AP Bio 6.1-6.2: DNA Structure and Replication
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
nucleotide (parts and definition)
monomor of nucleic acids
contains sugar, phosphate and nitrogeneous base
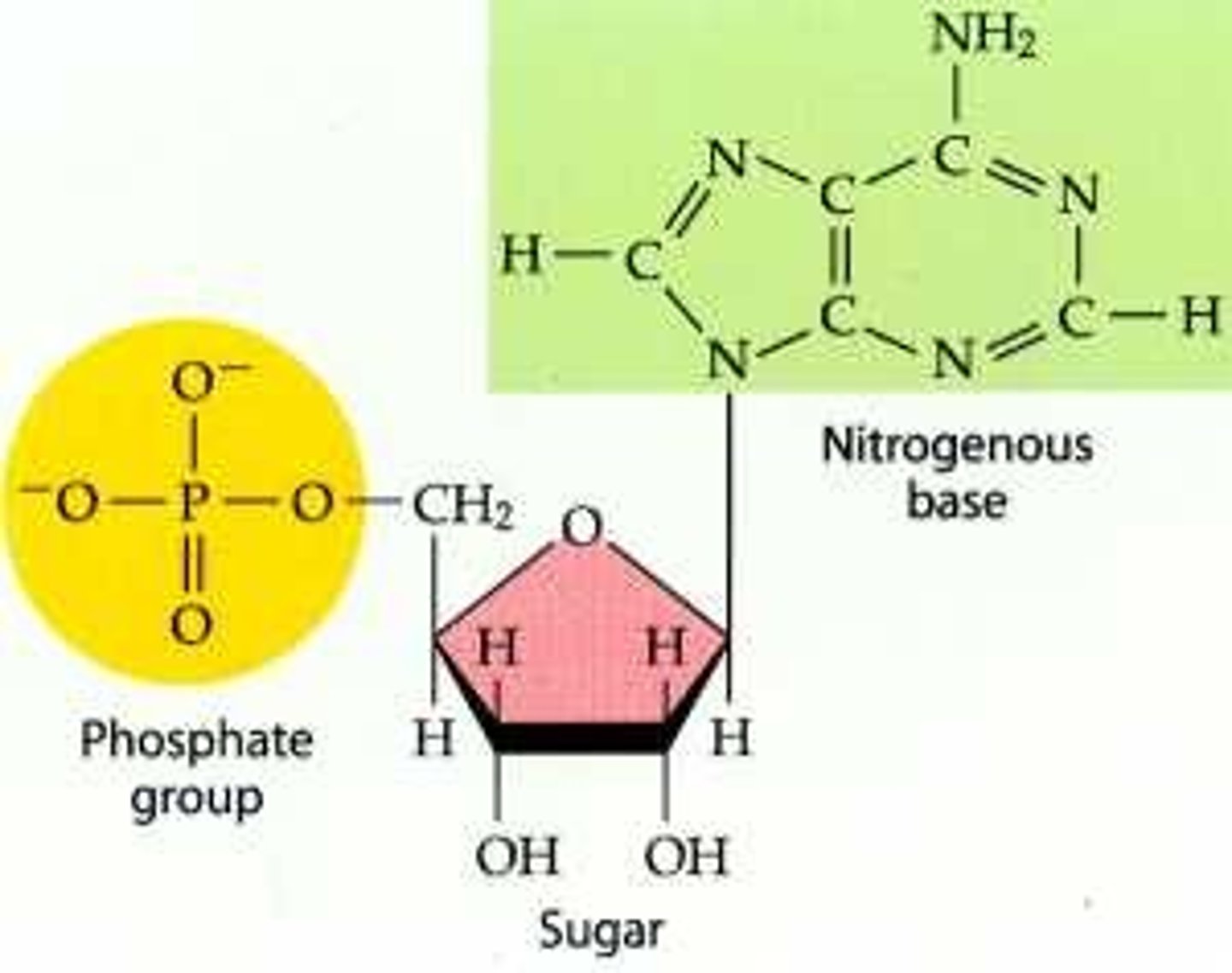
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA; contain elements PONCH
