program planning final
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Belmont
_____ report:
o stemmed from Tuskegee Experiment
o 1974, the national research law created the national commission for the protection of human subjects of biomedical and behavioral research
nuremberg
· ________ trials: Medical Case after WWII on research crimes
Nazi experiments on prisoners: high altitude, freezing, twins, sulfa drugs, poison, TB, Phosgene, transplantation, sterilization → set new conditions for research
Subjects must have knowledge, voluntary consent, ability to end participation
Scientists in charge are responsible for:
scientific basis or validity of hypothesis
Terminate experiments likely to cause injury, disability, death
respect, justice
Ethical principles in research involving humans
1. ____ for persons
2. Beneficence: promotion of well-being (maximize benefit, minimize harm)
3. _____
institutional
IRB (______ review board)
o identify the basic ethical principles that should underlie the conduct of biomedical and behavioral research involving humans species (and animals).
Includes:
o At least 5 people; qualified people, diverse groups represented, knowledgeable, outside member
o except, expedited, full review
assent
informed consent
o Implied consent: by completing the survey you consent
o _____: 4th grade – 17
o “If you don’t want your child to be present sign this otherwise we will assume they can”
o Deception: can be vague but not deceiving
issues, reporting
· Anonymity and confidentiality
· Data _____ (misuse, manipulation, analyses) vs ______ results (withholding, conflict of interest, duplication, plagiarism)
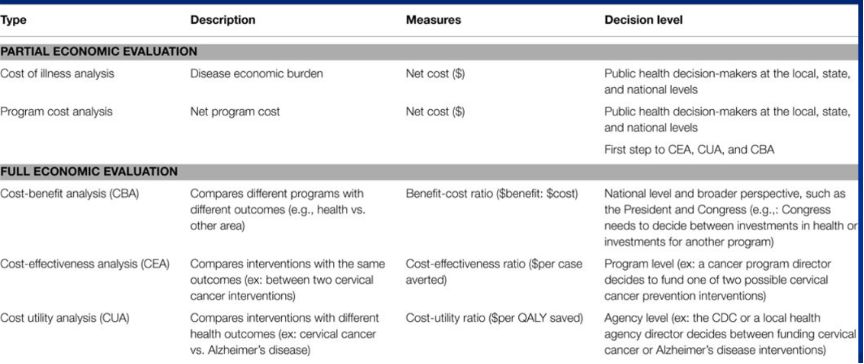
economic evaluation
_______ ________ of public health programs: the systematic appraisal of costs and benefits of projects, normally undertaken to determine the relative economic efficacy of programs (Is the program worth it?)
o Applied analytic methods to identify, measure, value, and compare the costs and consequences of treatment and prevention strategies
allocation
· Purpose: maximize outcomes, minimize costs, resource ______, demonstrate value (return on investment)
illness (COI)
5 types-partial and full economic evaluation analyses
1. Cost of _____ Analysis
Estimates total costs incurred b/c of disease
Reported as: annual total cost, avg per person lifetime cost
Shows potential benefits of prevention efforts
cost(CA)
5 types-partial and full economic evaluation analyses
_____ analysis
Estimates total costs of running a program
Realizing costs from varying perspectives; important for budget justification, decision making, forecasting
First step of full economic evaluation
cost benefits
5 types-partial and full economic evaluation analyses
_____ _______ analysis
Method used to compare costs & benefits of intervention
All costs & benefits are standardized/valued in monetary terms
Compare next savings of programs that have entirely different benefits. (Bike helmet program vs elderly fall)
Less useful when benefits defined as lives saved
net benefits
cost-benefit analysis provides a single value:
____ ______: NB
benefits ($) divided by cost ($)
willingness
Quantify benefits of CBA
Cost-of-Illness approach vs _____ to pay (how much is society willing to pay to reduce the annual morbidity & mortality risk associated disease or injury)
CBA used to
competing, implement
CBA is used to…
Choose among _____ options
implement program w/ highest NB
Decide whether to ____ specific programs
Net benefit > 0 “____”
For setting priorities on options given resource constraints
utility (CUA)
5 types-partial and full economic evaluation analyses
Cost ______ analysis
Method used to compare costs & benefits of interventions where benefits are expressed as # of life years saved adjusted to account for loss of quality
Combines
length of life (survival) & quality of life
ratio
CUA Cont
Compares disparate outcomes in terms of utility
Quality adjusted life years (QALY)
Disability adjusted life years (DALY)
Defines a ____ of cost per health outcome
$/QALY or $/DALY
QUALITY OF LIFE; CUA
CUA is used when
____ ___ _____ is the important outcome
When the program affects both morbidity & mortality
Ranging outcomes
Program being compared w/ program that has already been evaluated using ____
CA
First step of full economic evaluation?
