Anatomy - Intro to anatomy, cells, and homeostasis
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
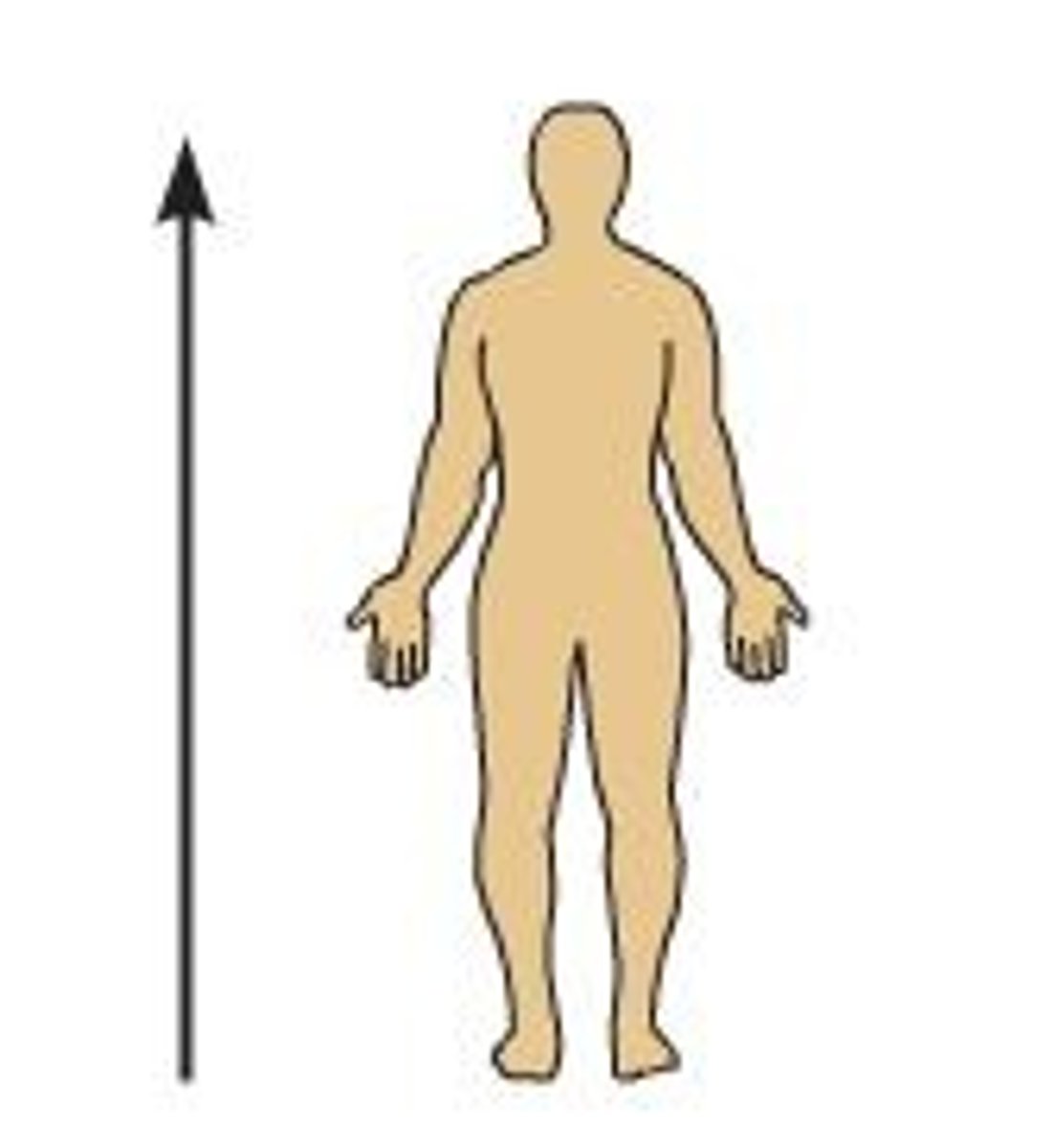
Superior
Toward the head end of upper part of body
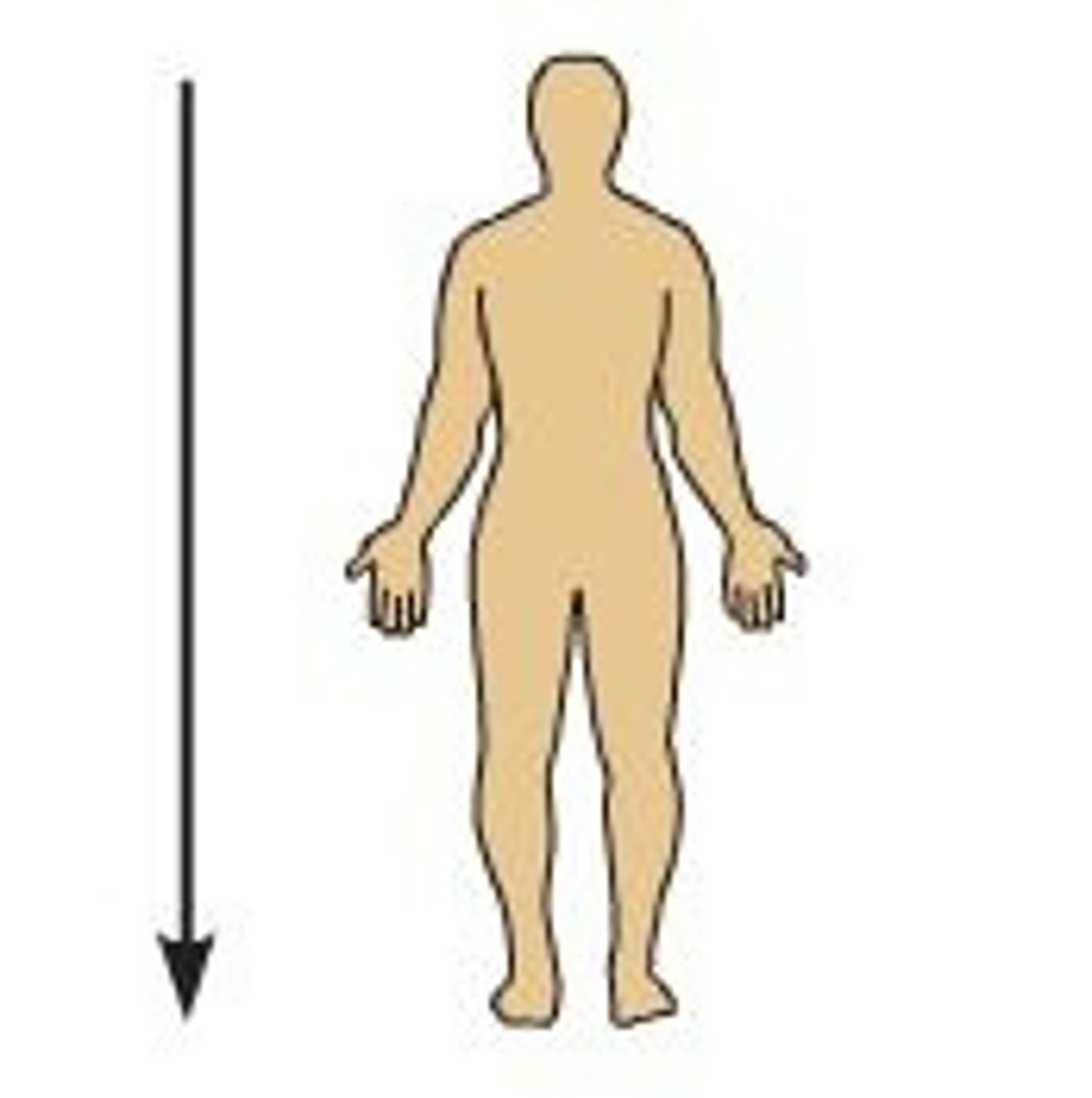
Inferior
Away from the head end and toward the lower part of the body
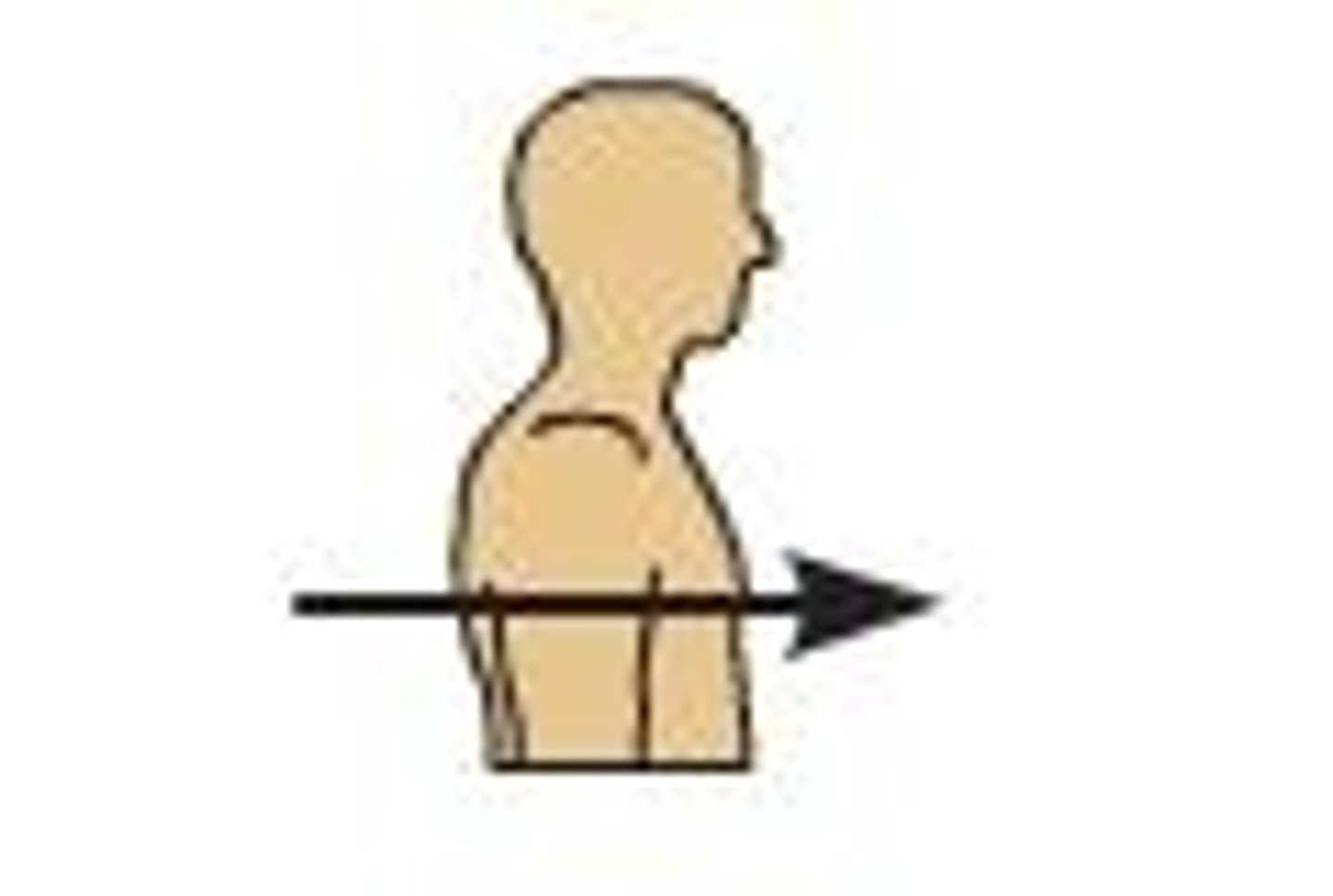
Anterior (ventral)
Toward the front or belly side
Posterior (dorsal)
Toward the back
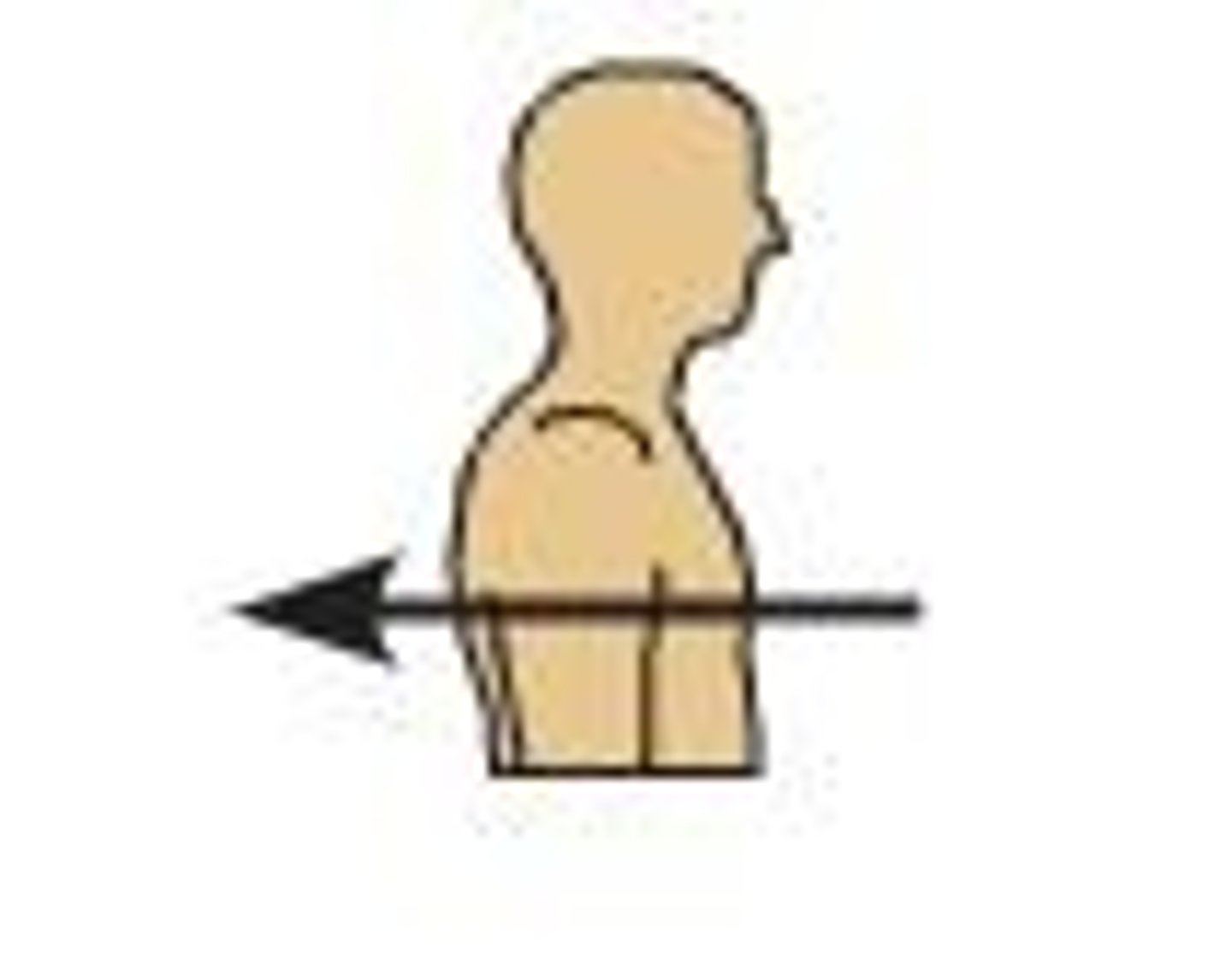
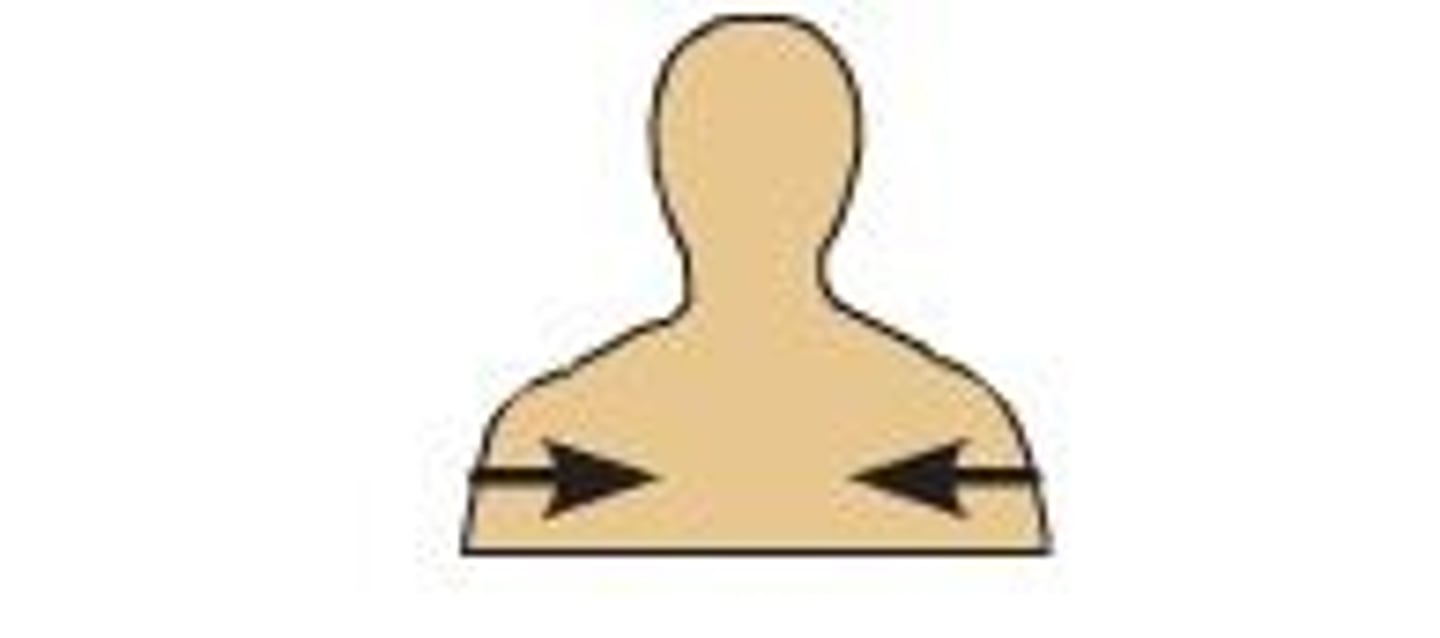
Medial
Toward the midline
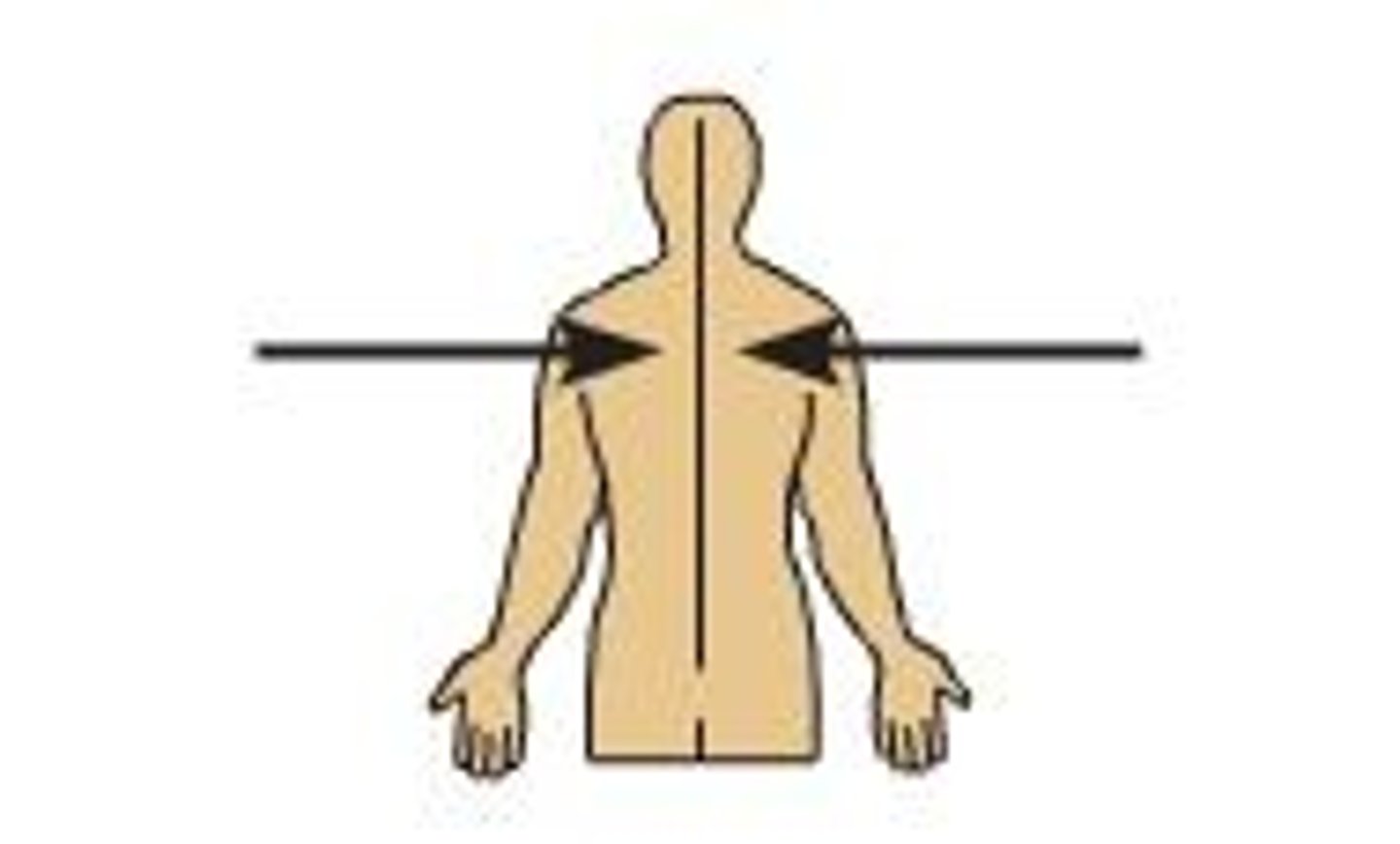
Lateral
Away from the midline
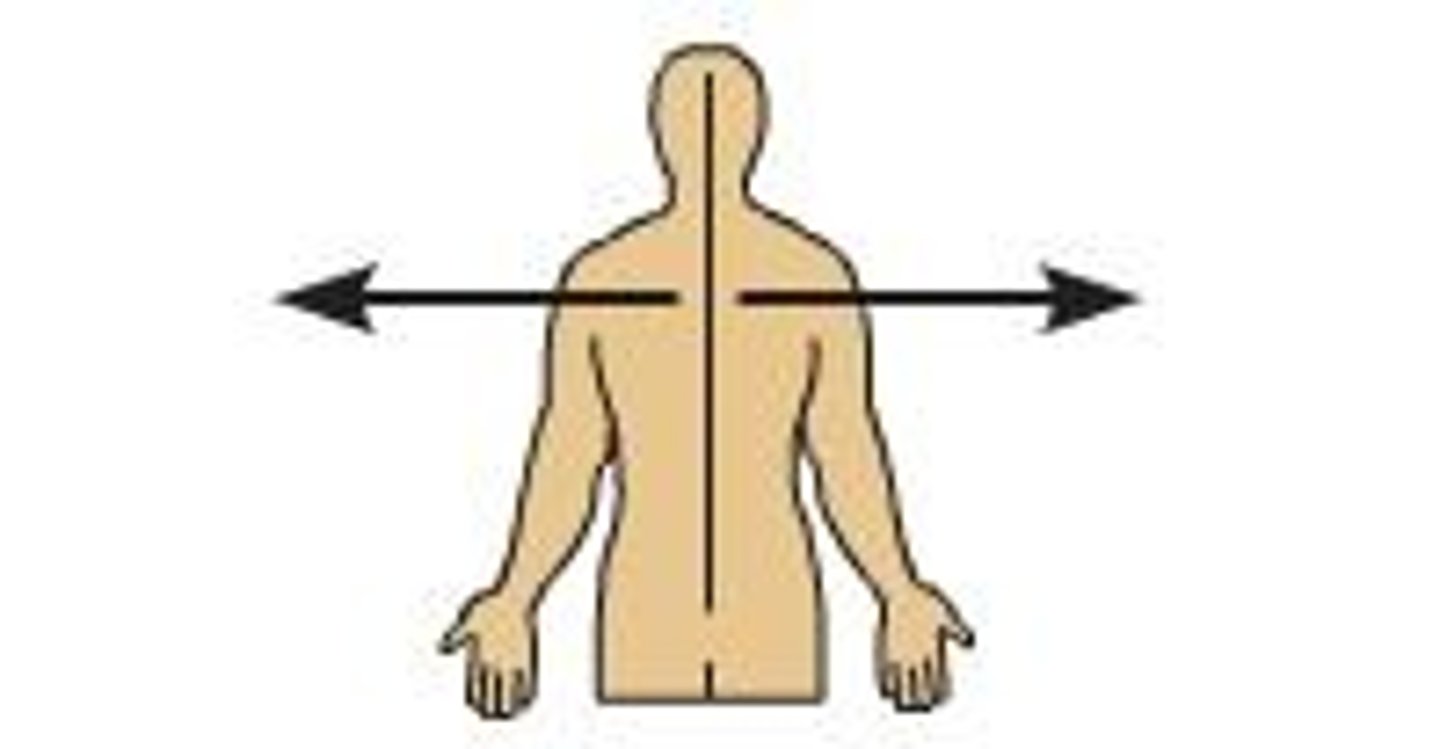
Superficial
Toward the surface of the body
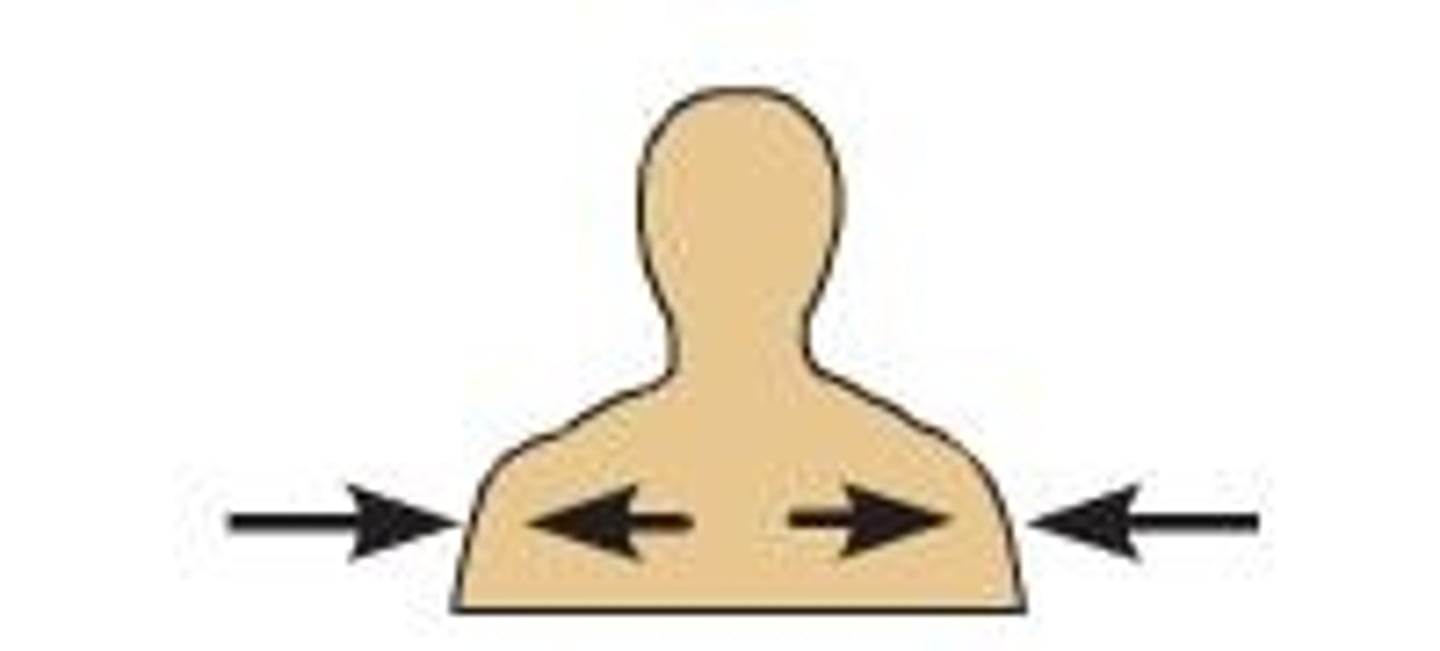
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
