Cellular organelles
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

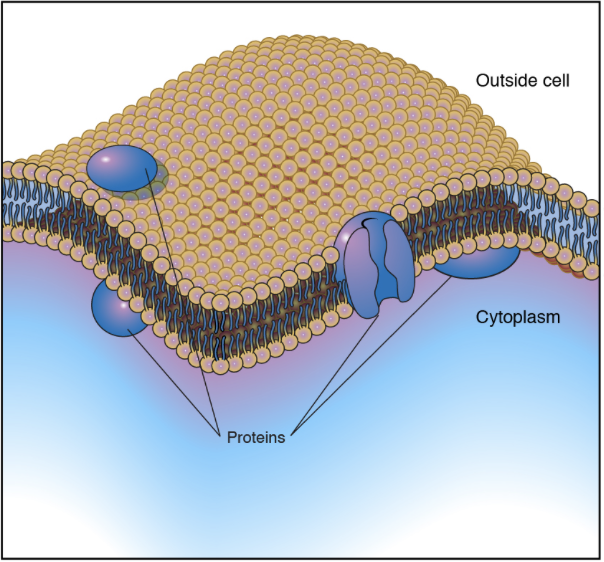
Plasma Membrane / Cell Membrane
Semi-permeable barrier that controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell. Has aquaporines that facilitate water transport and is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
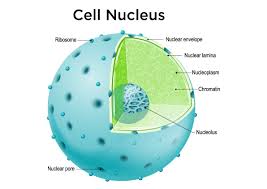
Nucleus
Stores genetic material (DNA) and controls cellular activities through gene expression. Its in animal cells
Nucleoid
Region in prokaryotic cells where the genetic material (DNA) is located.
Nuclear Membrane
Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, regulating the passage of molecules in and out.

Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, generates ATP through cellular respiration.
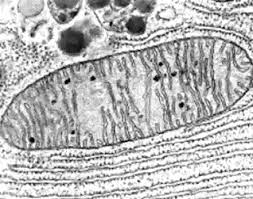
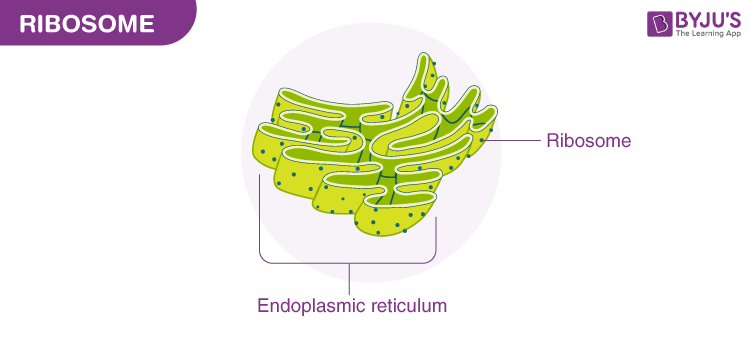
Ribosomes
Synthesize proteins by translating mRNA into polypeptide chains.