CUA
which evaluation uses QALY & DALY
cost effectiveness
5 types-partial and full economic evaluation analyses
______ ________ analysis
Estimates costs & outcomes of interventions
Expresses outcomes in natural units (cases prevented; lives saved)
Compares results w/ other interventions affecting the same outcome
ratio
Cost effectiveness analysis
Summary measure: cost effectiveness ____
Cost per outcome achieved (cost per case prevented, cost per life saved)
common; worth; empirical
Used to identify
most cost effective strategy from options that produce _____ effect
practices that are not ____ their costs
Used for _____ support for under funded programs
ok!
read over
lobby
Economic evaluation & policy
o Information —> _____ for more prevention resources to reduce burden
o Economic evaluation is valuable to decision making & for setting health policy; important special
investment
o Return on _____: the cost to implement effective interventions – economic intervention prevention
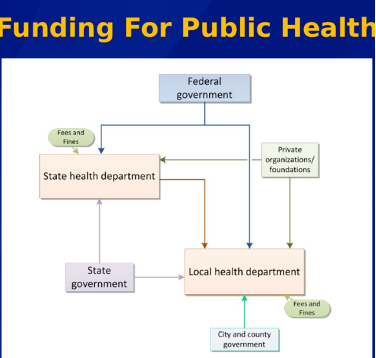
centralized
financing of public health
Types of governmental health structures
______: local health units are primarily led by employees of the state
decentralized
financing of public health
Types of governmental health structures
________: local health units are primely led by employees of local government
benefits
____ of decentralized : priorities meet local level needs; more accountable to local stakeholders; better fulfill local health needs; increased flexibility & transparence
poorer, workload
drawbacks of decentralized: _____ communities lack revenue; increased ______ of local frontline workers; mismanagement of funds; lack of training or capacity
mixed
financing of public health
Types of governmental health structures
________: some local health units are led by employees of the state and some are led by employees of local government
shared governance of health department
financing of public health
Types of governmental health structures
________: local health units might be led by employees of state or by employees of local gov.
fiscal
Shared: If led by state —> local gov has authority to make ____ decisions or issue public health orders
state
Shared: If led by local gov —> _____ has authority “”
federal
· Mechanisms of financing:
______: block (broad discretion) or categorial (specific; competitive & formula based)
Mixture of population based formula grant programs, incidence or prevalence based formulas, and a series of competitive grants
state & county
· Mechanisms of financing:
____ & _____ gov revenues through appropriation process
Varies dramatically based on state governance and health department structure/activities; taxes
statute
· Mechanisms of financing:
_____ language mandating state funding to local health agencies (LHA)
program
· Mechanisms of financing:
____ Fees & fines
Newborn screenings
Environmental health
Regulation & licensing (healthcare, facilities, body art salons)
Inspection certifications (restaurants, residential buildings)
Permits (swimming pools, water systems, mobile home parks)
reports, insurance
program fees & fines cont
____ & certificates
Vital records (birth, death, marriage
_____: Medicaid, private insurance
tax
· Mechanisms of financing:
_____:
property tax
sales tax
tobacco excise tax
taxing districts: need authority from state for local taxing districts
mosquito control, TB, property taxes
funding, unpopular
taxes
benefits/limitations
ability to align local _____ with local priorities
avoid annual funding fluctuation
______
federal
· Sources of funding of public health: health departments received most ______ funds via USDA, CDC, HRSA, EPA, FDA
authorizations; competitive, law
Factors influencing flow of funding from federal to other levels
o Congressional _______ & appropriations directives/limits
o Eligibility varies by funding opportunity
o Not all eligible apply for each opportunity
o Most federal funding awarded via a ______ or merit-based process; not all that apply are funded
o Some funding allocated according to a pre-set formula which is sometimes specified in by ___
congress
U.S. Congress relationship to public health funding
o Only _____ can raise revenue, borrow funds, and provide funding to federal agencies
decides: what each agency is authorized to do; purpose of funds; amount of funds; amount of time the funds are available to be spent; other parameters
legislations, transfers, fees
Ways CDC receives congressionally authorized/appropriated funding
o Annual appropriations process
o Individual pieces of congressional ______ appropriating funding anytime during the FY
o User ____ congress authorizes CDC to collect for services (CDC vessel sanitation program)
o _____ from other federal agencies:
funded activities must still fall under CDC authorities;
funds must be used according to original congressional intent
president, hhs, cdc
· Formal players: ____ (office of management & budget); ___ Secretary; ___ director, leadership, programs, congress
transfer; little
· Grants:
o Most appropriate when principle purpose is to ____ a thing of value, money, property, or services to the recipient to carry out public purpose
____ involvement expected on part of issuing agency
requires completion of program activities by the funded org only
____ grants are non-discretionary
categorical
_____ grants are specific ie: funds for diabetes must go to diabetes
FOAs
___: the document all federal agencies use to announce the availability of grant funds to the public
cooperative
_______ agreements: used when the principal purpose of the relationship is to transfer a thing of value & agency is expected to provide substantive involvement in carrying out the activities
Includes substantial participation on the part of the CDC
single, diverse
Observations: no ____ solution
o Funding must be a _____ mix of sustainable revenue streams beyond what currently exist
increased; highly
Public health business model: public support for _____ funding in some but not all public health priority areas
Public health is highly reliant on federal gov funding
fiscal
____ year (FY): Year of budgetary process, sometimes follows a calendar year, sometimes doesn’t
State, territory, local, and tribal gov have own fiscal cycles (different than fed)
1, 30
o Fed: Starts October __ and ends September _
FY18= October 1 2017 – September 30 2018
yes.
· Funding for public health flowchart- know who holds purse strings for diff labels