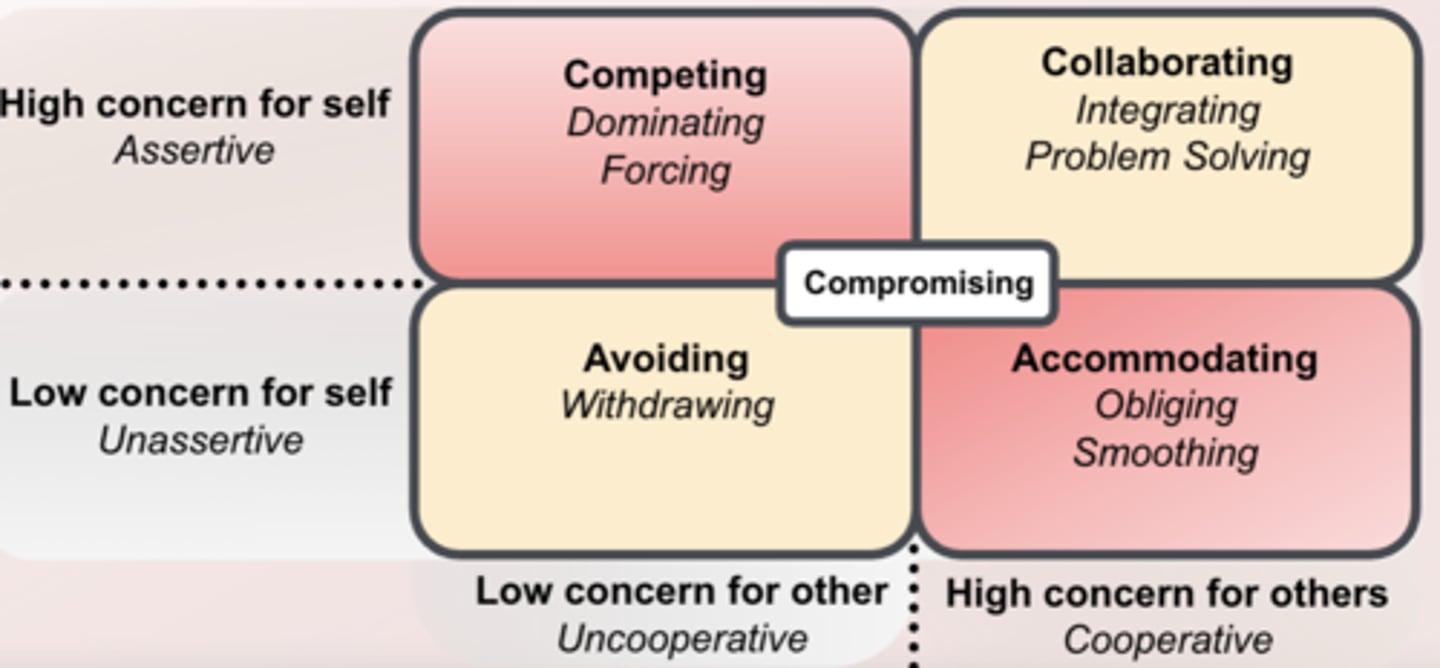
Accommodating
- Unassertive and cooperative
- submit to others' views
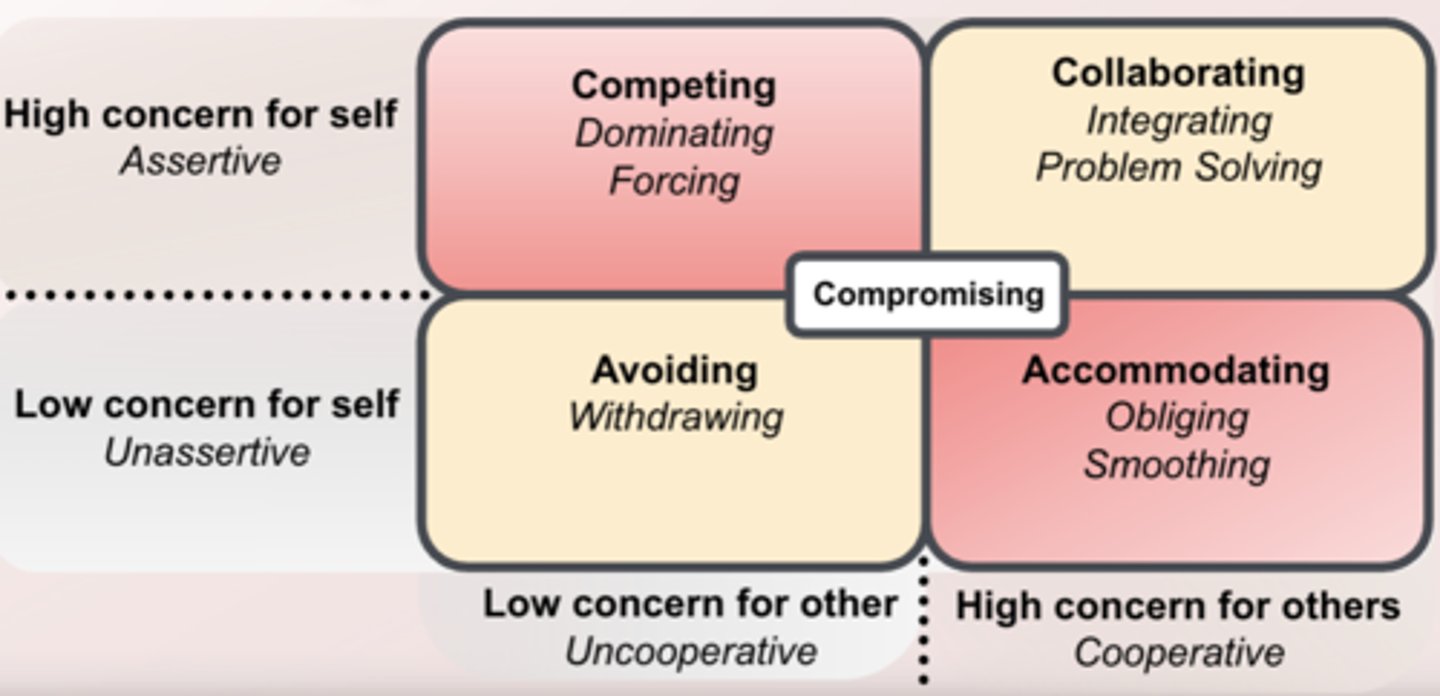
Compromising
- Moderate in both assertiveness and cooperativeness
- true"middle of the road" mentality
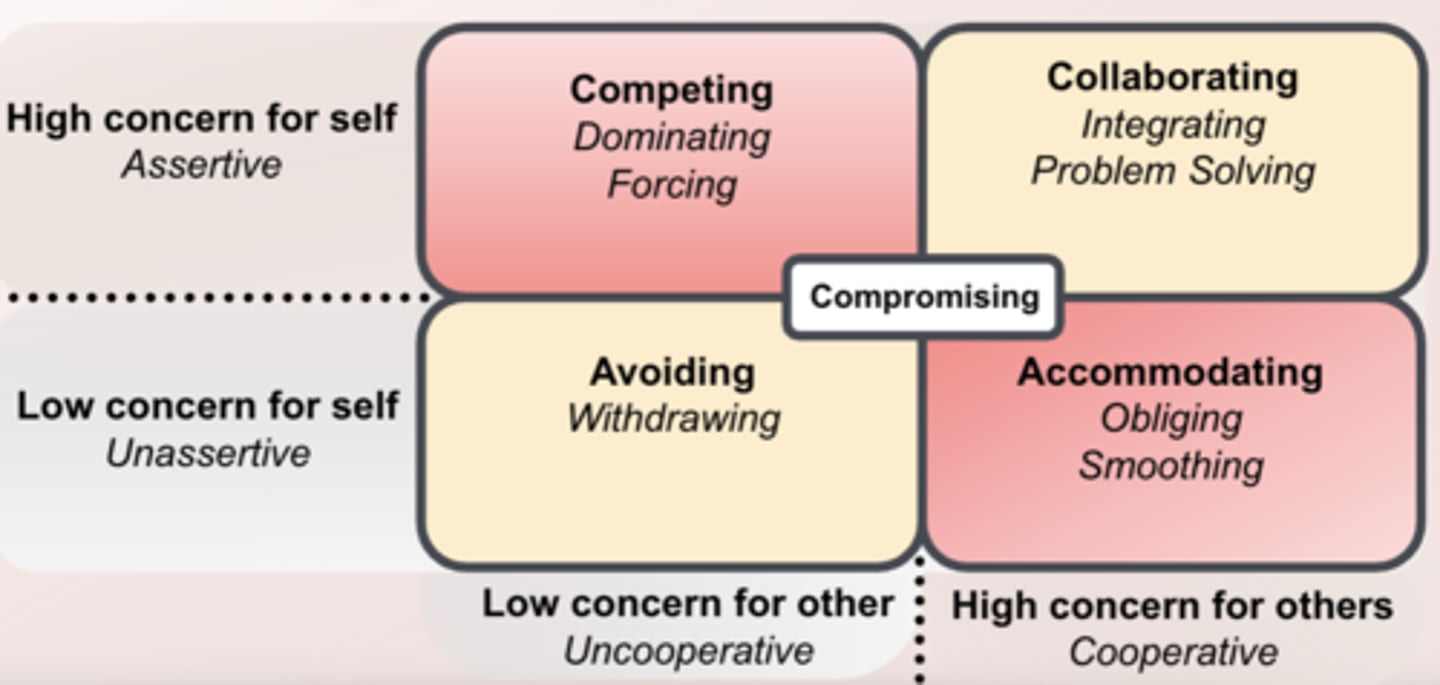
Collaborating
- Assertive and cooperative
- initiate communication to find mutually acceptable solutions
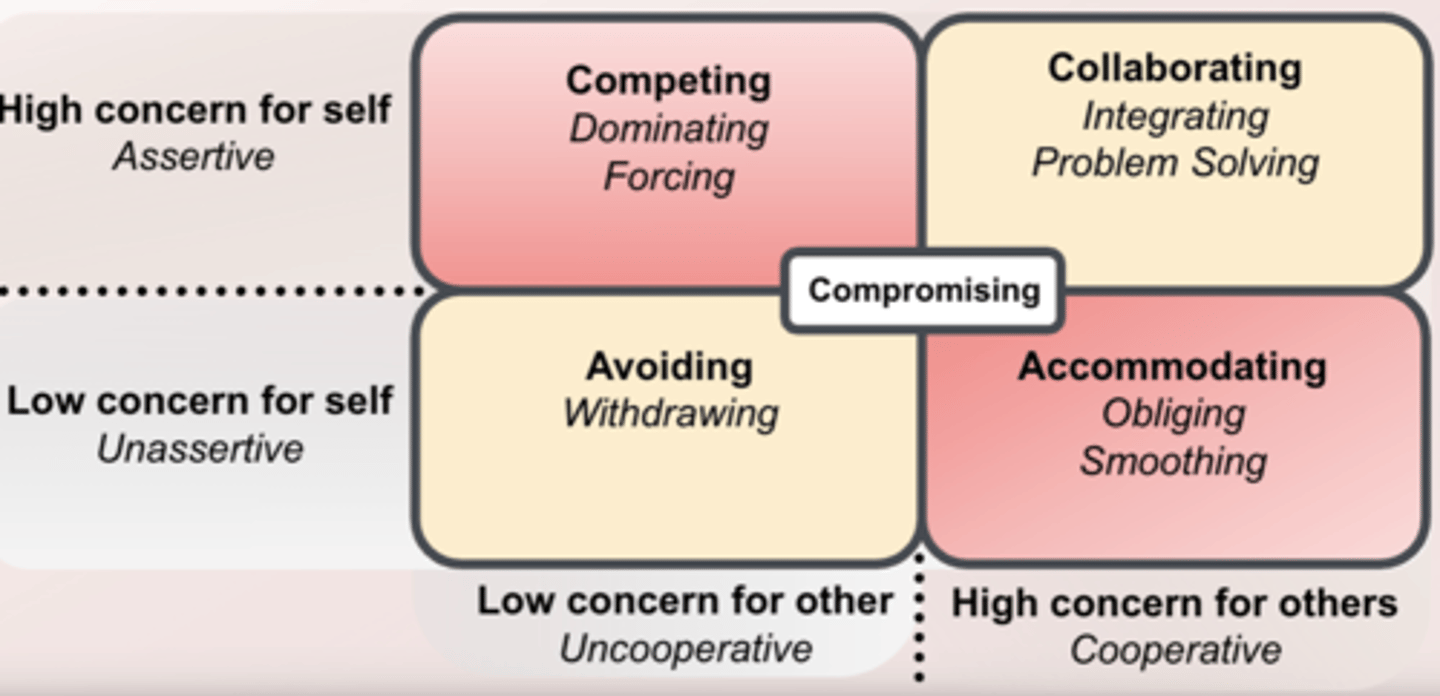
The 5 different conflict management styles are based on what? Who was it proposed by?
concern for themselves and others
- originally proposed by Mohammed Rahim in 1983
- Align with style inventories including Thomas-Kilman Conflict Mode Instrument
T/F: Individuals can be characterized as having only one style of dealing with conflict
FALSE
nobody can be characterized as having only one style of dealing with conflict
Everybody is capable of using...
the 5 conflict-handling styles, certain ppl use some styles better than others and rely on those styles more heavily
Conflict-management styles can be categorized as: (3)
- Win-lose strategies- competing, accommodating
- Lose-Lose strategies-avoidance, compromise
- Win-win strategies- collaborating/problem-solving

Win-lose: Competing (3)
- characterized by a high desire to satisfy your own concerns and a low desire to satisfy the concerns of the other party
- competing strategy focuses on the person and not on the issues of the conflict or problem