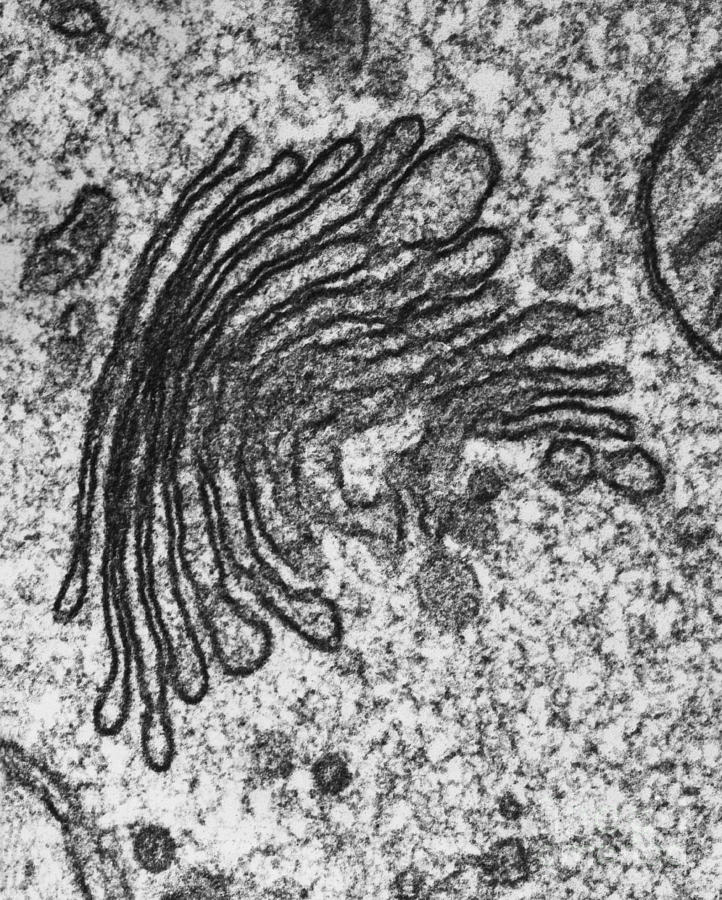
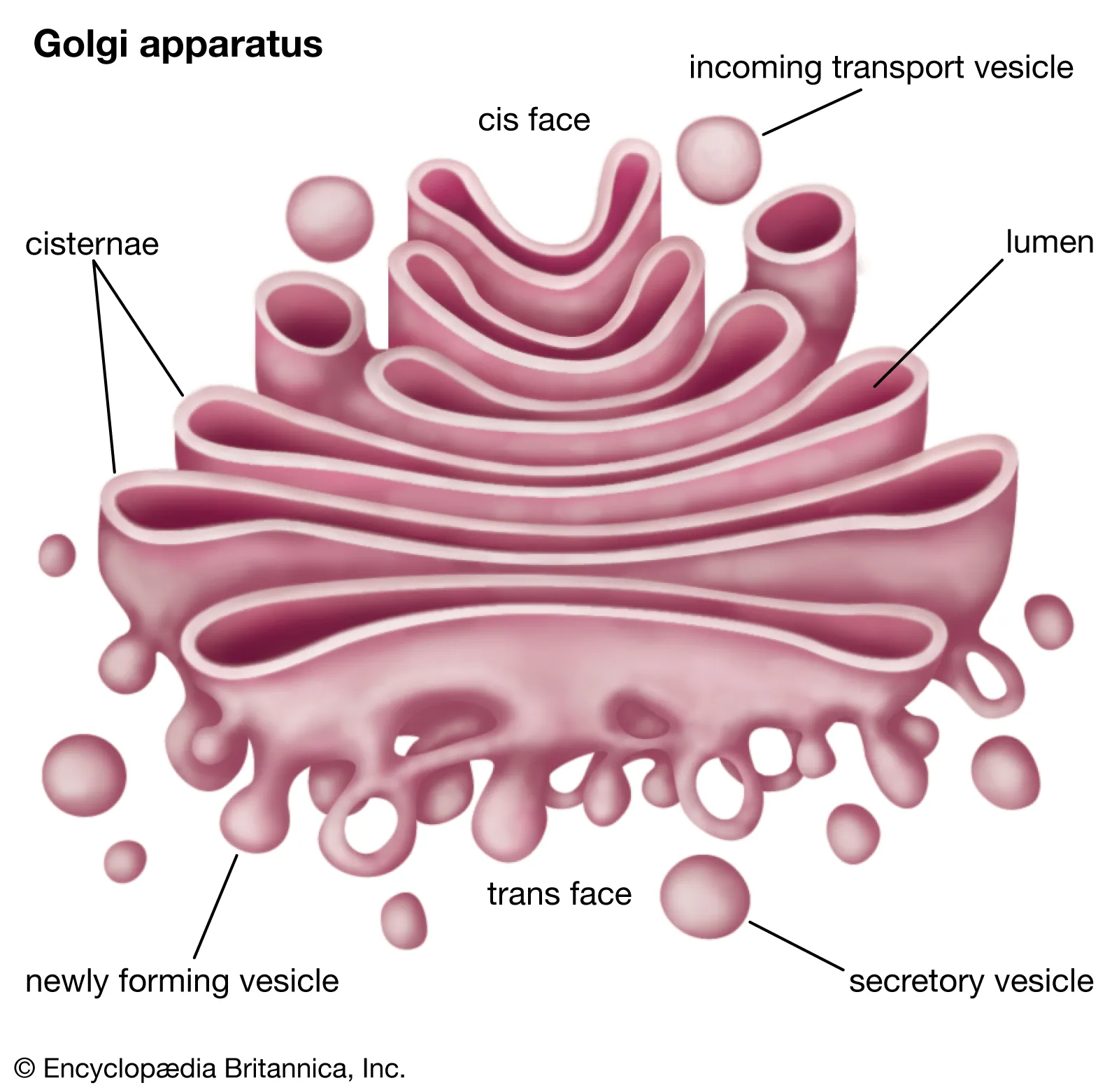
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for delivery within the cell.
