Sales Forecasting
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is Sales Forecasting?
The art/science of predicting future demand/sales by anticipating what consumers are likely to do in a given act of circumstances
Techniques allows business to predict sales,HRM needs, financial needs
What are the Quantitative Methods of Sales Forecasting?
Quantitative———> Time series analysis,Use of market research
When are they used?
When historical data is available
Outcomes are objective (numerical data)
External Factors affecting this method are
Economic Factors——>e.g unemployment rates ,inflation, interest rates, economic growth
Consumer Factors——> e.g consumers’ tastes and fashions
Competition Factors
What are the Qualitative Methods of Sales Forecasting?
Qualitative——->Delphi Technique,Brainstorming,Intuition,Expert Opinion
When are they used?
When historical data is not available
Outcomes are not subjective
External factors that affect this method?
Economic Factors——>e.g unemployment rates ,inflation, interest rates, exchange rates,economic growth
Consumer Factors——> e.g consumers’ tastes and fashions
Competition Factors
What is Time Series Analysis?
Uses evidence from past sales records to predict future sales patterns using experience of pass business data to forecast future sales is called extrapolation.
Methods of Time Series Analysis.
Seasonal Analysis——>Sales are measured on a monthly/weekly basis to examine the seasonality of demand
Trends Analysis——>This focuses on long-term data which has been collected over a number of
years.Objective is to determine the general trends of sales (rising, falling, stagnant)
Cycle Analysis——->This focuses on long-term data but objective is to examine relationship between demand levels and economic activity
Random Factor Analysis———>This attempts to explain how unusual, abnormal or extreme figure sales occur
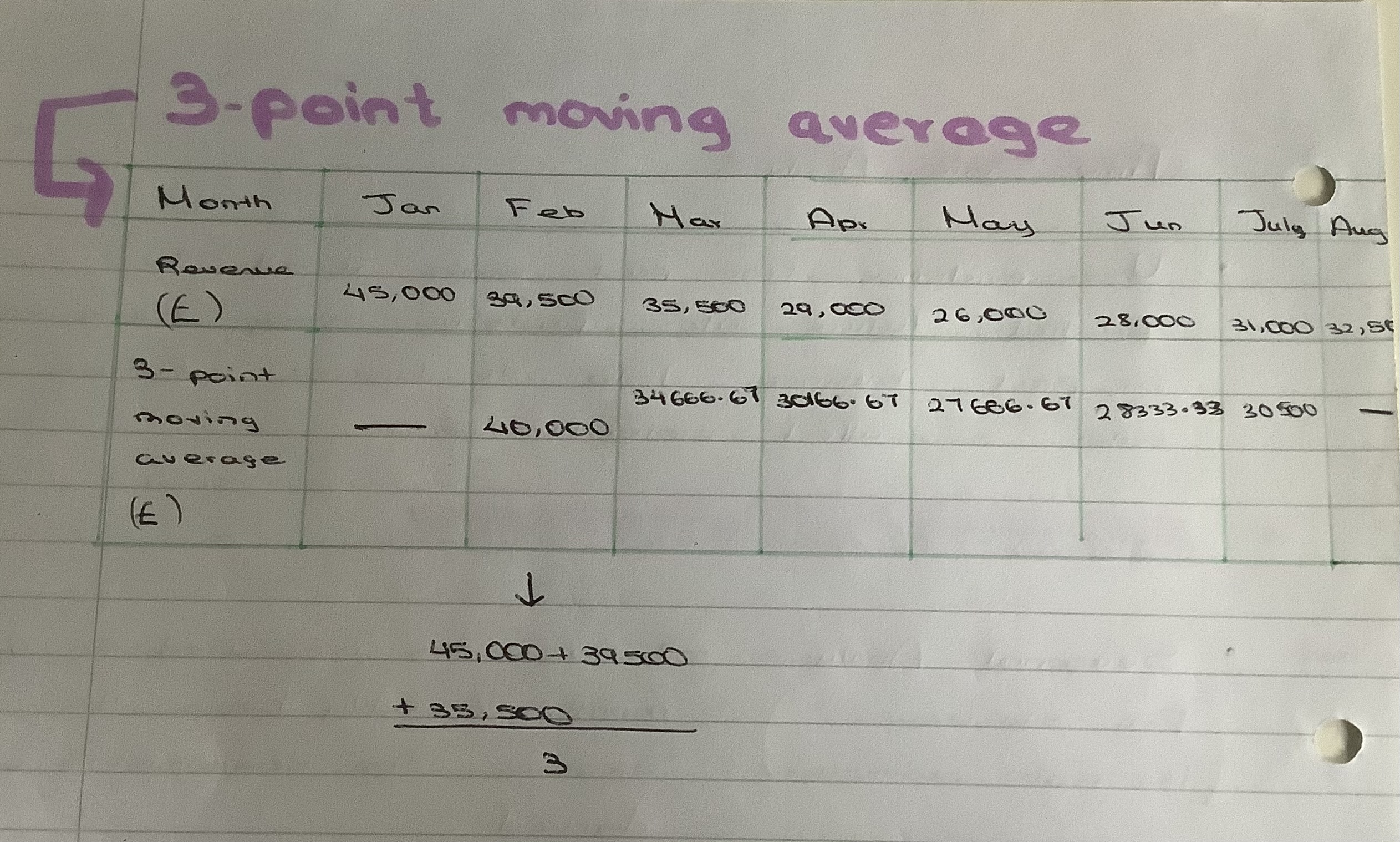
What is a 3-point Moving Average?
