Exam 1 - Chapter 2 Lecture
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
All cells must have a
cell membrane
Major functions of the cytoplasmic membrane
1. Permeability barrier
2. Protein anchor
3. Energy conservation
Cell membrane as a permeability barrier
Prevents leakage & functions as a gateway for transport of nutrients into, and wastes out of, the cell
Cell membrane is the site of proteins that participate in...
transport, bioenergetics, and chemotaxis
How does the cell membrane function in energy conservation?
Site of generation and dissipation of the proton motive force
Passive transport
Follows concentration gradient (energy-independent)
Active transport
Accumulate solutes against concentration gradient (energy-dependent)
Simple transport
Driven by the energy in the proton motive force
ABC Transporter
Periplasmic binding proteins are involved and energy comes from ATP
Group translocation
Chemical modification of the transported substance driven by phosphoenolpyruvate (common in bacteria and archaea)
3 classes of transport systems
simple transport, ABC transporter, group translocation
Antiporter
A carrier protein that transports two molecules across the plasma membrane in opposite directions.
Symporter
Transporter that carries two different ions or small molecules, both in the same direction
Functions of the cell wall
1. Withstand osmotic/turgor pressure to prevent cell lysis
2. Maintain cell shape & rigidity
Do all microbial cells have a cell wall?
No, but most do
Gram stain classification of bacteria is based on...
organization and cell wall structures
Cells without a cell wall are more sensitive to...
changes in osmotic/turgor pressure
Gram positive cell wall
Has one layer of membrane and a thick cell wall/peptidoglycan layer
Gram negative cell wall
Has 2 membrane layers with a thin cell wall/peptidoglycan layer in between
Peptidoglycan is not found in...
Archaea or Eukarya
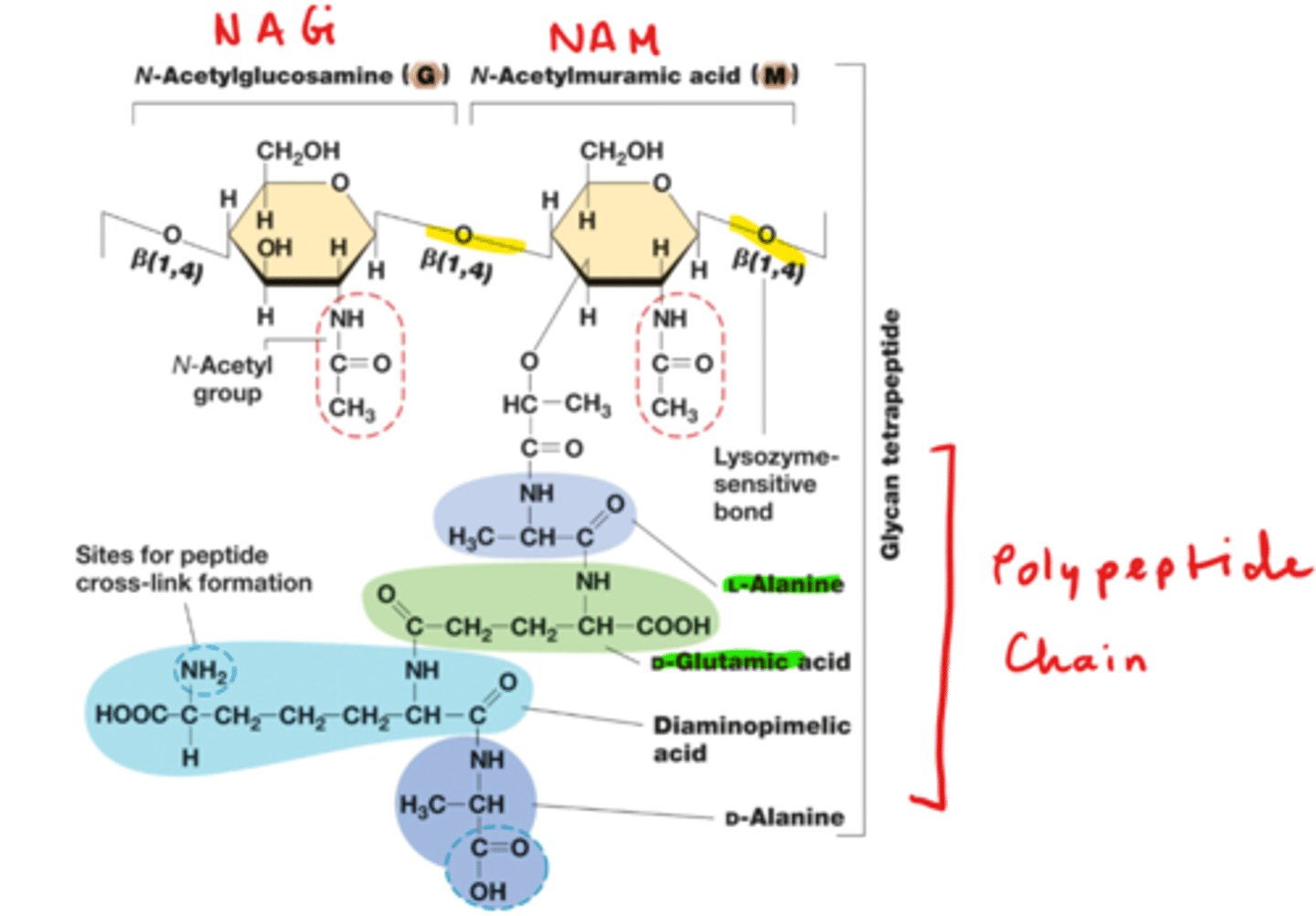
What structure is shown?
