2.2 KINESE The Spine
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Functions of the Spine
Transmits weight into the pelvis, protects spinal cord, absorbs shock, allows for wide range of motion
Cervical vertebrae
Top seven vertebrae
Thoracic vertebrae
Group of 12 vertebrae after the cervical vertebrae
Lumbar vertebrae
Group of 5 vertebrae after thoracic vertebrae
Sacral vertebrae
Group of 5 vertebrae below the lumbar vertebrae
Coccyx vertebrae
Group of bottom 3-5 vertebrae
Primary/posterior curves
Thoracic and sacral curves
Secondary/anterior curves
Cervical and lumbar curves
Tummy time
How we develop a cervical curve
Psoas strength through sitting up
How we develop a lumbar curve
2 parts of the vertebrae
Body and arch
Annulus Fibrosus
Outer layer of an intervertebral disc
Nucleus Pulposus
Insides of an intervertebral disc
Vertebral arch
A
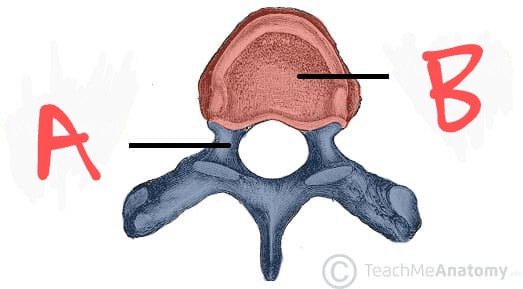
Vertebral body
B
Pedicle
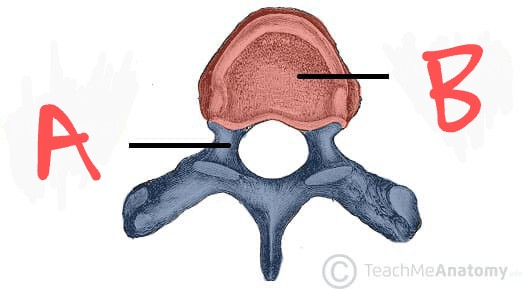
Lamina
Atlanto occipital joint
Joint connecting the base of the skull to the C1 vertebra, offering flexion and extension in the neck