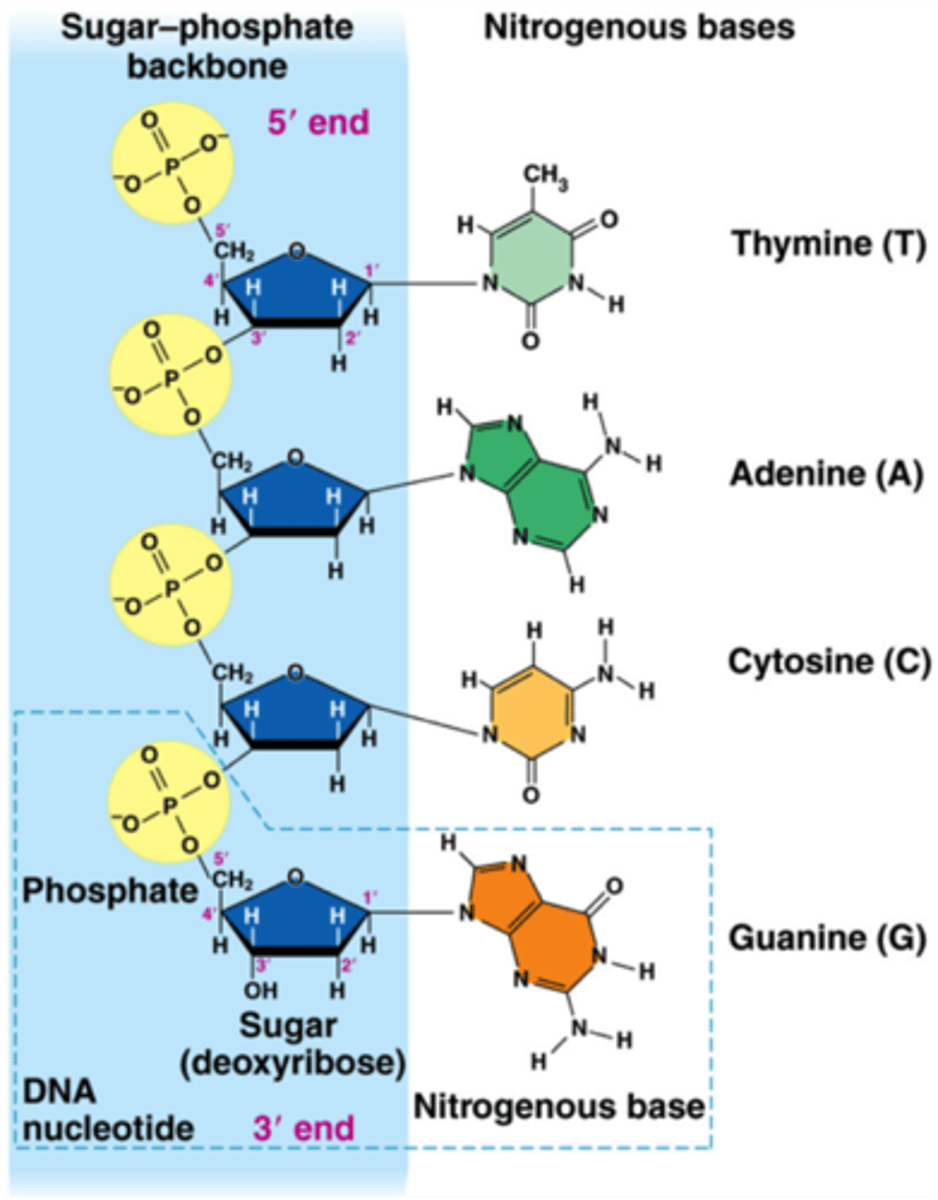
nucleotides found in RNA
A, U, C, G
nucleotides found in DNA
A, T, C, G
purines
adenine and guanine; have double ring structure
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil; have single ring structure
complementary base pairing (Chargaff's rules)