- you use your authority to get your way- one party is satisfied at the expense of the other
Win-Lose: Accommodating
- characterized by a low desire to satisfy one's own concerns and a high desire to satisfy the concerns of the other party
- have a desire to be accepted by others
- gives in to the other's desires when they are in conflict with his or her own desires
A person who uses the win-lose accommodating strategy would feel the need to....
preserve the harmonious relationship at all costs
- sees confrontation as a destructive and painful process
Lose-Lose: Avoidance
- characterized by a low level of cooperativeness and a low level of assertiveness
- conflict is seen as a useless and punishing experience
- avoidance means removing oneself from the conflict both mentally (emotionally) and physically—sidestepping the disagreement and tension
Lose-Lose: Compromise
- characterized by a moderate desire to satisfy one’s own concerns and a moderate desire to satisfy the concerns of the other party
- neither party is completely satisfied with the outcome
- a solution is chosen (often hastily) that is not the best, most effective one
- no direct confrontation about the issues and goals
- some consider this acceptable strategy if outcome is acceptable to both (good but not great)
Why do people use the lose-lose compromise strategy so often?
people avoid pain and the hard work of coming up with a solution that is acceptable to all parties
- Questions have to be asked and feelings have to be explored in orderto find out what is important to others, takes hard work, objecivity, and risking to come up with a solution
- even though change may be for the better, we often don't like to change
Which is the only true win-win strategy?
Problem-solving. Collaborating to find mutually agreeable solutions. both parties agree to an outcome that is successful
- Win-win strategies: Collaboration/Problem solving
Problem-solving/collaborating
Step 1: Identify the problem (3)
- Identify the exact problem and its nature (contributing factors)
- Identify who "owns" the problem—who has responsibility for the problem
- We are not responsible for solving other people's problems
Problem-solving/collaborating
Step 2: Identify all possible solutions (4)
- May require brainstorming with others
- Allows a group of 2 or more people to come up with many possible solutions to a problem
- The more solutions that are generated, the better is the chance of determining the best solution
- Parties understand that important decisions or solutions may take time, and all possible ideas must be expressed
Problem-solving/collaborating
Step 3: Decide which solution is the best
- After all the solutions have been identified, choose the solution that is best for the problem at hand
- Does this solution appeal to all parties involved?