Peptidoglycan
The gram + cell wall is more...
1. Rigid
2. Resistant to salt, dryness, and osmotic changes
3. Sensitive to peptidoglycan inhibitors
The gram - cell wall is more...
1. Flexible
2. Sensitive to salt, dryness, and osmotic changes
3. Resistant to peptidoglycan inhibitors
Gram - cell wall impact on transport
Makes it harder to transport nutrients due to 2 membrane layers
LPS
Additional protection in gram - cell wall that can trigger immune response
Bacterial Capsules/Slime Functions
1. Assist in attachment to surfaces
2. Role in development and maintenance of biofilms
3. Contribute to infectivity
4. Prevent dehydration/dessication
Bacterial Capsules/Slime
Coating on outside of cell wall present in some cells which can be lost by the cell
Capsules vs slime
Capsules: More rigid and more permanently attached to the cell wall
Slime: More loose and easier to lose
Fimbriae
Filamentous extracellular structures that help mediate attachment, used mostly for adhesion to surfaces and other cells (different from flagella!)
Pili
A type of fimbriae that can be used for adhesion or genetic exchange
What are the names for pili used for genetic exchange?
F-pili
Conjugative pili
Sex pili
Function of cell inclusions
1. Energy reserves
2. Carbon or phosphorus reservoirs
3. Special functions
4. Reduces osmotic stress
Cell inclusions are enclosed by...
thin protein membrane
Gas vesicles
Allow buoyant cyanobacteria to float to surface for exposure to air, sun, etc. or sink beneath the surface for darkness, to avoid predators, etc.
Bacterial endospore
Survival structures to endure unfavorable growth conditions (not for reproduction) - allow a cell to stay dormant for years until conditions become favorable to return to a vegetative cell
Life cycle of endospore-forming bacterium
1. Vegetative cell
2. Sporulation: develops endospore
3. Mature endospore
4. Germination: Conversion from endospore back to vegetative cell
How many parents yield 1 endospore?