hydrogen bonding between A and T (DNA) or A and U (RNA);
hydrogen bonding between C and G
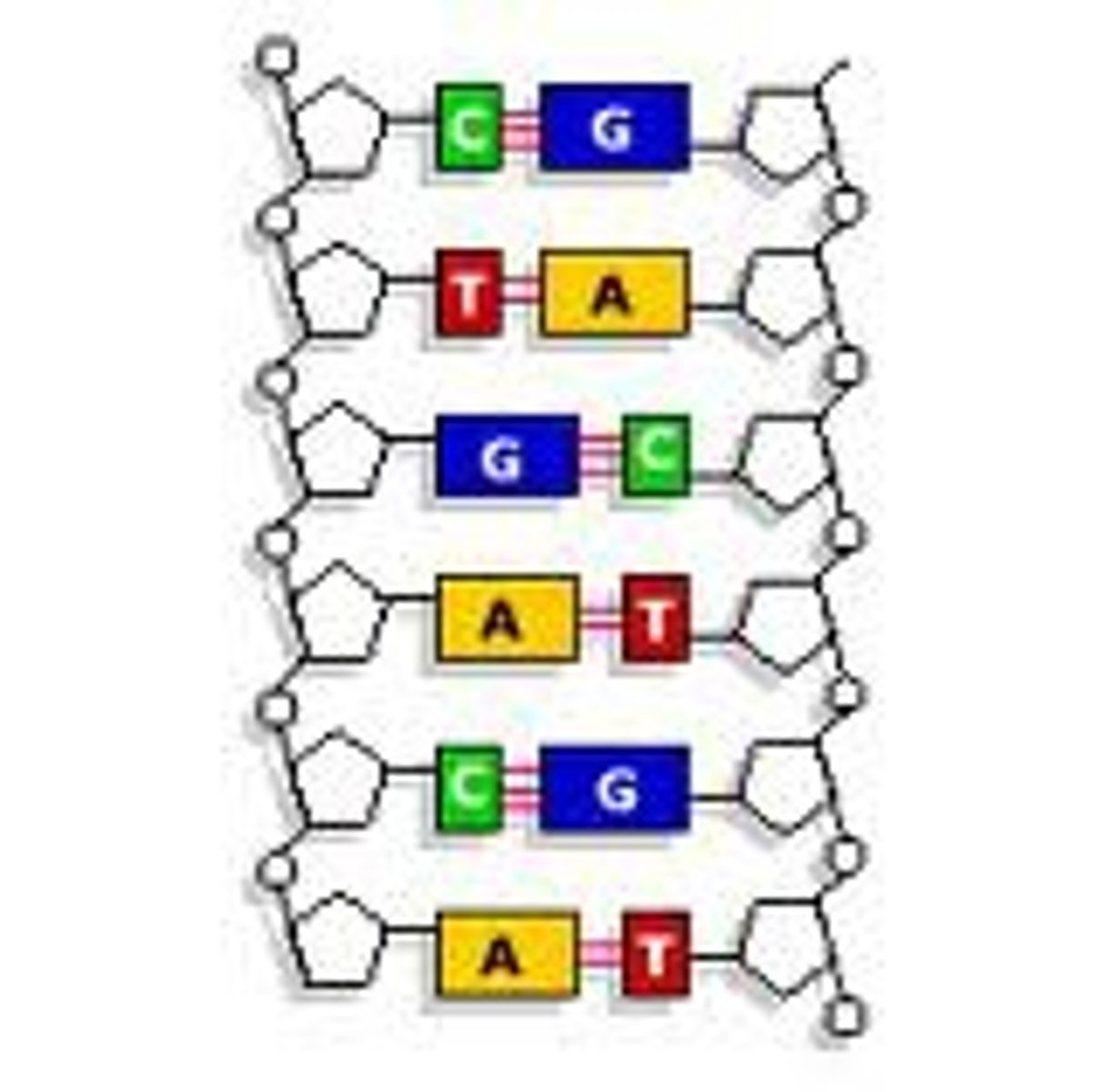
antiparallel strands
the two backbones of DNA run in opposite directions. One runs 3' to 5' and the other runs 5' to 3'
DNA "backbone"
sugars and phosphates of different nucleotides are linked by covalent bonds (phosphodiester bonds)