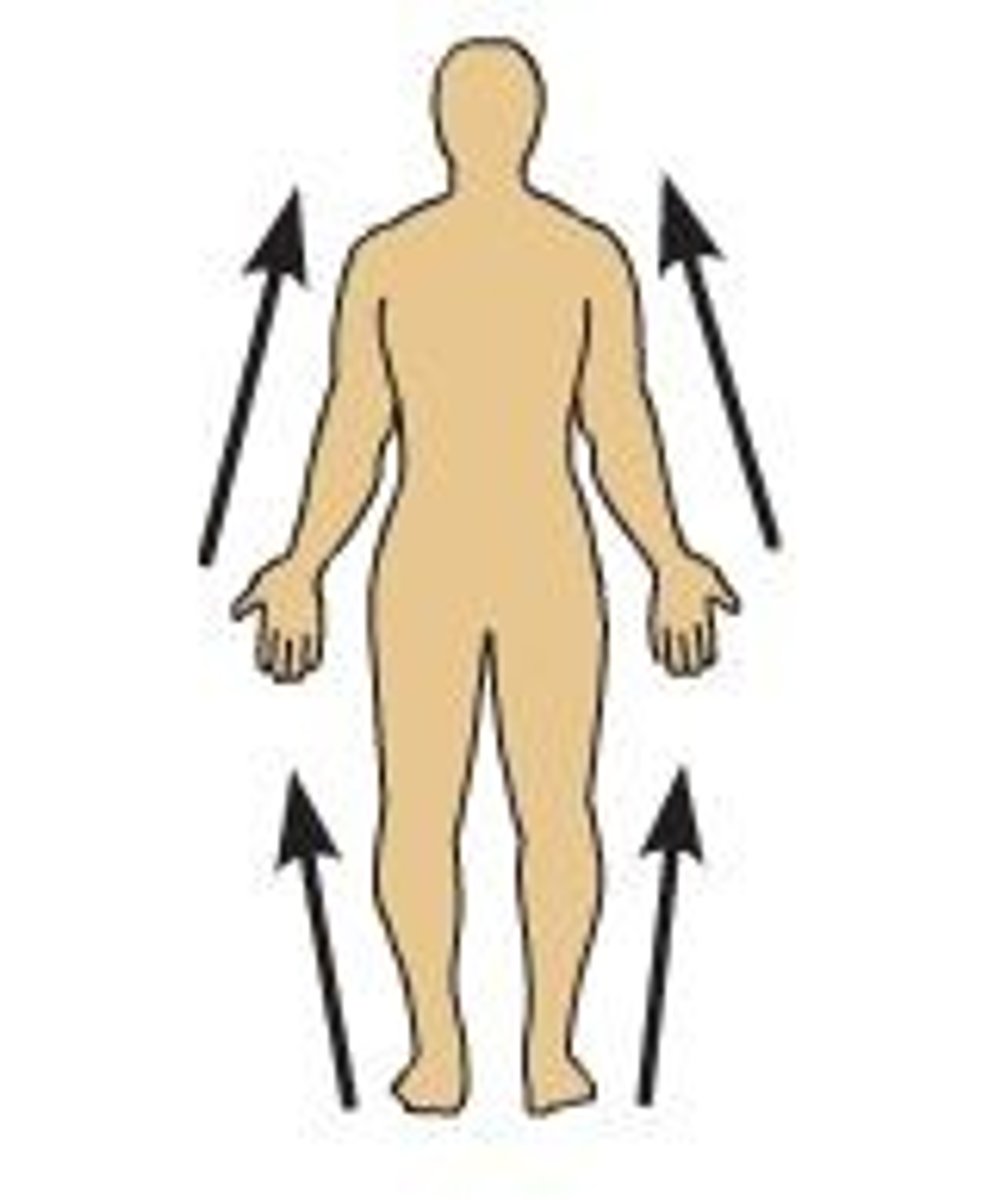
Proximal
Toward a structure's origin or point of attachment to the trunk
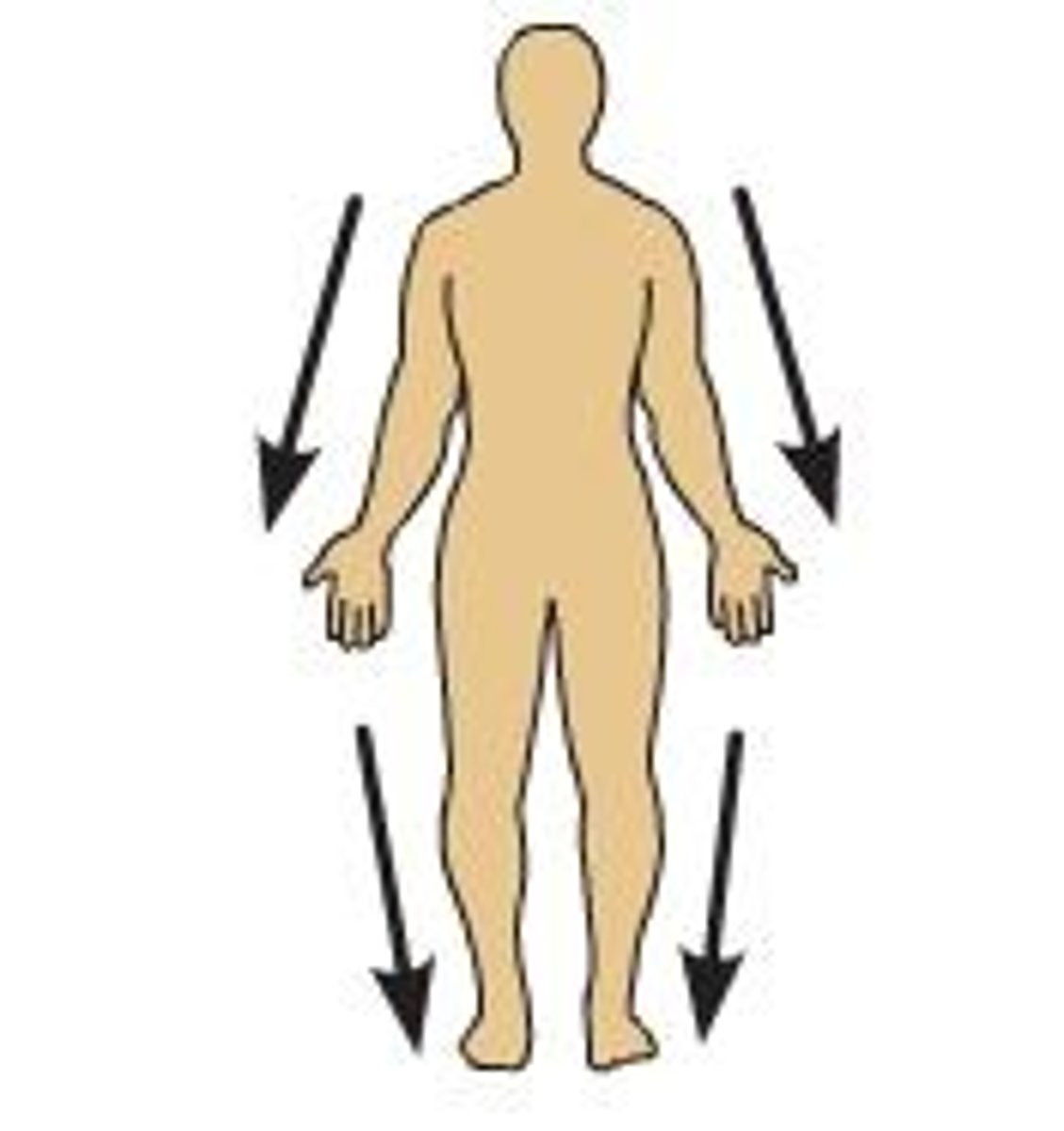
Distal
Away from a structure's origin or point of attachment to the trunk
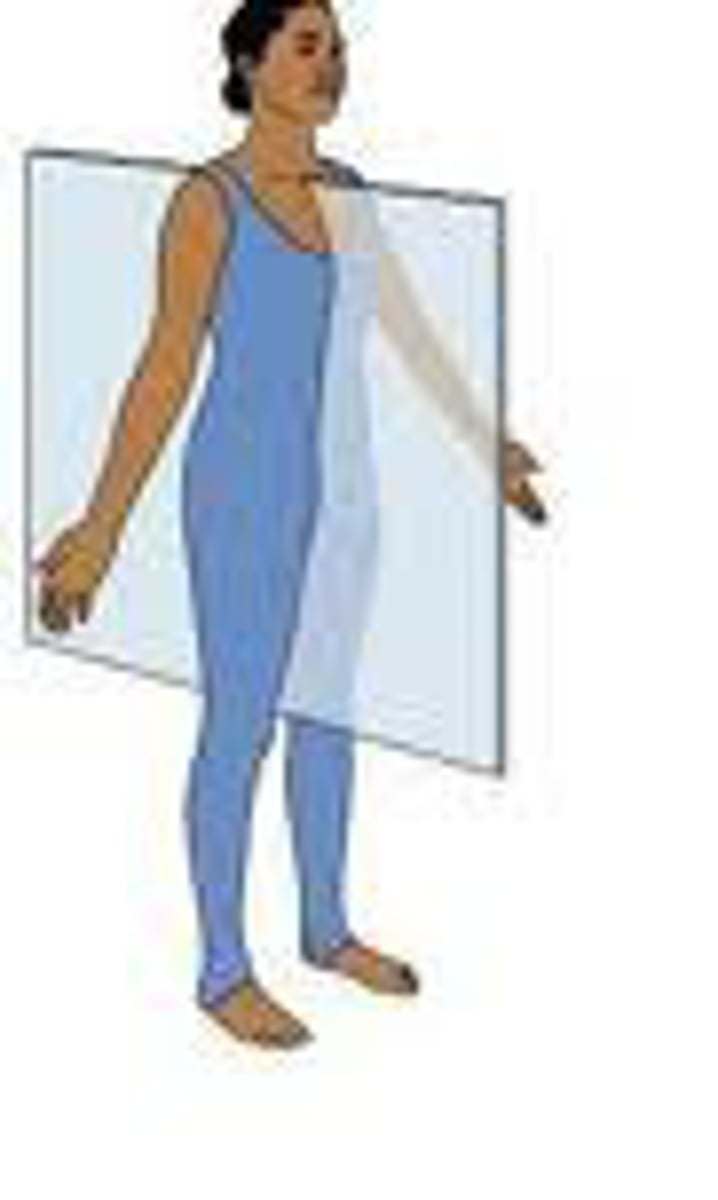
Coronal Plane/Frontal
Divides body into anterior and posterior portions (frontal plane)
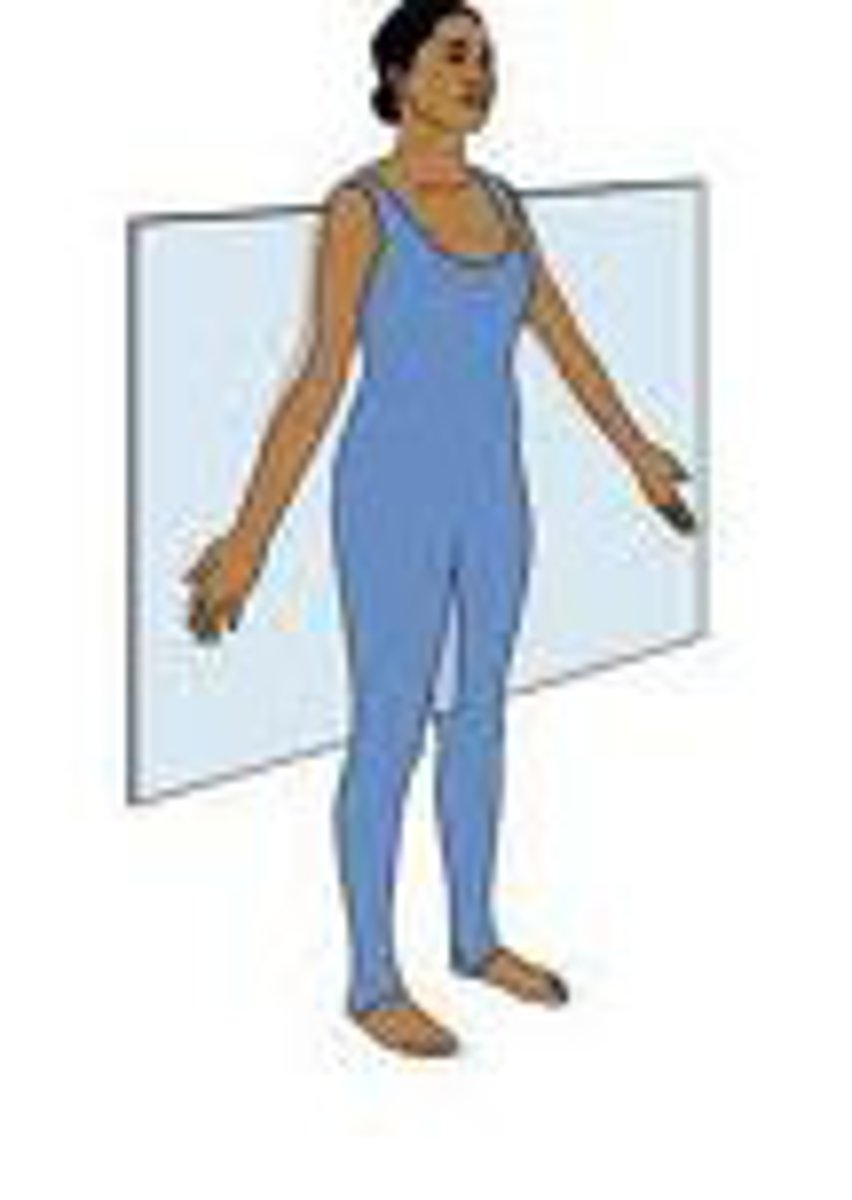

Sagittal Plane
Divides body into left and right portions
Midsaggittal Plane
Divides the body or organ into equal left and right sides
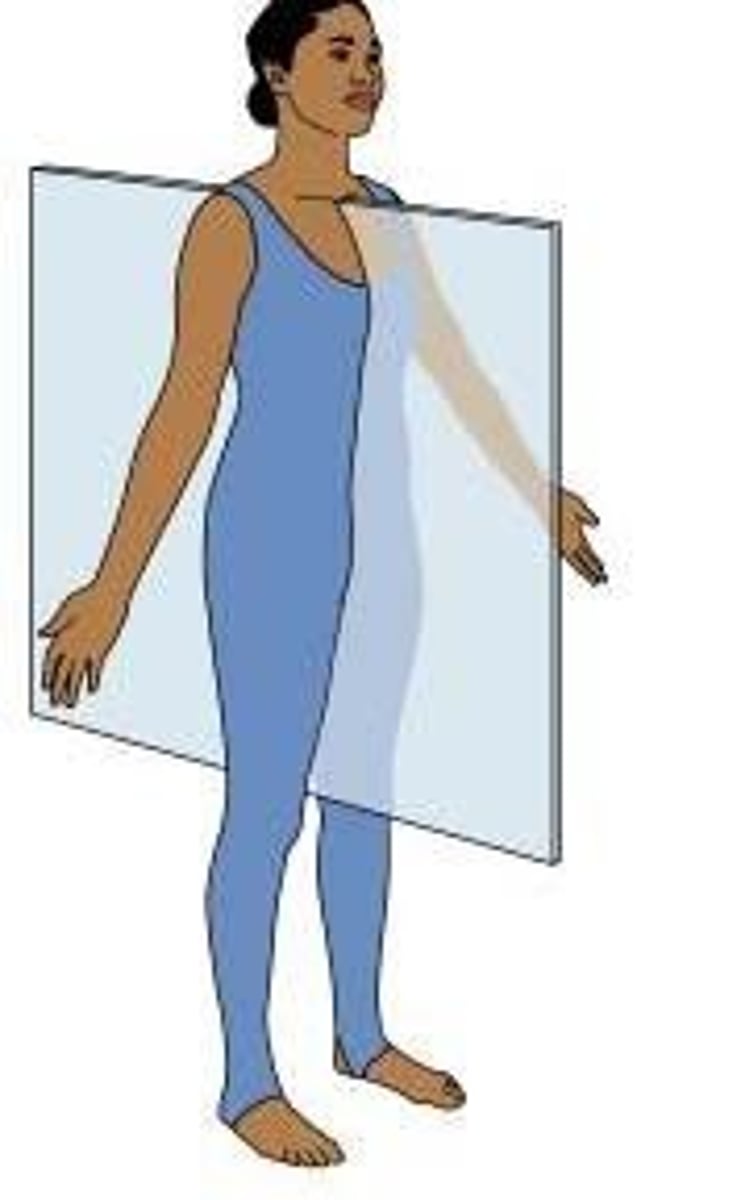
Sagittal Plane
Divides into unequal right and left parts
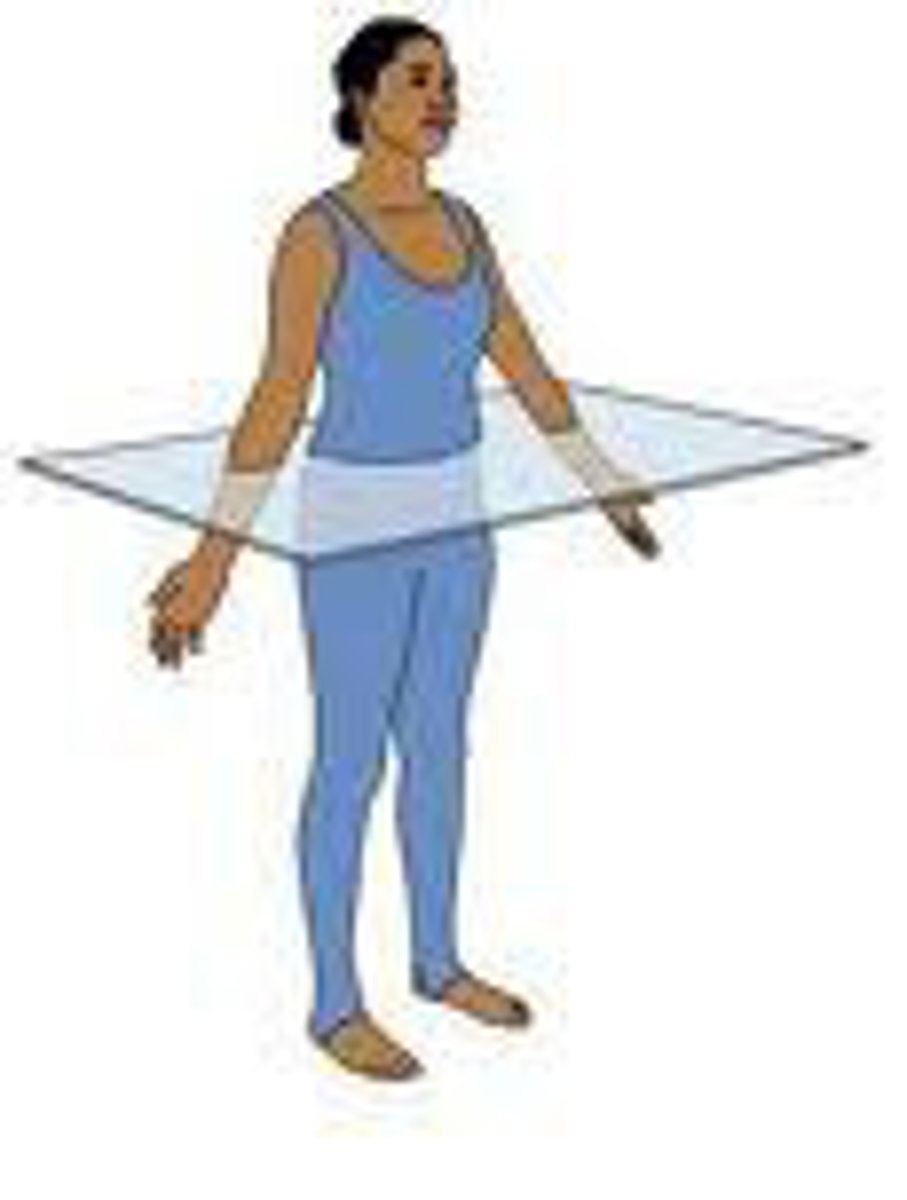
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into superior and inferior portions
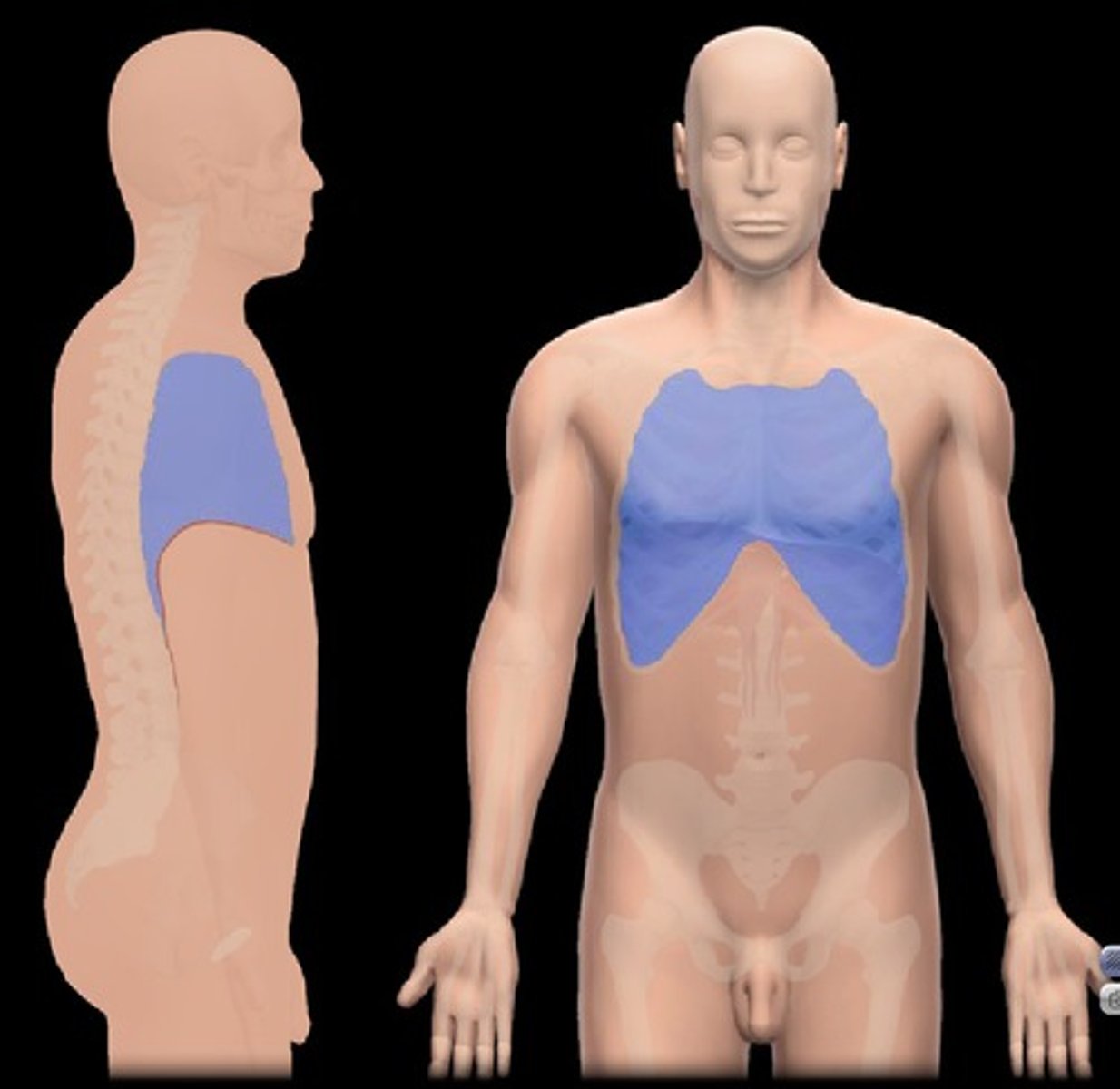
Thoracic Cavity
