Optical Isomerism
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
2 types of isomerism
Structural
Stereoisomerism
Define structural isomerism
Occurs when molecules have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
3 types of structural isomerism and their definitions
Chain→ Different organisation of carbon chain
Position→ Functional group in different position
Functional→ Functional group is different
Define stereoisomerism
occurs when molecules have the same structural formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms.
2 types of stereoisomerism and their definitions
E/Z isomers (geometrical)→ Double bond has restricted rotation
Optical isomerism→ Non-superimposable mirror images
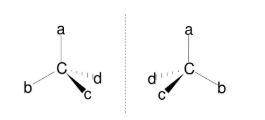
What is required for a molecule to show optical isomerism?
A chiral/asymmetric carbon
I.e. A carbon atom that has 4 different groups attached
What is meant by optically active?
A substance/sample is optically active if it rotates plane polarised light anticlockwise or clockwise
How can optical activity be detected in a sample?
Plane polarised light
Optically active samples will rotate plane polarised light
What is a racemic mixture?
A mixture where 50% of the enantiomers have rotated the plane polarised light clockwise
And the other 50% have rotated it anti clockwise
Racemic mixtures are NOT optically active
Because the effects of both enantiomers have been cancelled out
(A racemic mixture does contain optical isomers but the mixture it self is not optically active)
1 way racemic mixtures form
Nucleophilic addition to carbonyls
The carbon of the carbonyl group becomes the chiral centre
What is meant by a carbonyl group ?
Carbonyl group contains a carbon atom double bonded to oxygen atom
How does nucleophilic addition to carbonyls make racemic mixtures?
Carbonyl group is planar (flat)
Nucleophile can attack carbon from either side (top or bottom) with equal probability
Producing equal amounts of each enantiomer

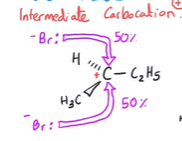
2nd way a racemic mixture can be formed
Electrophilic addition
How does electrophilic addition produce a racemic mixture?
The intermediate carbocation carbon has 3 bonds around it
Making the molecule planar
Allowing the nucleophile to attack from either side with equal probability
Producing equal amounts of each enantiomer
Why are optical isomers important?
Can have different biological properties due to different spatial arrangements
Example of a molecule that is an optical isomer and the enantiomers have differences in smell
Carvone
1 enantiomer smells like mint
The other of caraway seeds
Example of an optical isomer where the enantiomers have different effects?
Thalidomide
1 enantiomer alleviates nausea
The other causes birth defect
Important to use enantiomerically pure drugs→ Drug which is 100% 1 enantiomer to give the desired effect
What’s the significance of enzymes also having enantiomers?
Enantiomers of enzymes have different active sites specific to different substrates
How would you decipher if a molecule has a chiral centre from its formula e.g. C6H12
Assume it has 4 different groups attached and draw them out
(Check notes for additional guidance)