COMPLICATIONS OF POWER
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By: Melnie Rose D. Diaz , RN , MN
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1L PNSS + 20 units of oxytocin to run for 30 gtts/min
• It will be due within 8 hours time
what is the correct OXYTOCIN DRIP
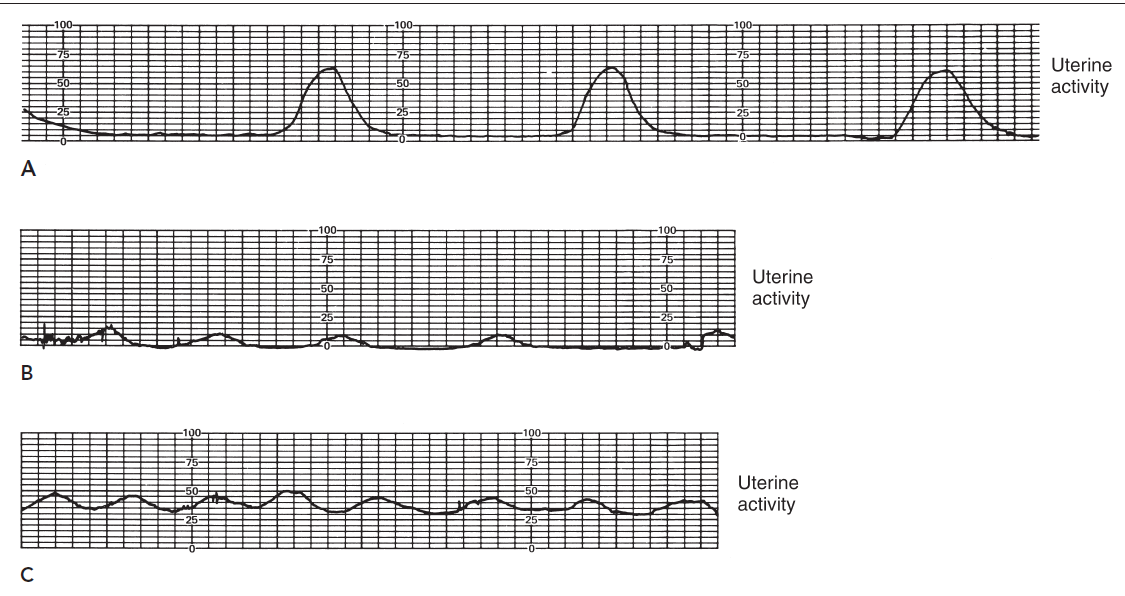
The graph that depicts normal uterine activity is likely graph A.
Which among here is the normal uterine activity?
Overdue –
If pregnancy is more than 40 weeks and above
Severe bleeding
HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK is caused by?
Hypotonic Uterine Contractions
The number of contractions is usually low or infrequent (Not more than 2 or 3 occurrring in 10 minute period.)
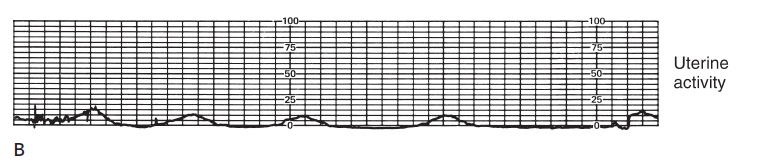
The resting of the uterus remains less than 10 mm Hg, and the strength of contractions doesn’t rise above 25 mm hg.
The resting tof the uterus remains less than _____ mm Hg, and the strenght of contractions doesn’t rise above ________mm hg.
Active phase of labor
When does the hypotonic contraction occur mostly?