cavity containing the heart and lung
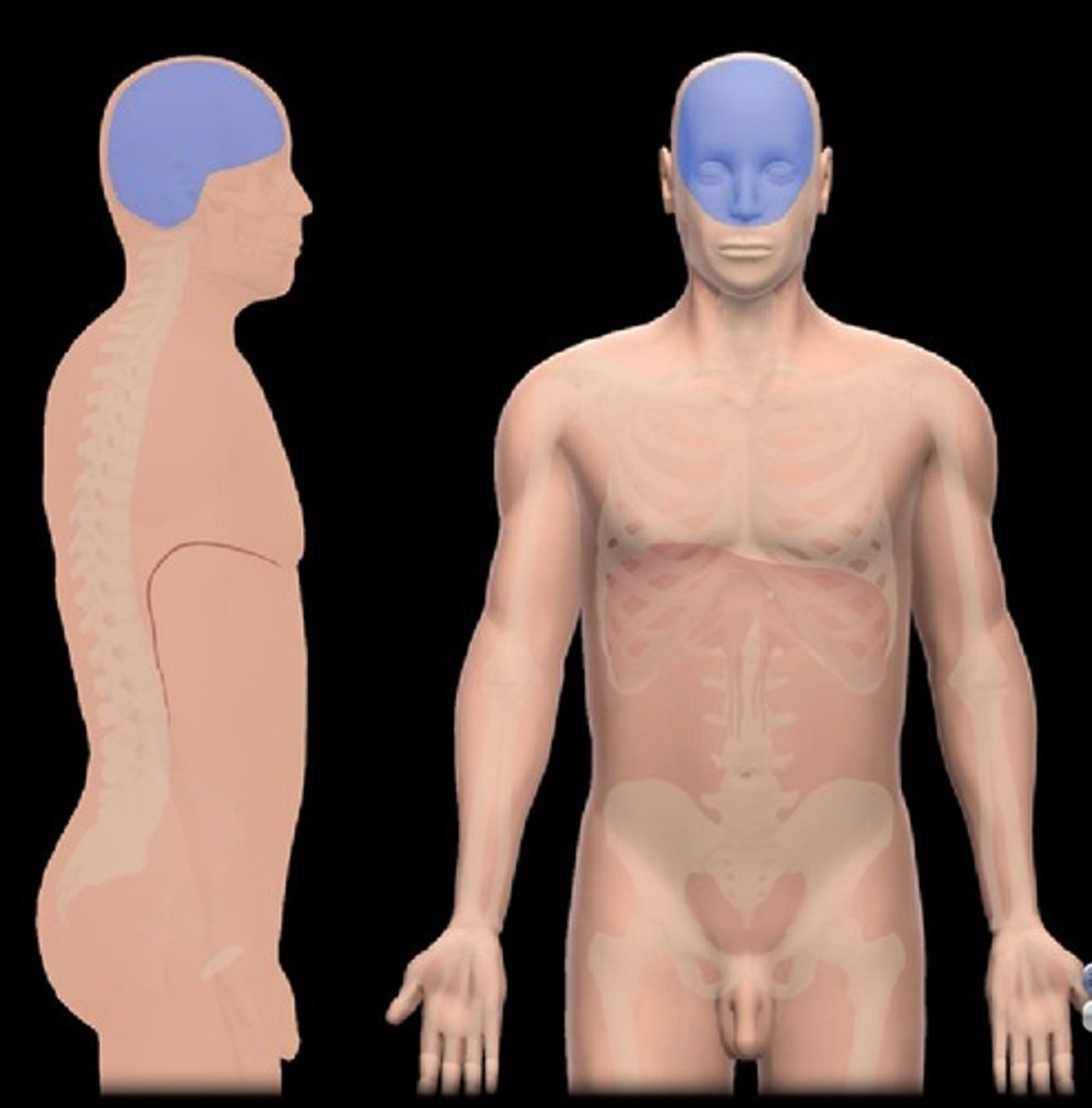
Cranial Cavity
- cavity containing the brain
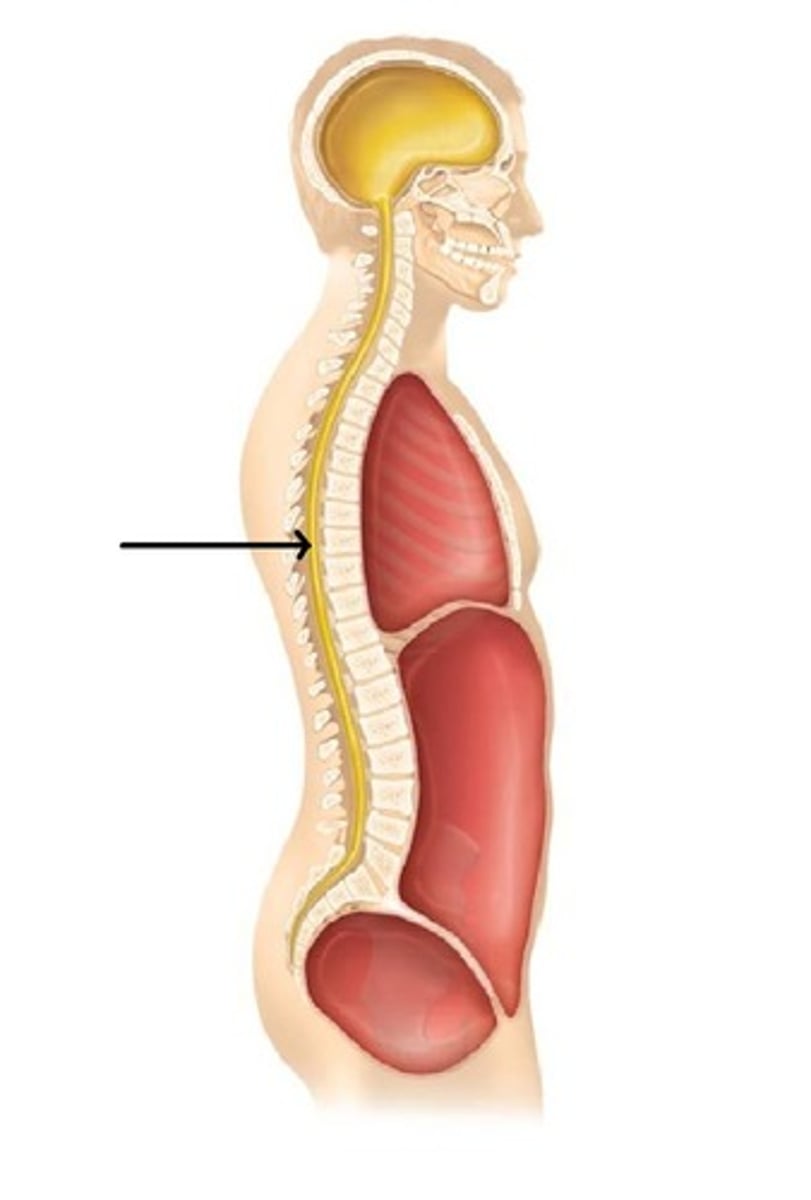
Vertebral cavity
- cavity containing the spinal cord
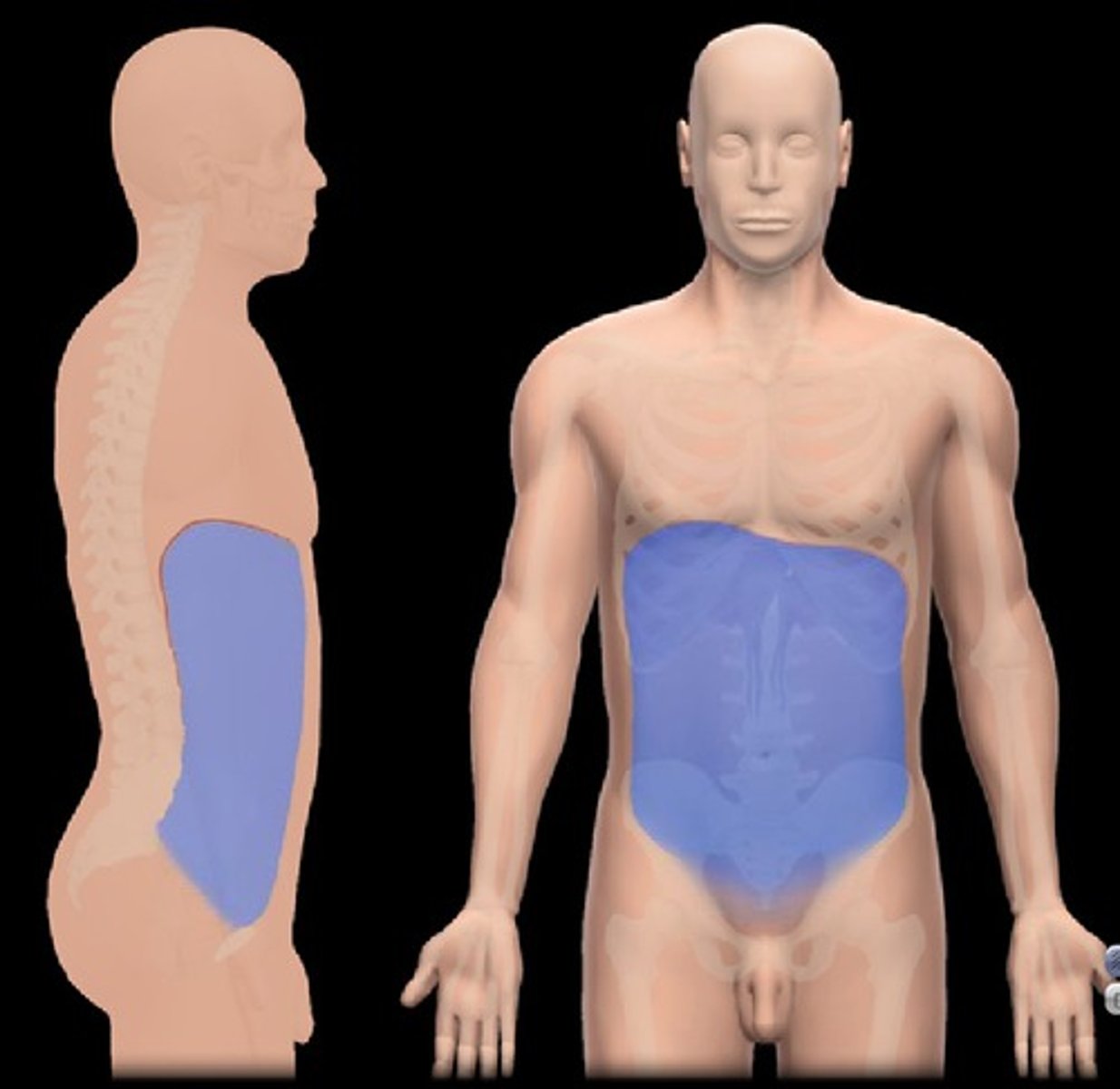
abdominopelvic cavity
cavity containing the kidneys, digestive and reproductive organs
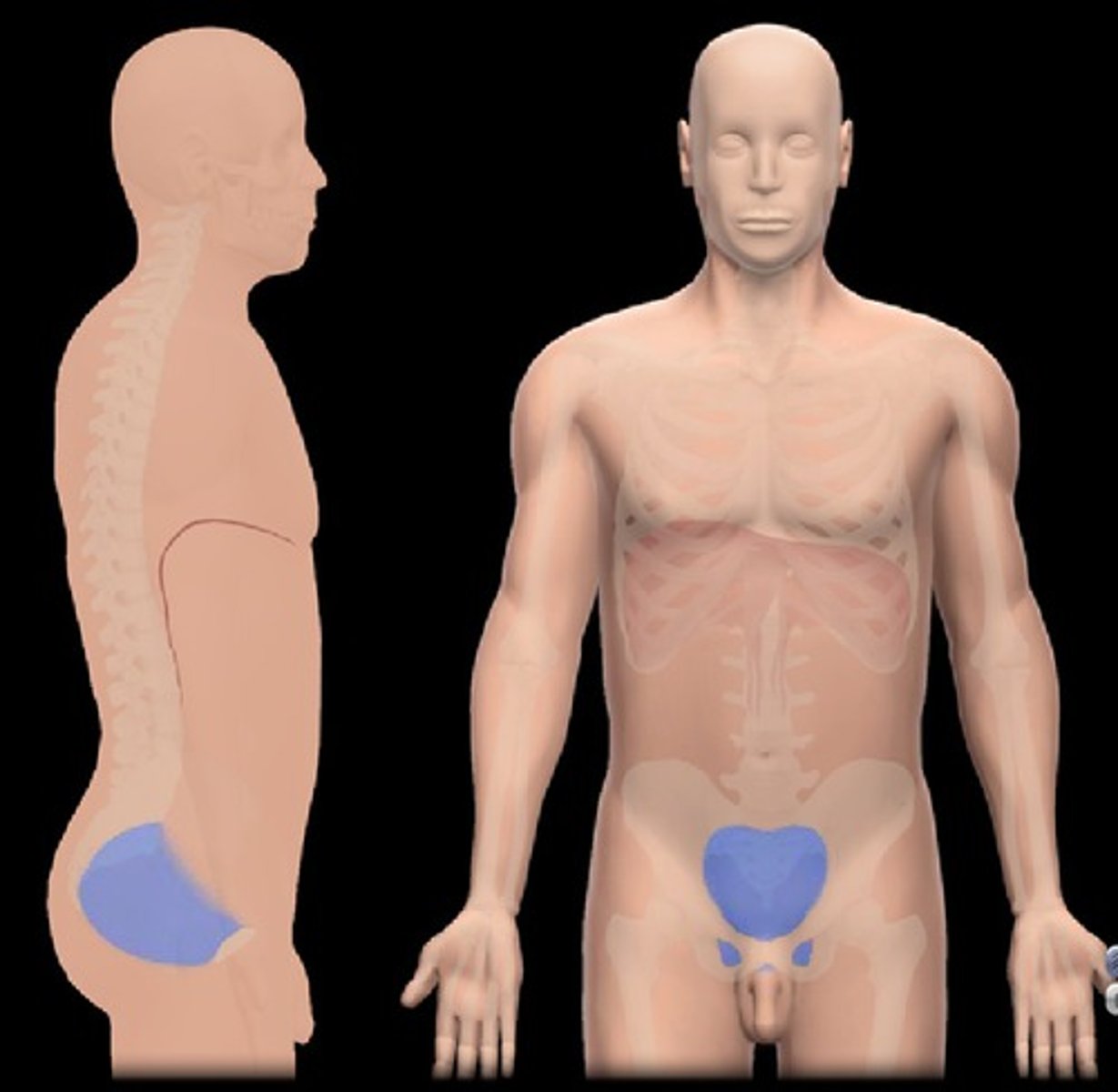
Pelvic Cavity
containing the bladder and reproductive organs
Cephalic
Head
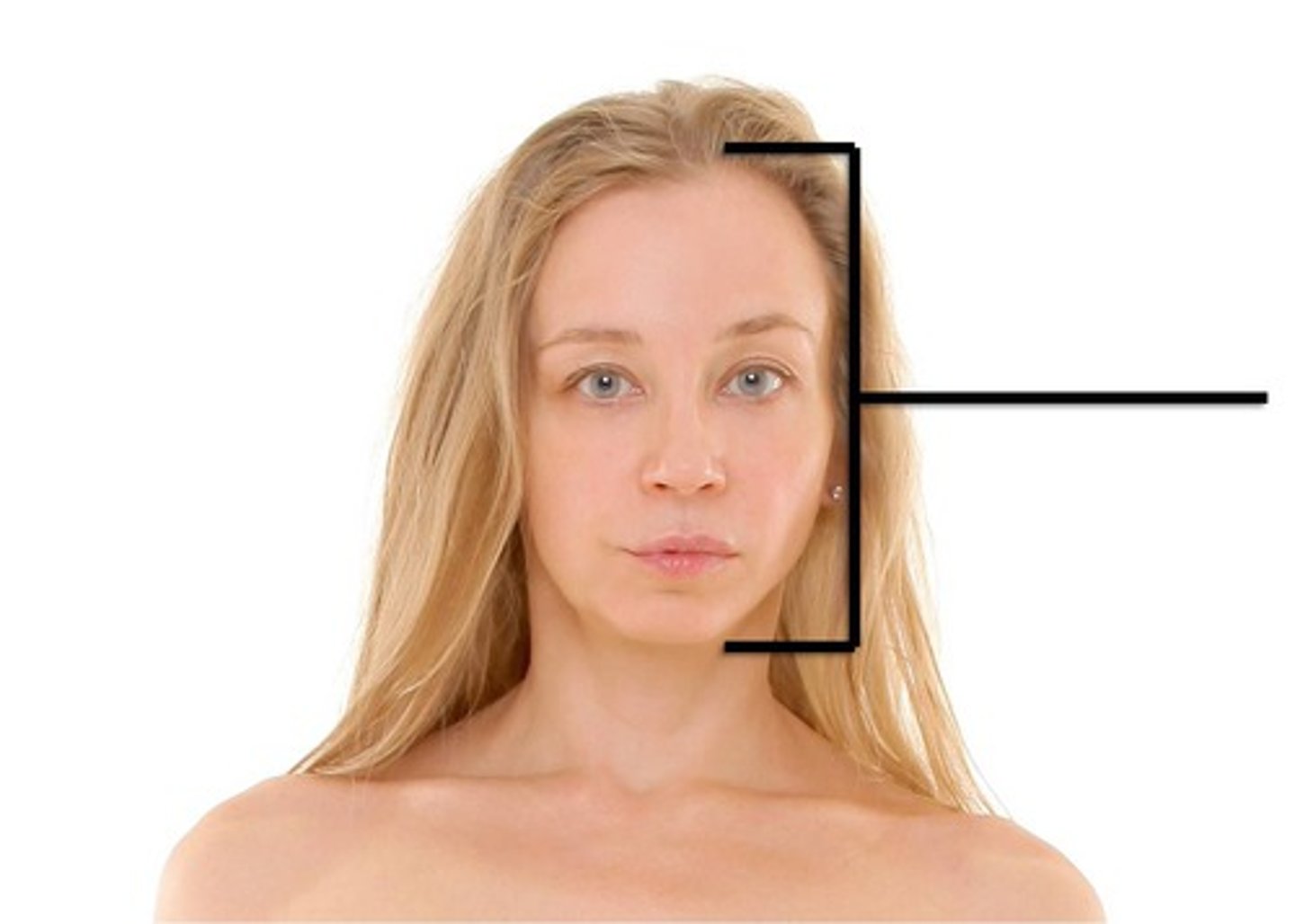
Frontal
Forehead
Orbital
Eye
Nasal
Nose
Buccal
Cheek
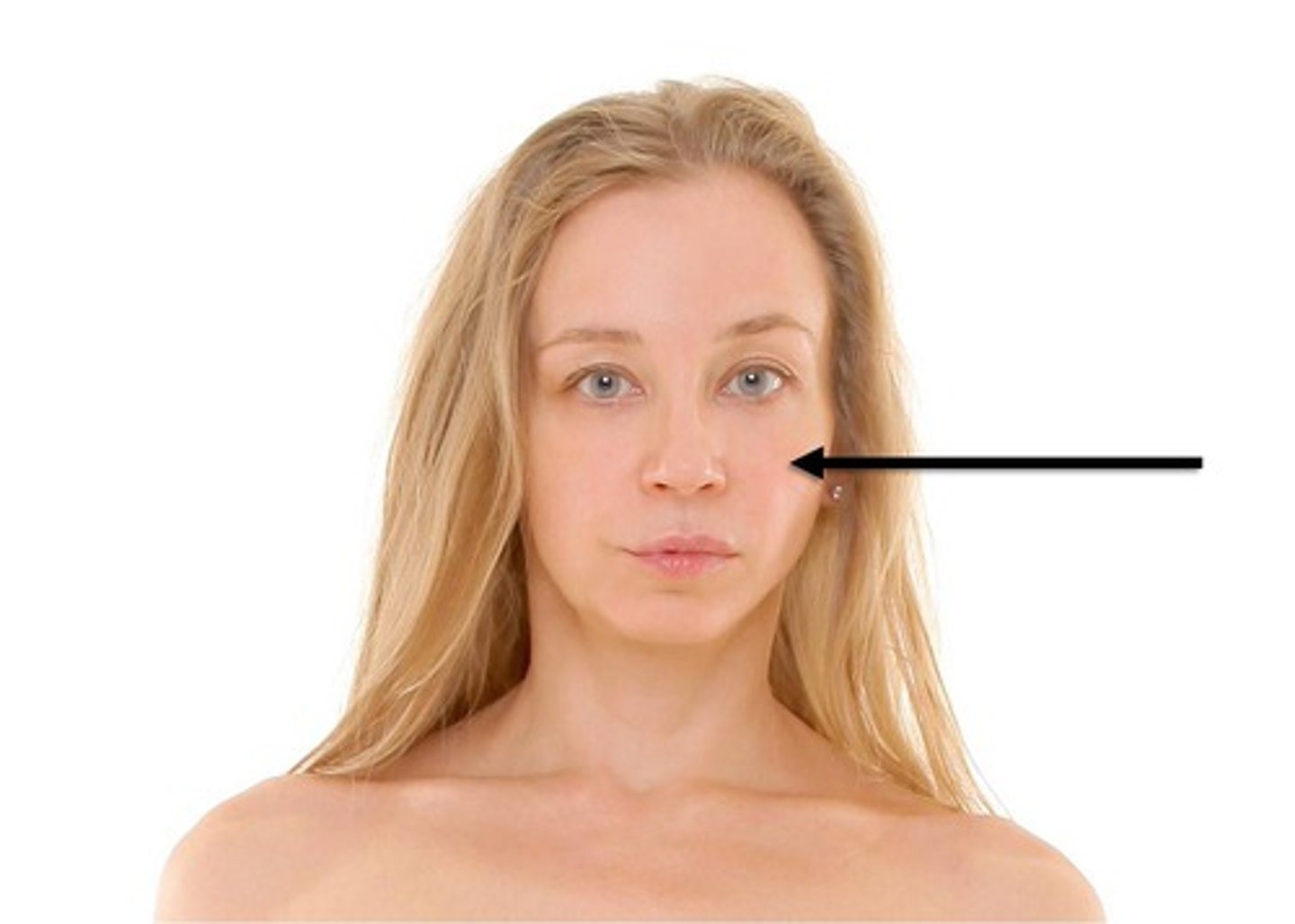
Oral
Mouth
Cranial
Brain
Occipital
Base of Skull
Cervical
Neck
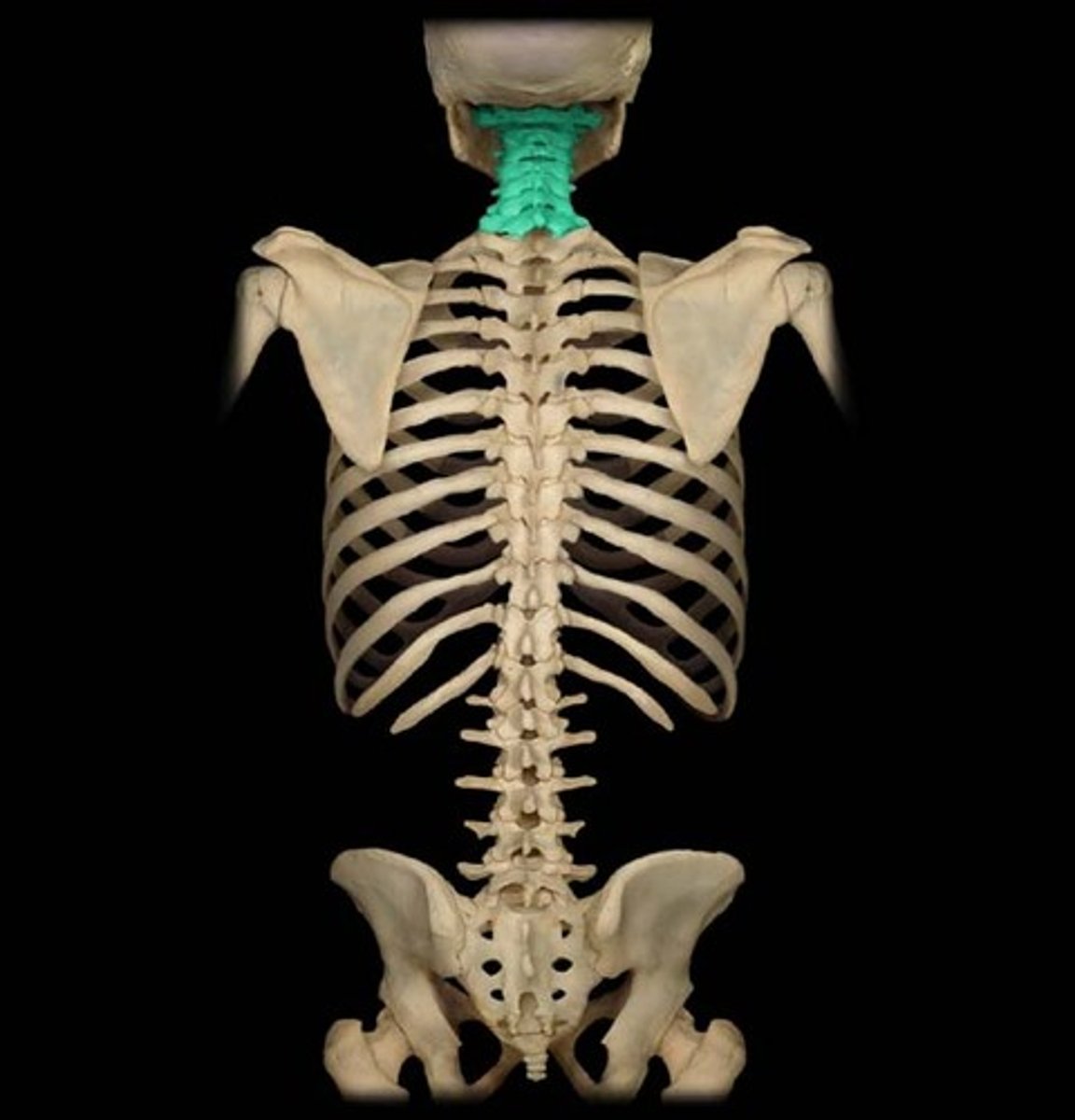
Thoracic
Chest
Sternal
Chestbone
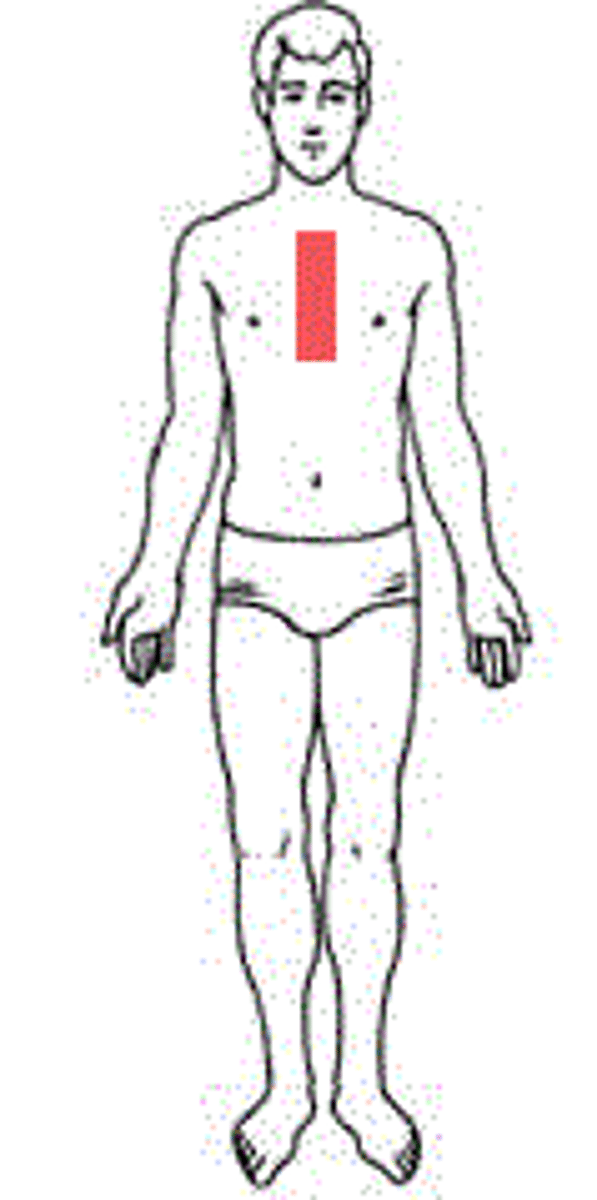
Pectoral
Breast
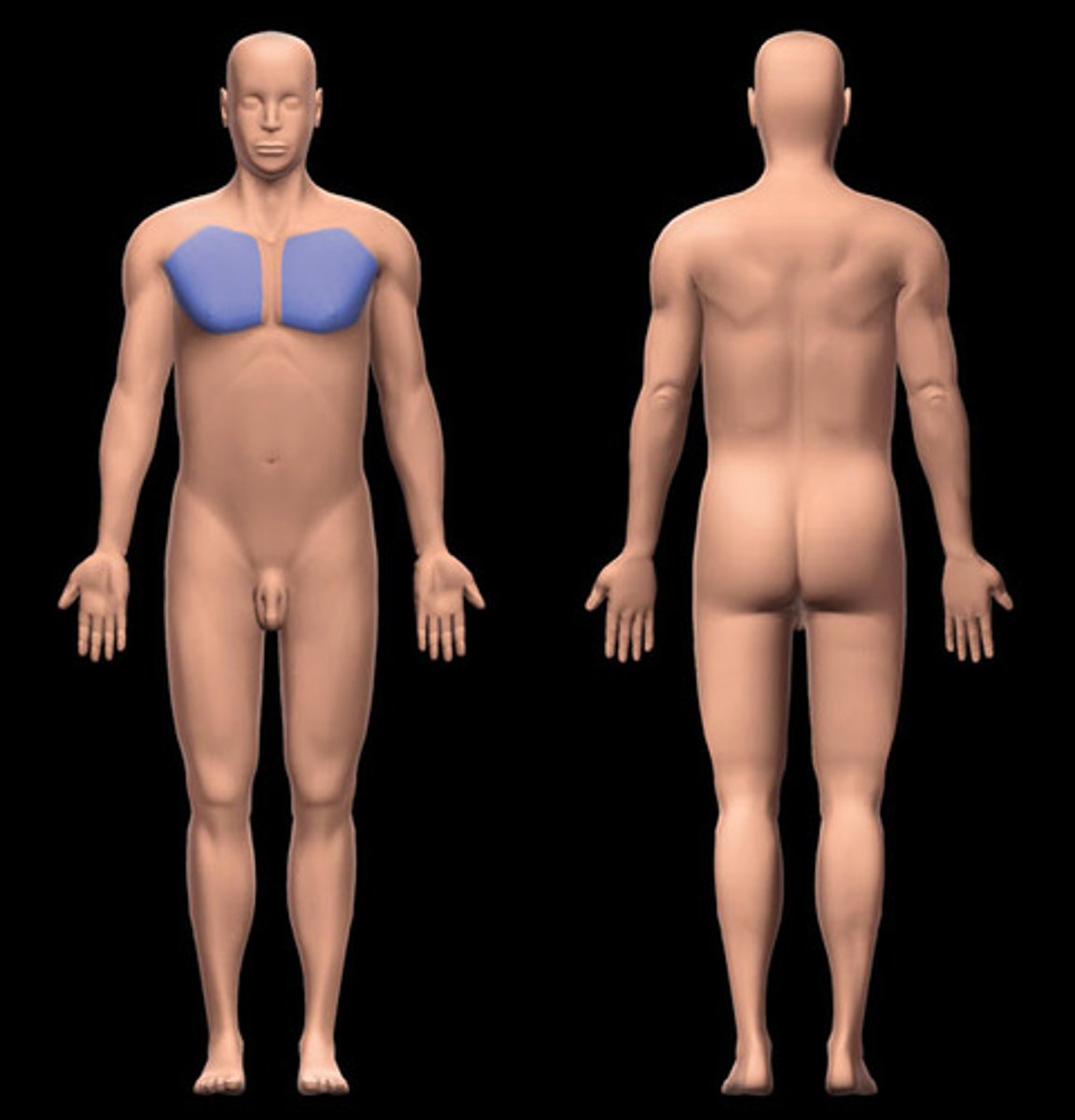
