HL IB Biology Unit 3 Test Review
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Covalent Bond
Electron pairs are SHARED between two atoms
Hydrogen Bond
Interaction between slightly positive Hydrogen and slightly negative other atom
Ionic Bond
Electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another
The 2 most common bonds in Biology
Hydrogen, Covalent
Organic Chemistry
The study of compounds that contain carbon
Valence
The number of covalent bonds an atom can form
4 most common elements of life
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and nitrogen
Valence of Carbon
4 valence electrons, 4 valence
Valence of Hydrogen
1 valence electron, 1 valence
Valence of Oxygen
6 valence electrons, 2 valence
Valence of nitrogen
5 valence electrons, 3 valence
Biological Macromolecules
Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins.
Metabolism
All chemical reactions in the cell.
Monomer
Small building block molecule
Polymer
Large molecules consisting of the same or similar building blocks
Monomer and polymer of Nucleic acid
Monomer: Nucleotide
Polymer: Polynucleotide
Monomer and polymer of Carbohydrate
Monomer: Monosaccharide
Polymer: Polysaccharide
Monomer and polymer of Protein
Monomer: Amino Acids
Polymer: Polypeptide
Monomer and polymer of Lipids
No true monomers or polymers
Carbohydrate
An organic molecule with Carbons, Hydrogens, and Oxygens in the following ratio (CH2O)n
Simple sugars
Monosaccharides and disaccharides
Complex carbs
Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides and disaccharides functions
Immediately broken down for energy, and used to build polysaccharides
Polysaccharides functions
Energy storage, and structural material
Number of carbons in Trioses
3 carbons
Number of Carbons in Pentoses
5 carbons
Number of carbons in hexoses
6 carbons
Glucose formula
C6H12O6
Glucose functions
Broken down for ATP energy during cell respiration, and building blocks for polysaccharides
Electronegativity
A measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons to itself. The strength that the atom pulls the shared electrons.
Polar Covalent Bonds
A bond between two atoms with different electronegativities
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
A bond between two atoms with similar electronegativities.
3 polysaccharides glucose can build
Starch, glycogen, and Cellulose
Hexose examples
Galactose, fructose
Pentose examples
Ribose, and Deoxyribose
Disaccharide
A molecule that is created when 2 monosaccharides join together during a condensation reaction
Glycosidic linkages
The bond that connects Monosaccharides together
Examples of disaccharides
Sucrose(Glucose + Fructose), Lactose(Glucose + Galactose), and Maltose(Glucose + Glucose)
Starch and Glycogen
The polysaccharides that are used for energy storage
Cellulose and Chitin
The polysaccharides that are used for structural material
Starch
Energy storage polysaccharide found in plants
Glycogen
Energy storage polysaccharide found in animals
Cellulose
Structural material polysaccharide found in cell walls of plants
Chitin
Structural material polysaccharide found in cell walls of fungi.
Glycoprotein
A sugar protein molecule with many functions, such as structural support and cell to cell communication.
Polarity and solubility rule
Polar molecules (like water) dissolve other polar molecules because of hydrogen bonding capabilities. And Nonpolar molecules dissolve other nonpolar molecules.
Lipids
A class of macromolecule that are united because of hydrophobic properties
4 classes of lipids
Triglycerides(fats and oils), phospholipids, steroids, waxes
Fats and oils building blocks
Glycerole molecule, and 1, 2, or 3 fatty acid chains
Tryglyceride
Fat with glycerole molecule and 3 fatty acid chains.
Ester linkage
The bond that fatty acids and glycerole
Fatty acid
Long hydrocarbon chains attached to a carboxyl group (carboxylic acid) - COOH
Saturated Fat
Only contains single bonds in the hydrocarbon chain.
Monounsaturated fat
Contains 1 double bond in the hydrocarbon chain.
Polyunsaturated fat
Contains 2+ double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain.
Cis-Unsaturated fat
The hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon double bond are on the same side - creates a bend in the hydrocarbon chain
Trans-Unsaturated fat
The hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon double bond are on different sides - no bend is created
Function of fats and oils
Long term energy storage, insulation, protection/cushioning of internal organs.
Adipose Tissue
Where fat is stored in animals for regulating body temperature and breaking down for energy.
Where plants store fat.
In seeds, being used to provide energy for photosynthesis.
Phospholipids
The major component of cell membranes in the form of a phospholipid bilayer
Components of a phospholipid
Glycerol, 2 fatty acid tails, and a phosphate head group.
Phospholipid diagram (Be able to draw this)
Phospholipid bilayer
The major structural component of the cell membrane. Where hydrophilic head on either side of the cell(In or out), and the hydrophobic tail is in the middle.