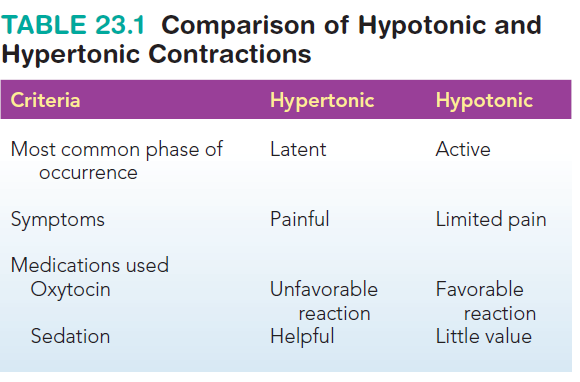
Differentiate Hyper and hypotonic Contracctions
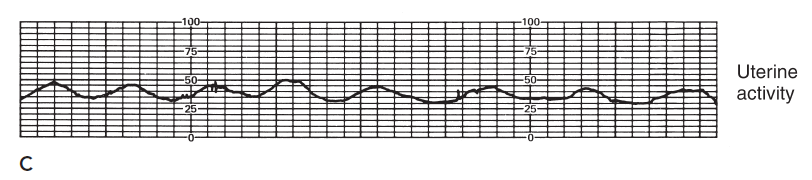
Hypertonic uterine contractions
In contrast to hypotonic
contractions, these occur frequently and are most commonly seen in the latent phase of
labor. Marked by an increase in resting tone to more
than 15 mmHg
Answer: 1. Inadequate relaxation of the myometrium between contractions.
Hypertonic contractions may occur because more than one uterine pacemaker is
stimulating contractions or because the muscle fibers of the myometrium do not
repolarize or relax after a contraction, thereby “wiping it clean” to accept a new
pacemaker stimulus.
Which of the following is a potential cause of hypertonic uterine contractions?
Inadequate relaxation of the myometrium between contractions.
Excessive fluid intake by the mother.
Early administration of epidural anesthesia.
Maternal hypotension.
Answer: 2. Hypotonic contractions
Rationale:
Hypotonic contractions are characterized by infrequent and weak contractions that are ineffective in dilating the cervix.
Hypertonic contractions are frequent and strong, often leading to fetal distress.
Precipitous labor involves rapid dilation and delivery, typically within 3 hours.
Tachysystole refers to excessive uterine activity with more than five contractions in 10 minutes.
A client in active labor is experiencing contractions that are infrequent and of low intensity. The nurse recognizes that these contractions are characteristic of which of the following?
A. Hypertonic contractions
B. Hypotonic contractions
C. Precipitous labor
D. Tachysystole
Answer: 1. Fetal Anoxia
Rationale:
The provided text states that hypertonic contractions can lead to fetal anoxia due to inadequate uterine artery filling during the short periods of relaxation between contractions.
Fetal anoxia (lack of oxygen to the fetus) can cause fetal bradycardia (slow fetal heart rate).
Distractors:
Early decelerations: These are typically caused by head compression during contractions, not necessarily related to anoxia.
Fetal tachycardia: While tachycardia can sometimes be a sign of fetal distress, it's not the most immediate concern in the context of hypertonic contractions and potential anoxia.
Variable decelerations: These are usually caused by umbilical cord compression, not directly related to the issue of inadequate uterine artery filling in hypertonic contractions.
A nurse is caring for a client experiencing hypertonic uterine contractions. Which of the following fetal complications is the nurse most concerned about?
Fetal anoxia
Early decelerations
Fetal tachycardia
Variable decelerations
Occur frequently in latent phase of labor
When does the hypertonic contraction usually occur
1. Evaluation of pelvic size
2. Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance
3. Therapeutic rest
✓ Analgesics (Morphine)
✓ Dark, quiet room
✓ Decrease noise and stimulation
4. Apply uterine and fetal monitor for 15 mins
5. Keep bladder empty – using straight-catheter
6. Encourage side lying position
7. Watch for danger signs
MANAGEMENT FOR HYPERTONIC
Answer: 3. Dimming the lights and minimizing noise.
Rationale: Therapeutic rest for hypertonic contractions aims to reduce uterine activity and promote relaxation. Dimming the lights and minimizing noise creates a calm and quiet environment, which can help the client relax and reduce uterine stimulation.
A client experiencing hypertonic uterine contractions is ordered therapeutic rest. Which of the following nursing interventions best supports this order?
Administering oral fluids as desired.
Encouraging frequent ambulation.
Dimming the lights and minimizing noise.
Applying continuous electronic fetal monitoring.
Answer: 2. Checking the client's blood pressure and respiratory rate.
Rationale: Morphine is an opioid analgesic that can cause respiratory depression. Therefore, assessing the client's vital signs, especially blood pressure and respiratory rate, is crucial before administration to identify any contraindications or potential risks.
A client with hypertonic contractions is prescribed morphine for pain management. What is the most important nursing assessment before administering this medication?