Problem-solving/collaborating
Step 4: Determine how to implement the solution (2)
- After the solution has been chosen, decide on a plan of action for carrying out the solution
- This will vary depending on the type of problem
Problem-solving/collaborating
Step 5: Assess the outcome of your solution
- Was it a win-win solution? Were both parties satisfied with the outcome?
- Was there something about this problem that could have been prevented in the first place?
Collaboration
- Description:
- Outcome:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- High concern with the interests of all ppl involved
- Win/win
- Builds commitment, reduces negative feelings
- takes a lot of time and energy
Compromises
- Description:
- Outcome:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- moderate concern for self interests and for the interests of others
- win some/lose some
- less time-consuming, avoids power struggles
- important values and long-term objectives may be lost
Competition
- Description:
- Outcome:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- high concern for self interests and less concern for the interests of others
- win/lose
- the "winner" gets what they want
- conflict may escalate. the "losers' of the conflict may retaliate
Accommodation
- Description:
- Outcome:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- low concern for self interests and high concern for the interests of others
- lose/win
- can be viewed as a goodwill gesture
- one party's ideas and concerns don't get attention. they may lose credibility and influence
Avoidance
- Description:
- Outcome:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- low concern for all persons involved
- lose/lose
- avoids the potential of damage that may arise from confrontation
- important decisions may be made by default
Language of conflict
attacks the other person
- ex: "you make me angry" "you're too sensitive!" "if it weren't for you.." "you always do that!"
Language of problem solving
attacks the problem
- expresses a desire for a solution that is mutually acceptable and achieves both parties' goals
- open, honest feelings, facts, and opinions expressed by both parties
- both parties share responsibility to ask questions and get clarification on the issues
- feedback is important in getting clarification and accurately defining the problem
What are needed ot solve problems and resolve conflict?
courage and introspection
When tackling conflict, use....
a problem-solving approach and language that focuses on attacking problems rather than people
It is Important to recognize our ________________________ in communication
own natural tendencies
Examples of styles in which we communicate: (4)
- Passive (non-assertive)
- Aggressive
- Passive-agressive
- Assertive- our goal
Assertion
- Involves __________, but not __________
- Understands that all have the right to be __________________
- Recognizes that we are responsible for our own ____________ and ______________
- Involves respect, but not deference (submission)
- Understands that all have the right to be respected
- Recognizes that we responsible for our own feelings and actions (and not that of others)
Assertive people have....
clear boundaries
• They are clear about who they are and how they feel
• They are clear about when their rights are being violated
Passive Communication Style has a tendency to do what?
judge and blame self - feel bad about self. 'I'm not ok - You're ok'
- Tends towards being self-critical, self-blaming, under-functioning
Passive Community Style (5)
• Compliant, 'people-pleasing'
• Emotional distancing- silence, withdrawal
• Softly spoken, mumbling or apologetic
• Vague
• Wary, watchful of self
Aggressive Communication Style has a tendency to...
judge and blame other person - feel annoyed with others. 'I'm not ok - You're not ok'
- Tends towards being perfectionist, overly critical, over-functioning
Aggressive Communication Style (6)
• Critical, blaming
• 'You made me feel...'
• Ineffective fighting
• Venting feelings, lashing out
• 'High Standards', demanding
• Overbearing, opinionated
The 2 types of respect involved in assertiveness
- Respect for oneself- expressing one's needs and defending one's rights
- Respect for the other person
Nonassertive people don't _______________
respect themselves
Why might nonassertive people be dishonest or hesitant to reveal the truth?
Because they don't believe they have the right to express their own thoughts and feelings
Nonassertive people can be expressed as...
passive-aggressive or manipulative behavior
- because of their lack of respect for their own rights
Passive-aggressive behavior
Individuals express negativity or anger indirectly, often through sarcasm, subtle digs, or other indirect behaviors, while appearing outwardly calm or submissive
What does nonassertive behavior often encourage? Why?
the inappropriate behavior of others
- because inappropriate behavior is not challenged
Aggressive people don't _____________
respect others
Aggressive people are:
- Willing to......