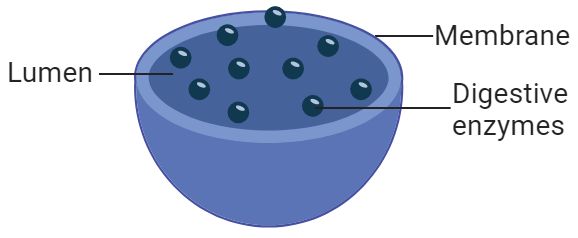
Lysosomes
Break down waste materials and cellular debris.
Peroxisomes
Break down fatty acids and detoxify harmful substances.
Mesosomes
Involved in cell division and maintaining the shape of the cell in prokaryotes.
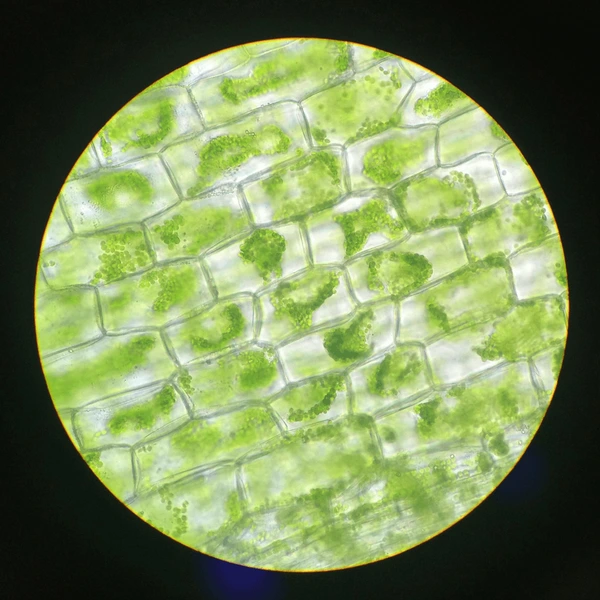
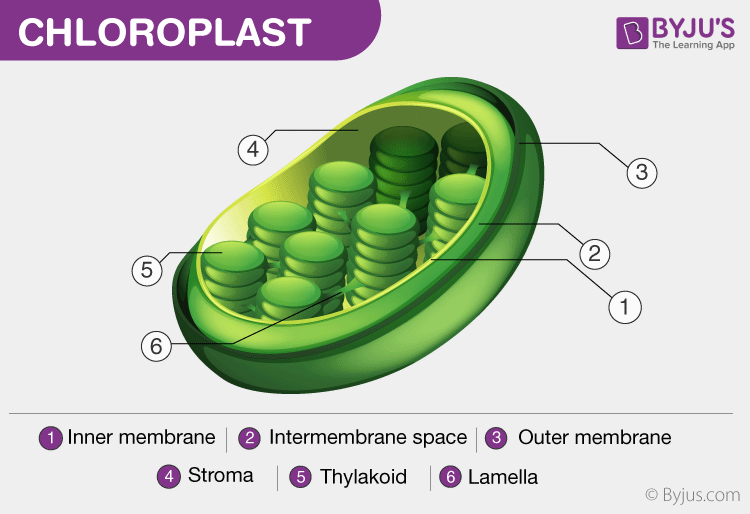
Chloroplasts
Perform photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
Cell Wall
Provides structural support and protection.
