Population Genetics and Microevolution Concepts
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Population genetics
The study of genes and genotypes in a population.
Population
Groups of interacting individuals of the same species that occupy the same environment/area at the same time.
Gene pool
All of the alleles for every gene in a given population.
Polymorphism
Traits display variation within a population; due to two or more alleles that influence phenotype.
Polymorphic gene
A gene that exists as two or more alleles in a population (most common; ex. blood type).
Monomorphic gene
A gene that exists as a single allele in a population (less common; ex. cheetahs).
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
Smallest type of genetic variation in a gene, resulting in approx. 99% of all variation in human gene sequences.
Allele frequency
Represents the percentage/incidence (or how common) an allele is found within a population.
Genotype frequency
Represents the percentage/number of individuals within a population that possess a specific genotype.
Hardy-Weinberg equation
Used to calculate the probability of genotype frequencies in a population and to track their changes from one generation to another.

p
The frequency of the dominant allele in the Hardy-Weinberg equation.
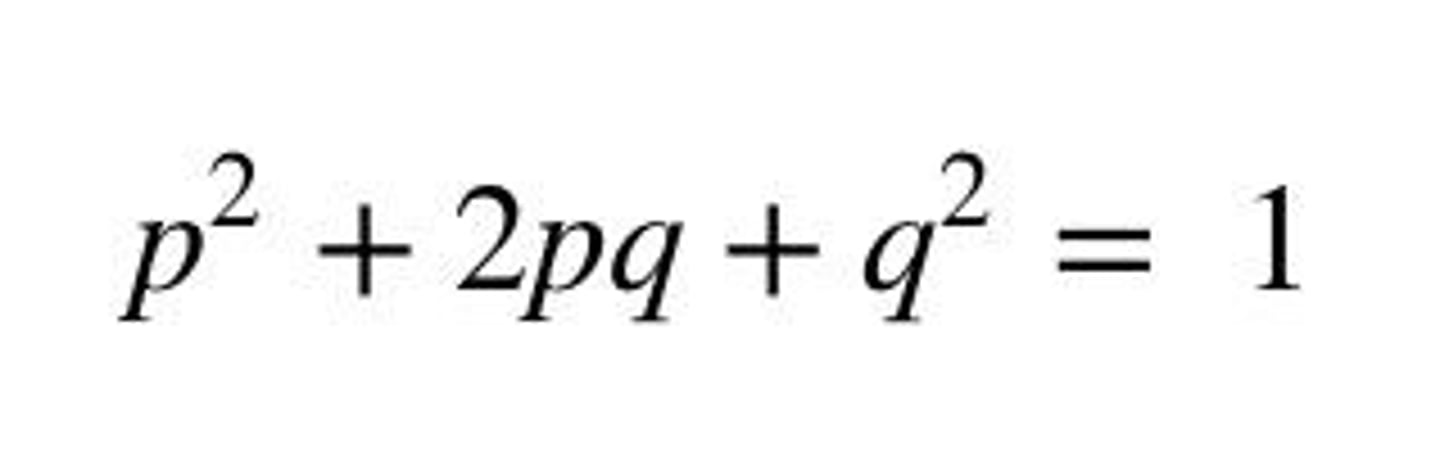
q
The frequency of the recessive allele in the Hardy-Weinberg equation.
p2
The predicted frequency of homozygous dominant (EE) individuals in a population.
Microevolution
Small-scale evolutionary changes within a population.
Natural selection
The process through which populations become better suited to their environments.