Steroids
A molecule that contains 4 fused hydrocarbon rings. EX: Cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone
Cholesterol functions
Reduces the permeability of the cell membrane by reducing fluidity at higher and lower temperatures. It is also modified into other steroids.
Steroid Hormones
A class of hydrophobic hormone molecules that control a wide range of physiological functions. EX: Testosterone, estrogen.
Waxes
Class of diverse lipids that are generally long hydrocarbon chains, used by plants and animals to make them “water proof”.
Protein
A diverse group of macromolecules with functions such as Enzymes, Hormones, Transport Structure, Movement, Storage, Defense, and Receptors.
4 components of amino acids
Alpha (central) carbon, amino group, carboxyl acid group, side chain/R group
Diagram of amino acids (Be able to draw this)
Amount of different side chains
There are 20 side chains that give amino acids their properties.
Essential amino acids
Amino acids humans cannot make on their own, and must get from food. The best sources being meat and eggs, making vegan/vegetarian diets difficult to maintain.
Non-essential amino acids
Amino acids are made by humans and therefore do not need to be received from another source.
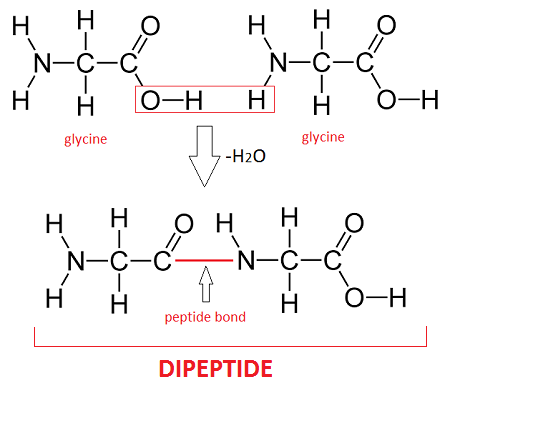
Dipeptide
A molecule composed of 2 amino acids held together by a peptide bond.
Peptide bonds
Bonds that hold together 2 amino acids to make a dipeptide, created during condensation reactions.
Drawing of 2 amino acids coming together to make a dipeptide (Be able to draw this)
Polypeptide
A chain of 3+ amino acids connected together using peptide bonds. They are the polymers of proteins and a protein is consists of 1 or more of these.
Variety of Dipeptides and Polypeptides
There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in any different way, meaning there are a possible 400 different dipeptides and 20n amount of polypeptides.
Polypeptide examples
Lysozyme, Glucagon, Myoglobin, and Alpha-nuerotoxins.
Primary Structure
Definition: The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
Bonds Involved: Peptide Bonds
Secondary Structure
Definition: Local folding of the polypeptide chain into alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
Bonds Involved: Hydrogen bonds between backbone
Tertiary Structure
Definition: Further folding of the polypeptide determined by interactions between the side chains
Bonds Involved: Hydrogen bonds, Ionic bonds, Disulfide bridges, Hydrophobic interactions
Quaternary Structure
Definition: Arrangement and interaction of two or more polypeptide chains to form a functional protein
Bonds Involved: Non covalent bonds and interactions
Conjugated Proteins
Proteins that contain a non-protein component (metal ion or carbohydrate). EX: Haemoglobin and glycoproteins
Non-Conjugated Proteins
Proteins that consist of only polypeptides. EX: Insulin and Collagen
Globular Proteins
Complex proteins that are usually spherical in shape with irregular folds.
Fibrous Proteins
Long, narrow, simple shape usually composed of repeating structures.
Integral Proteins
Proteins that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer of a cell membrane
Denaturation
A process where the protein’s structure is changed, therefore changing the function caused by changing the pH or the temperature.
Functions of Catalyst
Speeding up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process.
Enzyme macromolecule
Protein
Activation energy
The amount of energy it takes to make a reaction begin
Transition State
The point on the reaction coordinate diagram with the highest energy (aka at the top of the activation energy)
Why are enzymes essential?
Most of the reactions in living organisms would not occur without enzymes present.
How do enzymes impact the reaction coordinate diagram?
Enzymes LOWER the activation energy of a reaction
Anabolic pathways controlled by enzymes
Synthesizing polypeptides (catalyzed by ribosomes), Building glycogen (6+ enzymes including glycogen synthase), Photosynthesis in plants building glucose
Catabolic pathways controlled by enzymes
Digestion of starches (salivary amylase), Digestion of lactose (lactase), Cellular respiration - breaking down glucose to produce energy.
Active site
Where the substrate binds to the enzyme.
Induced fit
When the active site and substrate change shapes slightly to more tightly “fit” the substrate into the active site.