Assessing the client's pain level on a 0-10 scale.
Checking the client's blood pressure and respiratory rate.
Monitoring the fetal heart rate for at least 15 minutes.
Ensuring the client has voided within the last hour
Answer: 3. To ensure adequate bladder emptying to prevent uterine distention.
Rationale: A full bladder can impede the descent of the fetus and contribute to ineffective contractions. Inserting a urinary catheter ensures the bladder is empty, allowing for optimal uterine contractions and fetal descent.
A client with hypertonic contractions has a urinary catheter inserted. What is the primary rationale for this intervention?
To prevent urinary tract infection.
To facilitate frequent monitoring of urine output.
To ensure adequate bladder emptying to prevent uterine distention.
To provide comfort and reduce the need for frequent toileting.
Answer: 2. Hypotonic contractions
Rationale: Hypotonic contractions are characterized by infrequent and weak contractions that are ineffective in dilating the ce
A nurse is caring for a client in active labor who is experiencing contractions that are infrequent and of low intensity. The nurse recognizes that these contractions are characteristic of which of the following?
Hypertonic contractions
Hypotonic contractions
Precipitous labor
Tachysystole
Answer: 3. Postpartum hemorrhage
Rationale: The information states that hypotonic contractions can lead to uterine exhaustion, which can increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage due to ineffective uterine contractions after birth
A client with hypotonic contractions is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
Premature rupture of membranes
Fetal tachycardia
Postpartum hemorrhage
Preeclampsia
.
Answer: 2. Pain is a subjective experience, and some clients may find hypotonic contractions painful.
Rationale: While the information states that hypotonic contractions are generally not painful due to their low intensity, it also acknowledges that pain perception is subjective.
Which of the following statements about the pain associated with hypotonic contractions is most accurate?
Hypotonic contractions are typically very painful.
Pain is a subjective experience, and some clients may find hypotonic contractions painful.
Hypotonic contractions are usually painless due to their low intensity.
Pain management is not typically necessary for clients with hypotonic contractions.
Answer: 2. Augmenting labor with oxytocin.
Rationale: Oxytocin is a medication commonly used to stimulate uterine contractions and augment labor in cases of hypotonic contractions.
Which of the following interventions is most likely to be implemented in the management of a client with hypotonic contractions?
Administering tocolytics to reduce uterine activity.
Augmenting labor with oxytocin.
Performing an amniotomy to stimulate contractions.
Applying continuous electronic fetal monitoring.
Infection
Cervical Dilation in mostly likely risk for?
CAUSES
• Overdistention of the uterus
• Malpresentation and malposition
• Pelvic bone contraction
• Unripe or rigid cervix
• Congenital abnormalities of the uterus
• Unknown causes
CAUSES of hypotonic contraction
Answer: 3. Polyhydramnios
Rationale: Polyhydramnios, which is an excess of amniotic fluid, can lead to overdistention of the uterus, which is listed as a potential cause of hypotonic contractions.
A nurse is caring for a client in labor with hypotonic contractions. Which of the following factors may contribute to the development of hypotonic contractions?
Premature rupture of membranes
Fetal tachycardia
Polyhydramnios
Preeclampsia
Answer: 3. Pelvic bone contraction
Rationale: Pelvic inflammatory disease can lead to pelvic adhesions and scarring, which can potentially contribute to pelvic bone contraction, a listed cause of hypotonic contractions
A nurse is assessing a client in labor who has a history of pelvic inflammatory disease. Which of the following potential causes of hypotonic contractions is most relevant to this client's history?
Overdistention of the uterus
Malpresentation and malposition
Pelvic bone contraction
Congenital abnormalities of the uterus
.
✓ Maternal and Fetal infections
✓ Postpartum hemorrhage
✓ Fetal distress and death
✓ Maternal exhaustion
COMPLICATIONS for hypotonic Contraction
Answer: 2. Fetal distres
A nurse is caring for a client in labor with hypotonic contractions. Which of the following complications is the nurse most concerned about?
Premature rupture of membranes
Fetal distress
Preeclampsia
Premature labor
Answer: 1. Precipitous Labor
A client arrives at labor and delivery experiencing sudden, intense contractions that began 30 minutes prior. Vaginal examination reveals 8 cm dilation and 100% effacement. Which term best describes this "blitzkrieg" labor pattern?