- May be ________, ____________, and generally attempt to ___________________
- They need to be ________, and often will not acknowledge the validity of ______________, _____, or _________
- Often use _________, __________, _________, and ________________ in their communication with others
- violate the rights of others in order to meet their own needs
- may be loud, interrupt others, and generally attempt to dominate conversations
- They need to be right, and often will not acknowledge the validity of different opinions, values, or ideas
- Often use blaming, criticism, sarcasm, threats, and name-calling in their communication with others
Assertive people ________________________
respect themselves and others
Assertive people
- Respect _________, but also expect to be _____________
- Are ______________
- Own their own ___________, ________, and ________
- Willing to ___________ and __________ communicate their ______________, __________, and __________
- Willing to communicate when they do not feel ____________ or they believe that _____________ have been violated
- respect others, but also expect to be respected
- are courageous
- own their own feelings, thoughts, and ideas
- Willing to openly and honestly communicate their feelings, opinions, and needs
- Willing to communicate when they do not feel respected or they believe that boundaries have been violated
Passive vs. Aggressive vs. Assertive chart
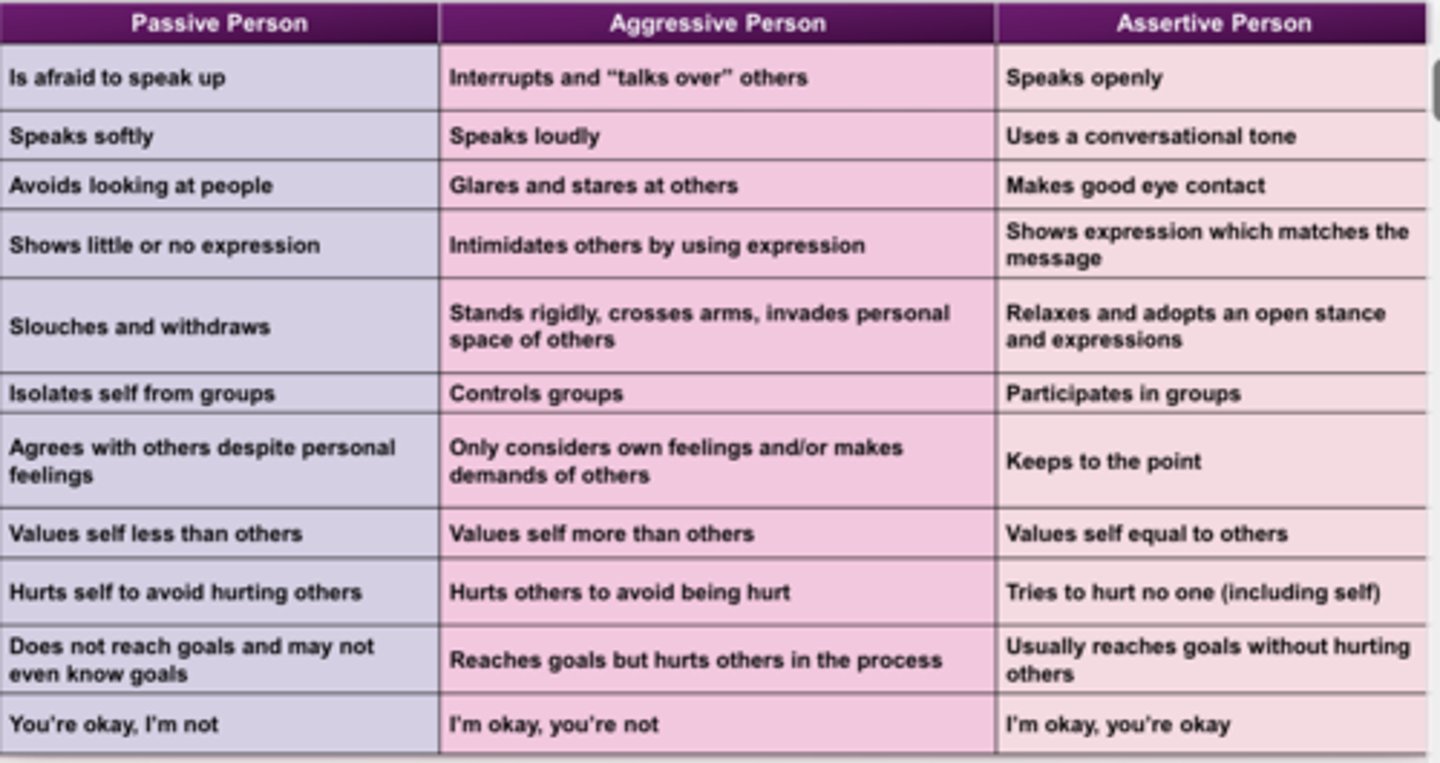
What is a hallmark of practicing being assertive?
Making "I" statements
What do "I" statements cause us/force us to do?
- "I" statements cause us to take responsibility for our feelings, ideas, and needs
- "I" statements often force us to "look inside" and decide what the issues are
Making "I" statements means being...
responsible for oneself
Making "I" statements allows us to come to the realization that....
we cannot change other people's behaviors
- we can only change our response and communicate what we need
It is important to use "I" statements to...(4)
- Respond in a way that will de-escalate conflict- avoid using "you" statements that will escalate conflict
- Identify feelings
- Identify behaviors that are causing the conflict
- individuals resolve the present conflict and prevent future conflicts
Examples of "I" Statements chart
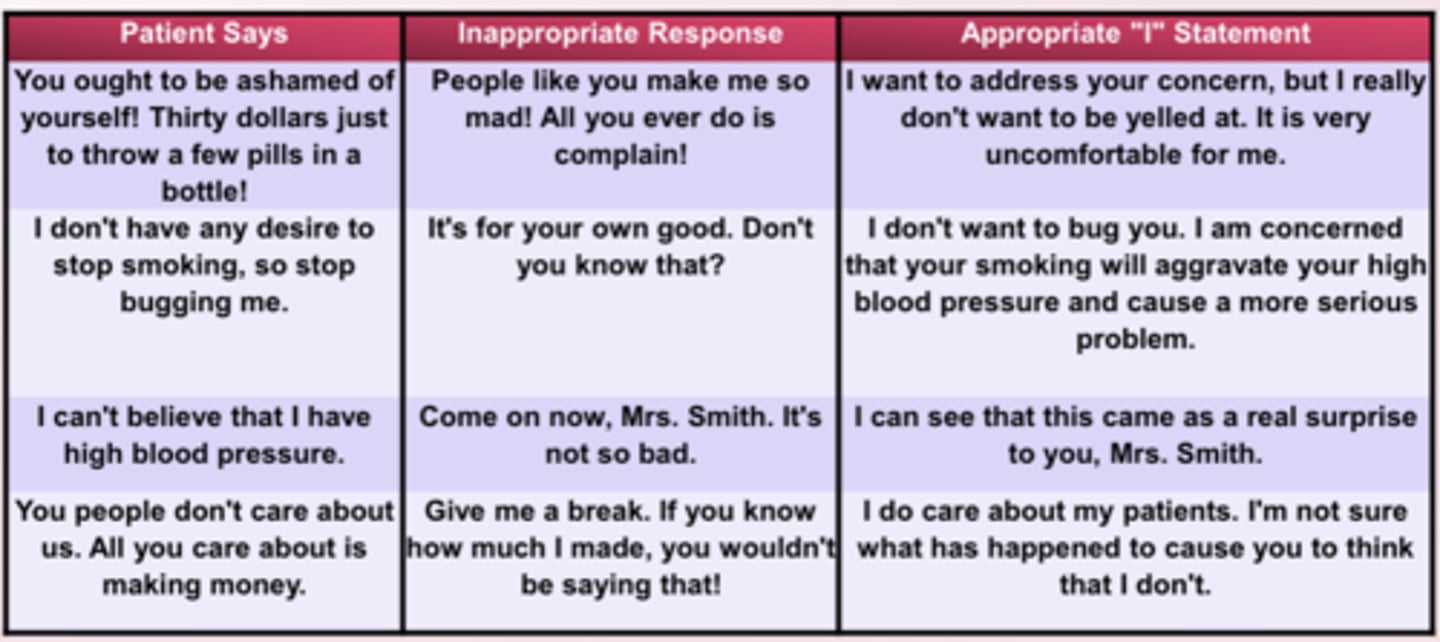
Husband gets silent instead of saying what's on his mind. Wife says, "I get the feeling that you're uncomfortable talking about what's bothering you. I think we can work that out if you tell me what's irritating you."
Identify whether the statement is....
- Nonassertive (or passive)
- Aggressive
- Assertive
Assertive
You'd like a raise and say, "Uh, do you think that you could consider giving me a raise?"
Identify whether the statement is....
- Nonassertive (or passive)
- Aggressive
- Assertive
Nonassertive or passive
A co-worker approaches you while you are busy and asks for help with a task. You respond "You always approach me at the last minute when you need help and expect me to drop everything and help you, but you never help me when I need help. So, no, I will not help you now."
Identify whether the statement is....
- Nonassertive (or passive)
- Aggressive
- Assertive
Aggressive
You've been talking for a while with a friend on the telephone. You would like to end the conversation and you say, "I'm terribly sorry, but my supper is burning and I haveto get off the phone. I hope you don't mind."
Identify whether the statement is....
- Nonassertive (or passive)
- Aggressive
- Assertive