Atlanto axial joint
Joint connecting the C1 and C2 vertebrae, allows for rotation in the neck
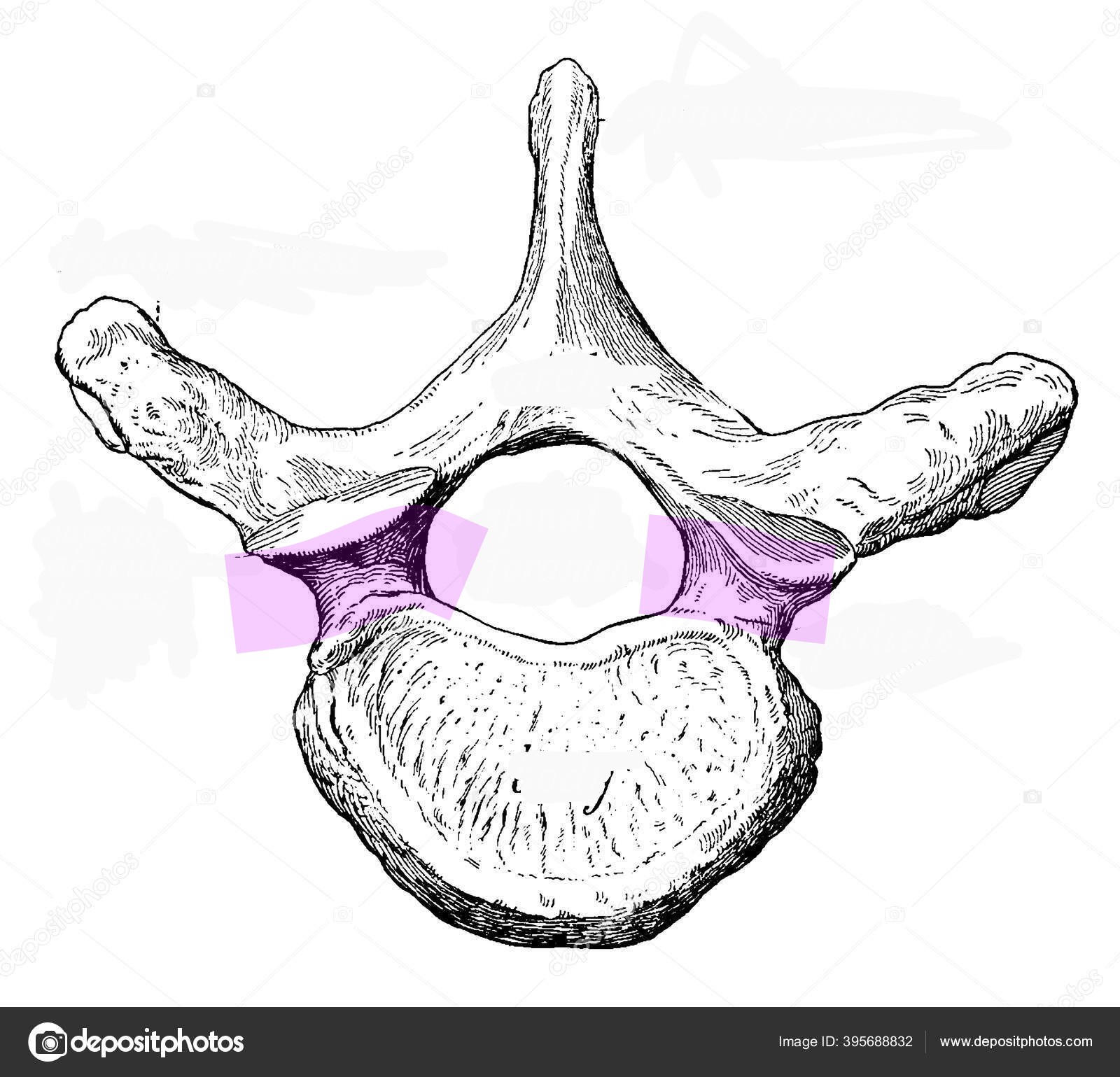
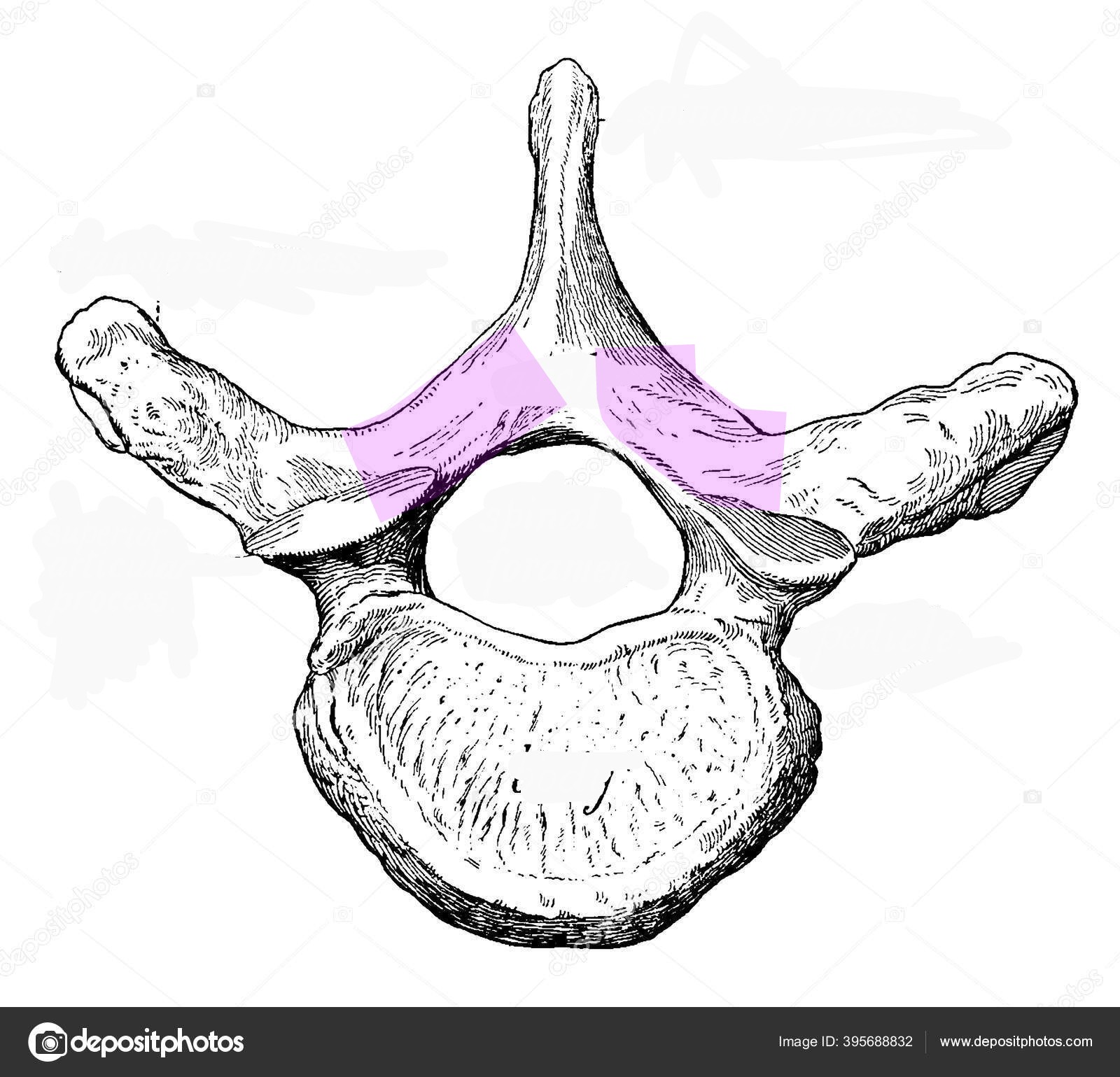
Costovertebral joint
Gliding joint connecting the ribs to the vertebrae
Costotransverse joint
Joint connecting the rib to the transverse process
Costocentral joint
Joint connecting the rib to the vertebral body
Lumbosacral angle
Degree of tilt in the lordotic curve
Superior articulating Facet
Vertebral articular surface that is closer to the body of the vertebra
Inferior articulating facet
Vertebral articular that is further from the body of the vertebra
Sacrum
Bone at the base of the spine made of 5 fused vertebrae, completely fused after 25
Sacral Iliac joint (SI)
Gliding joint that allows the sacrum to nutate and counter nutate
Nutation
The anterior top of the sacrum moves down
Counter Nutation
The anterior top of the sacrum moves up
Passive nutation
A back bend produces ________ in the SI joint.
Passive counter nutation
A forward bend produces _____________ in the SI joint.