Axillary
Armpit
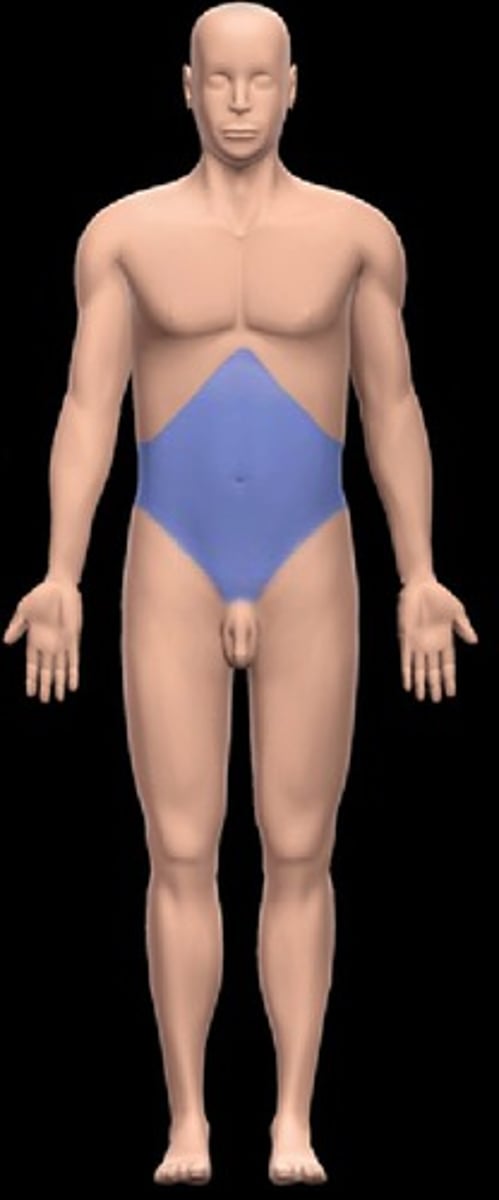
Abdominal
Front of trunk
Vertebral
Spine
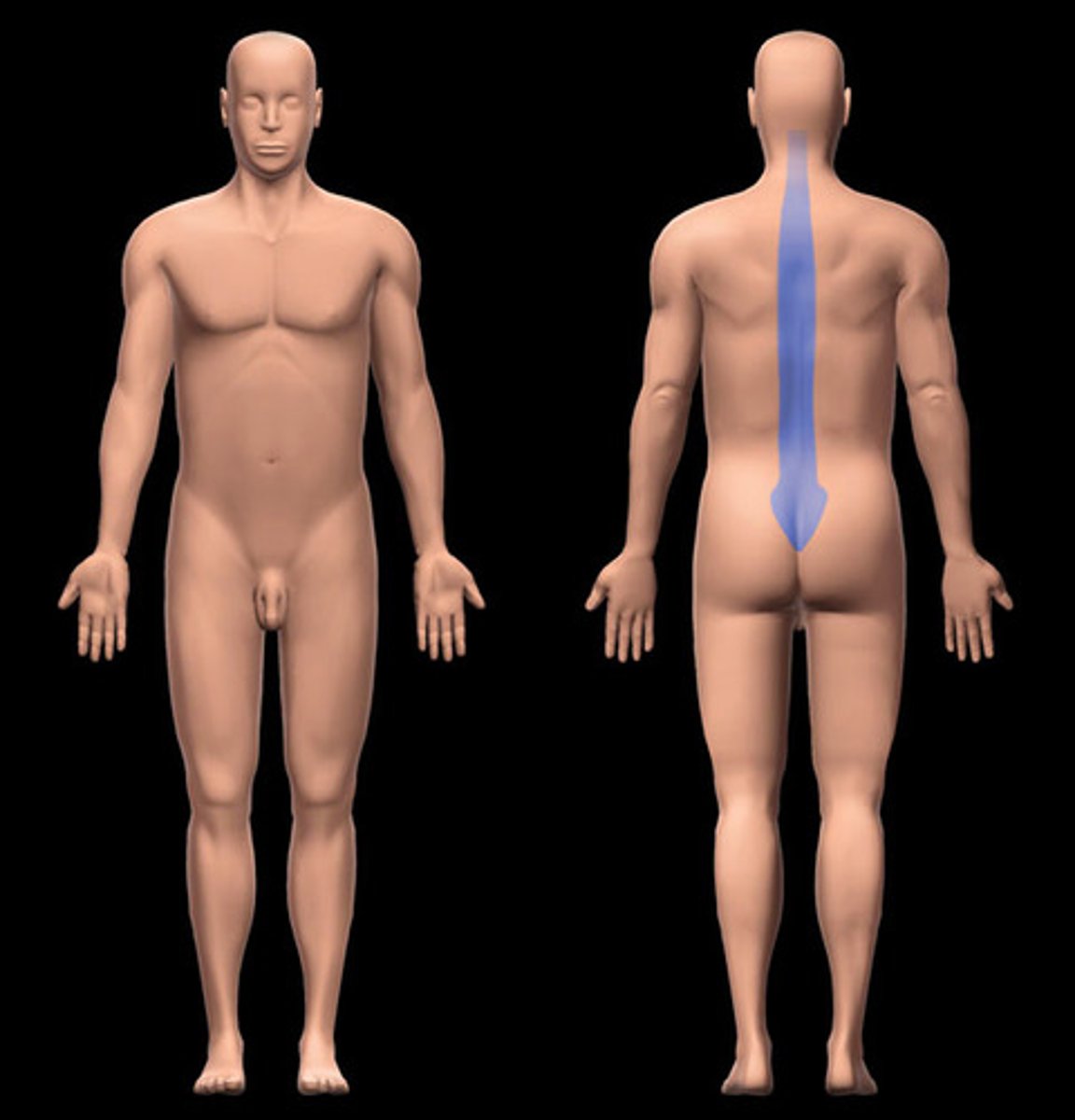
Lumbar
Lower back
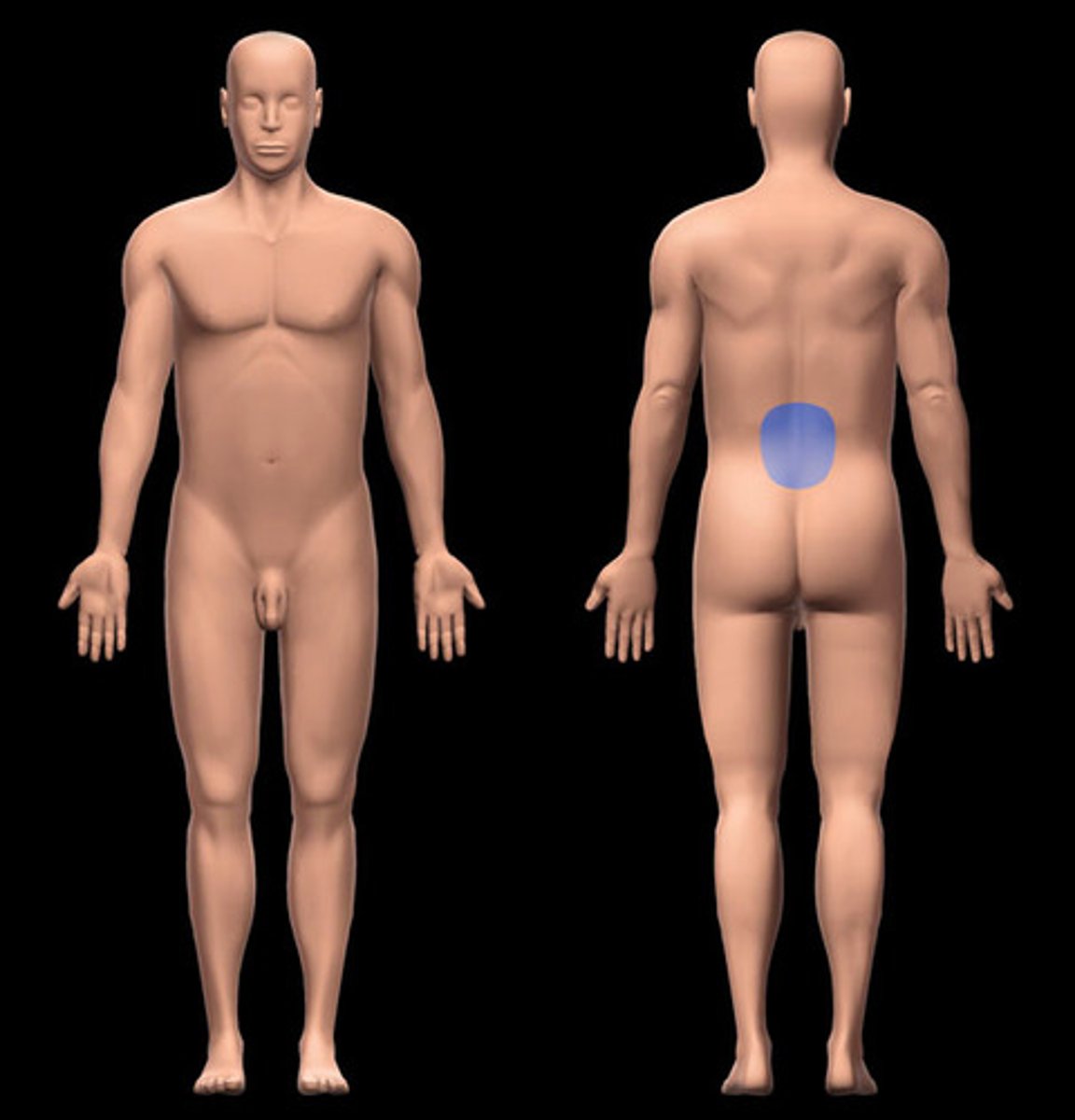
Sacral
Posterior region between the hip bones
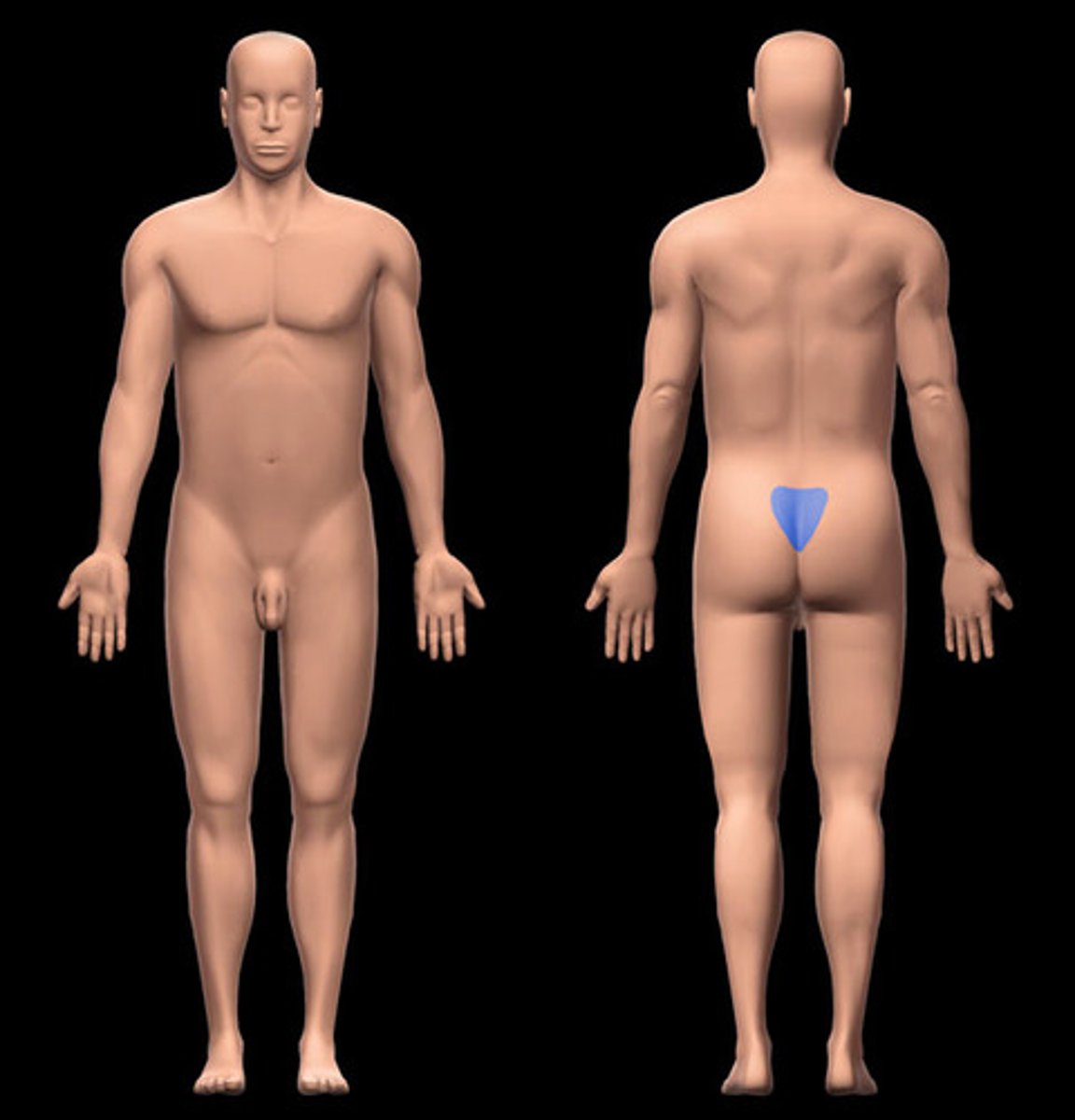
Pelvic
Between hips, anterior
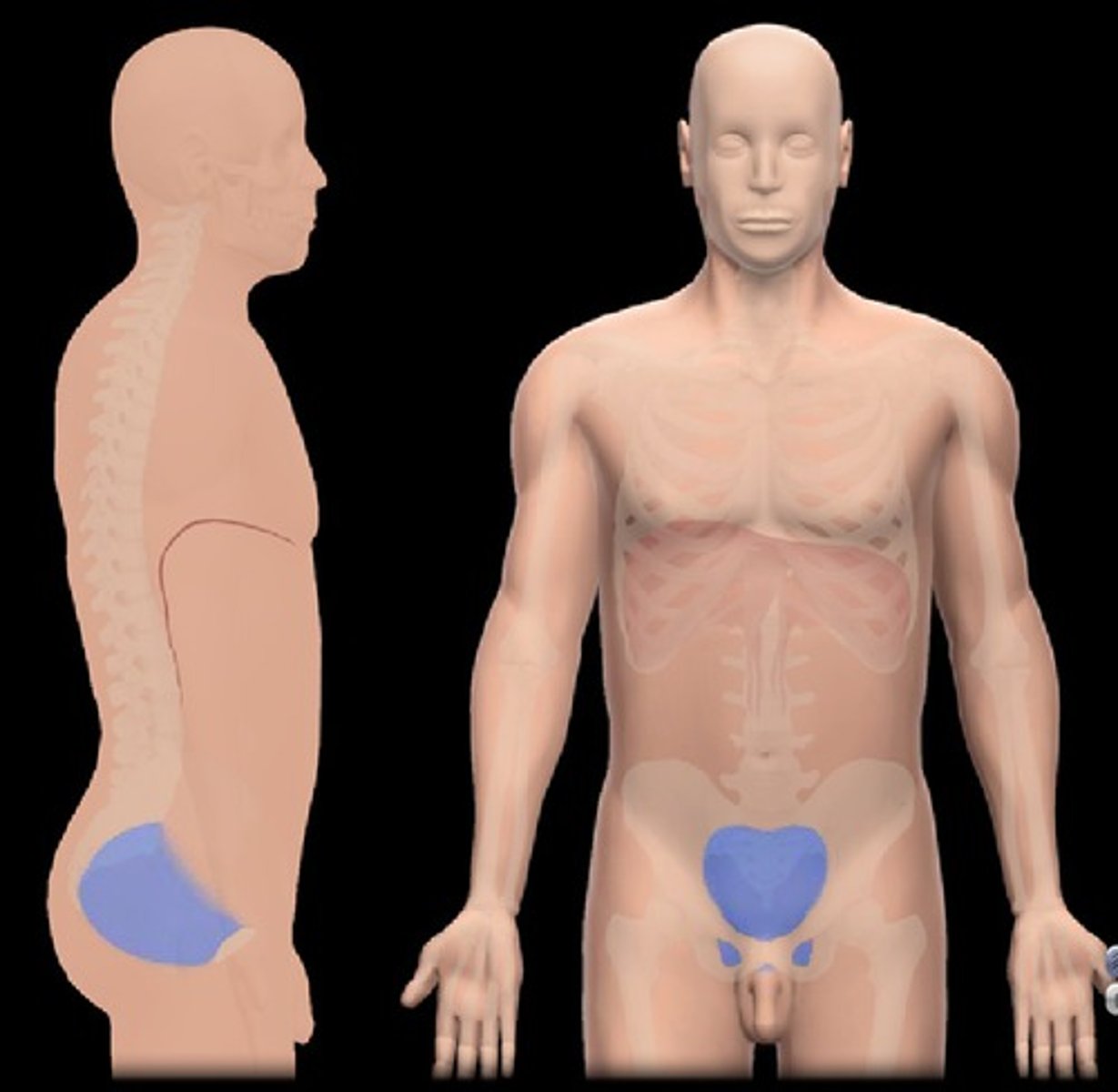
Coxal
Hip
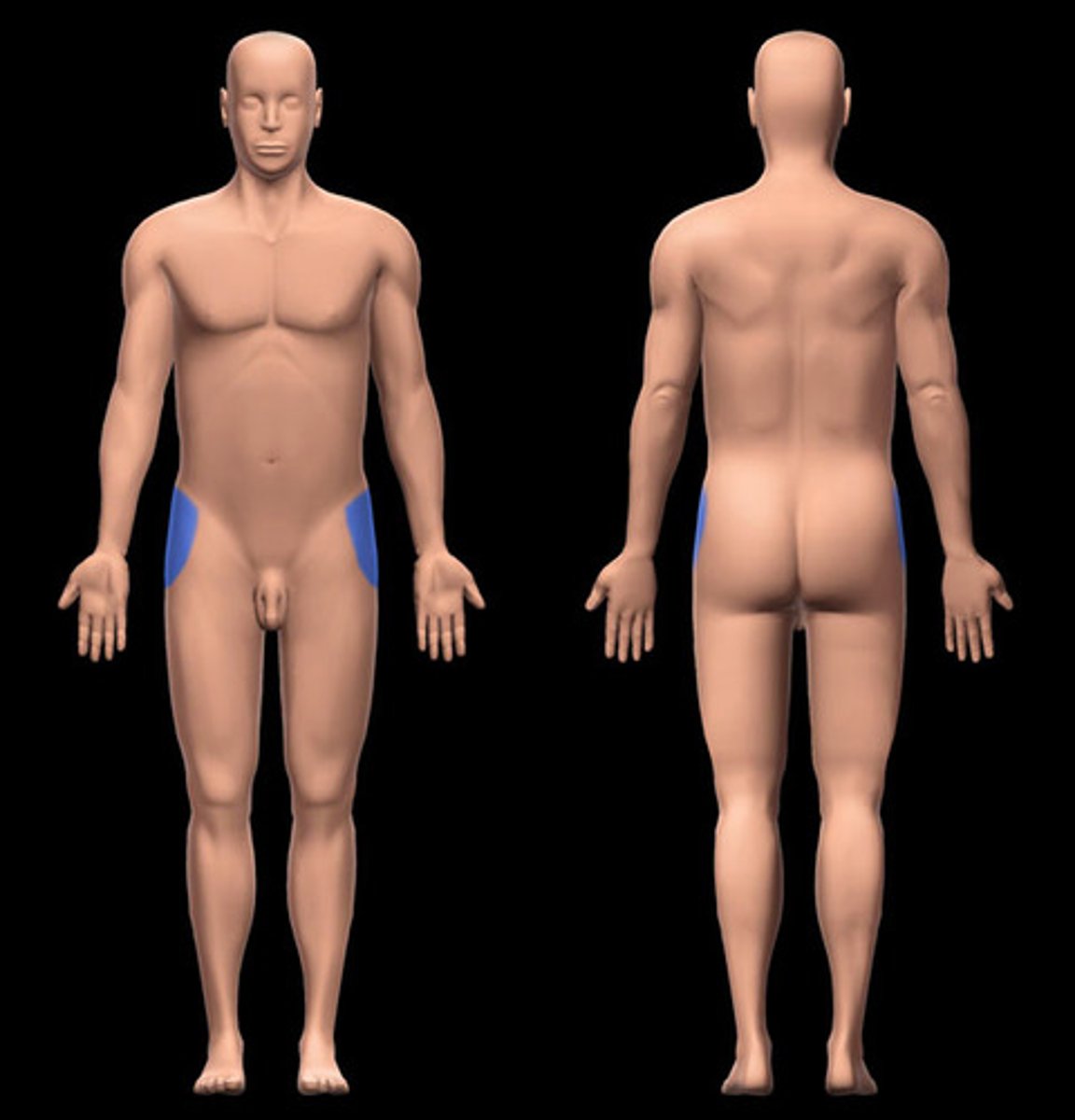
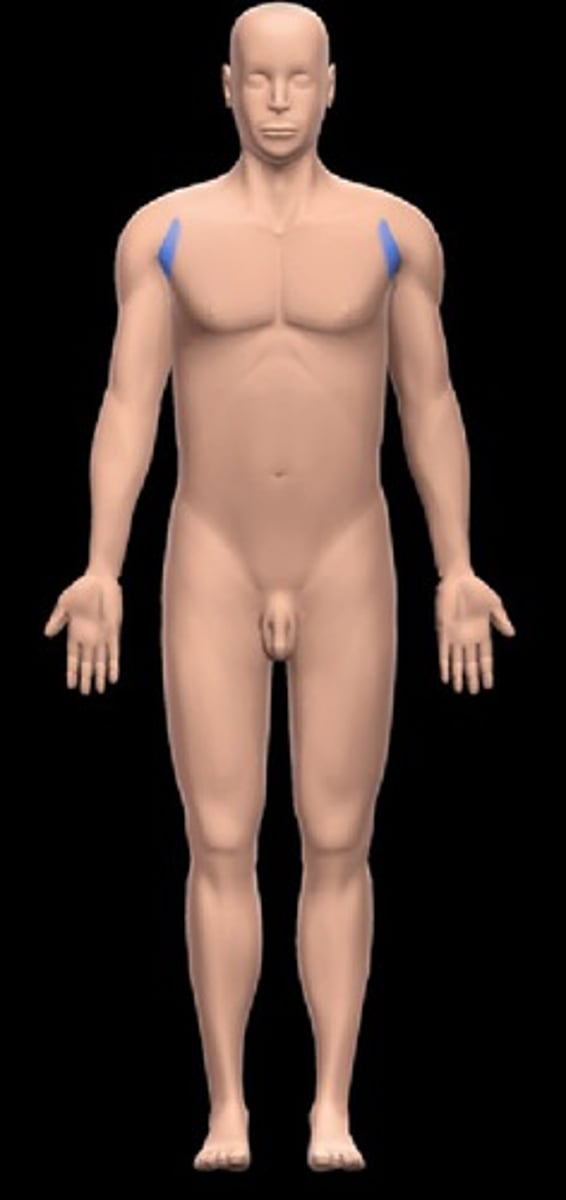
Brachial
Upper arm
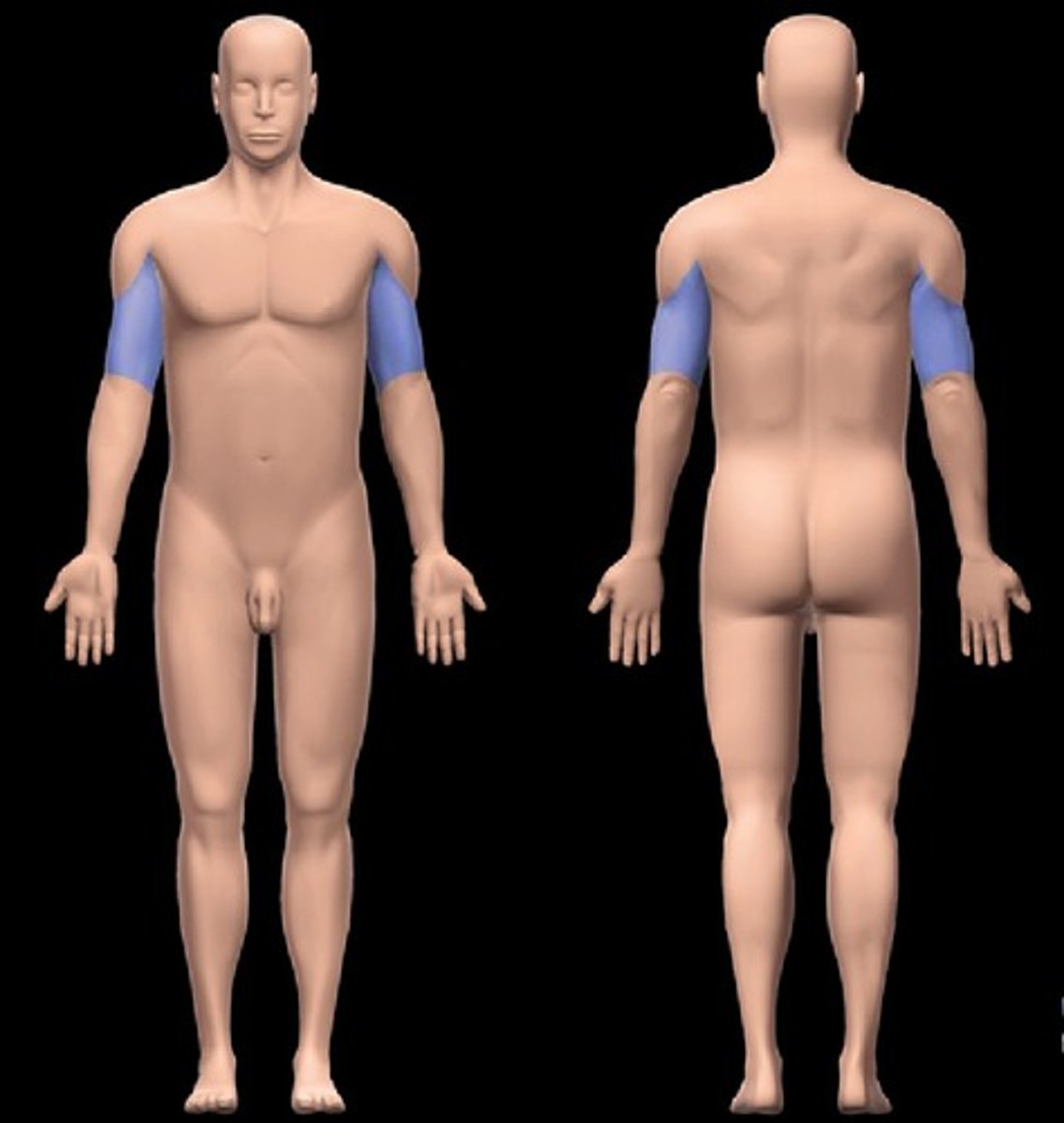
Antecubital
Front of elbow
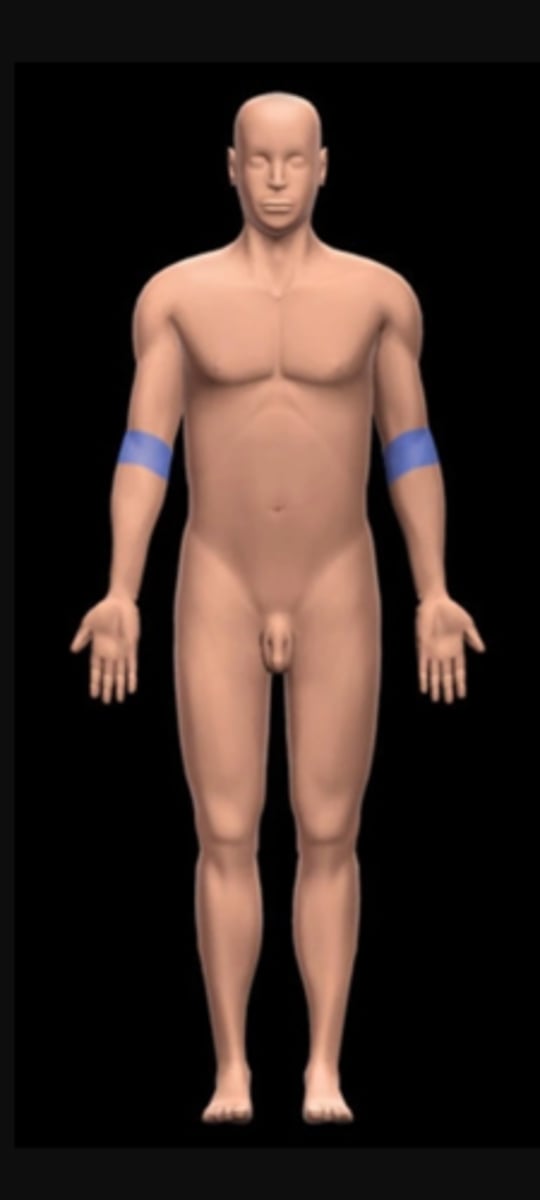
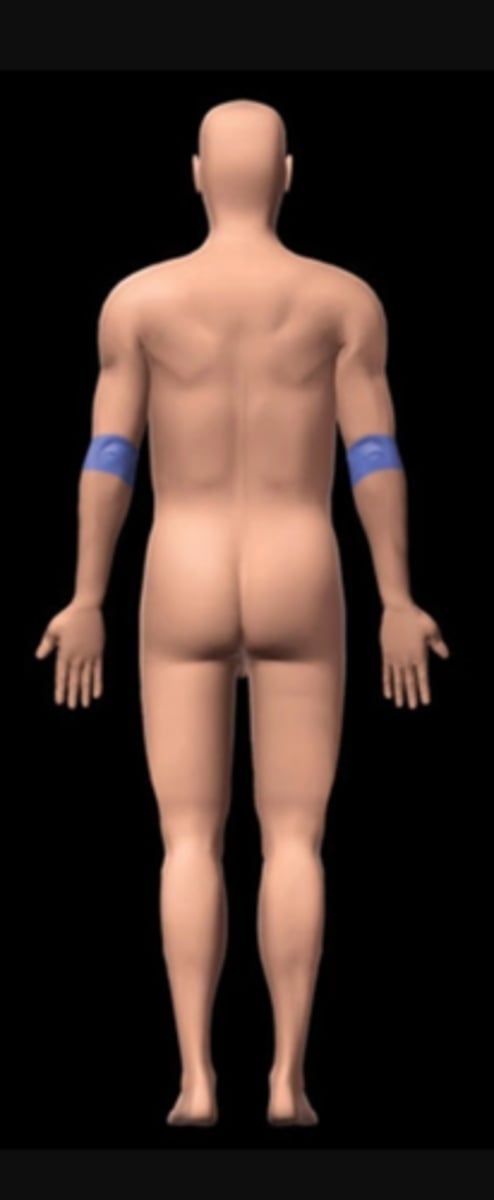
Olecranal
elbow (posterior)
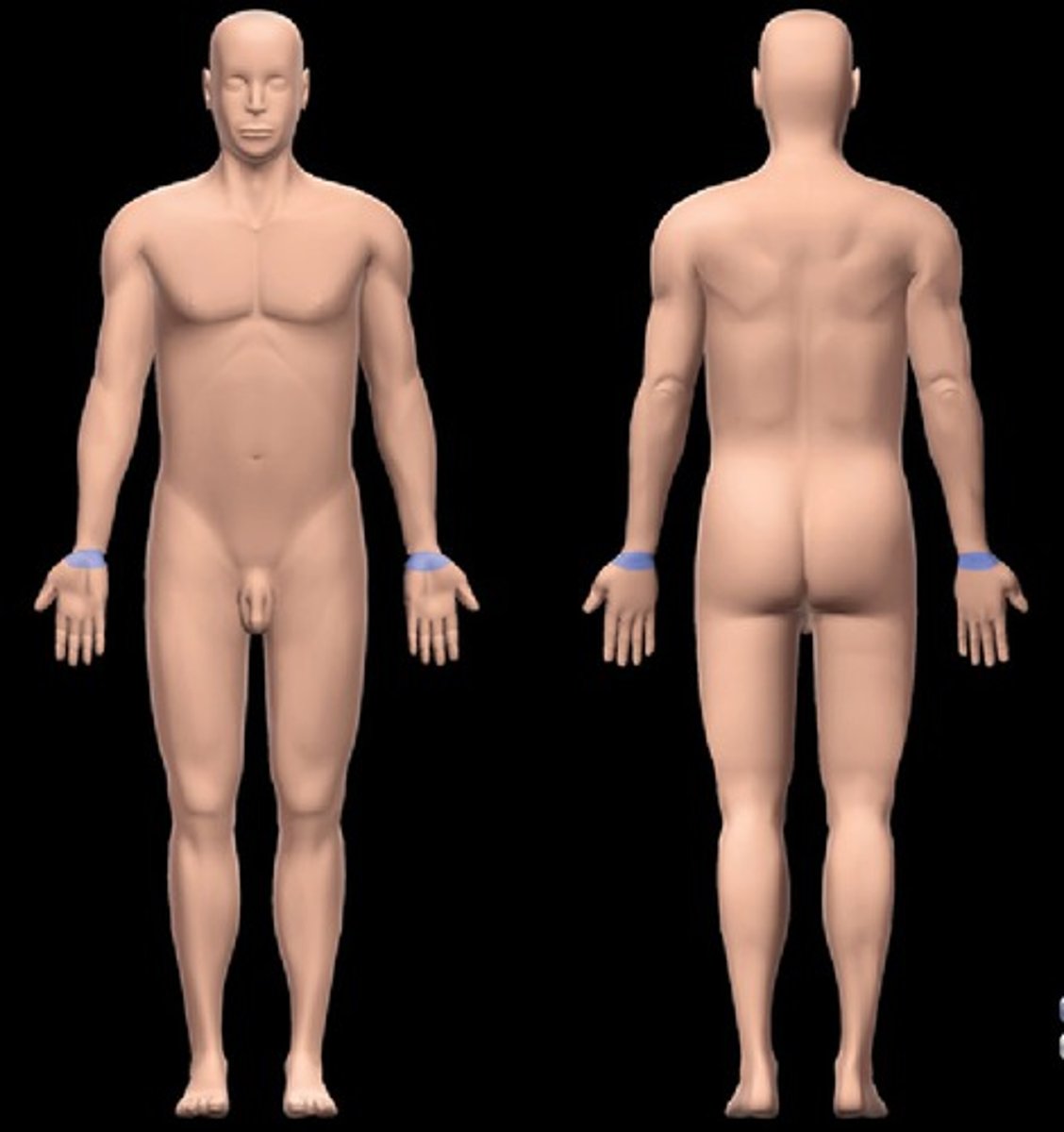
Carpal
Wrist
Digital
Fingers or Toes
Femoral
Thigh
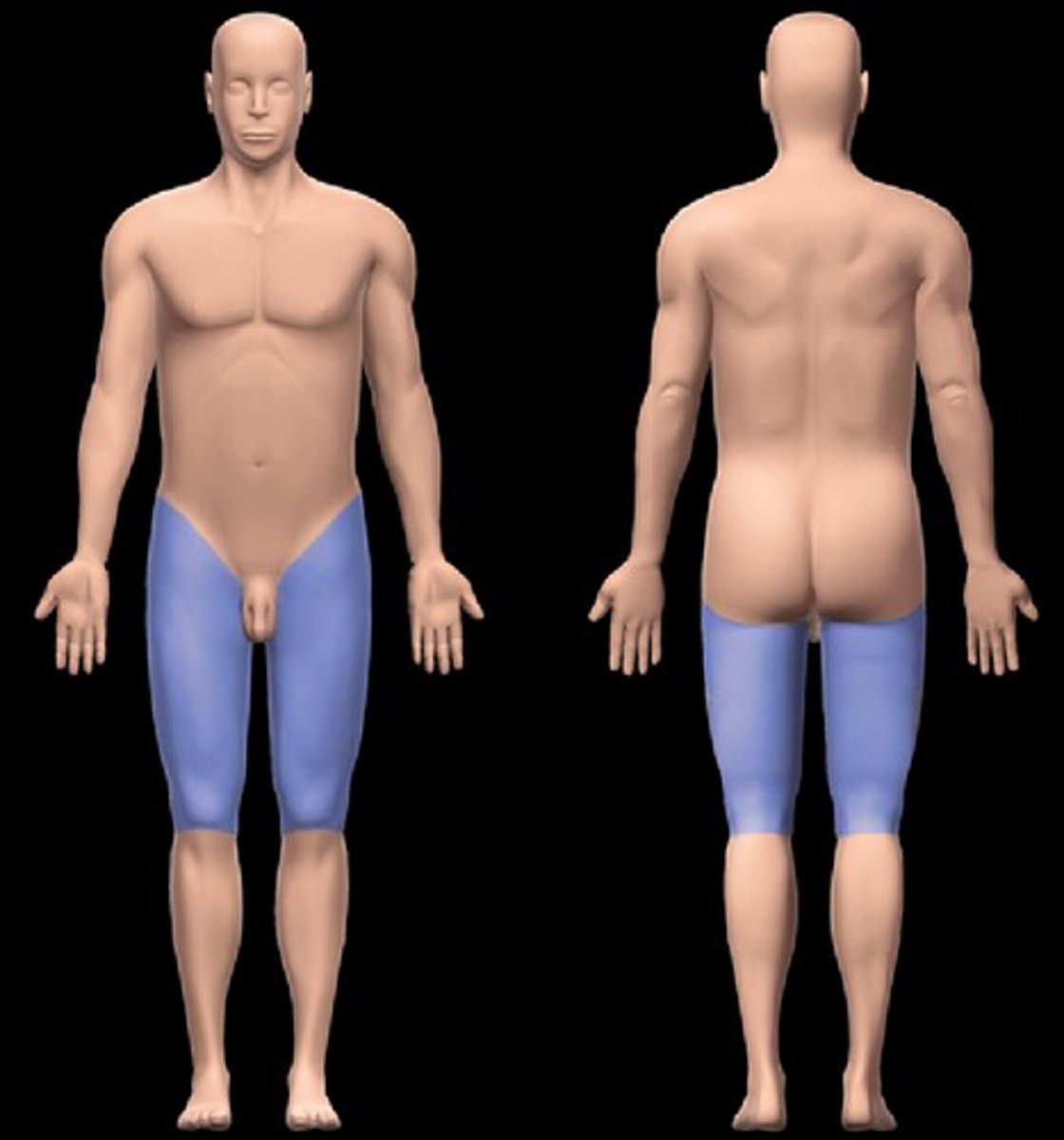
Patellar
Kneecap