Nonassertive (or passive)
At a meeting, one person often interrupts you when you're speaking. You calmly say, "Excuse me, I would like to finish my statement."
Identify whether the statement is....
- Nonassertive (or passive)
- Aggressive
- Assertive
Assertive
A student responds to a fellow classmate, "You really frustrate me when you forget our deadlines and make our projects late. Why can't you just get the work done on time?"
Identify whether the statement is....
- Nonassertive (or passive)
- Aggressive
- Assertive
Aggressive
To communicate effectively during your consultations with pts, stay in an....
assertive mode
Assertiveness: Present your views in a ____________ and ___________ fashion
- forthright and confident
People do not usually have a high level of __________________ in a nonassertive speaker
confidence
Conversely, they are frequently offended by....
aggression
Some misconceptions about assertiveness: (2)
- some think that assertive people tend to be rude, impolite, pushy, and uncaring
- a truly assertive communicator is none of these
Assertion is not....(6)
- aggressive
- hostile
- confrontational
- ambiguous
- demeaning
- condescending
The strategies that can help you be more assertive (8)
o Broken record
o Fogging
o Negative inquiry
o Workable compromise
o Sorting issues
o Disarming anger
o Selective ignoring
o Assertive withdrawal
Broken record
- use calm repetition
- saying what you want over and over again
- allows you to be persistent in your communication without having to rehearse arguments or angry feelings beforehand

Fogging
- accepting manipulative criticism by calmly acknowledging to your critic the probability that there may be some truth in what he or she says
- Aims to give a minimal, calm response using terms that are placating but not defensive, while at the same time not agreeing to meet demands
- remain your own judge of what you do during the situation

Negative inquiry
- actively promoting criticism to use the info (if helpful) or exhaust it (if manipulative)
- prompting your critic to be more assertive and less dependent on manipulative ploys
Workable compromise
- may be practical to offer a workable compromise to the other person
- can always bargain for your material goals unless the compromise affects your personal feeling or self-respect
- in the end goal involves a matter of your self-worth, however, there can be no compromise
- use whenever you feel that your self-respect it not in question

Sorting issues
- several issues will become sandwiched together
- unless these issues or messages are sorted out and dealt with separately, the individual may begin to feel confused, anxious, and overwhelmed
- it is to the assertive individual's and the recipient's advantage to deal with these issues separately

Disarming anger
- extremely useful protective technique
- offered to another person exhibiting a lot of anger and who may bordering on physical violence
- writing down an angry person's comments will often help to defuse the anger-slows person down, cant write as fast as they yell; will choose words more cautiously when a record is being kept

Disarming anger: Agree that you will talk about...
whatever issue the other person wants, but only after some of the anger dissipates

Selective ignoring
- involves deciding to address or not address specific content from another individual
- replies are not given to unfair or abusive interactions, but only to statements that are not destructive, guilt-producing, prejudicial, or unjust

Assertive withdrawal
- What does it involve?
