Anatomy bones and cartilage
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bones and cartilage!! not finished, label long bone and compact bone+ next lecture!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What are the 3 main things humans are made up of?
cartilage, joints, and bones
how many bones does an adult have?
206
How much body mass does the bones of a human adult take up?
20%
how many human bones are axial
80
how many bones are appendicular?
126
how many bones do infants have
350
functions of bones (vague)
offers muscle support, store minerals
functions of cartilage (vague)
supports movement, offers cushioning
functions of joints
where bones meet and articulate
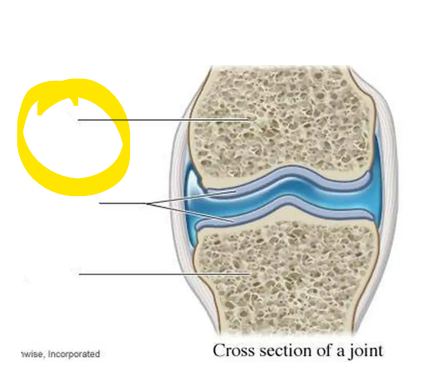
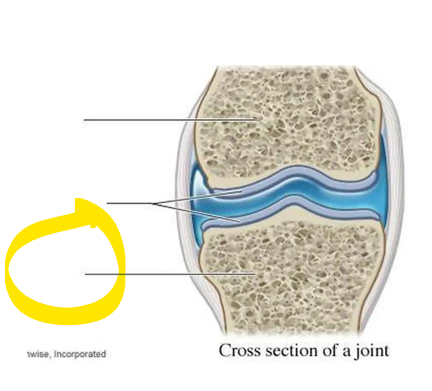
what is this?
bone
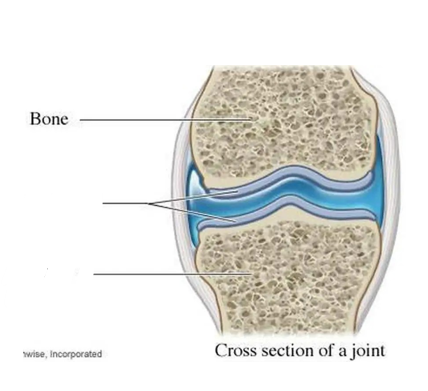
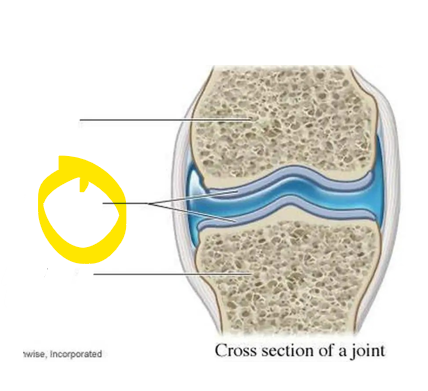
what is this?
cartilage
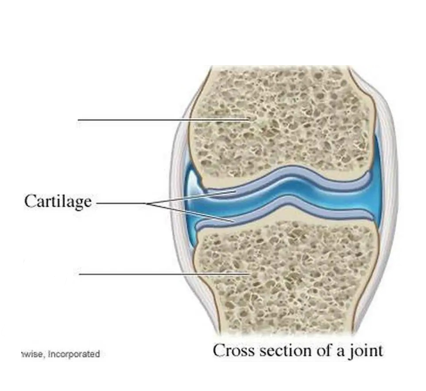
what is this?
bone
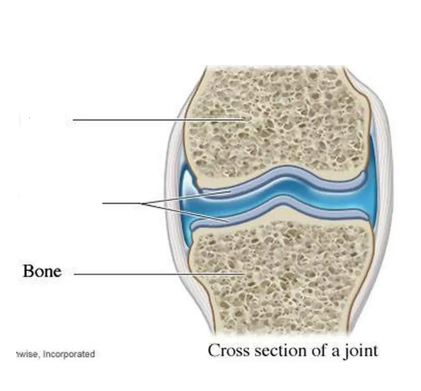
examples of cartilage
external ear, nose, back vertebrea, larynx airway
function of articular cartilage
covers end of bones
function of costal cartilage
connects ribs to sternum
what type of tissue does cartilage have?
resilient
meaning of resilient tissue
can be cmpressed and return to OG shape
does cartilage have high or low water content?
high
is cartilage vascular or avascular
avascular
does cartilage have nerve endings
no
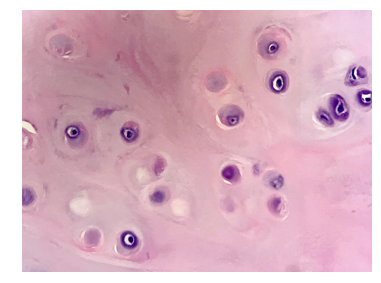
type of cartilage
Hyaline
what does hyaline cartilage have a lot of
h2o and collagen unit fibril
nickname for hyaline cartilage
glass
characteristic of hyaline cartilage
compressible, resilient, and flexible
where does hyaline cartilage go
end of bones, ribs to sternum, respiratory tract
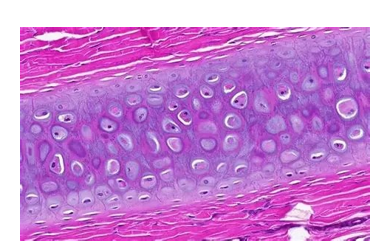
what type of cartilage is this
elastic
characteristic of elastic cartilage
matrix has collagen and elastic fibers, making it able to bend repeatedly
example of elastic cartilage
epiglottis, outter ear
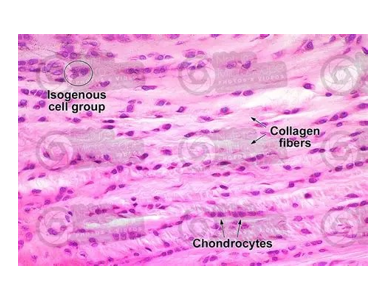
What type of cartilage is this
fibrocartilage
characteristic of fibrocartilage
withstands compression and pulling
example of fibrocartilage
knee miniscus:invertebral disc
types of growth of growth of cartilage
2, appositional and interstitial
what is appositional growth
adding new layers on top of already existing outer layers
what is interstitial growth
adding layers within cartilage and bone
example of appositional growth
outer surface of bone
example of interstitial growth
Epiphyseal plates
ALL functions of bone
gives shape to head
supports body weight
protects lungs and brain
mineral storage
blood cell formation (red marrow)
energy metabolism and storage
2 types of bone tissue
organic and inorganic
organic bone tissue characteristics
35%
collagen
ground substance
inorganic bone tissue characteristics
65%
hydroxyapetitie
pack together to give strength to bone
cells needed to BUILD and MAINTAIN bone
osteoprogenitor cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
function of osteoblasts
produces ground substance and collagen
cell involved in reabsorption
osteoclast
function of osteoclast
secretes hydrochloric acid and lysosomal enzymes
bone classifications
long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular
example of long bone
limb
example of a short bone
sesamoid
example of a flat bone
ribs, cranium
example of an irregular bone
vertebrae
what does spongy bone do
lightens bone weight
does the hollow center of a bone reduce bone strength
no
difference between long bone and other bones
other bones dont have diaphysis/epiphysis and no bone marrow cavity