1
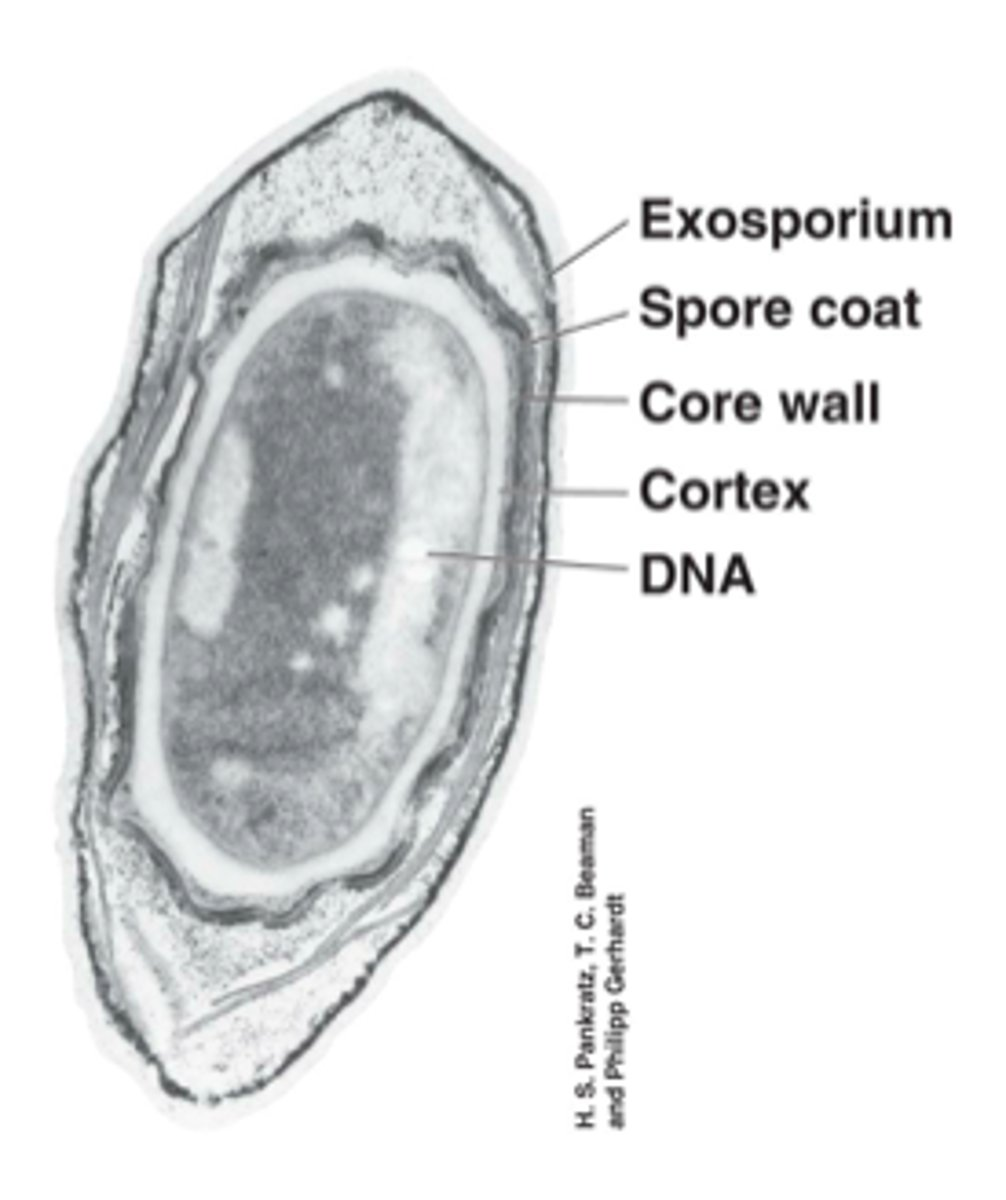
What structure is shown?
