IT - Summer exams S4
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This flashcard set should contain everything that I have covered in S4 GCSEs.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
What is the von Neumann architecture?
John von Neumann invented the processor architecture which stores a program in memory as instructions and executes them sequentially using the ALU, control unit and registers. This uses the FDE cycle.
Think of the diagram of the von Neumann architectue.
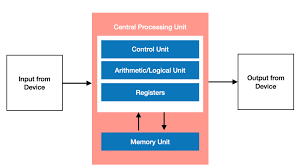
What are the devices called peripherals?
Input and output devices.
What is the role of the control unit?
Coordinates how data moves around the CPU by sending signals to control the flow of the data
Decodes the instructions fetched from memory
What is the role of the ALU?
Processes data using binary arithmetic and logical operation
What is the role of RAM?
Hold the data and instructions that the computer needs whilst it is working.
What are registers?
Extremely small, extremely fast memory located in the CPU
Each register has its very own specific purpose
What is the FDE cycle?
They cycle that the CPU runs through billions of times per second to make a computer work
Think of the diagram of the FDE cycle
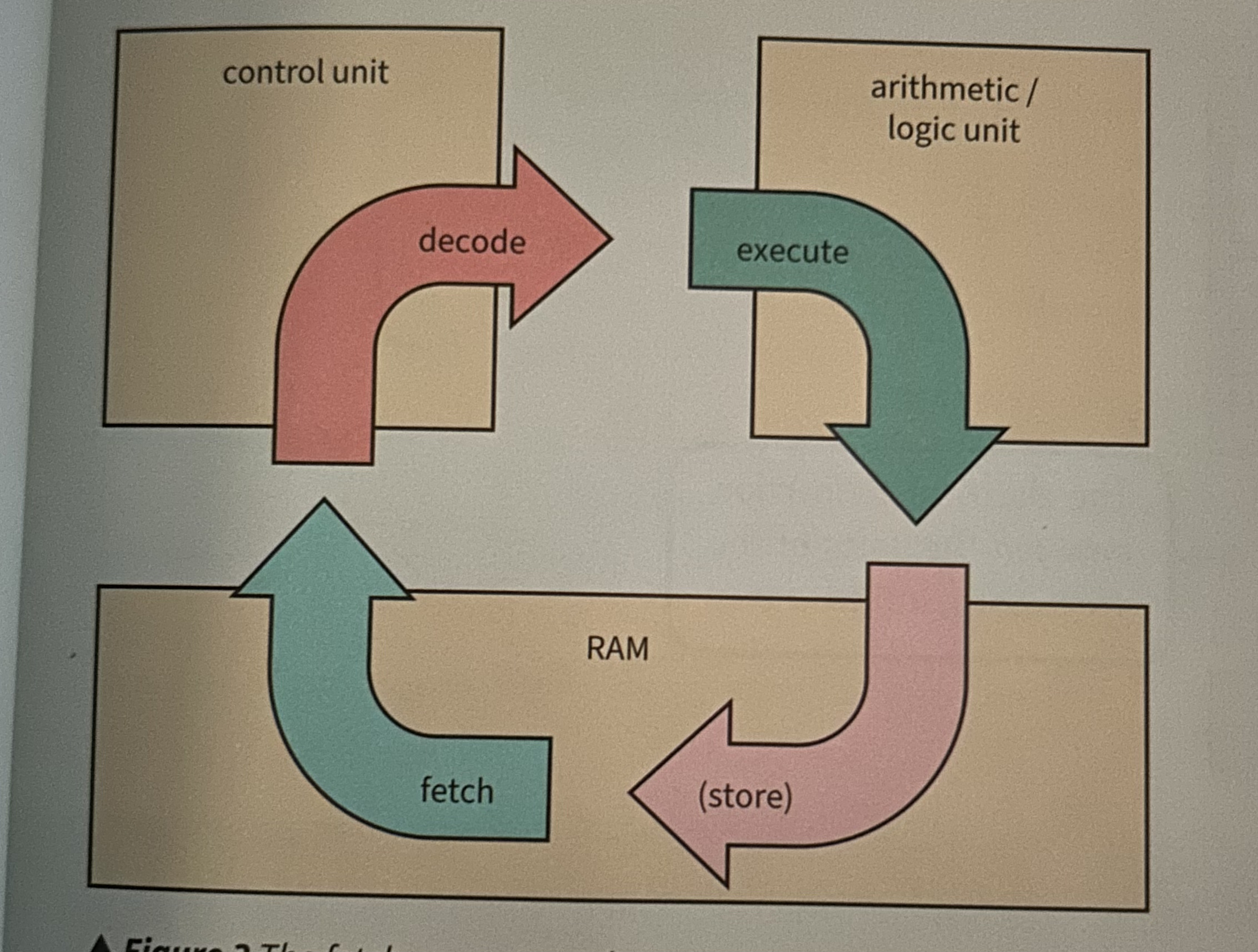
Describe the fetch part of the cycle
Instructions and data travel from RAM to the control unit. They are sent as binary numbers
Describe the Decode part of the cycle
The control unit changes a binary number from RAM into an instruction signal.