Precipitous Labor
Hypertonic Uterine Contractions
Hypotonic Uterine Contractions
Latent Phase of Labor
Answer: 1. Maternal exhaustion
Rationale: Prolonged labor associated with hypotonic contractions can lead to physical and emotional exhaustion in the mother.
A client with hypotonic contractions has a prolonged labor. Which of the following complications is a potential consequence of prolonged labor?
Maternal exhaustion
Premature rupture of membranes
Fetal tachycardia
Preeclampsia
Answer: 1. Postpartum infection
Rationale: The provided information lists maternal and fetal infections as potential complications of hypotonic contractions. Prolonged labor increases the risk of infection for both mother and baby
A nurse is caring for a client who delivered a baby after a prolonged labor complicated by hypotonic contractions. Which of the following postpartum complications is this client at increased risk for?
Postpartum infection
Preeclampsia
Gestational diabetes
Premature labor
.
Answer: 3. Precipitous labor
Rationale: Precipitous labor is defined by rapid cervical dilation and a short duration of labor.
A nurse is caring for a client in labor who progresses from 4 cm to 9 cm dilated within 1 hour. This rapid cervical dilation is characteristic of which of the following?
Hypotonic contractions
Hypertonic contractions
Precipitous labor
Prolonged labor
1. Reevaluate pelvic size to rule out fetopelvic disproportion.
2. Vaginal delivery
❑ Infusion of oxytocin –to augment labor
❑ Amniotomy may be done
3. If contracted pelvis is present, caesarian section is the method of delivery
4. Provide supportive nursing care
MANAGEMENT for hypotonic contraction
Answer: 2. Augmenting labor with oxytocin.
Rationale: The provided information lists oxytocin infusion as a method to augment labor in cases of hypotonic contractions.
A client in labor with hypotonic contractions is not progressing. Which of the following interventions is most likely to be implemented to stimulate labor?
Administering tocolytics.
Augmenting labor with oxytocin.
Performing an amniotomy.
Applying continuous electronic fetal monitoring.
Answer: 4. Cesarean section
Rationale: The information states that if a contracted pelvis is present, cesarean section is the recommended method of delivery.
A client with hypotonic contractions is found to have a contracted pelvis. Which of the following is the most likely method of delivery?
Vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC)
Forceps-assisted vaginal delivery
Vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery
Cesarean section
PRECIPITATE LABOR
is cervical dilatation that occurs at a rate of 5 cm or more per hour
in a primipara or 10 cm or more per hour in a multipara.
Answer: 4. A multiparous client who is undergoing labor induction with oxytocin.
Rationale: The information states that precipitous labor can occur with the induction of labor by oxytocin.
Which of the following clients is at increased risk for precipitous labor?
A nulliparous client with a history of gestational diabetes.
A multiparous client who has undergone previous cesarean deliveries.
A nulliparous client with a history of preeclampsia.
A multiparous client who is undergoing labor induction with oxytocin.
Answer: 3. Subdural hemorrhage
Rationale:
The provided text states that rapid labor can increase the risk of subdural hemorrhage in the fetus due to the rapid release of pressure on the head during delivery.
Which of the following fetal complications is a potential risk associated with rapid labor?
✓ Hemorrhage and lacerations
RISK FACTORS for PRECIPITATE LABOR
Multiparity
• Large pelvis
• Small baby in good position
• Induction of labor
• Absence of painful sensation and thus a lack of awareness of vigorous labor
PREDISPOSING FACTORS THAT CAN CAUSE PRECIPITATE LABOR
• Laceration of birth canal and uterine rupture
• Postpartum hemorrhage
• Amniotic fluid embolism
Maternal Complications in relation to Precipitate labor
• Hypoxia
• Intracranial hemorrhage
• Premature separation of placenta
• Injuries
Fetal Complications in relation to Precipitate labor
Answer: 1. Uterine rupture
Rationale: The provided information lists uterine rupture as a potential maternal complication of rapid labor
A nurse is caring for a client experiencing precipitous labor. Which of the following maternal complications is the nurse most concerned about?
Uterine rupture
Gestational diabetes
Preeclampsia
Premature labor
Answer: 1. Hypoxia
Rationale: The provided information lists hypoxia as a potential fetal complication of rapid labor, which can occur due to rapid delivery and potential for oxygen deprivation.