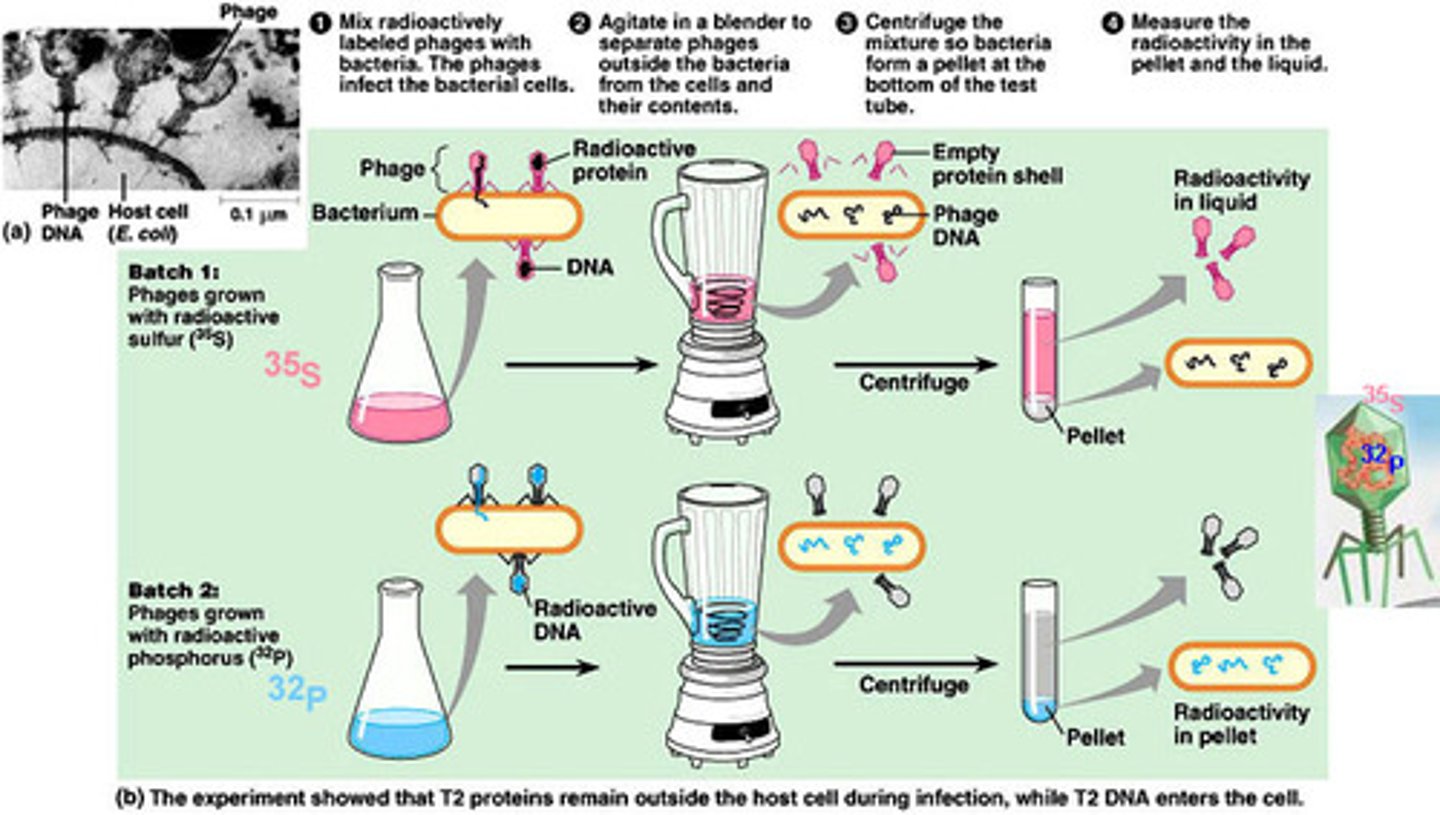
Hershey-Chase Experiment
Used radioactive isotopes to label DNA and protein in viruses that infect bacteria; provided evidence that DNA is the genetic material
Helicase
An enzyme that breaks the H-bonds between the nitrogenous bases on the two strands of the DNA