Describe the Execute part of the cycle
The control unit sends the instruction signal to the ALU, which executes the instruction
What are “clock signals”?
Clock signals are regular pulses of electricity that the control unit send out. It is used to time the fetch-execute cycles.
How much pulses per second does a modern computer send out?
“Billions”
What is a core?
A core is a processor unit within a CPU.
How do cores make modern computers work faster?
More cores = more instructions executed simultaneously… e.g a dual - core processor has two CUs and ALUs that can execute 2 instructions at the same time.
Definition of a “bus”
The electrical connection between the parts of the processor.
What is cache memory?
Cache memory is used to store frequently used instructions and data.
Cache is a type of memory that a CPU can
access faster than it can access RAM.
What is Hardware?
Physical parts of the computer system.
What is software?
Any program that runs on the computer
3 examples of computer systems
Mobile phones, Washing machines, Games console
What functions do all computers perform, what do
they all have in common?
They all process data, store information, and execute instructions.
What is an input device?
An input device is a hardware device that transmits
information/data into the CPU.
What is an output device?
An output device is any hardware device used to transmit to the outside world the results of data
processed by the CPU.
3 examples of input devices?
Keyboard, Mouse, Joystick
3 examples of output devices?
Monitor, Speaker, Printer
What is the purpose of a CPU?
The PURPOSE of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) is to fetch, decode and execute program instructions and manage the rest of the hardware.
What is clock speed?
The clock speed measures the number of fetch-decode-execute cycles that can take place per second - measured in hertz
What is the effect of clock speed on CPU performance?
A CPU with a higher clock speed will process more instructions per second.
What is Level 1 cache and what is it used for?
Level 1 cache is extremely fast but small (between 2-64KB). It is used to hold instructions.
What is level 2 cache and what is it used for?
Level 2 cache is very fast and medium-sized (256KB-2MB). It is used to hold data.
What is parallel processing?
the double the cores, the double the instructions executed at the same time.
What is the effect of RAM size on CPU performance?
It is quicker to fetch data from RAM than from storage. Increasing the CPU performance.
What can volatile be defined as?
Memory that uses electricity to hold data, everything held in volatile memory is lost if power is turned off.
What are the differences between RAM and ROM?
.RAM is Volatile, ROM is non-volatile
.RAM you can change contents, ROM you cannot change
.RAM have high capacity, ROM have low capacity
.RAM holds data and instructions, ROM holds start-up instructions
Why do we need primary storage?
Access speeds are quicker compared to secondary storage.
Why do we need secondary storage?
. Storage spaces are large
. They are non - volatile
What do primary storage consist of?
.RAM
.ROM
.Registers and cache
What is primary storage (and RAM)?
Holds the data and instructions which the CPU needs to access while a computer is running.
Why is RAM referred to as
‘random’ access memory?
Because data stored in RAM can be accessed
in any order.
What are the differences between SRAM and DRAM?
.Static RAM does not need continuously recharging and is therefore
much quicker than DRAM – data can be accessed by the CPU more rapidly
.SRAM is more expensive.
What does the Program counter hold? And when is it used in the FDE cycle?
It holds a address and is used at the start of the cycle.
What is the purpose of a program counter?
The PC holds the address of the next line of the program. It counts through the program line by line.
What does the memory data register hold? And when is it used in the FDE cycle?
It holds data and is used at the Fetch and store part of the cycle
What is the MDR’s job?
During the fetch part, the MDR holds the data that has been fetched from memory
During the store part, it holds the data before and is ready to be saved.
What does the MAR store? And when is it used in the FDE cycle?
It holds an address and is used at the Fetch and store part of the cycle
What is the MAR’s job?
During the fetch part, the MAR holds the memory address to fetch from
During the store part, it holds the address to save to
What does the accumulator hold? And when is it used in the FDE cycle?
It holds data and is used in the Execute stage of the cycle?
What is the accumulator’s job?
Saves the results of each calculation carried out by the ALU
What is an embedded system?
An embedded system is a computer system with a single function, inside a larger mechanical unit
3 examples of embedded systems?
Washing machines
Dishwashers
Traffic lights
What are the properties of an embedded system?
They are small in size
They use less power than a general-purpose computer
They have a lower cost
What is secondary storage?
Secondary storage is non-volatile (permanent), long term storage for programs and data.
What are the 3 types of secondary storage?
.Optical
.Magnetic
.Solid state
Give me 3 examples of Optical?
CD, DVD, BLURAY
Give me 3 examples of Magnetic?
Hard drives, magnetic tape
3 examples of solid state?
USB stick, solid - state drive, SD card
What are the 6 characteristics of storage devices?
. Capacity
. Speed
. Portability
. Durability
. Reliability
. Cost
What is the use of CDs?
What is the use of DVDs?
What is the use for Blu - Ray?