Vacuole
Stores water, nutrients, and waste products; maintains turgor pressure in plant cells.
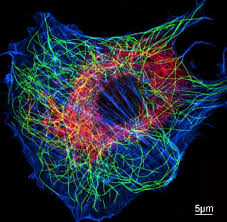
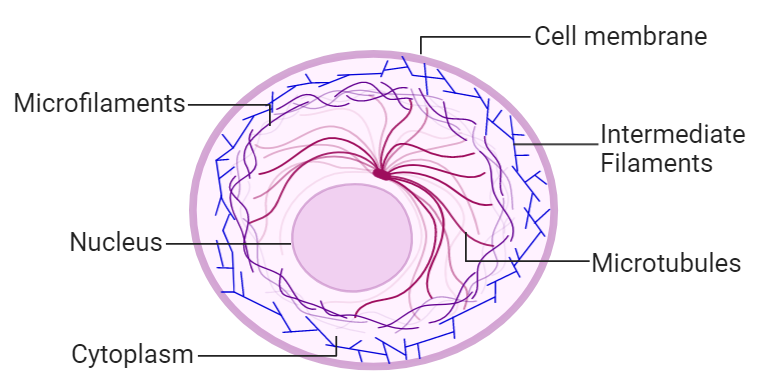
Cytoskeleton
Provides structural support, facilitates cell movement, and helps with intracellular transport.
Capsid
Protective protein coat surrounding viral genetic material.
Envelope
A lipid bilayer surrounding some viruses, derived from the host cell membrane.
DNA
Stores genetic information and directs cellular functions.
mRNA
Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
tRNA
Brings amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
rRNA
Structural and catalytic component of ribosomes.
ssRNA / dsRNA
Single-stranded RNA and double-stranded RNA used in viral replication and gene expression.
Centrioles
Help organize microtubules during cell division.
Plasmodesmata
Channels between plant cells allowing for communication and transport.
Flagella
Movement of the cell.
Pili
Attachment and DNA transfer in prokaryotes.
Inclusions
Storage of nutrients and waste products.
Types of Cells
Viruses lack membrane-bound organelles; Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles; Eukaryotic plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts; Eukaryotic animal cells lack a cell wall but have various organelles.
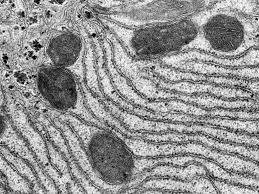
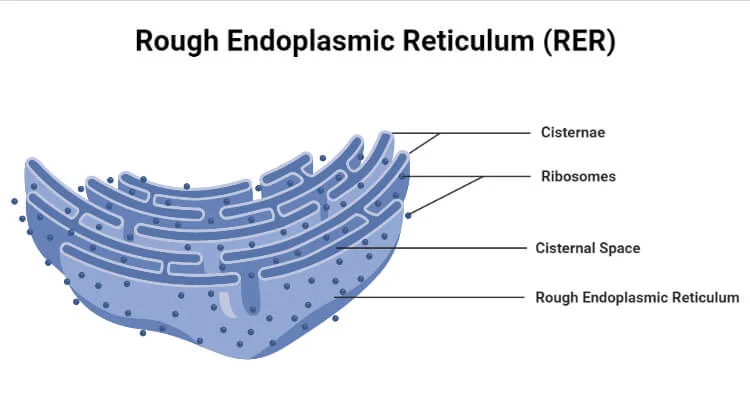
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough)
Synthesize proteins; has ribosomes attached to its surface, which translates mRNA into polypeptide chains.