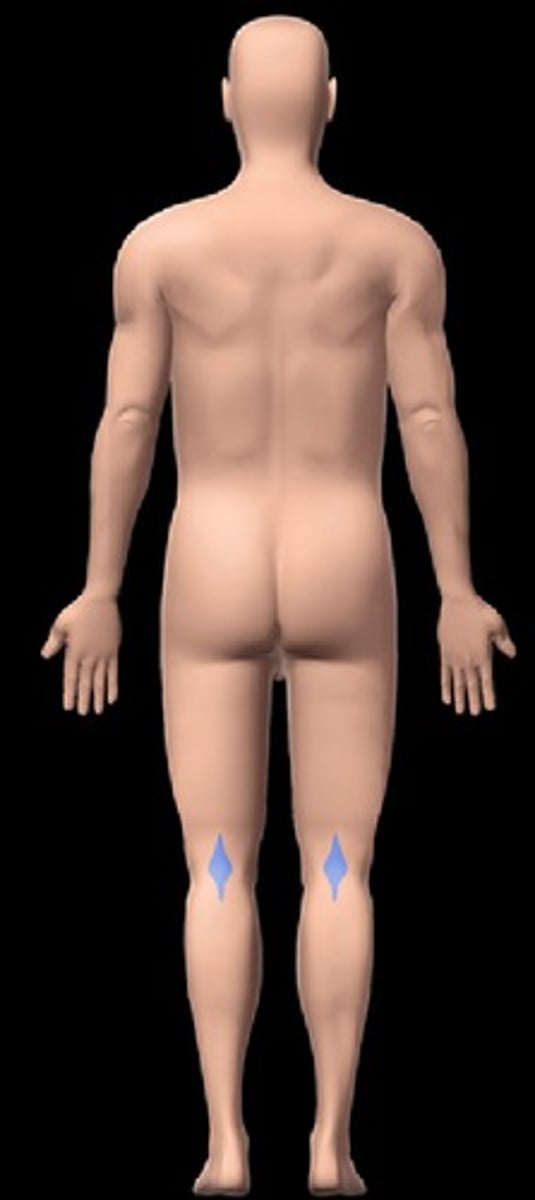
Popliteal
Back of knee
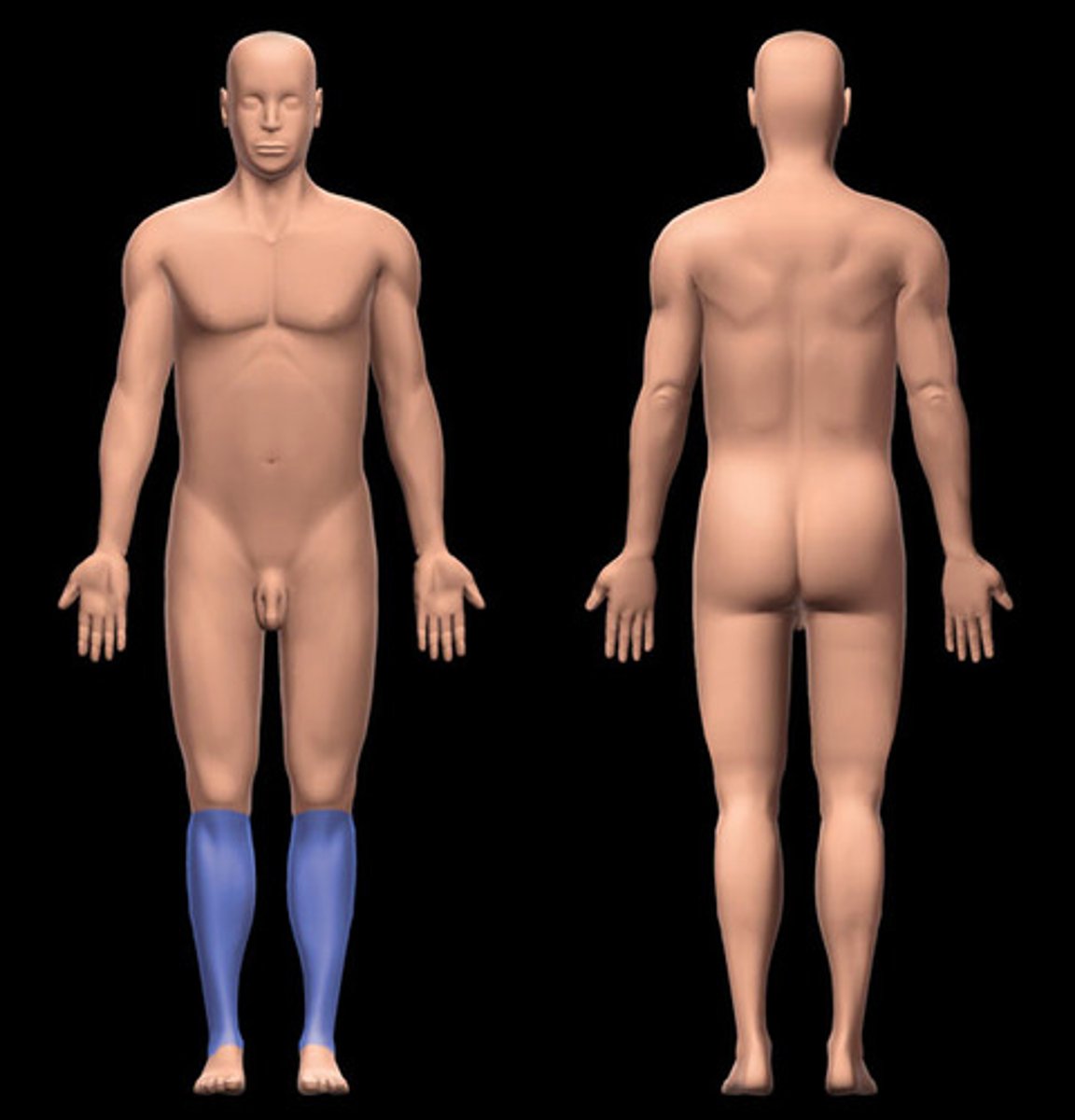
Crural
Shin
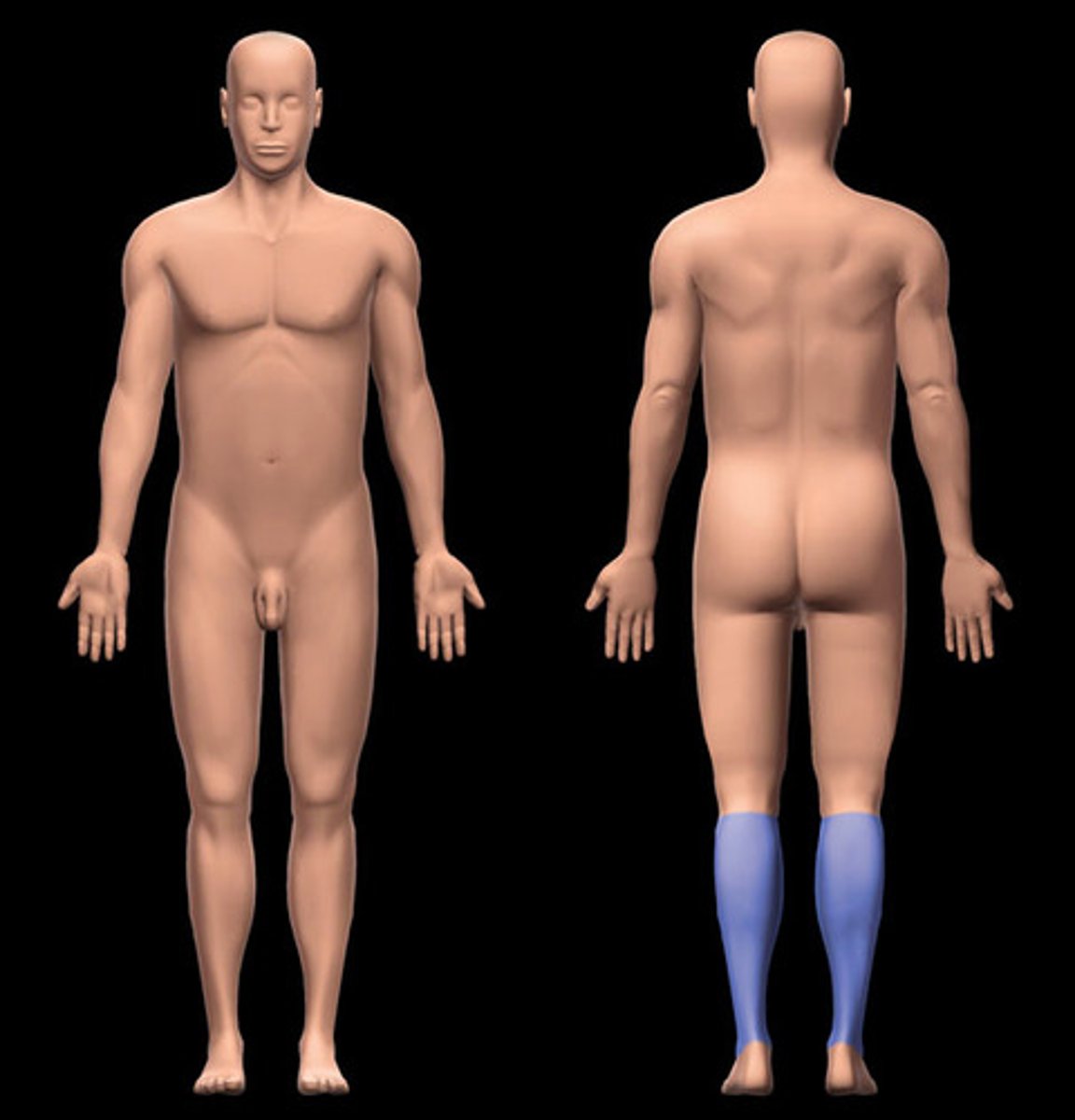
Sural
Calf
Tarsal
Ankle
Calcaneal
Heel
Plantar
Bottom of foot
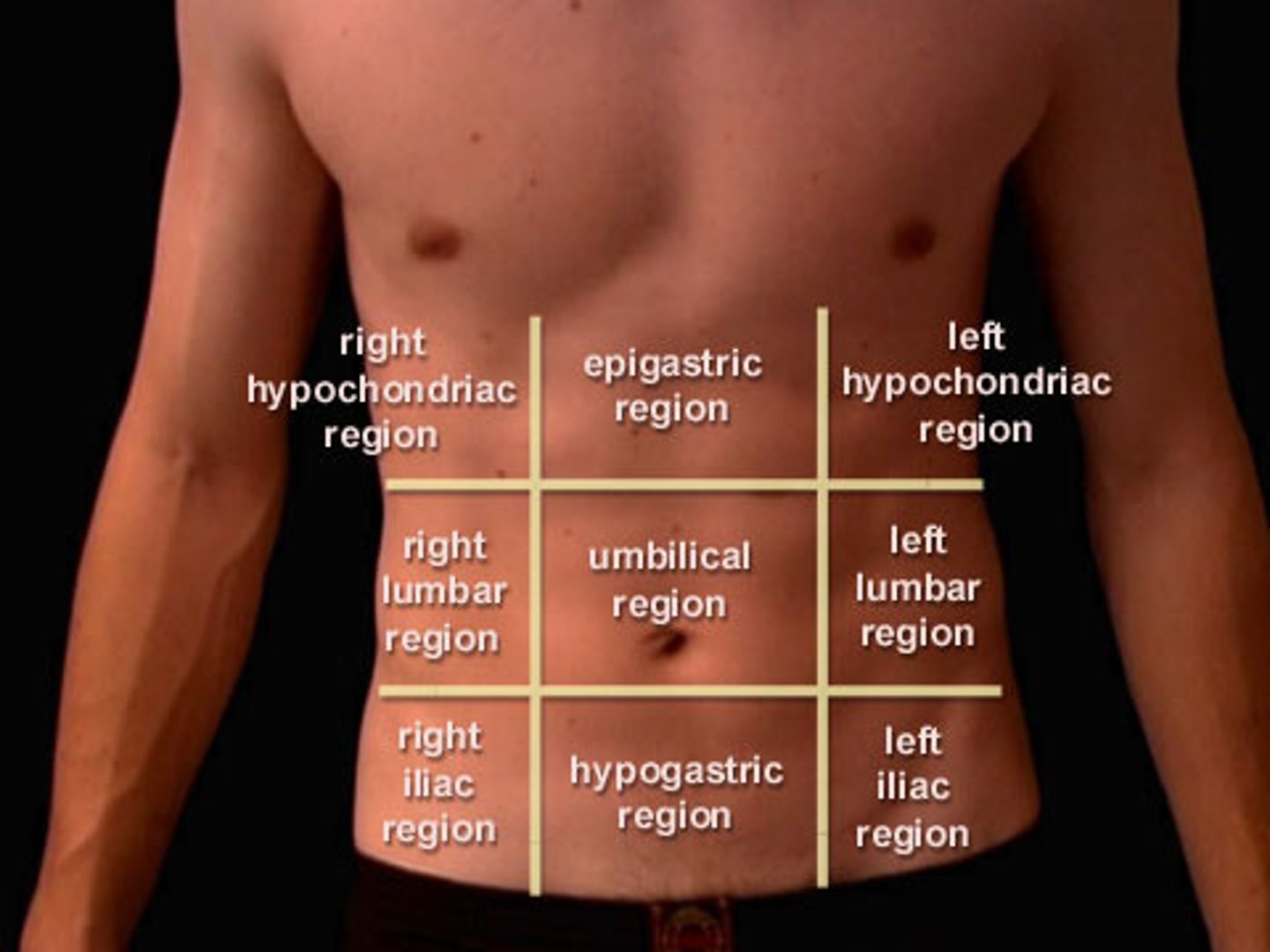
Abdominal regions
Divided into 9 sections
Gross anatomy
Study of structures that can be seen with the naked eye
Microscopic anatomy
deals with structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
Relationship between anatomy and physiology
structure determines function
Necessary Life Functions
1. Maintaining boundaries
2. Movement
3. Responsiveness
4. Digestion
5. Metabolism
6. Excretion
7. Reproduction
8. Growth
Survival needs
nutrients, oxygen, water, normal body temperature, appropriate atmospheric pressure