To smooth out any fluctuations in the sales data
Delphi Technique (Qualitative Methods)
1) -Assemble panel of experts
-Unlike other approaches to group decision making, they don’t need to meet face to face
(Saves business travel expenses—→more convenient for exports)
2)Create a questionnaire consisting of series of open-ended questions for the group
3)Group members written responses are analysed, summarised and fed back to the group for reactions until the members reach an agreement.
Advantages of the Delphi Technique.
Flexible enough to be used in a variety of situations and can be applied to a range of complex problems
• Provides a structured way for a group of people to make decisions
• Participants have time to think through their ideas leading to a better quality of response
•It seeks to aggregate opinions from a diverse set of experts, and it can be done without having to bring everyone together for a physical meeting.
•Responses of the participants are anonymous, meaning individual panellists don't have to worry about repercussions for their opinions
• Creates a record of the expert group’s responses and ideas which can be used when needed
Disadvantages of Delphi Technique
•Method will more than likely require a substantial period of time to complete as the process is time consuming to coordinate and manage
• It assumes that experts are willing to come to a consensus and allow their opinions to be altered by the views of other experts
• Monetary payments to the experts may lead to bias in the results of the study.
•No guidelines for determining consensus, sample size and sampling techniques
•Requires time/participant commitment
Brainstorming
Subjective technique for generating new, useful ideas and promoting creative thinking, usually between a group of people.
Can be used to predict outcomes based on the group’s subjective thoughts and feelings.
Basis of brainstorming is the problem Statement’, which is the focus of discussion.
E.g. ‘How can we improve the product to increase sales?’
No wrong answers,Participants encouraged to be creative
Most effective with groups of 6-12 people and works best
with a varied group. It should include participants from
various departments from across the organisation and with
different backgrounds.
Can lead to a high quantity of ideas is a short amount of
time
Even when the brainstorm is supposed to be focused on a
specific or even specialist area, outsiders can bring fresh
ideas that can inspire the experts
Intuition
With limited data available to collect and examine, business leaders and managers may instead use their ‘gut feeling’ or intuition
They may have experience of other existing markets and products that can be transferred to new markets and products.
Sometimes referred to as Genius Forecasting –which combines intuition, insight, and luck.
Cheap and fast
But gut feeling and experience should not be the only guide. There is no excuse not to carry out some further forecasting techniques.
There are many examples of experienced entrepreneurs and business managers who have lost a lot of money due to their intuitive decision making
Expert Opinion
There is a huge variety of expert opinions available on individual markets, and more general business issues which may also be considered by businesses trying to forecast the future
Experts are useful for gaining specialised insights into likely future patterns and trends but should not be used on the “standalone basis”
Panels of experts are more reliable than consulting individual experts.Opinions of experts should also be combined with info gathered from other sources
Experts also make mistakes and fail to forecast future trends correctly, particularly in long-term
How is Sales Forecasting Useful?
If accurate it is useful to help businesses create successful plans
Helps a business to check that it has sufficient capacity
Helps a business check it has sufficient resources (e.g Staff)
How is Sales Forecasting NOT Useful?
May underestimate predicted sales
May overestimate predicted sales
Economy may affect actual sales
An inaccurate prediction is no better than no prediction
Benefits of Quantitative Methods of Sales Forecasting
Helps the business plan ahead
Helps financial planning, including cash flow management
HR Planning— getting right number of staff in jobs that are needed
Useful in identifying seasonal variations
Reduces risk of unexpected surprises
Drawbacks of Quantitative Methods of Sales Forecasting
Not always easy to predict the future
No forecast can be 100%
Less useful for long-term forecasts
Historical data is not always a good indication of what might happen in the future
Benefits of Qualitative Methods of Sales Forecasting
More flexibility in forecasting
Helps plans staff, production, capacity and resources
Reducing ambiguous data
Doesn’t rely on historical data
Outsiders can bring fresh opinions
Drawbacks of Qualitative Methods of Sales Forecasting
Recent events may influence predictions
Selective perception means that forecasters ignore relevant information that may conflict with their view of how the future will unfold
Even experts can get it wrong
More difficult to predict long-term