A client has just delivered a baby after experiencing precipitous labor. Which of the following fetal complications is the nurse most concerned about?
Hypoxia
Fetal bradycardia
Early decelerations
Premature rupture of membranes
• Patient complains of sudden, intense urge to push
• Sudden increase in bloody show
• Sudden bulging of the perineum
• Sudden crowning of the presenting part
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS of precipitous labor
Answer: 3. Prepare for immediate delivery.
Rationale: The sudden crowning of the presenting part indicates that delivery is imminent. The nurse should prepare for immediate delivery by gathering necessary supplies and assisting the healthcare provider as needed.
A client in labor suddenly experiences crowning of the presenting part. Which of the following nursing interventions is most appropriate?
Apply gentle pressure to the fetal head.
Assist the client to push with each contraction.
Prepare for immediate delivery.
Administer oxygen via facemask
1. Anticipatory guidance for prevention
2. If accelerated labor pattern occurs during augmentation, stop the infusion.
3. Prepare for imminent delivery – wash hands, if the time permits. Never hold the baby back
MANAGEMENT for precipitate labor
Induction of labor
means labor is started artificially
Augmentation of labor
refers to assisting labor that has started spontaneously but is not effective
When labor contractions are ineffective, several interventions, such as induction and augmentation of labor with oxytocin or amniotomy (artificial rupture of the membranes), may be initiated to strengthen them
When labor contractions are ineffective, several interventions, such_______________________________________ with oxytocin or amniotomy (artificial rupture of the membranes), may be initiated to strengthen them
False: It should be 39 weeks of gestaion
T/F: Induction of labor is not used as an elective procedure until the fetus is at term (over 35 weeks of gestation).
CONTRACTION RINGS
refers to a tightening or induration of the uterine muscle fibers. It's a normal physiological phenomenon that occurs during labor.
SIMPLE TYPE
PATHOLOGIC RETRACTION (BANDL’SRING)
2 types of contraction ring
SIMPLE TYPE
can occur at any point in myometrium and anytime during labor
PATHOLOGIC RETRACTION (BANDL’SRING
most common, occurs at juncture of upper and lower uterine segments.
Answer: 2. A temporary tightening of the uterine muscle fibers that occurs during contractions.
Rationale: The information states that a physiologic contraction ring is a normal, temporary tightening of the uterine muscle that aids in labor progression.
A nurse is caring for a client in labor. Which of the following best describes a physiologic contraction ring?
A deep groove that forms across the uterus, typically at the junction between the upper and lower segments.
A temporary tightening of the uterine muscle fibers that occurs during contractions.
A permanent indentation across the abdomen that is visible during labor.
A condition that always requires immediate cesarean section.
Answer: 1. A horizontal indentation across the abdomen.
Rationale: The information states that a pathologic retraction ring can be identified by a horizontal indentation across the abdomen.
A client in labor is experiencing a pathologic retraction ring (Bandl's Ring). Which of the following clinical findings is most likely to be observed?
A horizontal indentation across the abdomen.
A rapid and steady cervical dilation.
A decrease in the frequency of contractions.
An increase in the strength of contractions.
• Appears late in 2nd stage of labor
• Horizontal indentation across abdomen
• Fetus is gripped by retraction ring and cannot advance beyond that point
• Warning sign of dysfunctional labor
• Uterine rupture or fetal death can occur • Also, will grip the placenta –leads to hemorrhage
MANIFESTATIONS of CONTRACTION RINGS
Answer: 2. Postpartum hemorrhage
A client with a pathologic retraction ring has delivered the baby. Which of the following postpartum complications is the nurse most concerned about?
Postpartum infection.
Postpartum hemorrhage.
Urinary tract infection.
Mastitis.
Excessive retraction of upper uterine segment • In early labor – due to uncoordinated contractions (obstetric manipulation or oxytocin
What is the etiology of the Contraction rings
1. Sonogram
2. IV morphine or inhalation of amyl nitrite
3. Cesarean birth
4. If it develops during the placental stage, it should be removed manually.
TREATMENT/MANAGEMENT for contraction rings
Relax Uterine Muscles: Both morphine and amyl nitrite have a relaxing effect on the uterine muscles
Rationale for using IV morphine or inhalation of amyl nitrite in the management of a pathologic retraction ring:
Answer: 2. Cesarean section
Rationale:
The provided information states that cesarean section is a common treatment option for a pathologic retraction ring, as it is often necessary to deliver the baby when the ring is obstructing labor.