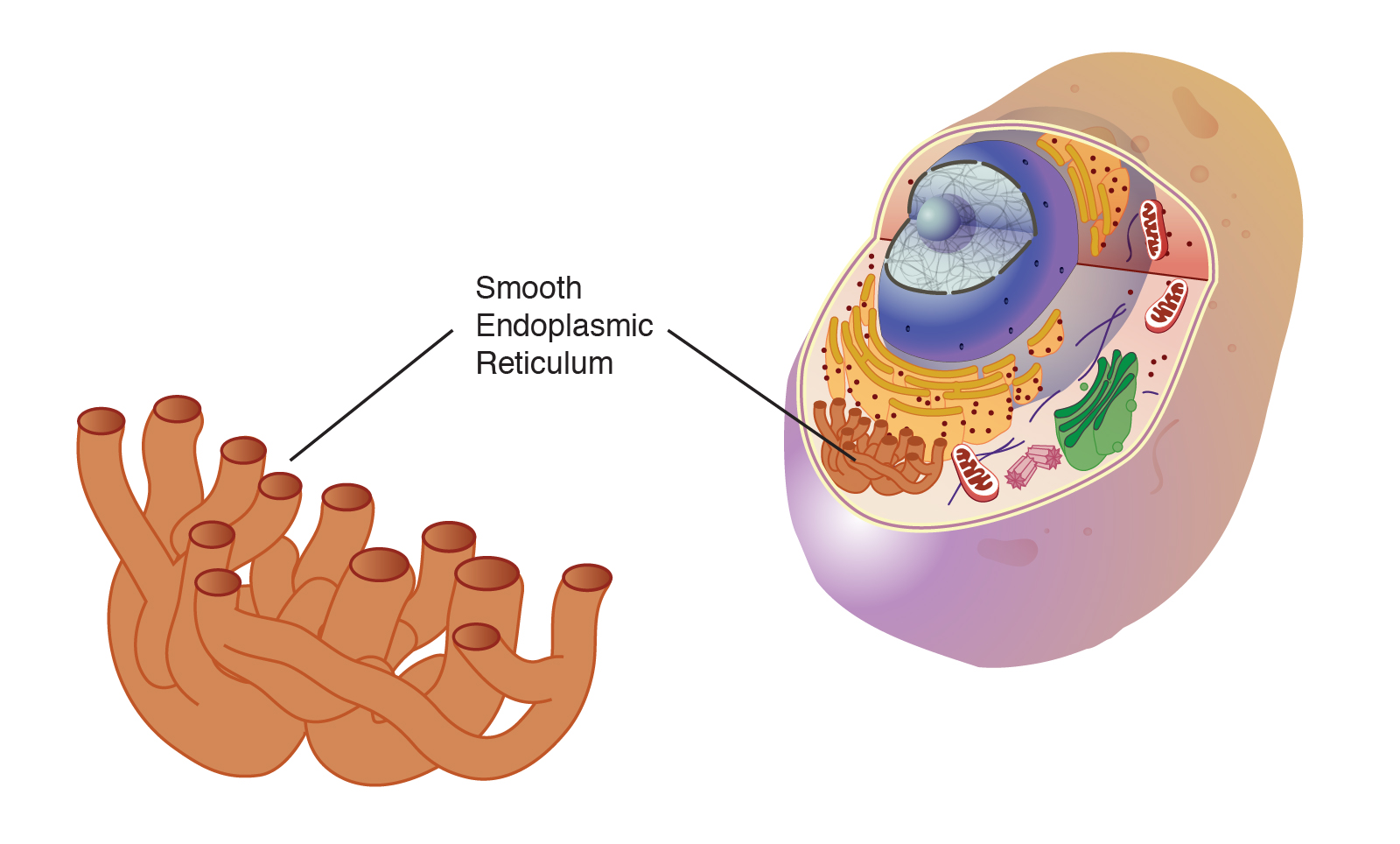
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth)
Synthesizes lipids; detoxifies and stores calcium.