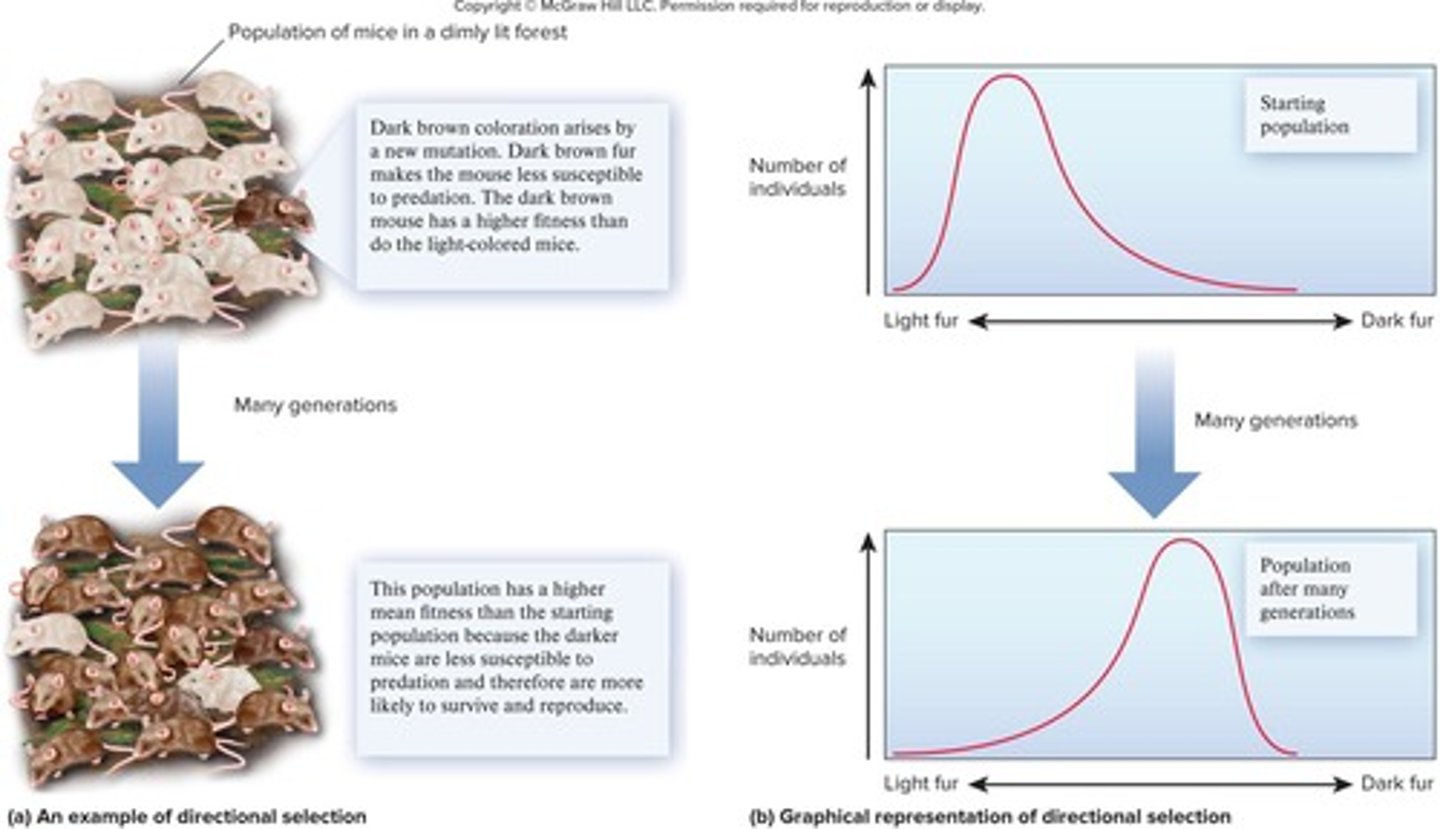
Directional selection
A type of natural selection that favors one extreme phenotype over others.
Stabilizing selection
A type of natural selection that favors intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes.