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state
How homeostasis is maintained
1. Receptor responds to change
2. Control center decides what to do
3. Effector provides response to stimulus
Negative feedback systems
reverses a change in a controlled condition
positive feedback system
1.Childbirth
2. Lactation
3. Blood clotting
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
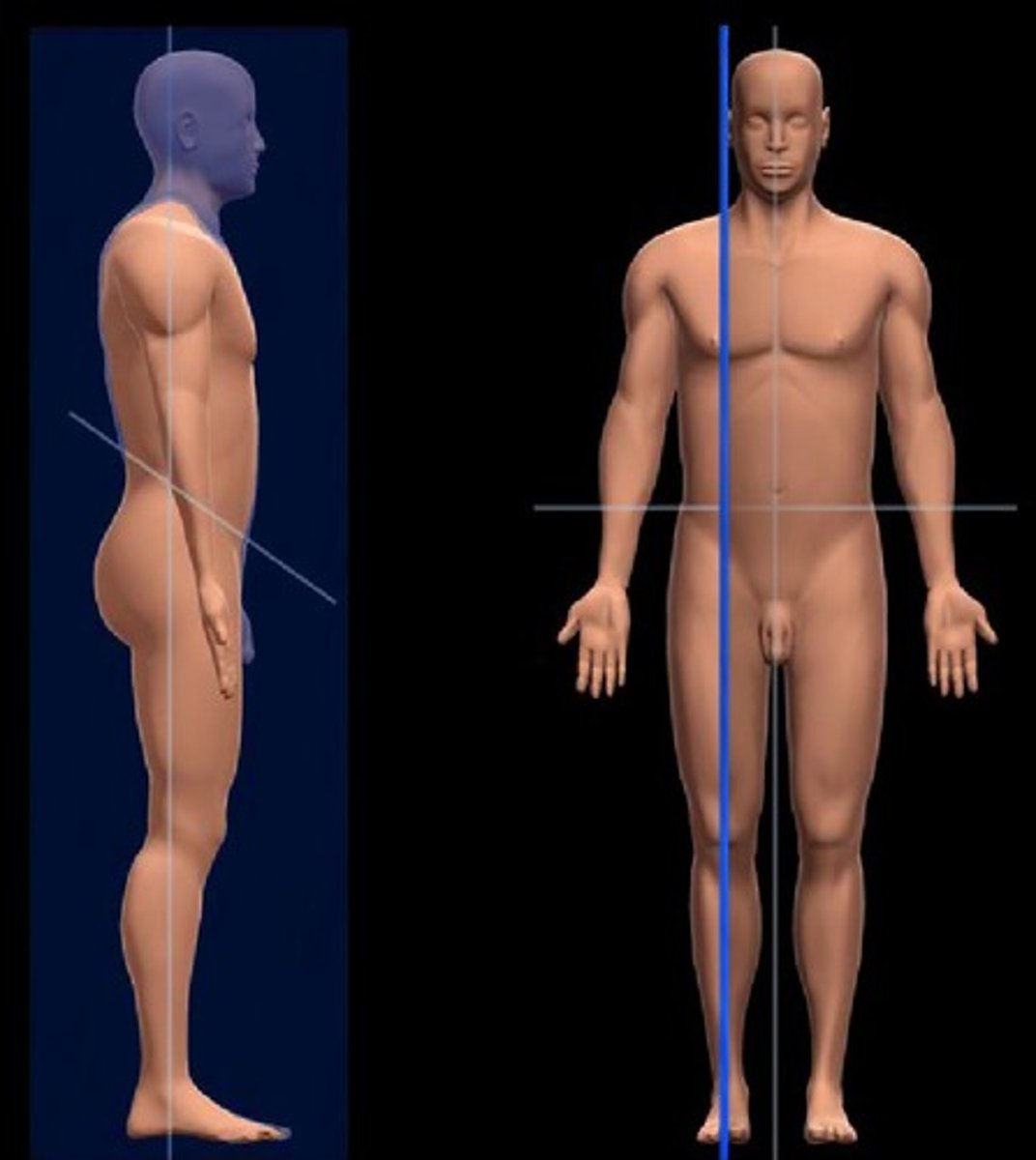
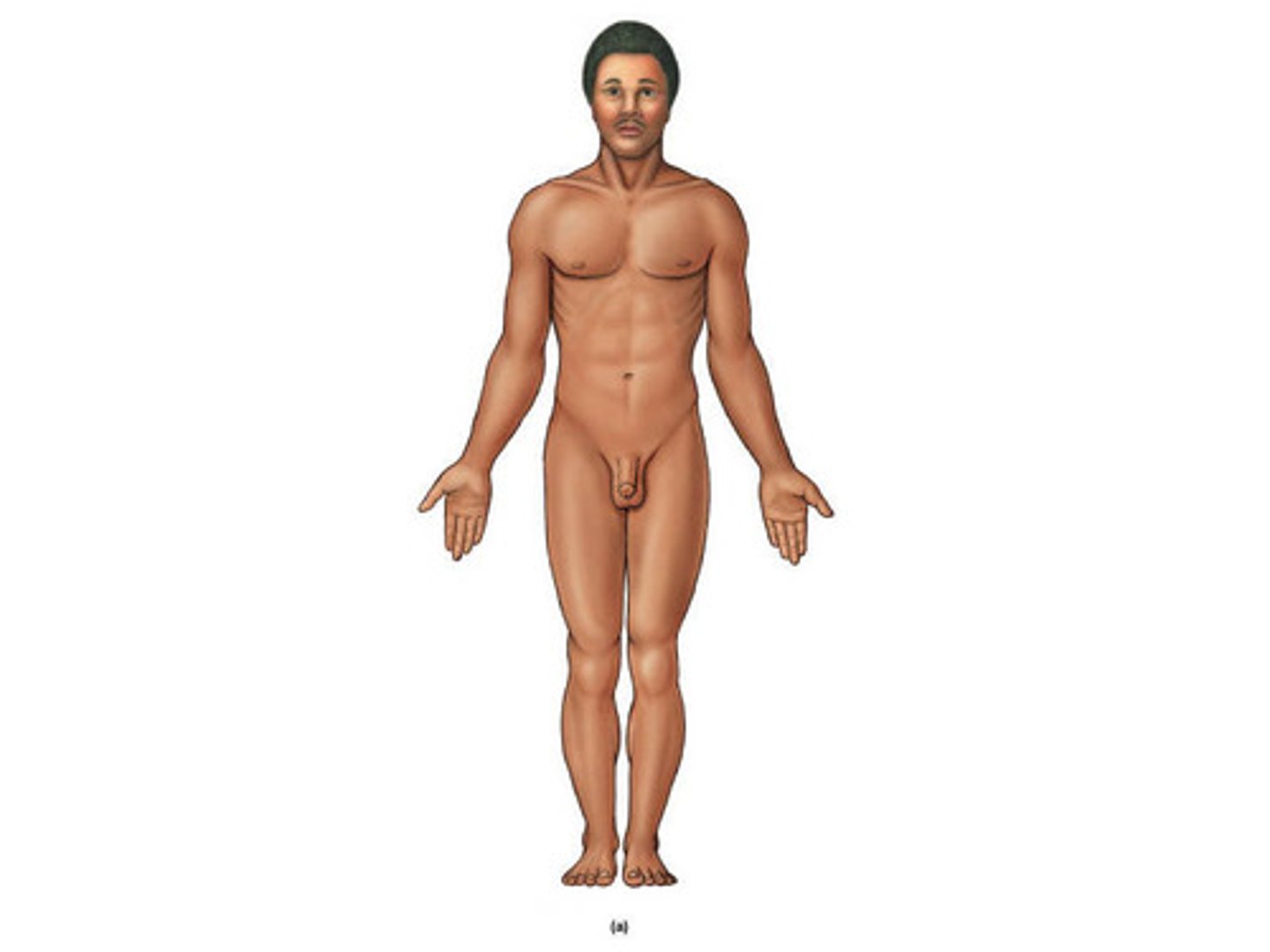
anatomical position
erect, feet forward, arms at side with palms facing forward, head facing forward

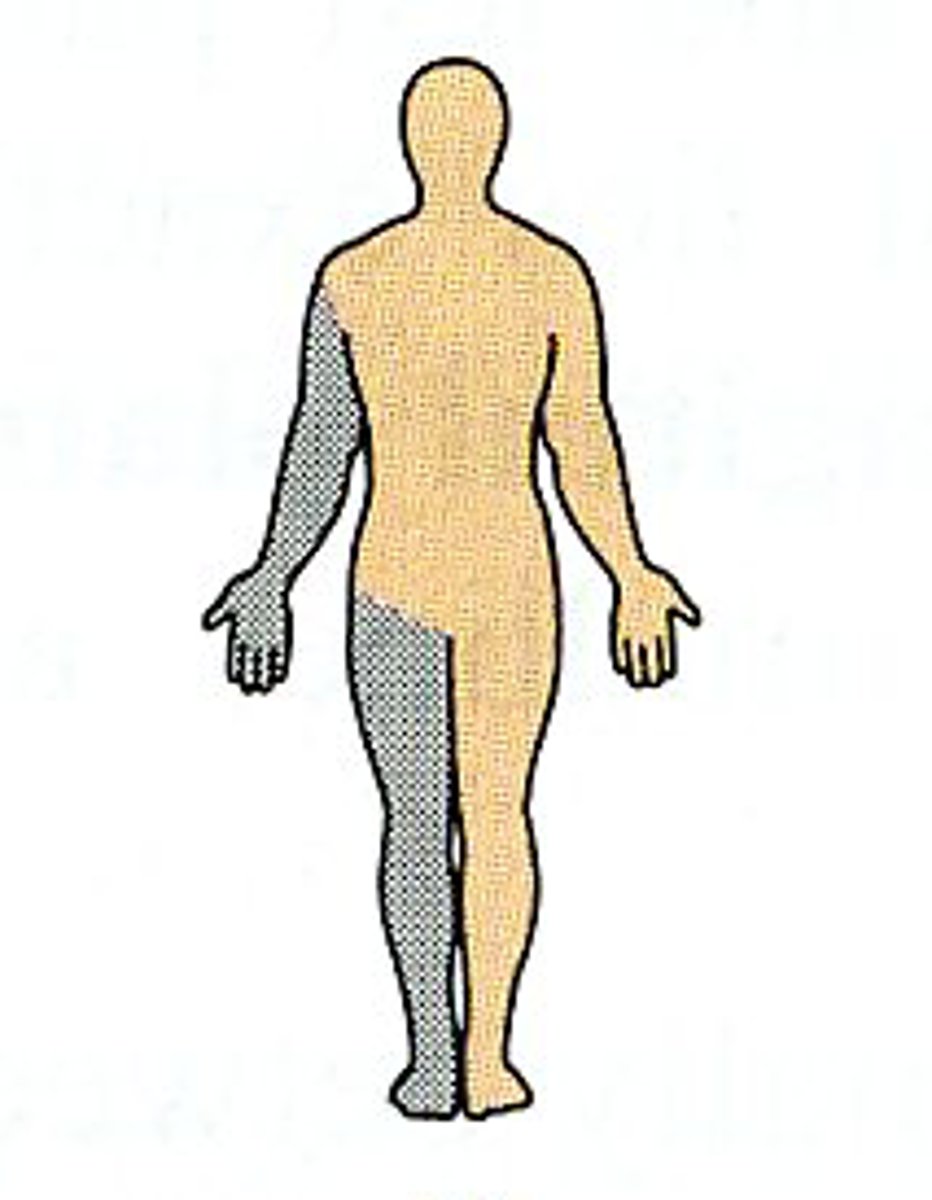
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
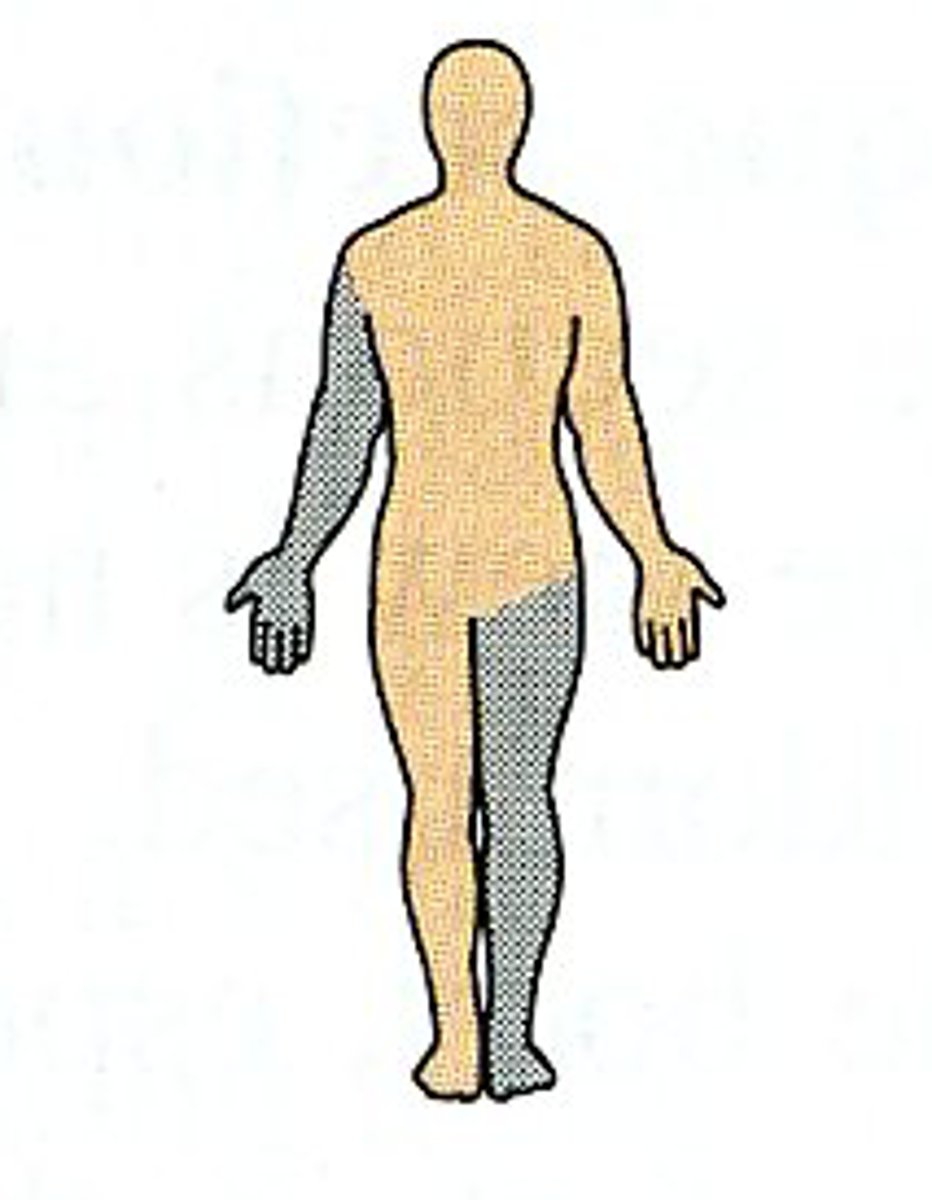
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
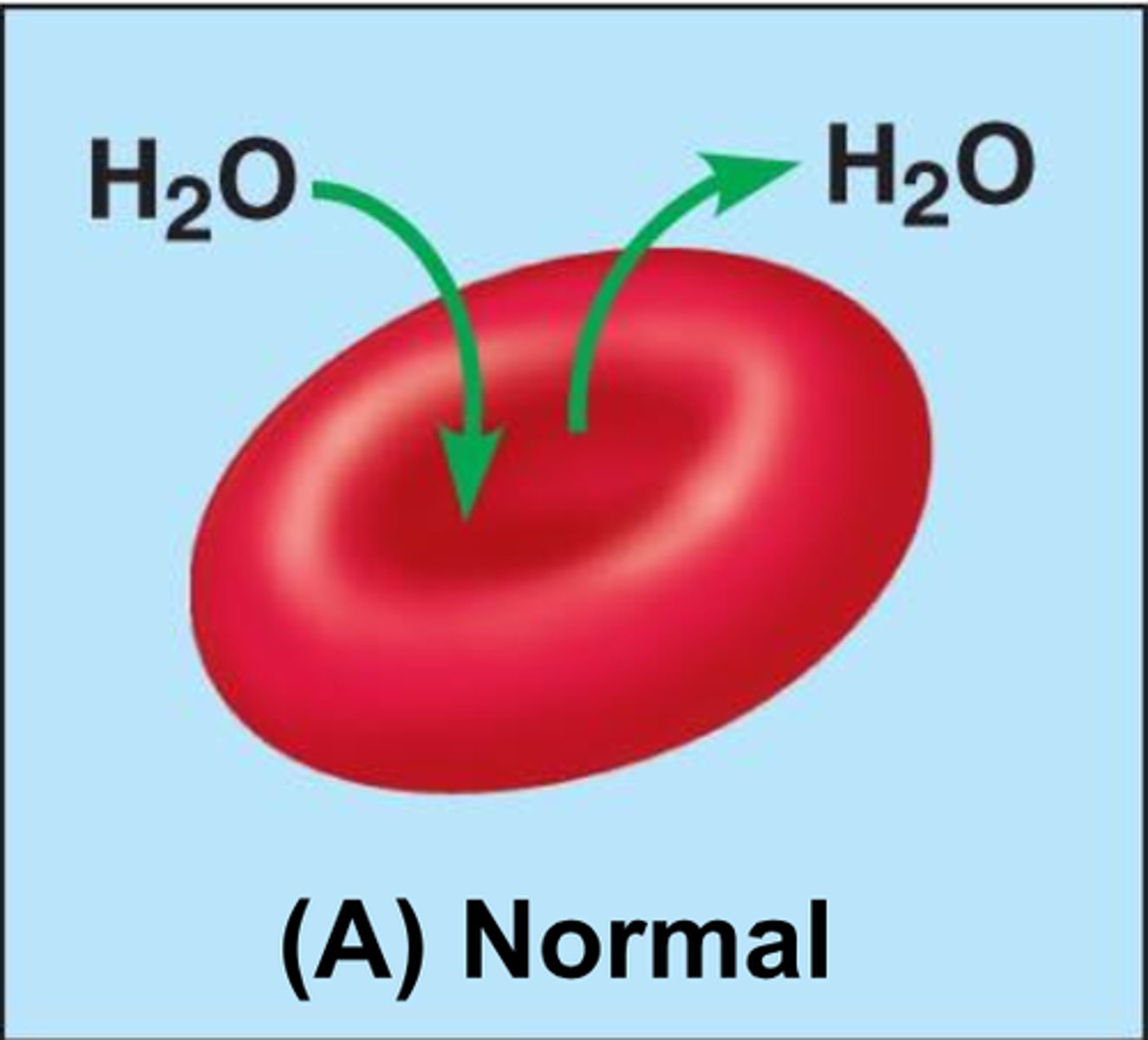
Isotonic solution for RBC