Endospore
Endospore structures
1. Exosporium
2. Endospore coat
3. Outer spore membrane
4. Cortex
5. Inner membrane
6. Core
7. DNA
Bacterial flagella
Functions in cell motility but not present in all motile cells
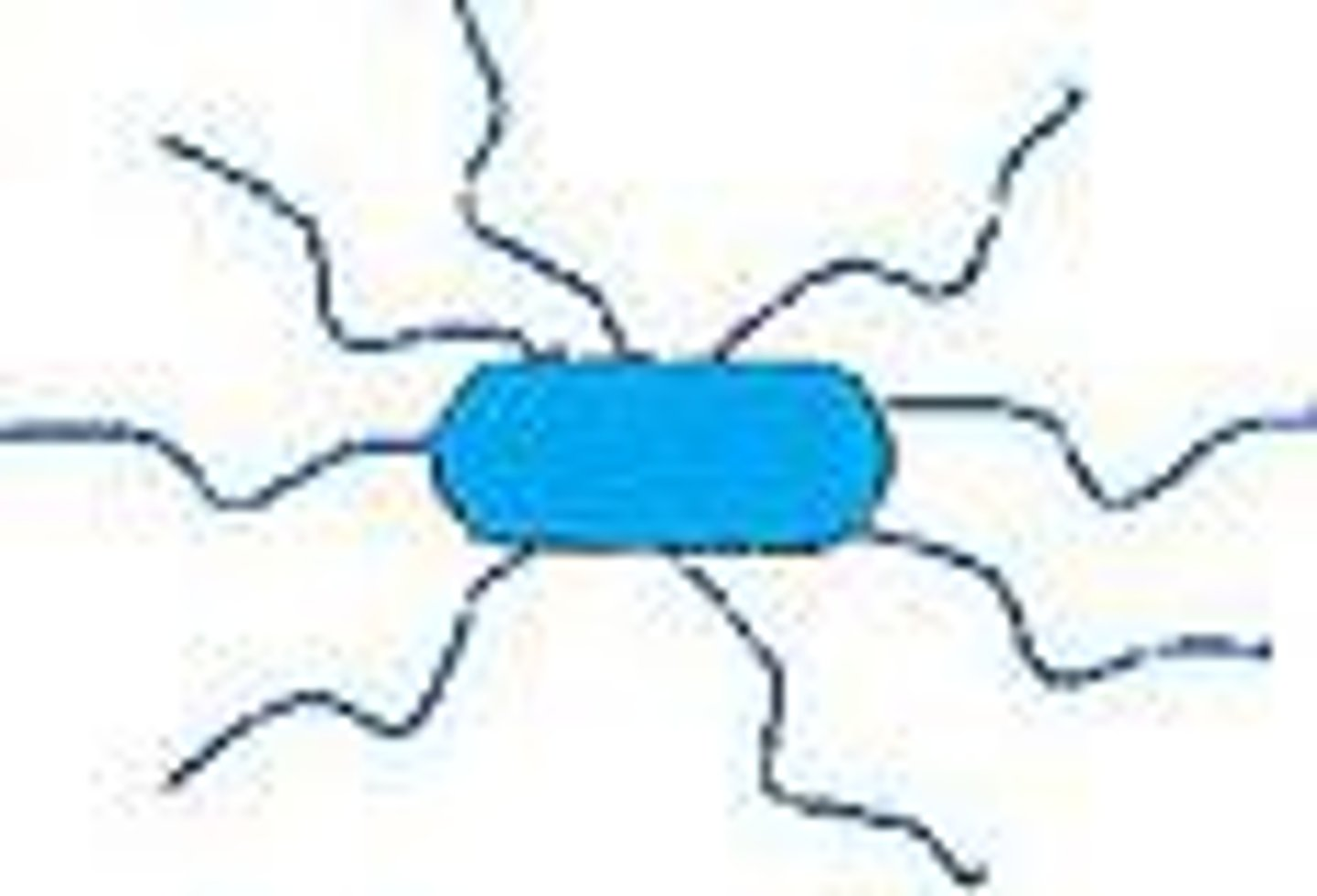
What arrangement of flagella is shown?