molecule during DNA replication. "Unzips" the strands

Topoisomerase
an enzyme that "untwists" the DNA double helix in preparation for DNA replication
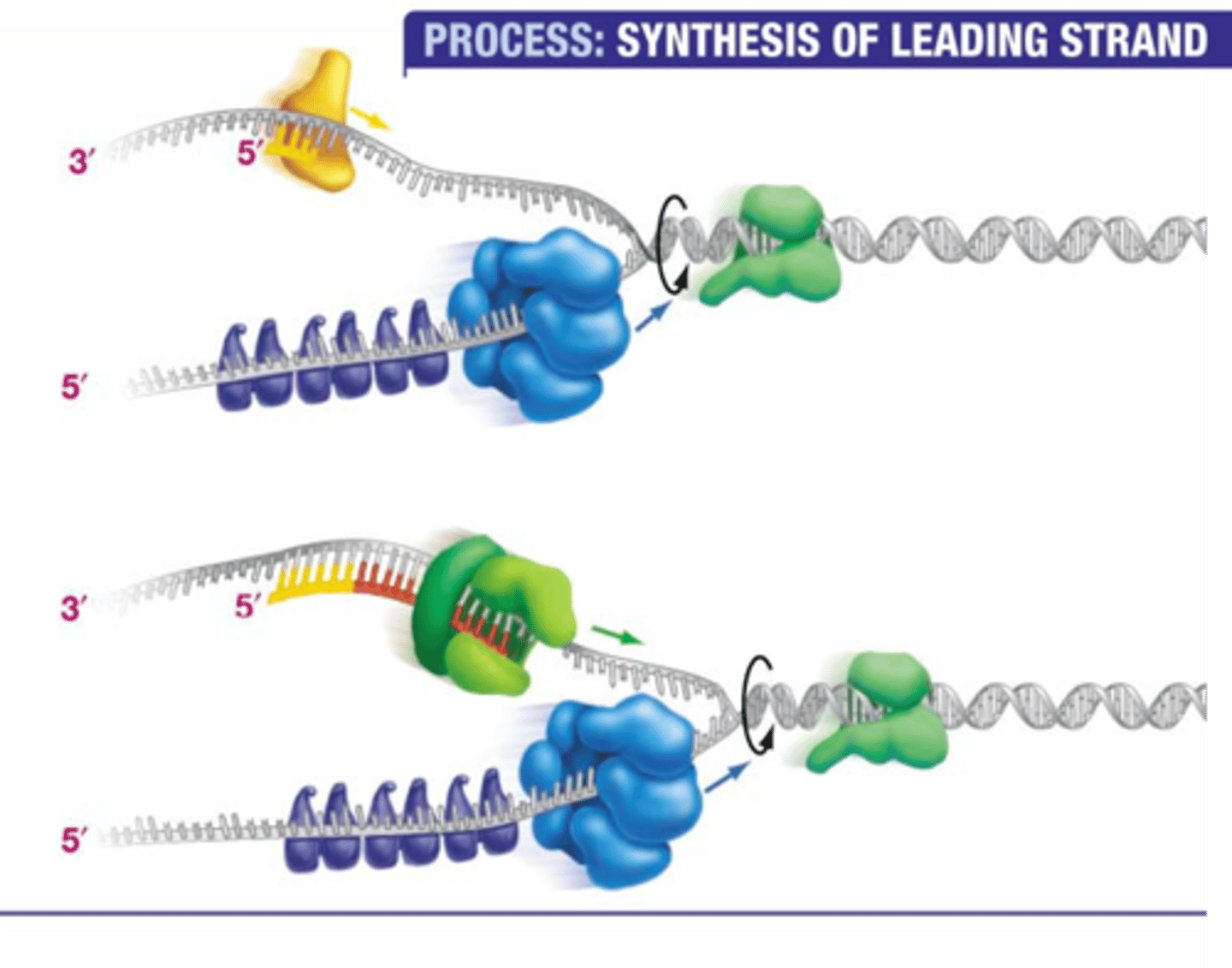
Primase
an enzyme that adds a short RNA strand, a "primer" that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis. Primer strands are built in the 5' to 3' direction