A client in labor is diagnosed with a pathologic retraction ring (Bandl's Ring). Which of the following is the most likely intervention?
Administration of IV morphine
Cesarean section
Induction of labor with oxytocin
Application of external fetal monitoring
If it develops during the placental stage, it should be removed manually
What happens if If it develops during the placental stage, should the patient wait until 39 weeks of pregnmamcy?
UTERINE RUPTURE
s a serious obstetric emergency that involves a tear in the wall of the uterus. This can occur during pregnancy or labor.
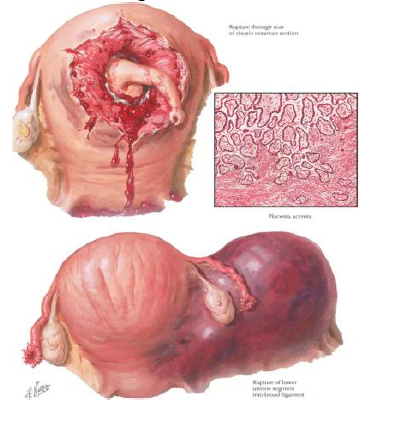
• Vertical scar from cesarean section
• prolonged labor
• faulty presentation
• multiple gestation
• unwise use of oxytocin
• traumatic maneuvers using forceps or traction
ETIOLOGY of uterine rupture
• Impending uterine rupture is often manifested by pathologic retraction ring
• With rupture a sudden severe pain, tearing feeling then pain stops
• Hemorrhage, shock
• Change in contour of abdomen • FHR absent
• changes in VS
MANIFESTATIONS for uterine rupture
Answer: 4. A horizontal indentation across the abdomen.
Rationale: The provided information states that a pathologic retraction ring, often manifested by a horizontal indentation across the abdomen, is a warning sign of impending uterine rupture.
A nurse is caring for a client in labor. Which of the following clinical findings is most suggestive of impending uterine rupture?
A sudden gush of clear fluid.
A gradual increase in the frequency and intensity of contractions.
A decrease in the frequency of contractions.
A horizontal indentation across the abdomen.
Answer: 3. Monitoring the fetal heart rate.
Rationale: The information states that uterine rupture can lead to fetal distress and absent fetal heart rate. Assessing the fetal heart rate is crucial to identify potential fetal compromise.
A client in labor suddenly experiences severe abdominal pain and reports a "tearing" sensation. Which of the following assessments is the nurse's priority?
Assessing the client's blood pressure and pulse.
Checking the client's temperature.
Monitoring the fetal heart rate.
Assessing for the presence of vaginal bleeding.
Answer: 2. Incomplete uterine rupture
Rationale: The information states that in incomplete uterine rupture, contractions may continue despite the presence of pain and other signs of rupture.
A client with a history of a previous cesarean section is experiencing persistent abdominal pain during labor, but contractions continue. Which type of uterine rupture is this most consistent with?
Complete uterine rupture
Incomplete uterine rupture
Dehiscence of the uterine scar
Physiologic retraction ring
Complete
Incomplete
TYPES OF UTERINE RUPTURE
INCOMPLETE
Localized tenderness and persistent pain over the abdomen
• Contractions may continue or stop but there is no progress
• Vaginal bleeding may or may not be present
• Signs of maternal shock and fetal distress are observed
Answer: 1. Complete uterine rupture
Rationale: The information states that complete uterine rupture is often characterized by sudden, excruciating pain at the peak of a contraction, followed by a cessation of contractions.
A nurse is caring for a client in labor who suddenly experiences excruciating abdominal pain at the peak of a contraction, followed by a cessation of contractions. Which type of uterine rupture is this most consistent with?
Complete uterine rupture
Incomplete uterine rupture
Dehiscence of the uterine scar
Physiologic retraction ring

COMPLETE
• Sudden excruciating pain at the peak of a contraction, then contractions stops altogether.
• Two swellings will be visible in the abdomen • Internal hemorrhage will soon follow, and vaginal bleeding may or may not occur
• Fetal hypoxia and death
Answer: 2. Assessing the client's blood pressure and pulse.