- What can it be accomplished by?
- What does it reinforce?
- involves a clear verbal or nonverbal signal that indicates you are postponing or terminating a conversation
- walking away, hanging up the phone, nonverbally removing your attention by starting other work
- Reinforces the verbal message that the conversation has ended
- approach this in a professional and calm manner

Assertive withdrawal is a drastic measure that should only be used when...
a situation is clearly out of hand
Assertiveness is an essential strategy for managing what?
managing conflict
One must also commit to knowing __________________ in addition to understanding and practicing your _____________ rights
- personal style
- assertiveness
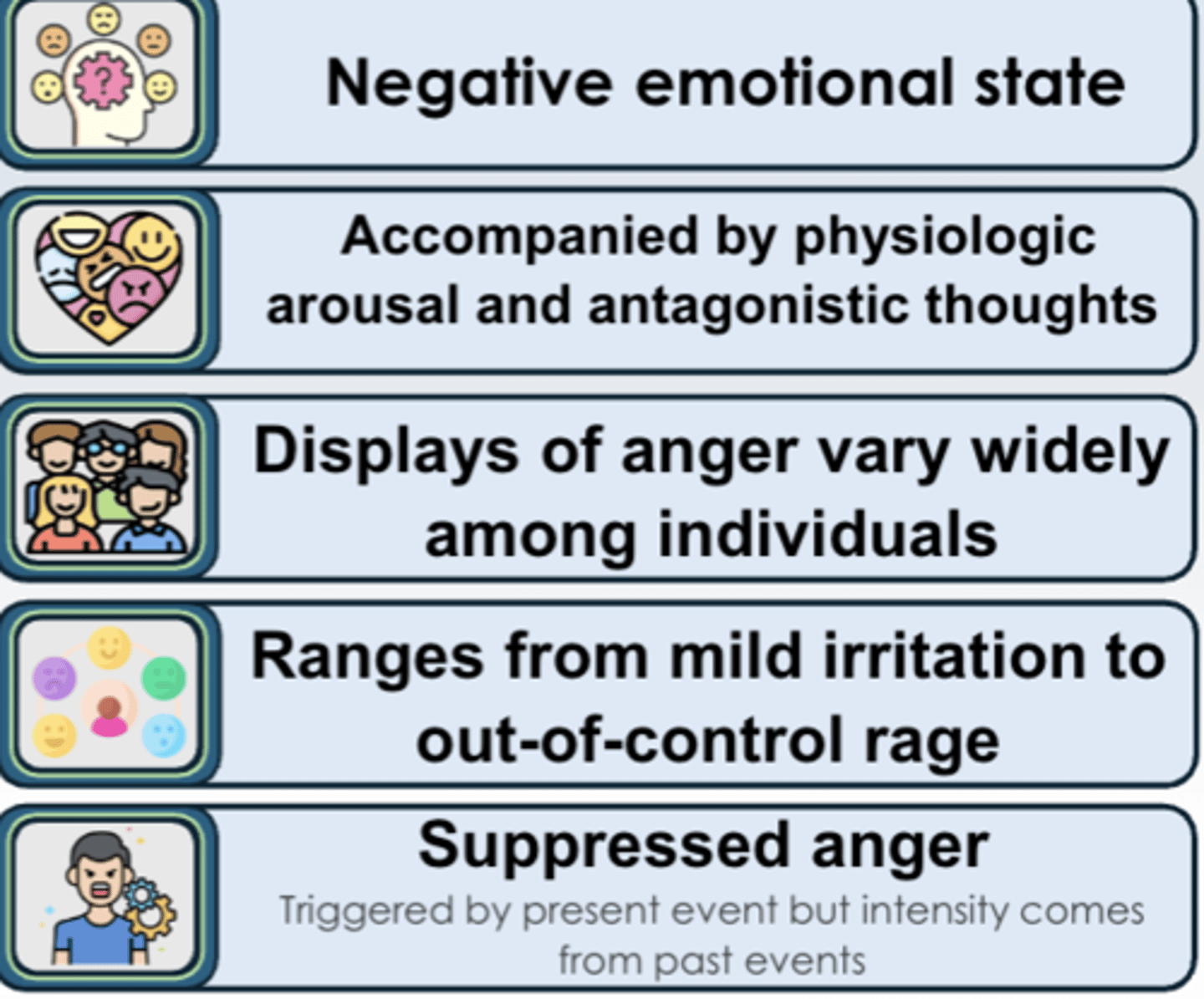
Anger
- negative emotional state
- accompanied by physiologic arousal and antagonistic thoughts
- displays of anger vary widely among ppl