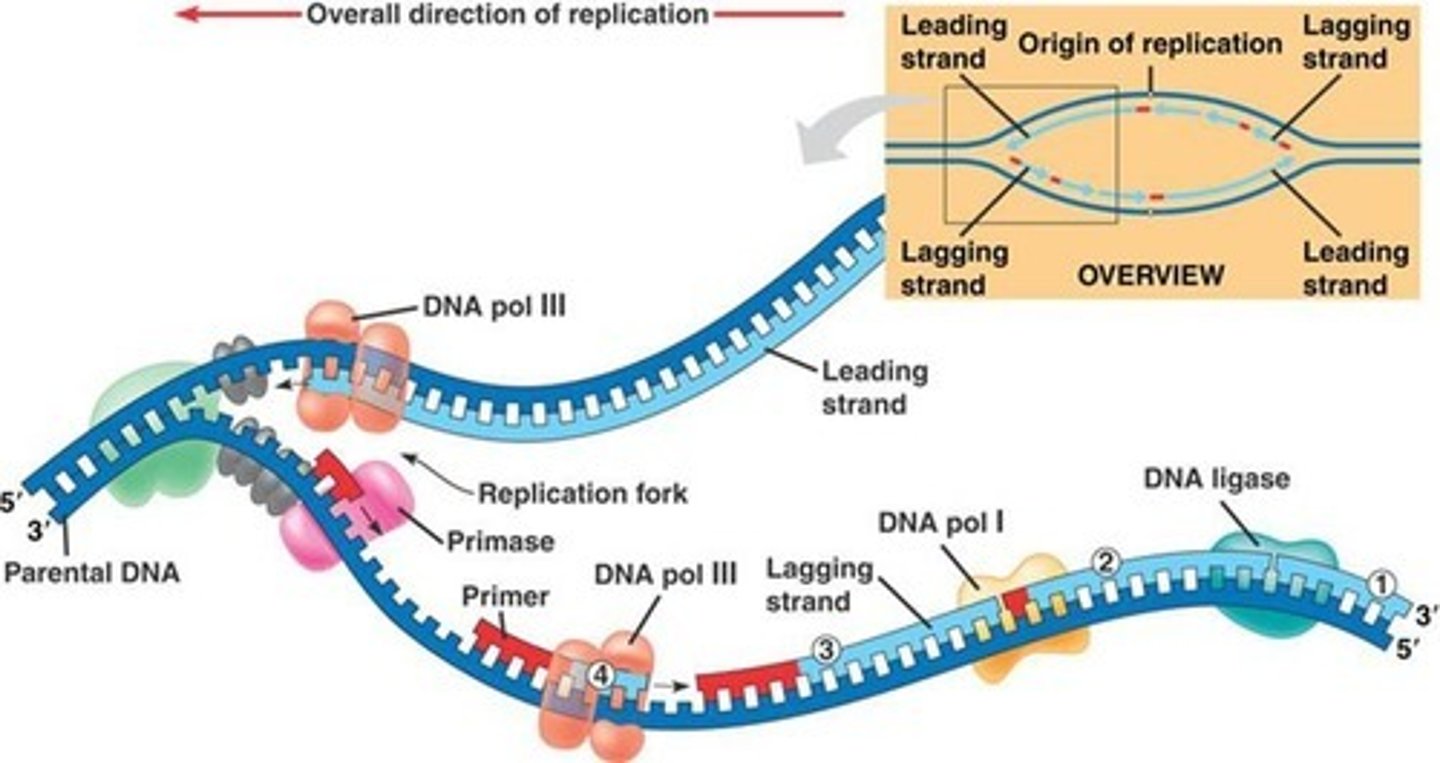
DNA polymerase
an enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the growing strand during DNA replication. New strands are always built in the 5' to 3' direction
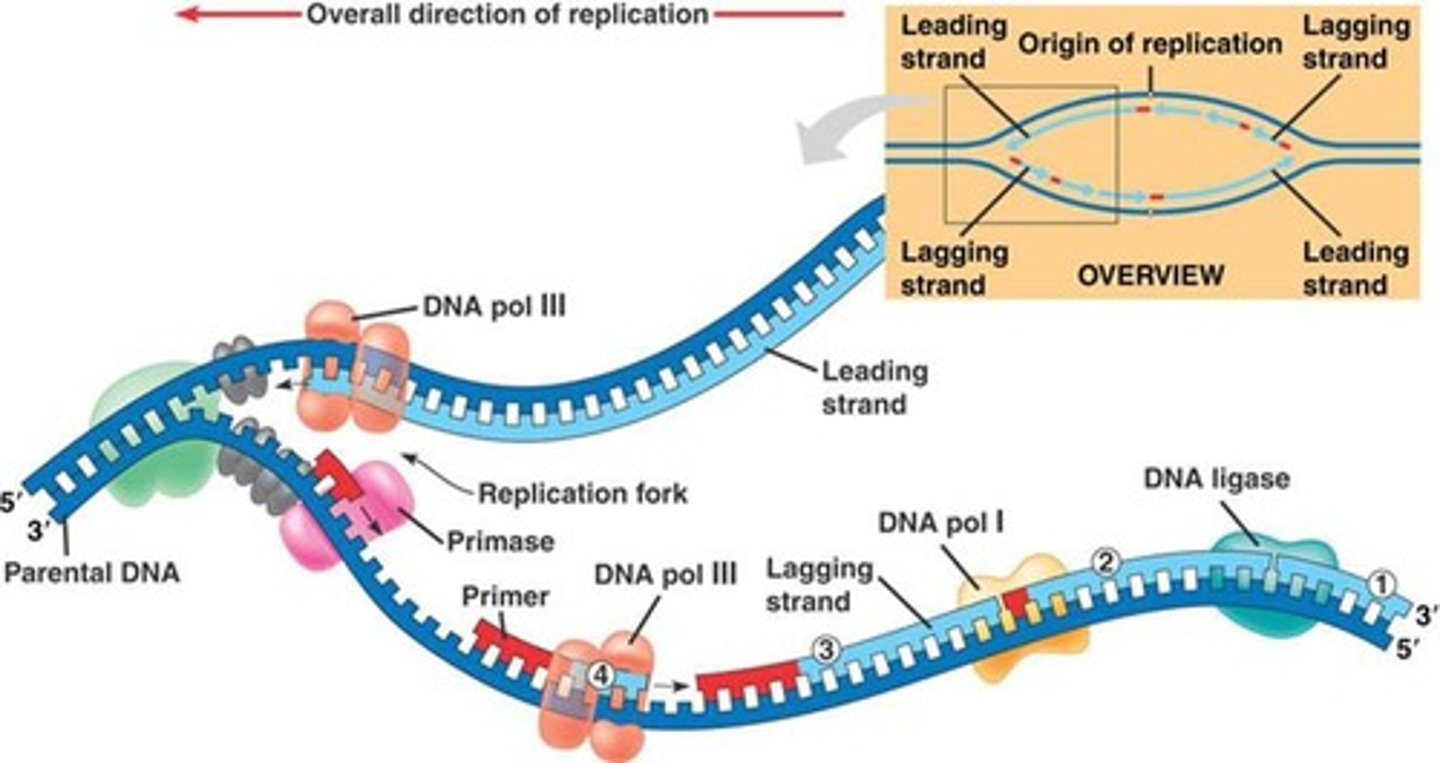
DNA ligase