Rationale: Maternal shock is a significant complication of uterine rupture, characterized by hypotension and tachycardia. Assessing the client's vital signs is crucial to identify and manage shock.
A client with suspected uterine rupture is exhibiting signs of maternal shock. Which of the following assessments is the nurse's priority?
Monitoring the client's temperature.
Assessing the client's blood pressure and pulse.
Checking the client's urine output.
Monitoring the fetal heart rate.
1. Blood transfusion and administration of IVF
2. Administer oxygen
3. Provide emotional support
4. Stat Cesarian section
• may need a hysterectomy
• mother and/or fetus is in extreme jeopardy
MANAGEMENT for uterine rupture
Answer: 2. Preparing the client for a stat cesarean section.
Rationale: While all options are important, preparing for an immediate cesarean section is the priority intervention in a uterine rupture. This is a life-threatening emergency for both the mother and fetus, and rapid surgical intervention is crucial.
A client is diagnosed with a uterine rupture. Which of the following interventions is the PRIORITY for the nurse?
Administering pain medication.
Preparing the client for a stat cesarean section.
Providing emotional support to the client and family.
Initiating intravenous fluids and preparing for blood transfusion.
Answer: 4. Start an IV infusion with a large-bore needle.
Rationale: In cases of shock due to uterine rupture, rapid fluid resuscitation is critical. Establishing IV access with a large-bore needle allows for rapid administration of intravenous fluids and blood products to stabilize the client.
A client with a uterine rupture is exhibiting signs of shock. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform FIRST?
Administer oxygen.
Obtain informed consent for surgery.
Insert a Foley catheter.
Start an IV infusion with a large-bore needle.
iNVERTED UTERUS
Serious complication of the third stage of labor wherein the uterus is partly or completely turned inside out.
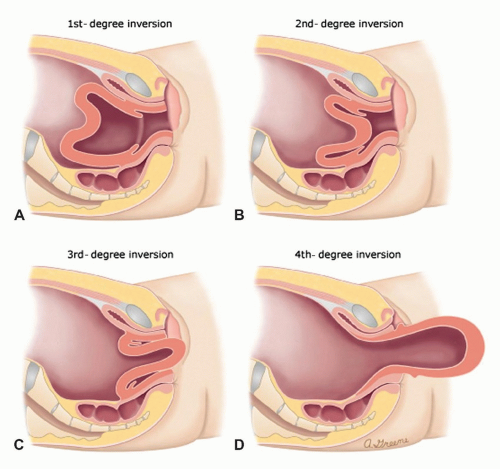
False.
In an inversion of the uterus, the fundus of the uterus (the top part) is no longer invertible. It has essentially turned inside out, becoming invaginated into the vagina.
T/F: In the inversion of the uterus, the fundus is still invertible
• Pulling of the umbilical cord or applying pressure on
• uncontracted uterus
• Placenta accrete
• Uterine relaxation due to effects of analgesia
• Sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure
CAUSES OF INVERTED UTERUS
• Fundus is no longer palpable
• Sudden gush of blood from the vagina
• Uterus appear in the vulva
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF INVERTED UTERUS
Answer:
3. A sudden gush of blood from the vagina.
Rationale:
The provided information states that a sudden gush of blood from the vagina is a key sign and symptom of uterine inversion
A nurse is caring for a postpartum client. Which of the following clinical findings is most suggestive of uterine inversion?
A firm, contracted uterus fundal height at the umbilicus.
Moderate lochia rubra.
A sudden gush of blood from the vagina.
Mild uterine cramping.
