Neonatal Brain
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are the 3 parts of the brain?
~ Cerebrum
~ Cerebellum
~ Brainstem
Arachnoid
The middle layer of meninges covering the brain and spinal cord
Atrium (Trigone) of Lateral Ventricles
Area where the Anterior, Occipital, and Temporal Horns join
Brainstem
The part of the brain that’s connected to the forebrain and spinal cord. Consists of Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata
Caudate Nucleus:
Where and What does it consist of?
Next to LAT wall of LAT ventricle
Consists of a head, body, and tail
Cavum Septum Pellucidum
A thin, triangular hole that’s filled w/CF that lies between ANT Horns of the LAT Ventricles. If it extends POST » Cavum Vergae
**Forms the medial wall of the LAT ventricles
Central Nervous System (CNS)
What does it consist of?
Cerebellum, Cerebrum, Spinal Cord, Pons (brainstem), and Medulla
Cerebellum
Portion of brain that lies POST to Pons and Medulla below tentorium
Cerebral Hemispheres
Paired brain matter separated from ML by falx cerebri
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain, which consists of 2 hemispheres and is made up of 6 lobes
~ 1 Frontal
~ 1 Occipital
~ 2 Parietal
~ 2 Temporal
Choroid Plexus
Mass of special cells located in the atrium of the LAT Ventricles. It regulates the intraventricular pressure by secreting or absorbing CSF (Cerebrospinal Fluid)
**Appears ovoid and echogenic**
What lies between each layer of meninges?
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Cistern
Enclosed space serving as a reservoir for CSF
Corpus Callosum
Large group of nerve fibers visible SUP to third ventricle connecting the brain’s LT + RT hemispheres
**Thick band of white matter connecting the 2 hemispheres and forms the roof of the LAT ventricles**
Ependyma
The membrane lining the cerebral ventricles
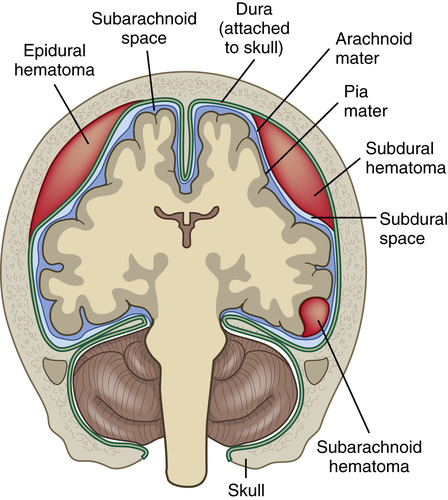
Epidural
Space that lies outside the dura mater
Falx Cerebri
(Interhemispheric Fissure)
A fibrous structure separating the 2 cerebral hemispheres
Germinal Matrix
Periventricular tissue including the caudate nucleus. Before 32w, it’s fragile and easily bleeds
Gyri
Convolutions on the brain’s surface caused by the infolding of the cortex
Meninges
3 protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord
Parenchyma
Cortex tissue of the brain
Pia Mater
Innermost meningeal membrane
Subdural Mater
The meningeal membrane between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater
Subependymal region/zone
Area immediately beneath the ependymal lining of the brain’s ventricles
**Hemorrhage site in the caudate nucleus from the germinal matrix**
Subarachnoid Mater
The meningeal layer between the arachnoid and the pia mater
Sulcus
A groove or depression on the brain’s surface separating the gyri
Sylvian Fissure
Lateral cerebri fissure that separates the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain
**MCA runs through here**
Telea Choroidea
Point where the choroid attached to the floor of the LAT ventricles and located behind the Foramen of Monro
**Most common site of hemorrhage**
Tentorium
V-shaped echogenic structure that separates the cerebrum and cerebellum and is an extension of the falx cerebri
Thalamus
2 ovoid brain structures situated on either side of the third ventricle SUP to brainstem
Ventricles
Cavities within the brain containing CSF
Vermis Cerebellum
Median part of the cerebellum which lies between the 2 hemispheres
The cranial end of the neural tube differentiates into which 3 primary vesicles?
1) Prosencephalon (Forebrain)
2) Mesencephalon (Midbrain)
3) Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain)
**Cranial end of neural tube differentiates at the end of the 4th week
The caudate nucleus is a common site for …
… Intracranial hemorrhage
The diencephalon is [SUP / INF] to the brainstem
SUPERIOR
What does the neural plate form?
Neural Tube + Neural Crest
The neural tube differentiates into the …
… CNS = Brain + Spinal Cord
The neural crest differentiates or gives rise to the …
… PNS
The nuchal fold is … to CM (Cisterna Magna)
SUP and POST
The caudate nucleus is … to LAT ventricles
ADJACENT
The cerebrum’s divided into 2 cerebral hemispheres by the … and is connected by …
Longitudinal Fissure ; Corpus Callosum
*Longitudinal Fissure AKA Interhemispheric fissure, Great/Median longitudinal fissure
The cerebellum is divided by the … into 2 hemispheres and separated from the occipital lobe by the … superiorly
Vermis ; Transverse Fissure
What are the “ropes” that help connect the cerebellum to the brainstem?
Cerebellar peduncles
What site is where the Anterior, Occipital, and Temporal horns join together?
Atrium or Trigone
The body of LAT ventricle extends from the … to trigone
Foramen of Monro » Trigone
Foramen of Monro
AKA Intraventricular Foramen
Divides frontal horn ANT from body of ventricle POST and connects 3rd Ventricle » LAT Ventricle
Aqueduct of Sylvius
AKA Cerebral Aqueduct
Connects the 3rd Ventricle » 4th Ventricle
Foramen of Luschka
The opening in the roof of the 4th Ventricle for circulation of CSF
**AKA LAT apertures of 4th Ventricle
Foramen of Magendie
AKA Median Aperture
The opening in the INF roof of the 4th Ventricle for circulation of CSF
**Gateway that enables CSF to reach spinal cord via subarachnoid space and exit ventricular system and enter CM
Spalding Sign
Overlapping of fetal cranial bones » Intrauterine fetal demise
Anterior Fontanelle
Located at the top of neonatal head and felt as “soft spot”
**Bulges w/hydrocephalus
Glomus of Choroids
Prominent tuft of choroidal tissue located in the atrium/trigone of each LAT Ventricle
What’s the most common intracranial pathology in neonates and infants?
Intracranial Hemorrhage
Subependymal Hemorrhage (SHE)
Occurs in the caudate nucleus and can be seen INF to the floor of the LAT Ventricles
The cavum vergae completely closes by … months after birth
3-6 months
Intraparenchymal hemorrhages…