0.9% NaCl
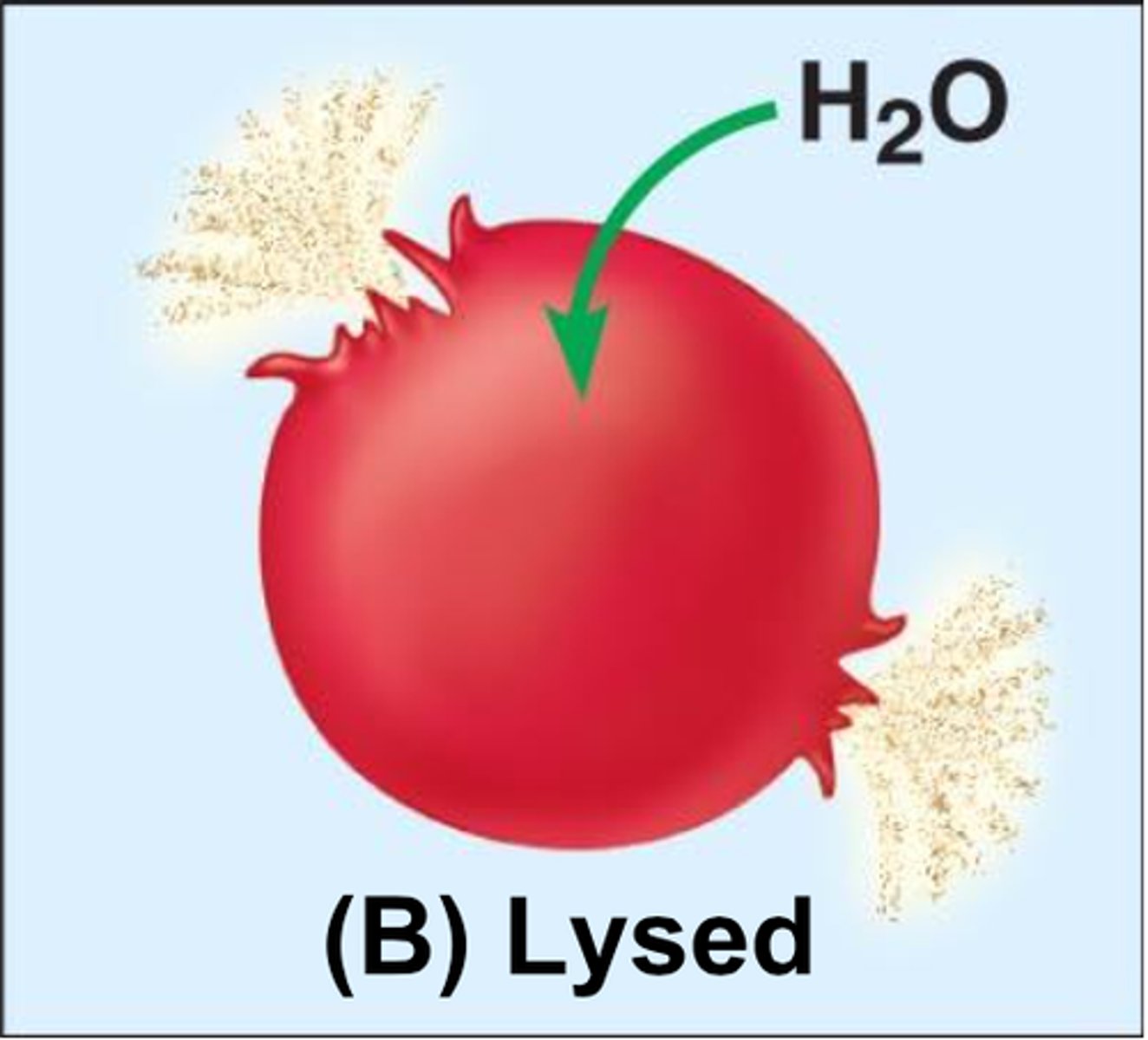
Hypotonic solution
a solution that causes a cell to swell because of osmosis
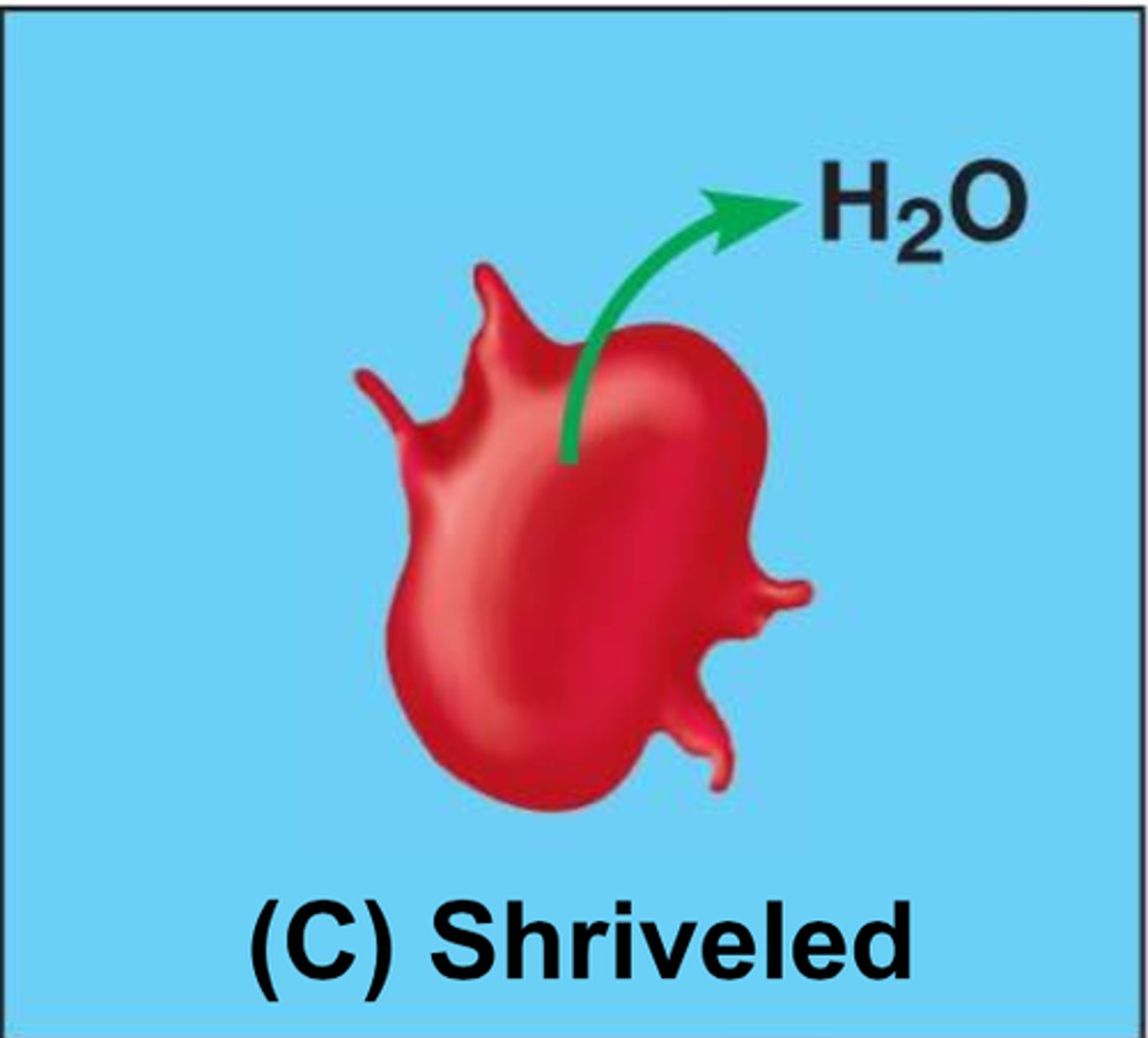
Hypertonic solution
a solution that causes a cell to shrink because of osmosis
Water intoxication
blood becomes hypotonic
cells swell
headache, nausea, death
Osmosis
when water molecules move from a high concentration to a low concentration
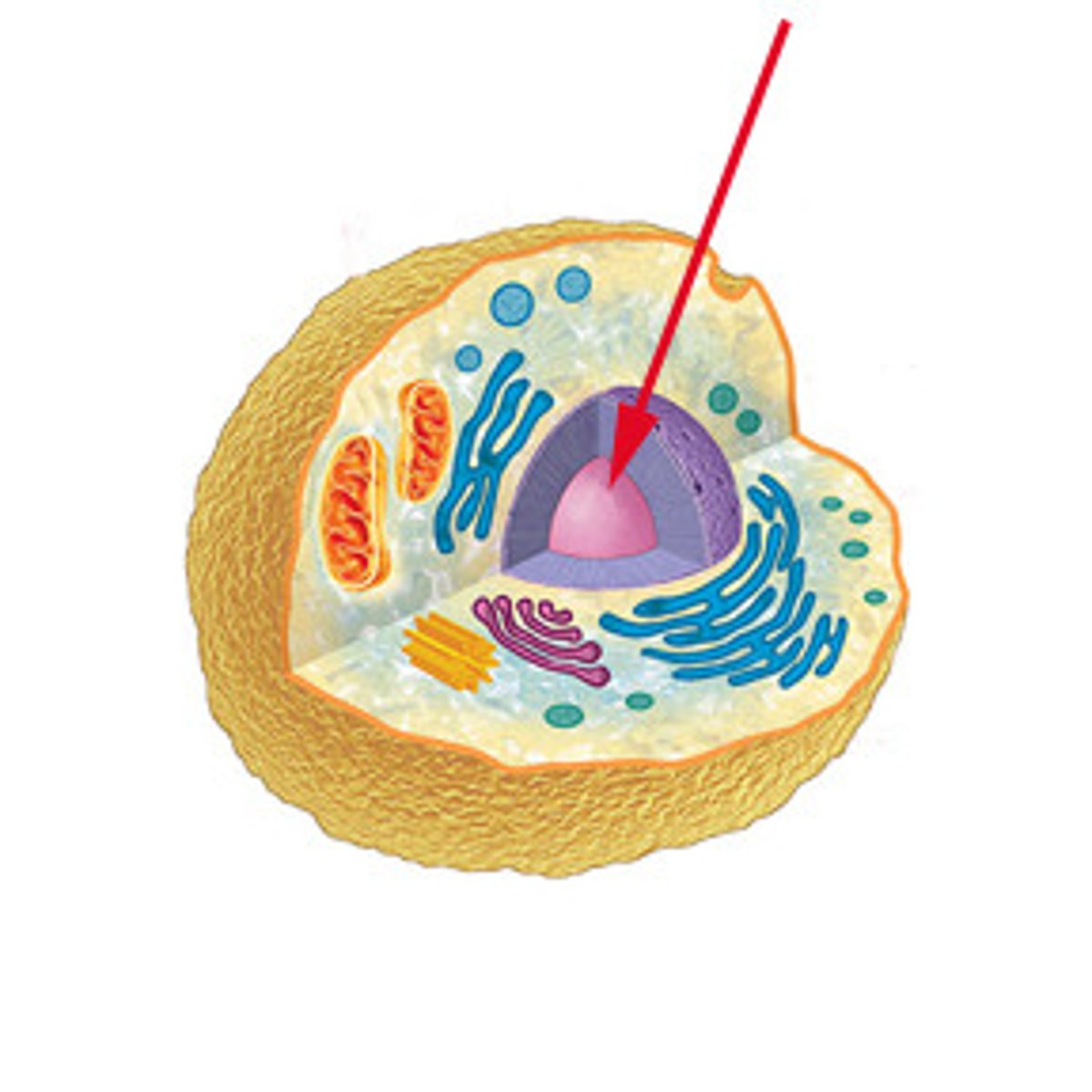
Nucleus
contains genetic information
controls the cell
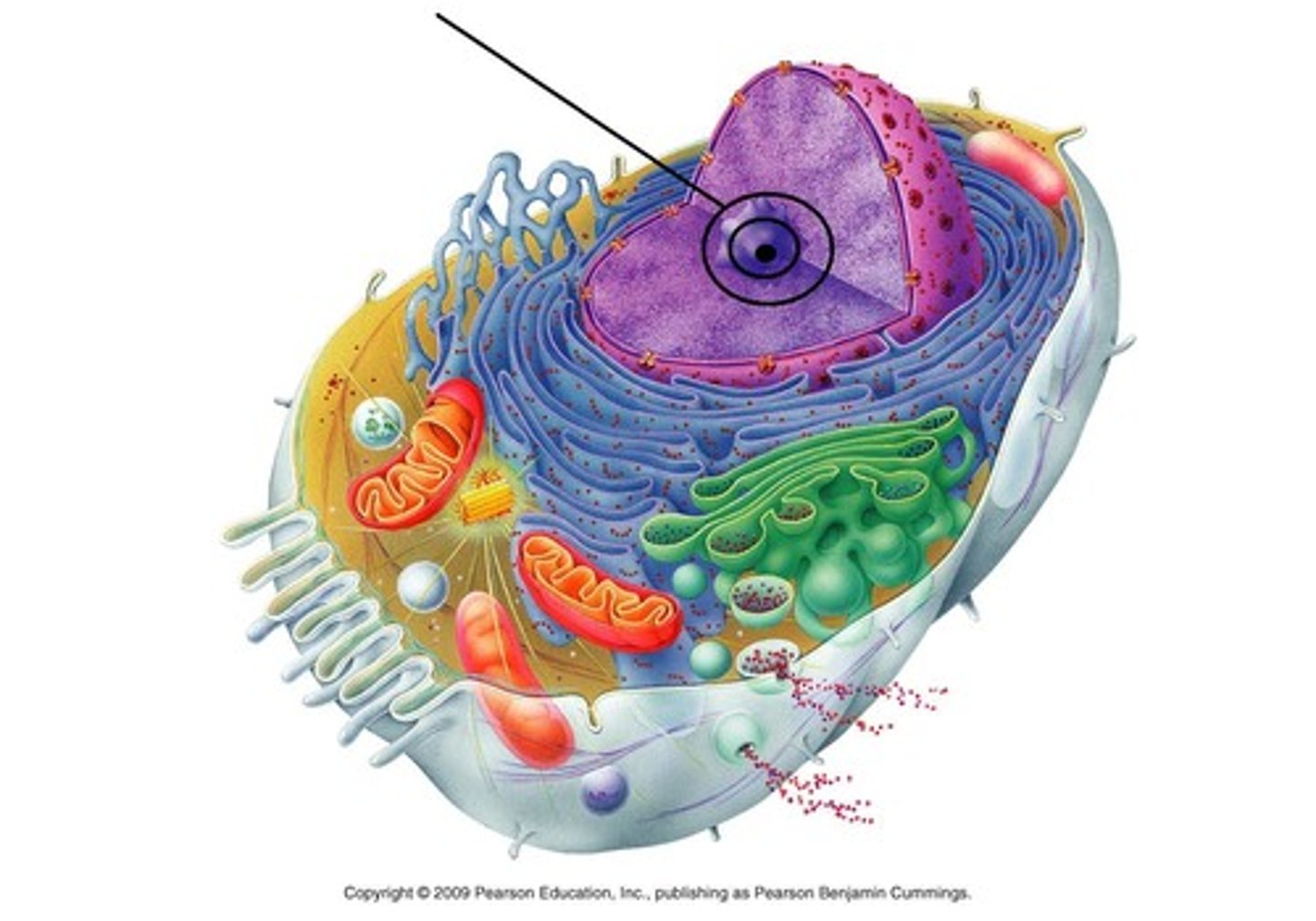
Nucleolus
Makes ribosomes
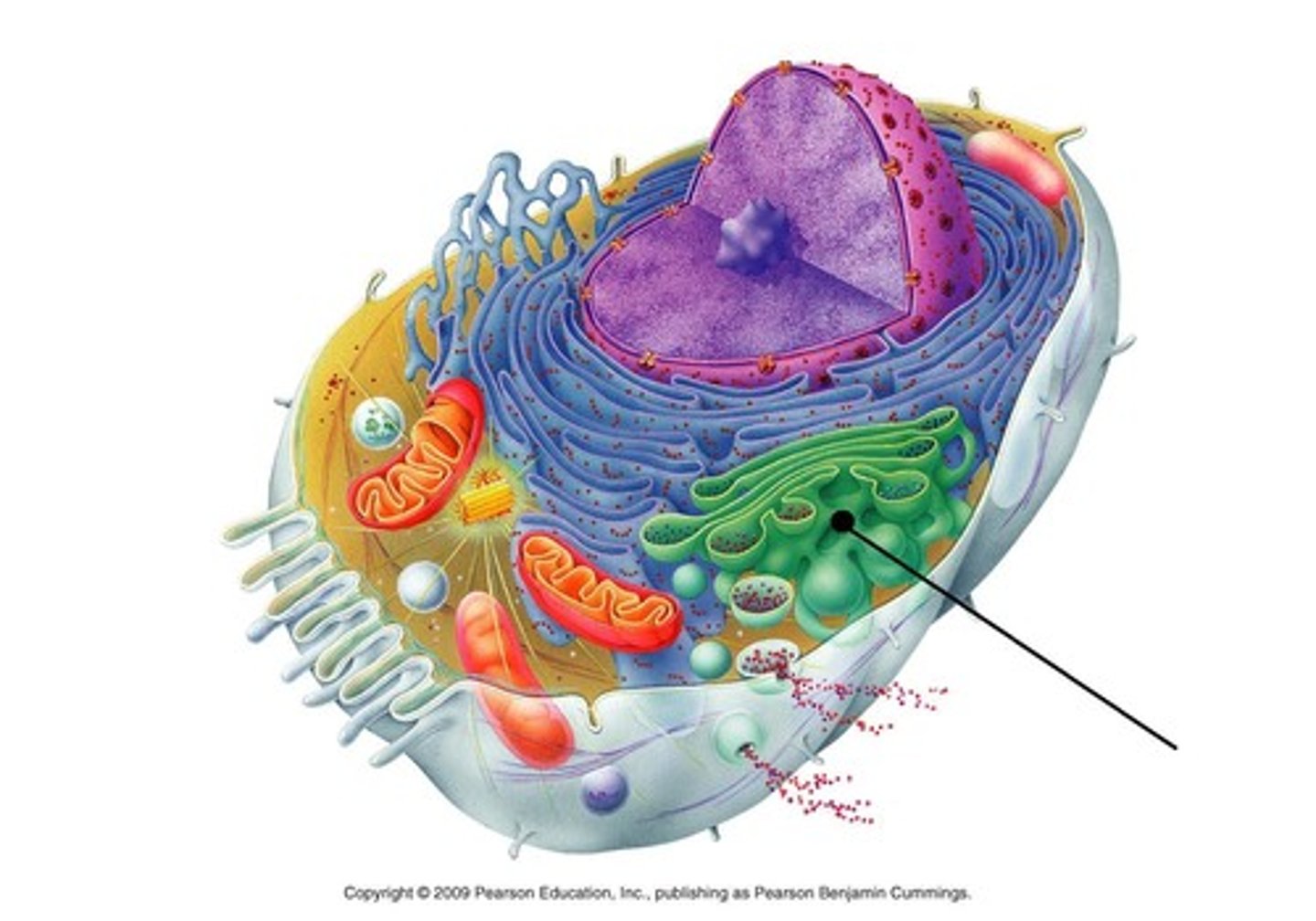
Golgi apparatus
stack of membranes that packages cell products
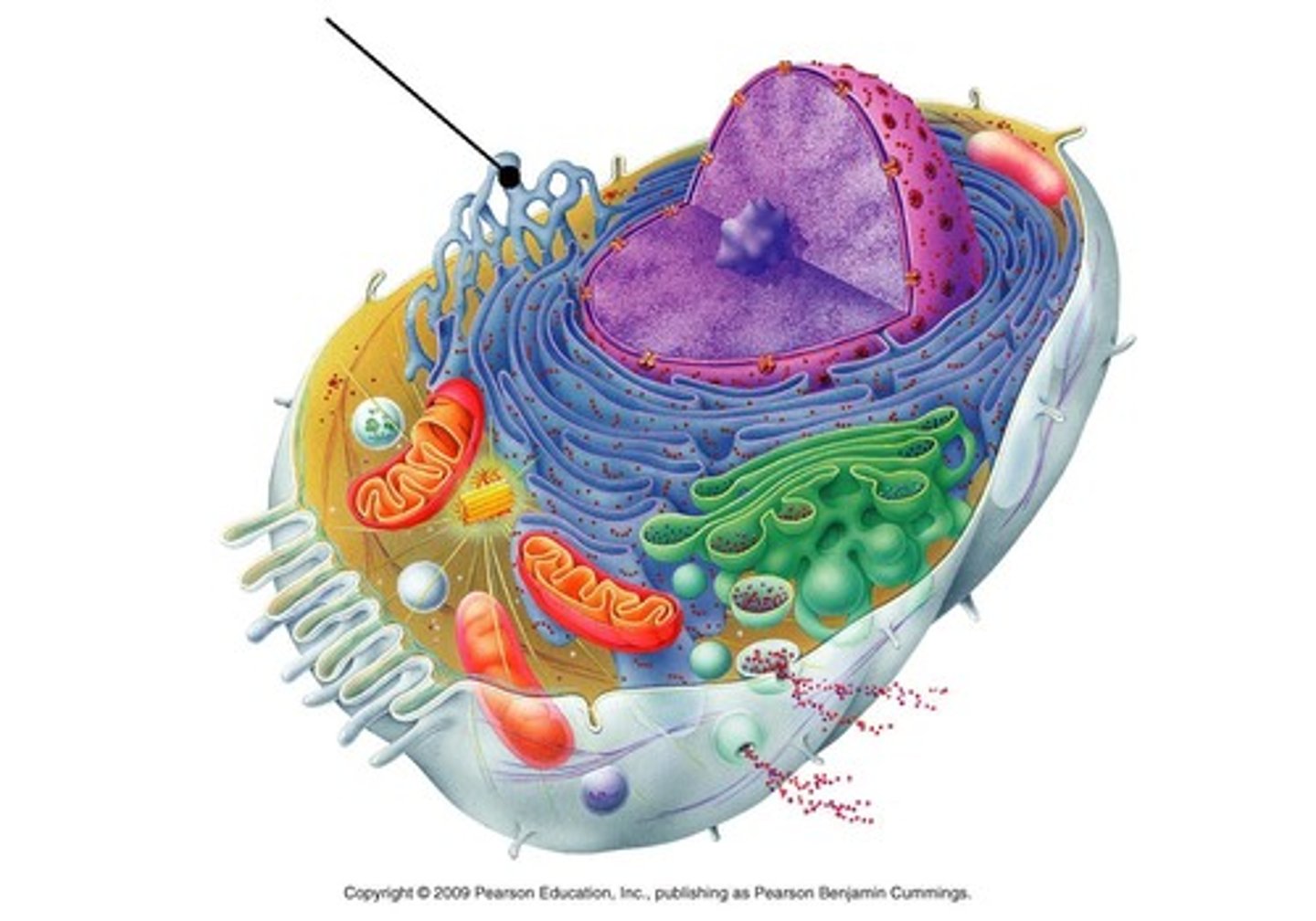
Microtubules
Thick hollow tubes that make up the cilia, flagella, and spindle fibers.