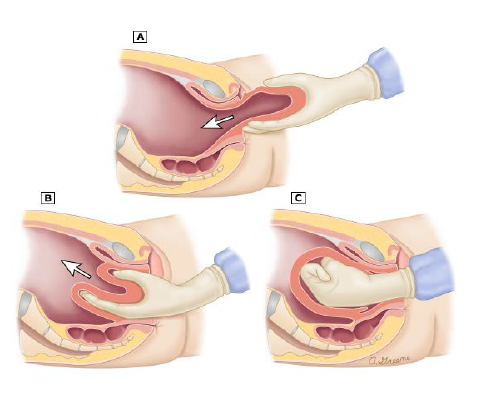
1. PREVENTION
✓ Never apply pressure on an uncontracted uterus
✓ Never pull the cord to hasten placental delivery
2. If the placenta has already separated: the uterus is replaced in the uterine cavity then oxytocin is administered.
3. If the placenta is still attached: woman is placed under anesthesia to cause muscular relaxation and facilitate reinsertion of the uterus into the pelvic cavity. 4. Blood transfusion and administration of IVF
5. Monitor vital signs
MANAGEMENT OF INVERTED UTERUS
AMNIOTIC FLUID EMBOLISM
occurs when amniotic fluid is forced into an open maternal uterine blood sinus after a membrane rupture or partial premature separation of the placenta
labor or in the post-partal period.
AMNIOTIC FLUID EMBOLISM, This condition may occur during___________
✓ Induction of labor
✓ Multiple Pregnancy
✓ Polyhydramnios
AMNIOTIC FLUID EMBOLISM may be associated with
False.
Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is not highly preventable. It's a rare and unpredictable complication of pregnancy and childbirth. While some risk factors may be identified, it's generally considered an unpredictable event. There aren't reliable ways to prevent it from occurring.
T/F: AMNIOTIC FLUID EMBOLISM is highly preventable
• Usually, patient is in active phase of labor
• Suddenly and grasps her chest
• Inability to breathe
• Skin is pale and may turn bluish gray
• May become unconscious
• Fetus may be in danger
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
of AMNIOTIC FLUID EMBOLISM
Answer: 3. Amniotic fluid embolism
Rationale: The provided information states that sudden respiratory distress and chest pain are key clinical manifestations of amniotic fluid embolism.
A nurse is caring for a client in active labor who suddenly complains of difficulty breathing and grasps her chest. Which of the following complications is the nurse most concerned about?
Preeclampsia
Pulmonary embolism
Amniotic fluid embolism
Uterine rupture
1. Oxygen administration by face mask or cannula
2. Prepare for CPR
3. Watch for signs and symptoms of DIC
4. Anticipate intubation and fibrinogen therapy
MANAGEMENT
for Amniotic fluid embolism
Answer: 1. Administering oxygen via facemask.
Rationale: The provided information states that oxygen administration is a priority in the management of AFE to support respiratory function.
A client experiencing suspected amniotic fluid embolism is exhibiting signs of respiratory distress. Which of the following interventions is the priority?
Administering oxygen via facemask.
Preparing for cesarean section.
Monitoring fetal heart rate.
Administering pain medication.
Answer: 3. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Rationale: The provided information states that monitoring for signs and symptoms of DIC is crucial in the management of AFE.
A client with suspected amniotic fluid embolism is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
Postpartum hemorrhage
Preeclampsia
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Urinary tract infection
LABOR INDUCTION
deliberate intention of labor before it occurs spontaneously.
AUGMENTATION OF LABOR
refers to the stimulation of effective uterine contractions when contractions are inadequate
• No cephalopelvic disproportion exist
• Fetus is mature, or pregnancy is at term
• Cervix is ripe soft & dilatable, with some degree of cervical dilatation and effacement
• Fetus is longitudinal lie, presenting part is engaged
PREREQUISITES FOR LABOR INDUCTION
✓ Maternal complications
✓ Premature Rupture of Membranes
✓ Placental Insufficiency
✓ Intrauterine growth retardation
✓ Intrauterine fetal death
What is INDUCTION & AUGMENTATION OF LABOR indicated for
Oxytocin (Pitocin): Synthetic hormone to stimulate contractions.
Prostaglandins (Cervidil, Cytotec, Prepidil): Soften and ripen the cervix.
Amniotomy (Artificial Rupture of Membranes - AROM): Breaking the amniotic sac.
Mechanical Methods (Foley catheter): Dilate the cervix.
METHODS OF LABOR INDUCTIONS
False.
Nipple stimulation is a non-pharmacological method of labor induction. It works by stimulating the release of oxytocin, a hormone that causes uterine contractions. Since it doesn't involve any medications, it's not considered pharmacological
T/F: Is stipple stimulation considered a pharmacological method of labor induction?
AMNIOTOMY
It is the artificial rupturing of membranes using amniotomy forceps such as amniohook or allis forceps.
AMNIOHOOK
Allis
What equipments are being used fo amniotomy