- ranges from mild irritation to out-of-control rage
- suppressed anger
Why is it important to detect and manage anger in the healthcare setting? (4)
• Keep Health Care Providers Safe (reports of anger leading to violence)
• Keep Patients Safe
• Avoid Disruptions In Care, Adherence, And Follow-up (can lead to worse outcomes)
• Anger That Is Not Addressed Can Contribute To Malpractice Lawsuits (rates of lawsuits decline when healthcare providers admit their mistakes and apologize)
Continuum of Anger in Health Care Setting (6)
1. Calm and nonthreatening
2. Verbally agitated
3. Verbally hostile
4. Verbally threatening
5. Physically threatening
6. Physically violent
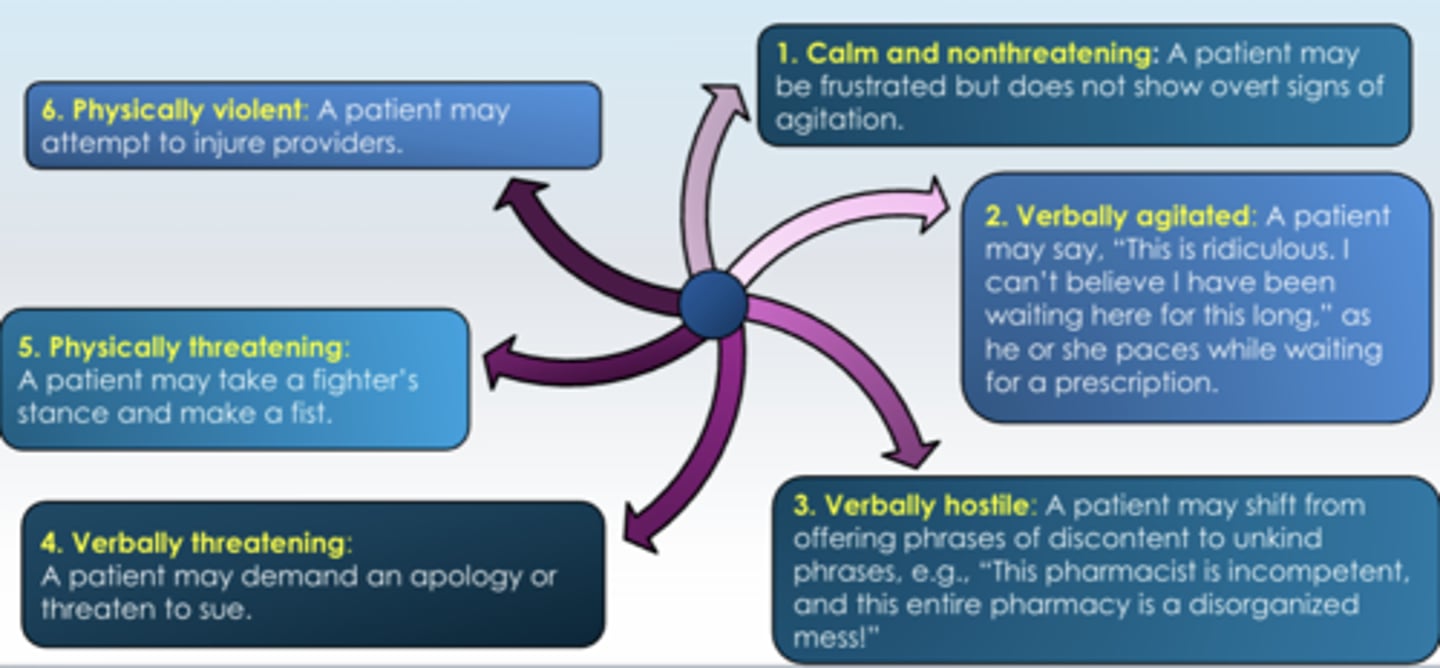
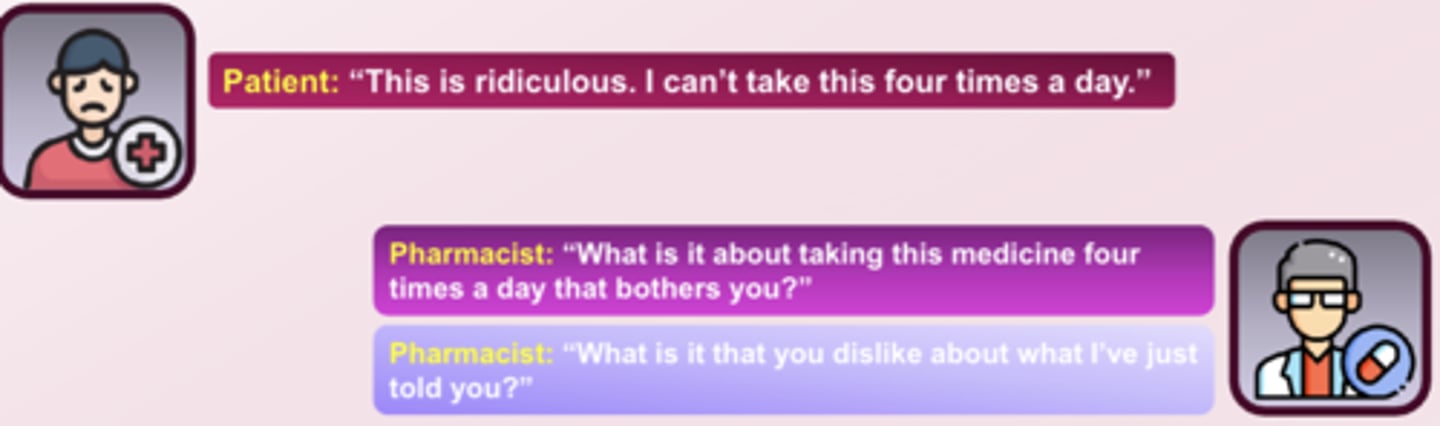
Continuum of Anger in Health Care Setting: 1. Calm and nonthreatening
A patient maybe frustrated but does not show overt signs of agitation