an enzyme that seals up any gaps in the sugar-phosphate backbone during DNA replication

Leading strand
The strand of DNA that can be built continuously in the 5' to 3' direction (because the template strand is running 3' to 5')
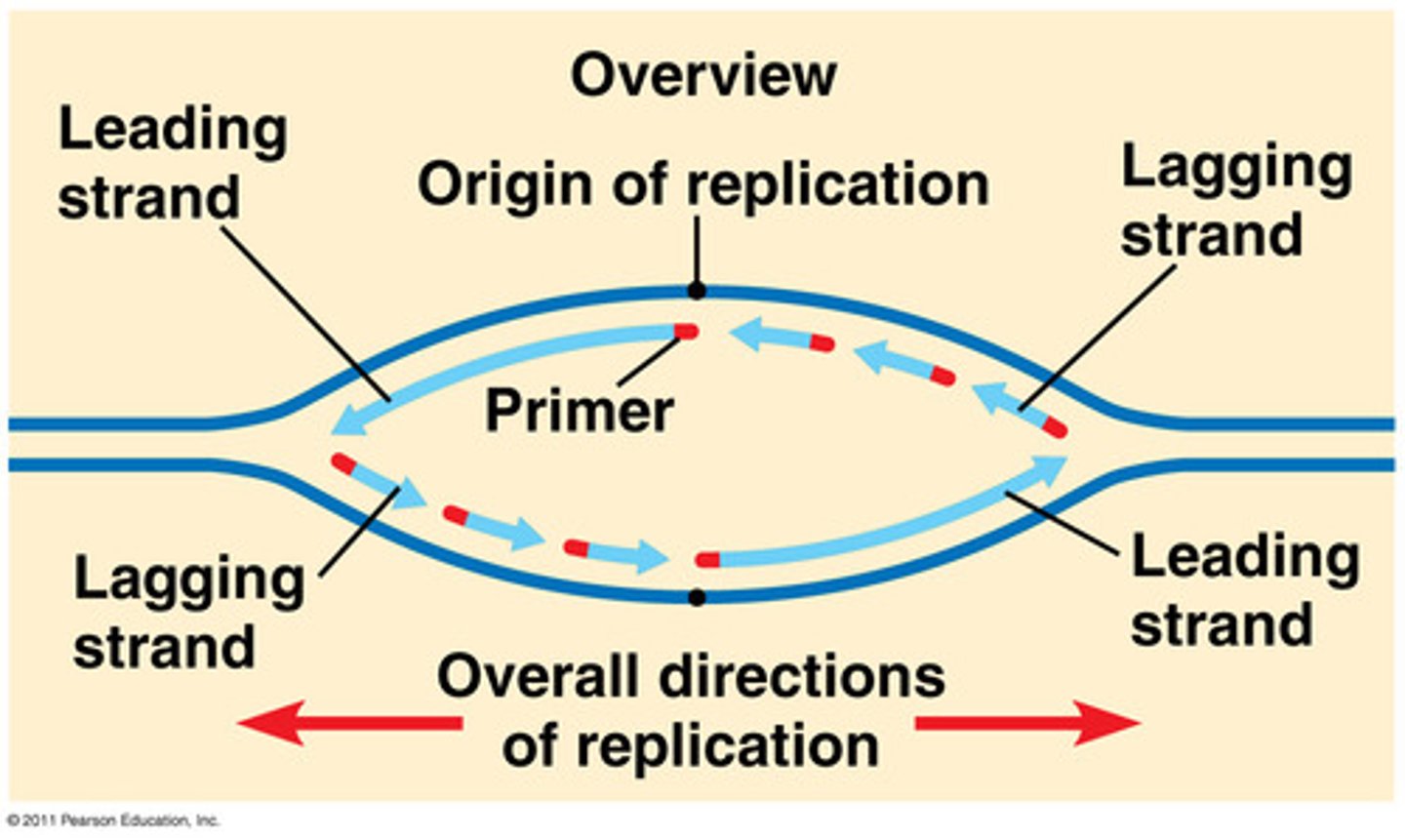
Lagging strand
The strand of DNA that must be built in 5' to 3' fragments because the template strand is running 5' to 3'. Enzymes have to loop ahead and then work backward to build in the 5' to 3' direction
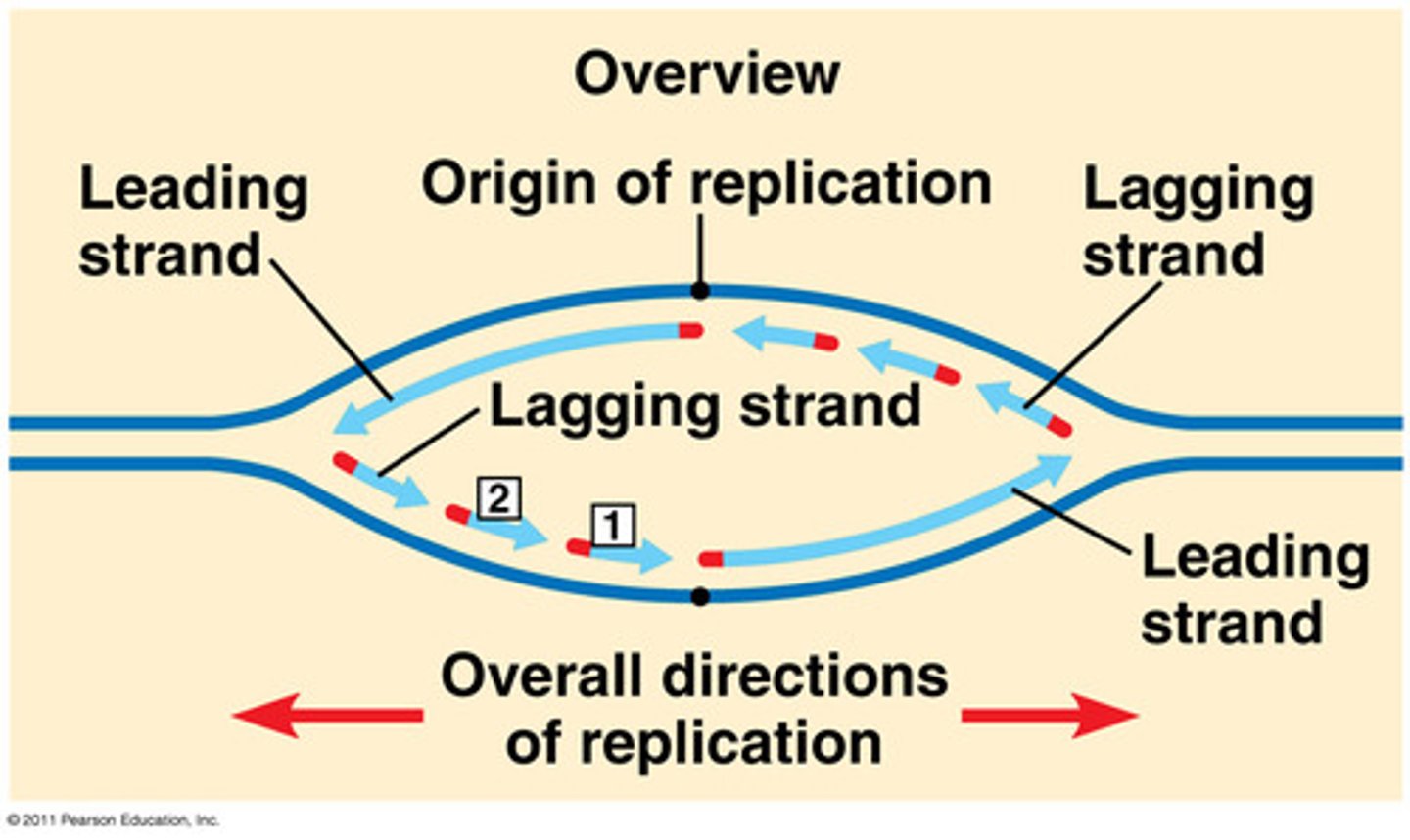
Okazaki fragments
short DNA fragments that are built on the "lagging" template strand. These will later be sealed together with the help of DNA ligase.