Music
Film
High def videos/ films
What is the use of a hard disk drive?
What are the applications for a solid stage storage?
Main storage for computers, used to store files (music, vids…)
Portable storage devices and same as hard disk drives
How does optical storage work?
How does magnetic storage work?
How does solid state storage work?
Hold data using pits burned into a plastic surface. Is then read by a laser beam.
Holds data using grains of magnetised metal.
Holds data using electrons trapped in solid matter.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Optical?
. Capacity - Not a lot of memory capacity
. Speed - Fast data transfer rates
. Portability - Lightweight
. Durability - Easily scratched (data not read)
. Cannot be wiped and reused
. Cost - Cheap to buy
Advantages and Disadvantages of Magnetic storage?
. Capacity - Holds a lot of data
. Speed - Very fast data access
. Portability - Heavy and usually large
. Durability - Has moving parts ( can break when dropped)
. Reliability - Has moving parts (will eventually fail)
. Cost - Cheap per GB
Advantages and disadvantages of Solid State Drives?
. Capacity - High capacity
. Speed - Faster access time than hard disk
. Portability - Small and light
. Durability - Shock - resistant
. Reliability - No moving parts
. Cost - Very expensive
How many bits in a nibble?
4 bits
How many bits and nibbles in a byte?
8 bits, 2 Nibbles
Order of byte size in terms of size?
Byte
Kilobyte
Megabyte
Gigabyte
Terabyte
Petabyte
How to calculate sound file size?
Sample rate X duration X bit depth
How to calculate image file size?
colour depth X image height (px) X image width
How to calculate text file size?
Bits per characters X number of characters
REVISE BINARY CONVERSION USING TEXTBOOK
What are the 2 common character sets?
ASCII and Unicode
Difference between ASCII and UNICODE
UNICODE as more characters than ASCII.
What is a character set?
A defined list of characters recognised by the computer hardware and software, with each character being represented by a unique number, that is stored in binary format.
What is the relationship between number of bits per character and the number of characters which can be represented?
More bits per character = more characters represented
Number of characters represented = 2n where n = bits per pixal
What are pixels?
. a “picture element”
.Smallest unit of data that can be represented in an image.
. A single block of colour.
. More pixels = more detailes images
What is resolution?
The resolution of an image is how many pixels are displayed in a specific area of an image. (dots per inch, pixels per inch)
What is colour depth?
Colour depth is how many bits will be used to store
the colour for each pixel in an image.
What is the effect of resolution and colour depth on an image?
Higher the resolution and colour depth of an image - the higher the quality but the higher the file size.
What is metadata?
What does metadata hold?
“Data about data”
. The type of file (e.g., image, document)
.When it was created
.Who created it
.The dimensions of the file (like image size)
.The colour depth of images
What does pixelated mean?
In a low quality image, the pixels will be larger, this is called pixelation.
How to convert analogue sound into a digital version?
Measure the amplitude of the sound waves at regular intervals. Then store each sample as a binary number.
What is the sample rate? and what is it measured in?
How often the amplitude of a sound wave is measured per second
. It is measure in hertz
What is bit depth? (Sound)
Number of bits used to store each sample
How is sound quality affected by bit depth and sample rate?
The bigger the bit depth and the sample rate, the better the playback quality and accuracy, but the file size will also increase.
What is the need for compression?
Compressed files take up less space
It can be quicker to transmit files - for example, over the internet
What are the 2 types of compression?
Lossy
Lossless
What is compression?
Compression reduces the file size.
What are the 2 methods of Lossless compression?
Run length encoding (Images)
Dictionary encoding (Txt docs)
What is lossless compression?
Lossless compression can compress data files without losing
any of the information.
What is lossy compression?`
Lossy compression compresses data files but does lose some of the
information.
Advantages and disadvantages for lossless compression?
Advantages:
No Loss of Quality: The original data is preserved, so there is no loss of quality.
Reversible: You can decompress the file back to its original form without any data loss.
Disadvantages:
Larger File Sizes: The file sizes are usually larger compared to lossy compression, which means they take up more storage space.
Slower Compression: It can take longer to compress and decompress files compared to lossy methods.
Advantages and disadvantages for lossy compression?
Advantages:
Smaller File Sizes: It reduces the file size significantly, making it easier to store and share.
Faster Transmission: Smaller files take less time to upload or download, which is great for streaming and online use.
Disadvantages:
Loss of Quality: Some detail is permanently lost during compression, which can affect the quality of images or sound.
Not Suitable for All Uses: It’s not ideal for files where quality is crucial, like professional images or audio.
Describe a LAN?
Joins computers on the same site/ in a small geographical area
Describe a WAN?
Joins computer on different sites/ over a large area
What type of connection do LANs use?
Uses cables or wireless owned and used by a single organisation
What type of connection does WAN use?
Uses shared transmission media such as publicly owned cables
Example of LANs
The network in Birkdale school
Examples of WANs?
The network that connects an ATm in a village to a bank in a distant city
What are different network shapes called?
Topologies