Peritrichous flagella
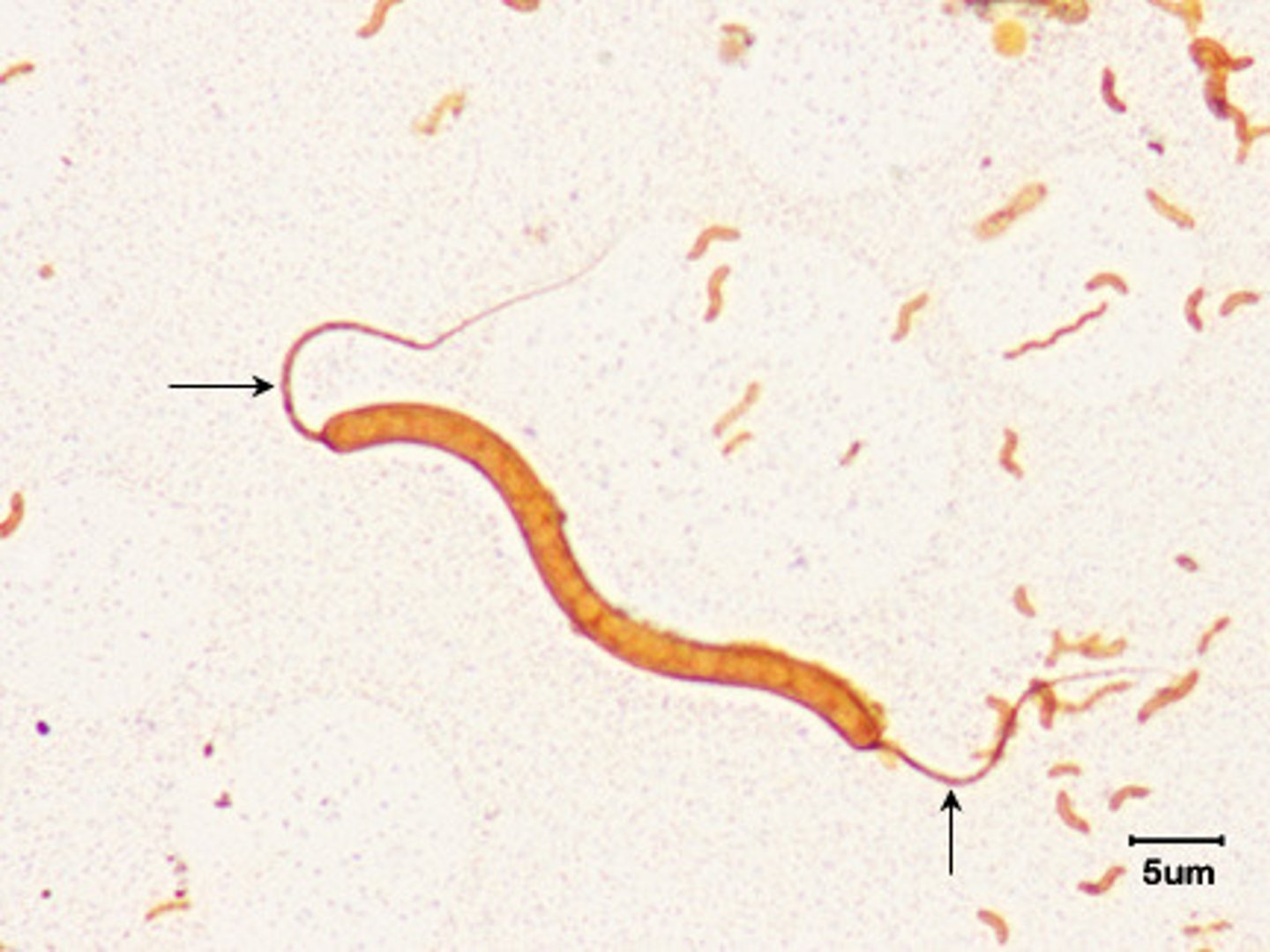
What arrangement of flagella is shown?
Polar flagella
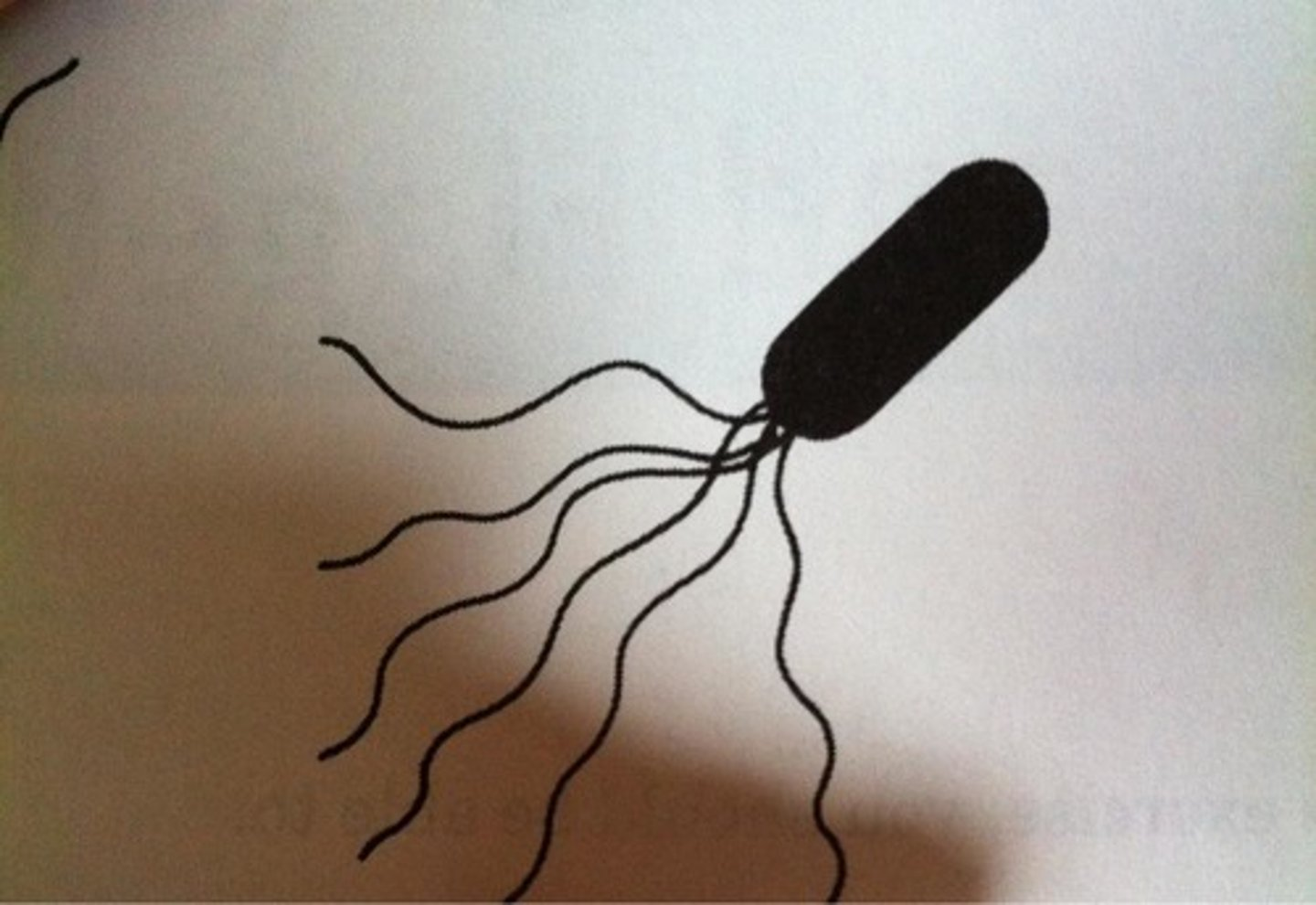
What arrangement of flagella is shown?
Lophotrichous flagella
Peritrichous flagella
flagella that cover the surface of a cell
Polar flagella
flagella only at the end of a cell (one or both ends)
Lophotrichous flagella
multiple flagella on either end
Movement in peritrichously flagellated prokaryotic cells
1. Bundled flagella rotate counterclockwise to facilitate cell runs
2. Flagella spread apart and rotate clockwise to facilitate cell tumbles
3. Random reorientation
4. Repeat
Movement in polarly flagellated prokaryotic cells (reversible)
1. Flagella rotates counterclockwise for cell run
2. Flagella rotates clockwise & cell reverses
Movement in polarly flagellated prokaryotic cells (unidirectional)
1. Flagella rotates clockwise for cell run
2. Rotation stops and random reorientation occurs
3. Clockwise rotation for cell run (repeat)
Chemotaxis in Peritrichously Flagellated Bacteria
1. No attractant present: cell runs and tumbles randomly - random movement; no net movement
2. Attractant present: Directed movement - cell runs, tumbles, and runs in direction of attractant (tumbles to reorient towards attractant); net movement toward attractant
Chemotaxis
Response to chemicals
Osmotaxis
response to ionic strength
Hydrotaxis
response to water
Aerotaxis
response to oxygen
Phototaxis
response to light
T/F: Only motile cells can perform taxis
True
T/F: Cells must have flagella to perform taxis
False
Eukaryotes compared to prokaryotes
Bigger and more complex cells; evolved from prokaryotes
Cilia
Extracellular structures that are functionally equivalent to flagella but different in chemical composition and motion
Cilia composition
Made of microtubules
Cilia motion
waving/undulation motion (no rotation)