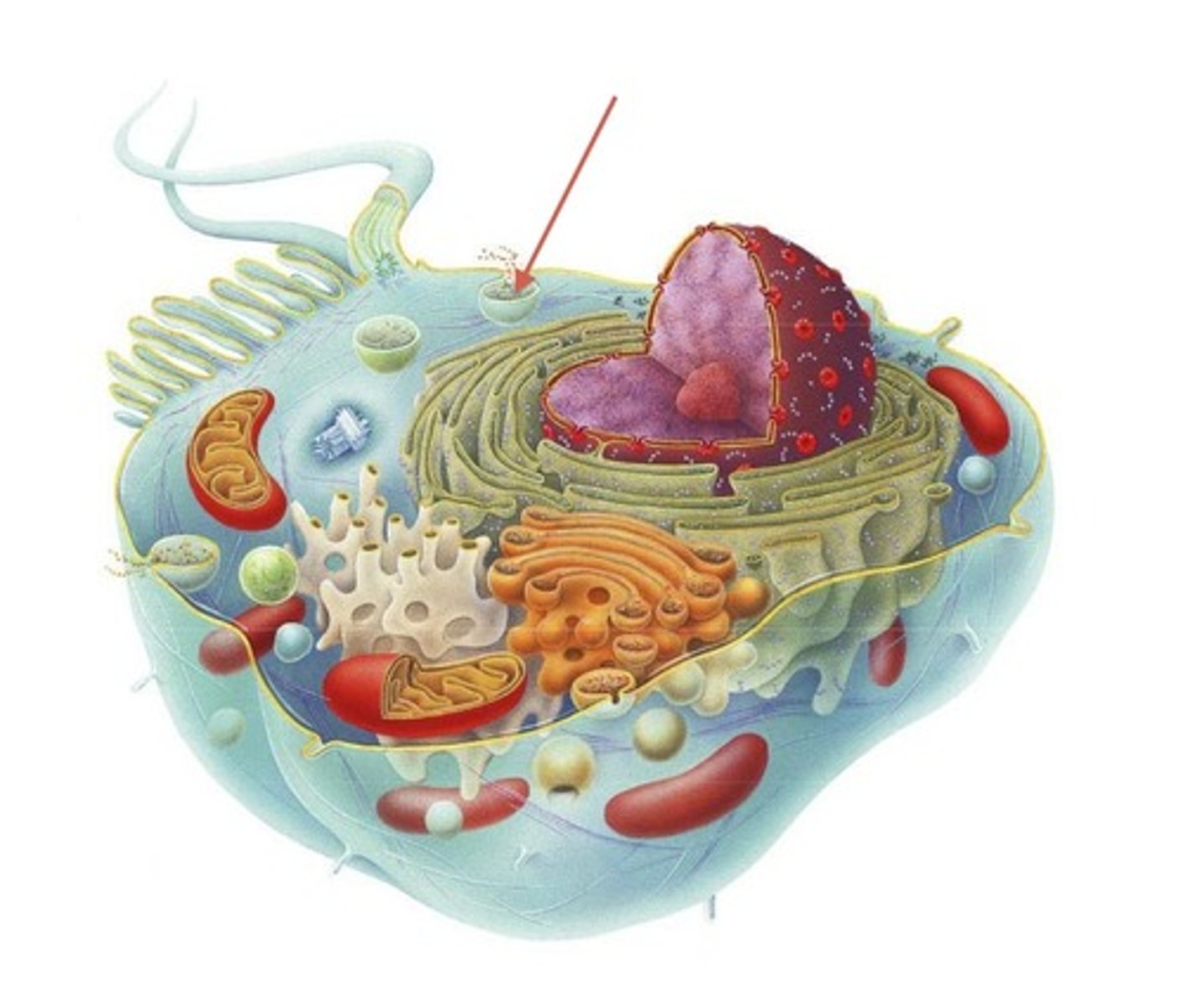
Vesicle
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
Smooth ER
Makes lipids
Rough ER
ER that is dotted with ribosomes, makes proteins
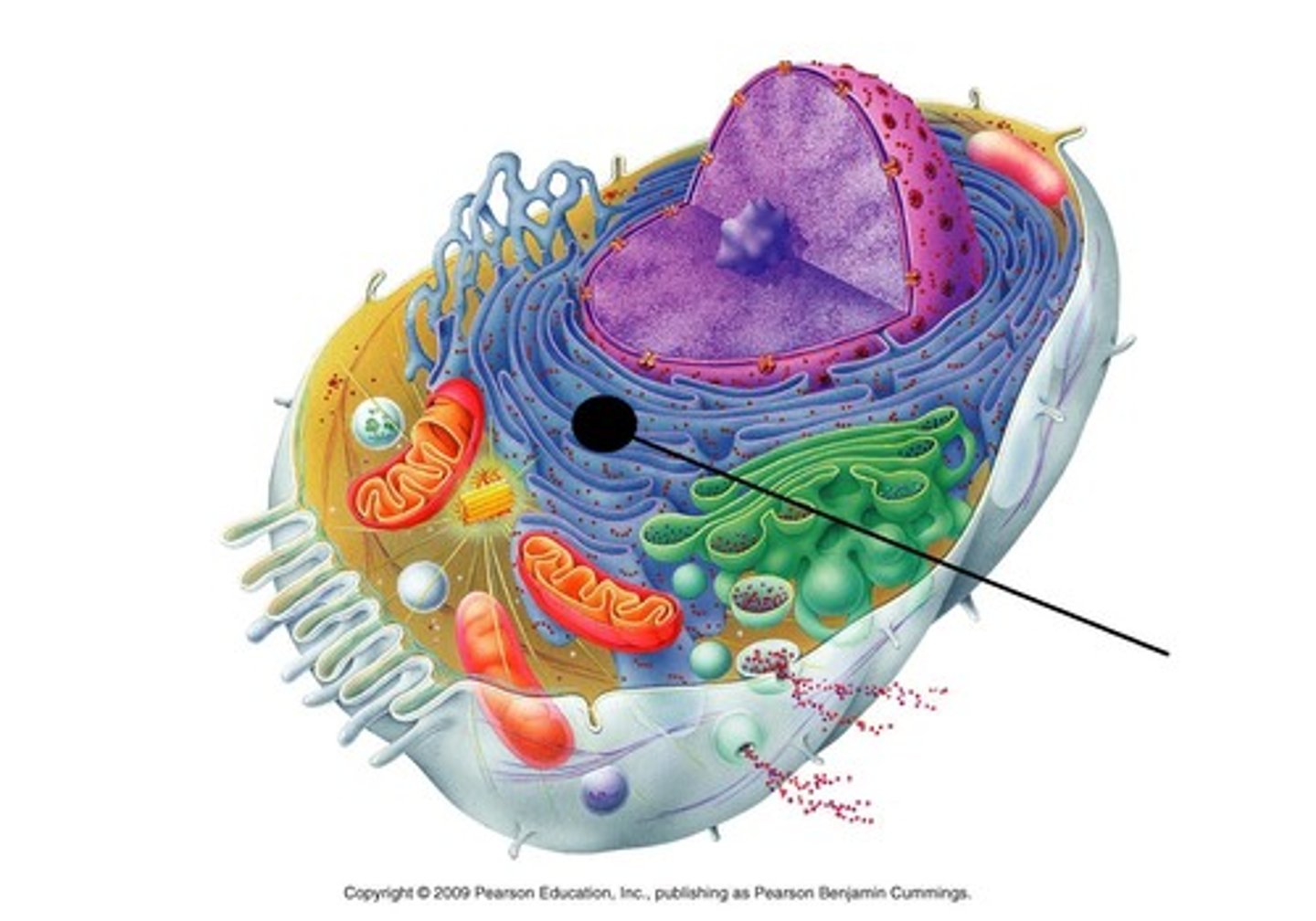
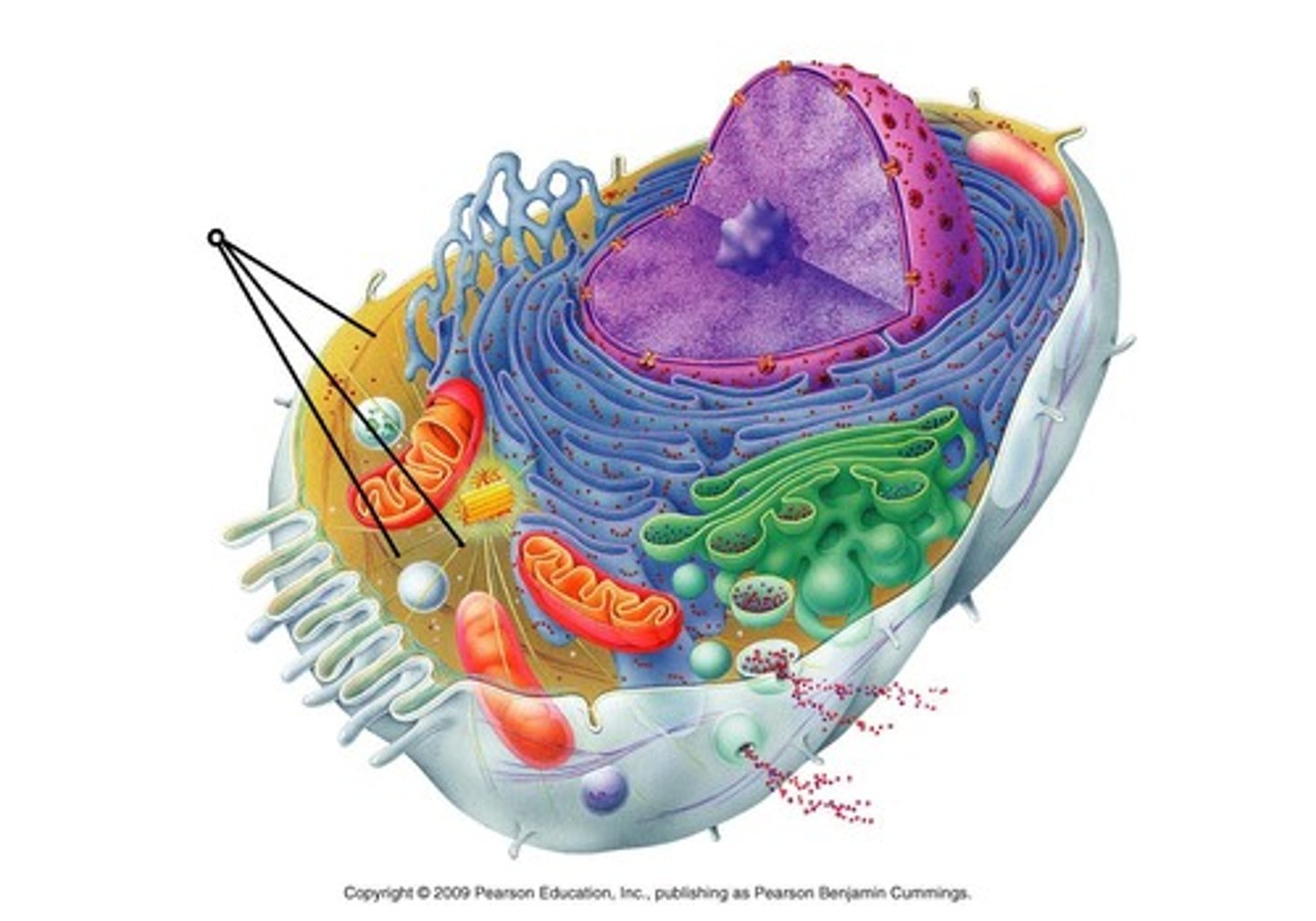
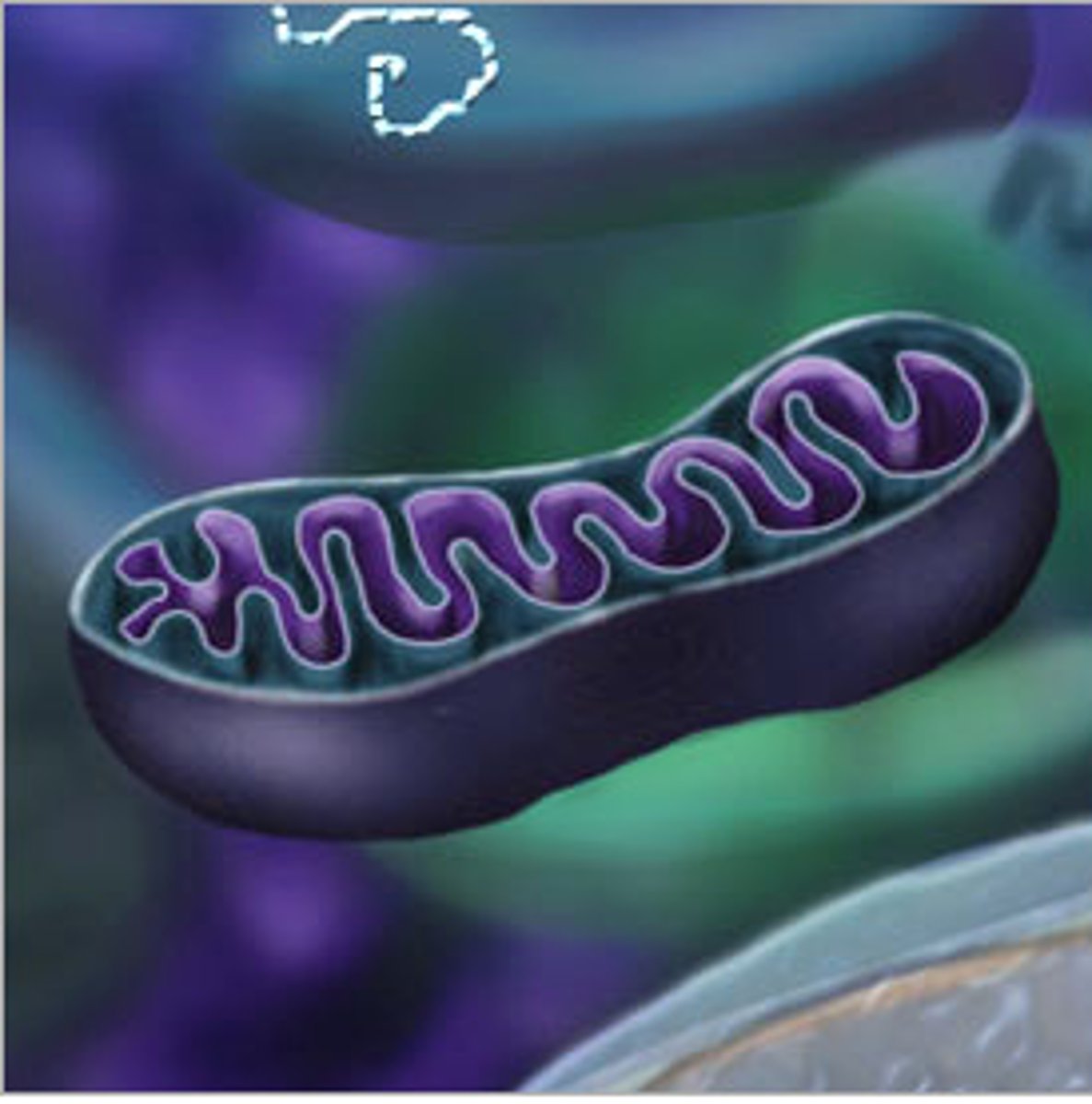
Mitochondria
part of the cell that makes energy molecules from glucose
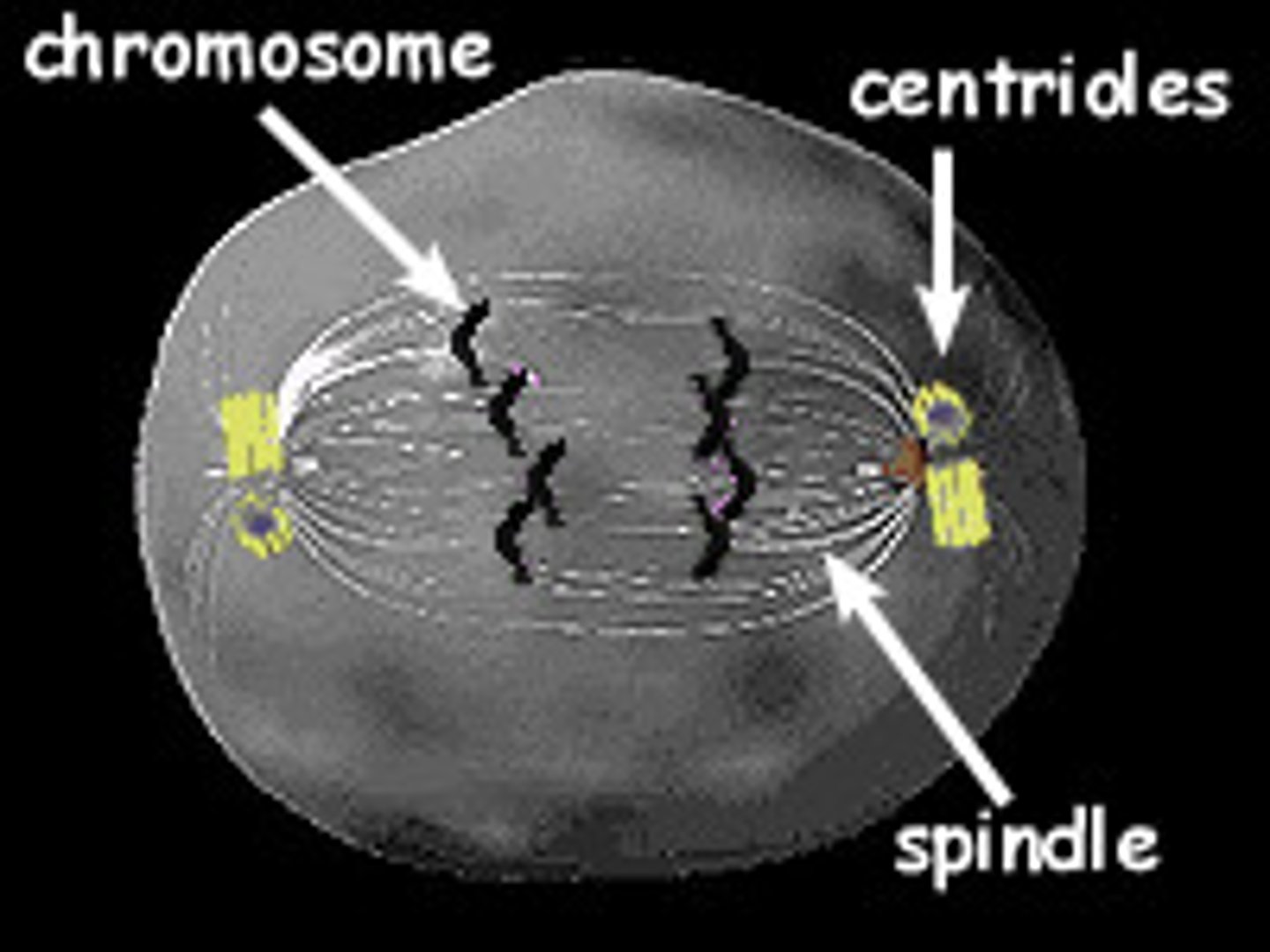
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
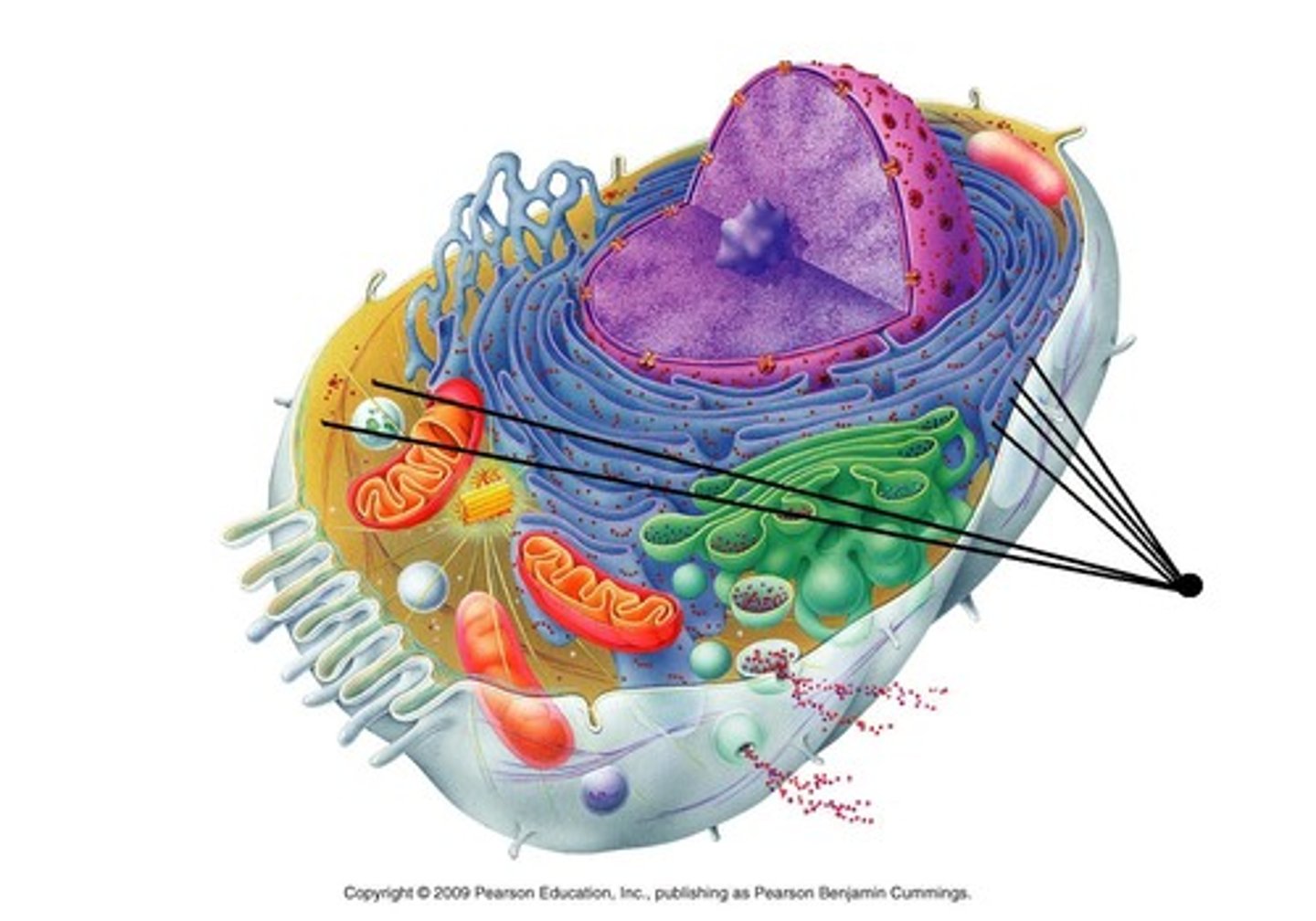
Plasma membrane
The membrane at the boundary of every cell that acts as a selective barrier,
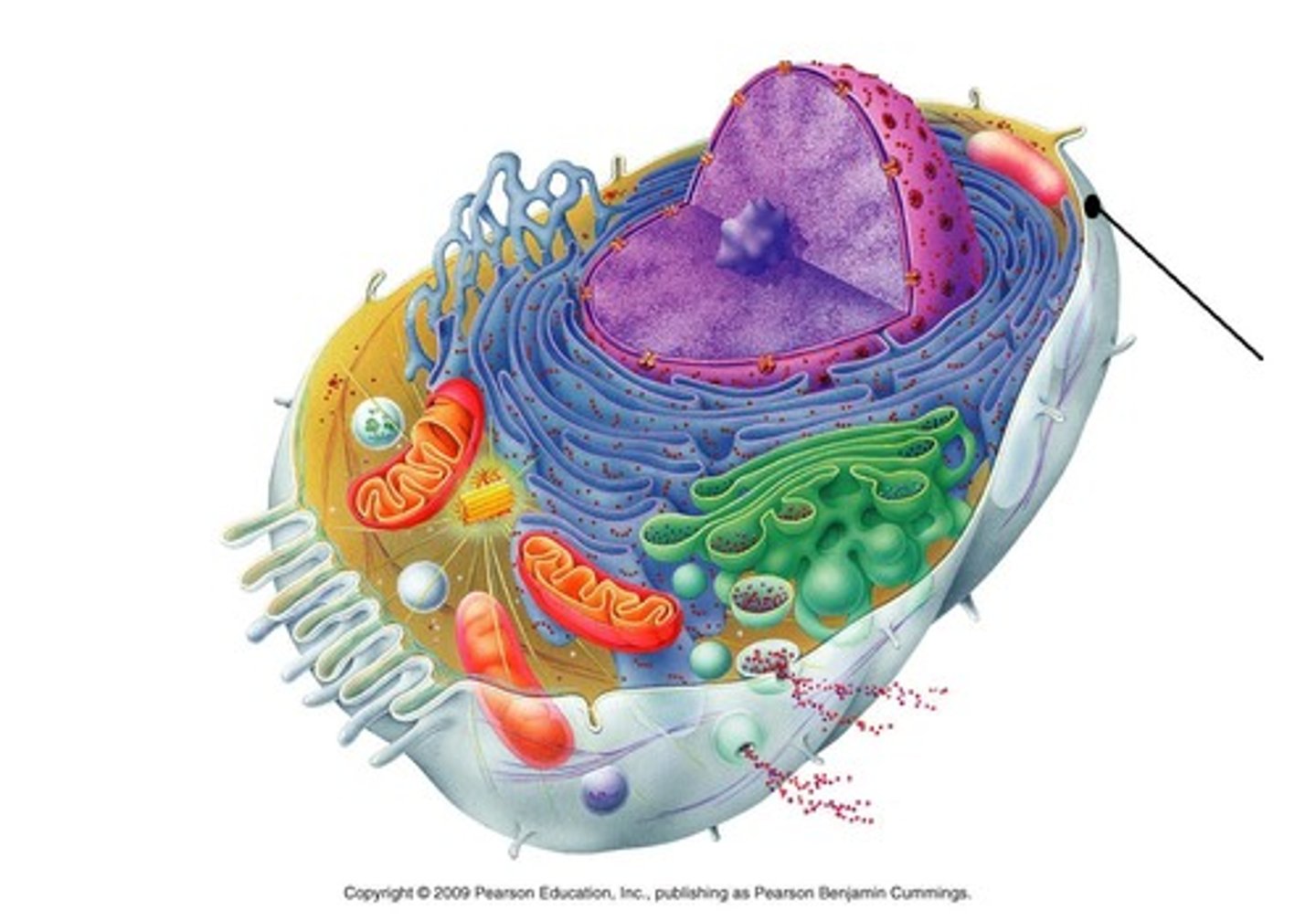
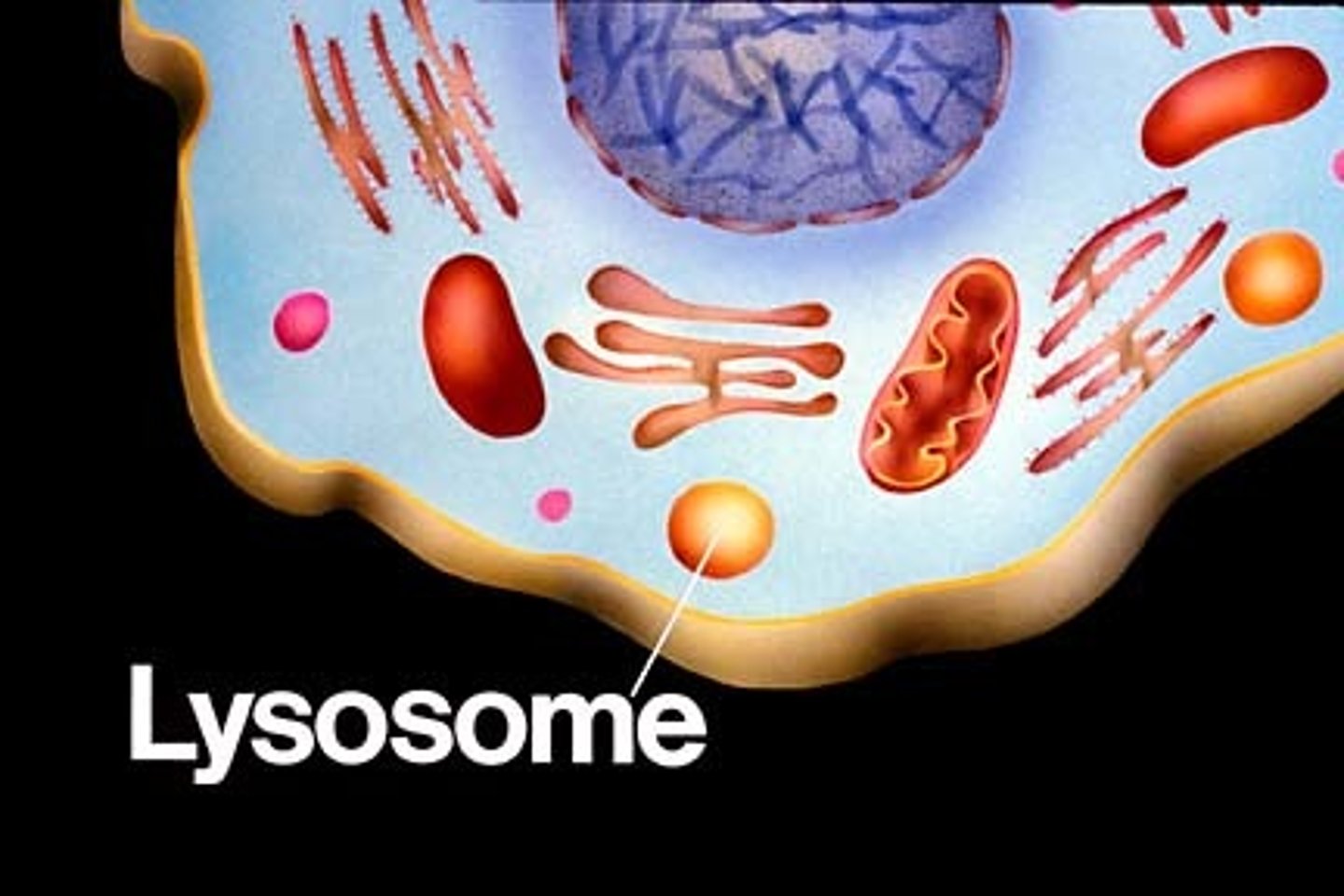
Lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes