Biology AQA-7.Ecology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
ecosystem
the interaction of a community of living organisms (biotic) with the non-living (abiotic) parts of their environment.
Plants in a community or habitat often compete with each other for…
light and space, and for water and mineral ions from the soil.
Animals often compete with each other for…
food, mates and territory.
Within a community each species depends on other species for…
food, shelter, pollination, seed dispersal etc
interdependence
all the species in a community rely on each other, If one species is removed, it can affect the whole community, potentially leading to major changes in population sizes or ecosystem balance.
Abiotic factors
light intensity
temperature
moisture levels
soil pH and mineral content
wind intensity and direction
carbon dioxide levels for plants
oxygen levels for aquatic animals.
Biotic factors
availability of food
new predators arriving
new pathogens
one species outcompeting another so the numbers are no longer sufficient to breed.
adaptations
enable Organisms to survive in the conditions in which they normally live. These may be structural, behavioural or functional.
extremophiles
organisms that live in environments that are very extreme, such as at high temperature, pressure, or salt concentration
What are photosynthetic organisms and why are they important in ecosystems?
Photosynthetic organisms like plants and algae are producers that make glucose by photosynthesis. They are the source of biomass for life on Earth.
What do all food chains start with?
producer(level 1)
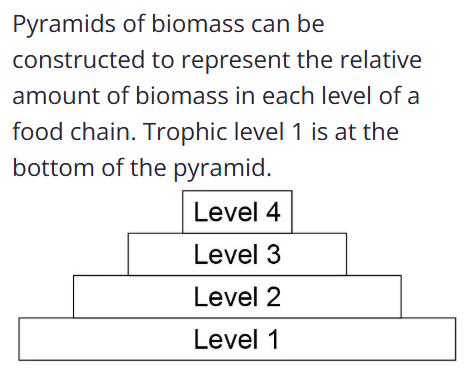
Producers are eaten by…
primary consumers(level 2)
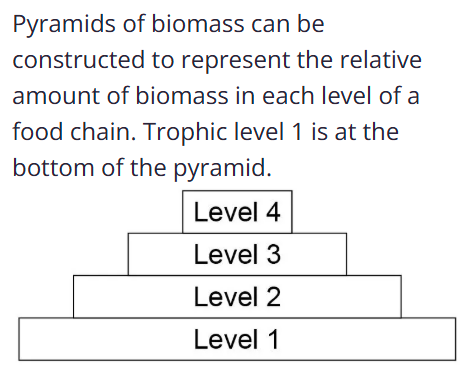
what is after secondary consumers(level 3)?
tertiary consumers(level 4)
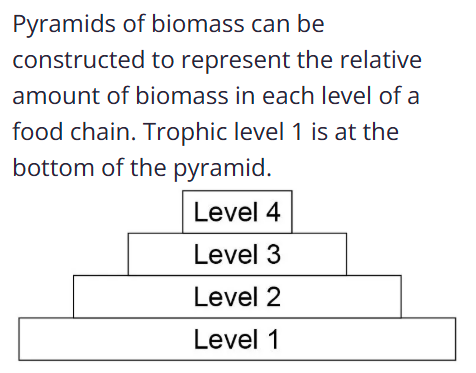
predators
kill and eat other animals
prey
those eaten
In a stable community the numbers of predators and prey…
rise and fall in cycles.
Why is material cycling important in ecosystems?
It recycles materials from abiotic and biotic components, providing building blocks for future organisms to grow and survive.
What is the importance of the carbon cycle?
returns carbon (as CO₂) to the atmosphere through respiration and decay, allowing plants to photosynthesise and support food chains.
How does the water cycle benefit living organisms?
It provides fresh water for plants and animals on land.
Anaerobic decay produces…
methane gas
Biogas generators can be used to produce…
methane gas as a fuel
Environmental changes affect the distribution of species in an ecosystem. These changes include:
temperature
availability of water
composition of atmospheric gases.
Biodiversity
variety of all the different species of organisms on earth, or within an ecosystem.
Pollution can occur:
in water, from sewage, fertiliser or toxic chemicals
in air, from smoke and acidic gases
on land, from landfill and from toxic chemicals.
Pollution…
kills plants and animals which can reduce biodiversity.
The decay or burning of the peat…
releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Large-scale deforestation in tropical areas has occurred to:
provide land for cattle and rice fields
grow crops for biofuels
Levels of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere are increasing, and contribute to…
global warming
How do breeding programmes help biodiversity?
They help to increase population numbers of endangered species and prevent extinction.
How do hedgerows and field margins benefit biodiversity in agriculture?
They provide habitats and food sources for insects, birds, and small animals in areas of monoculture farming.
Biomass is lost due to:
not all food being digested(faeces), energy being used for respiration and some parts of organisms arnt eaten such as bones
What biological factors affect food security?
Increasing birth rate
Changing diets in developed countries
New pests and pathogens
Environmental changes (e.g. drought)
High cost of farming inputs
Conflict disrupting farming and supply
Modern biotechnology techniques enable…
large quantities of microorganisms to be cultured for food.
How is mycoprotein made?
Fusarium fungus is grown on glucose syrup in aerobic conditions. Biomass is harvested and purified to make protein-rich mycoprotein.
How is human insulin made using genetic engineering?
A GM bacterium with the insulin gene produces insulin. It is harvested and purified to treat diabetes.
Give two benefits of GM crops.
Higher yields
Improved nutrition (e.g. Golden Rice with vitamin A)
Resistance to pests/disease