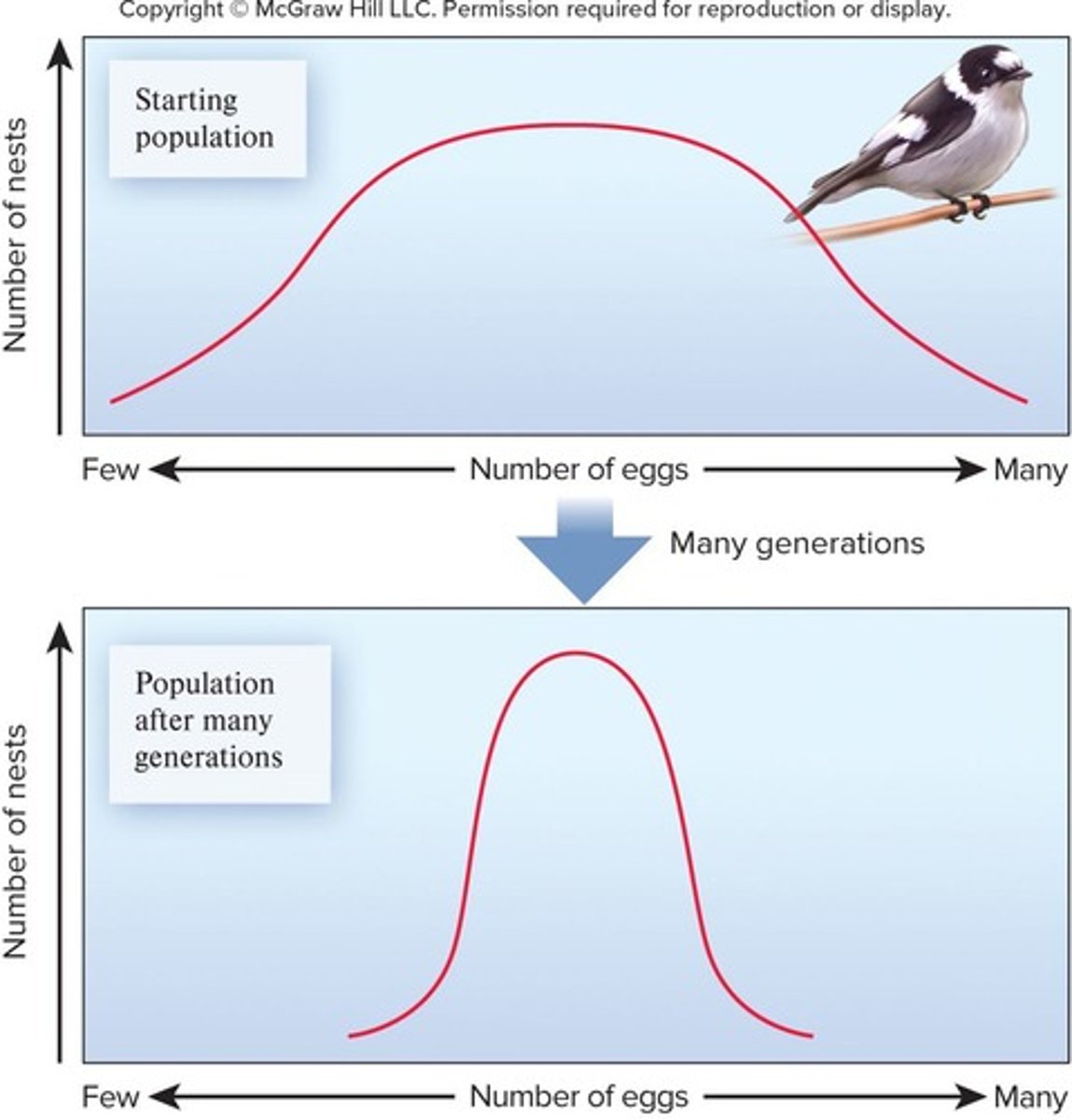
Diversifying selection
A type of natural selection that favors extreme phenotypes over intermediate ones.
Balancing selection
A type of natural selection that maintains genetic diversity in a population.
Intrasexual selection
A type of sexual selection where individuals compete directly for mates.
Intersexual selection
A type of sexual selection where individuals are choosy in selecting their mates.
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in a population, often having a more significant effect in small populations.
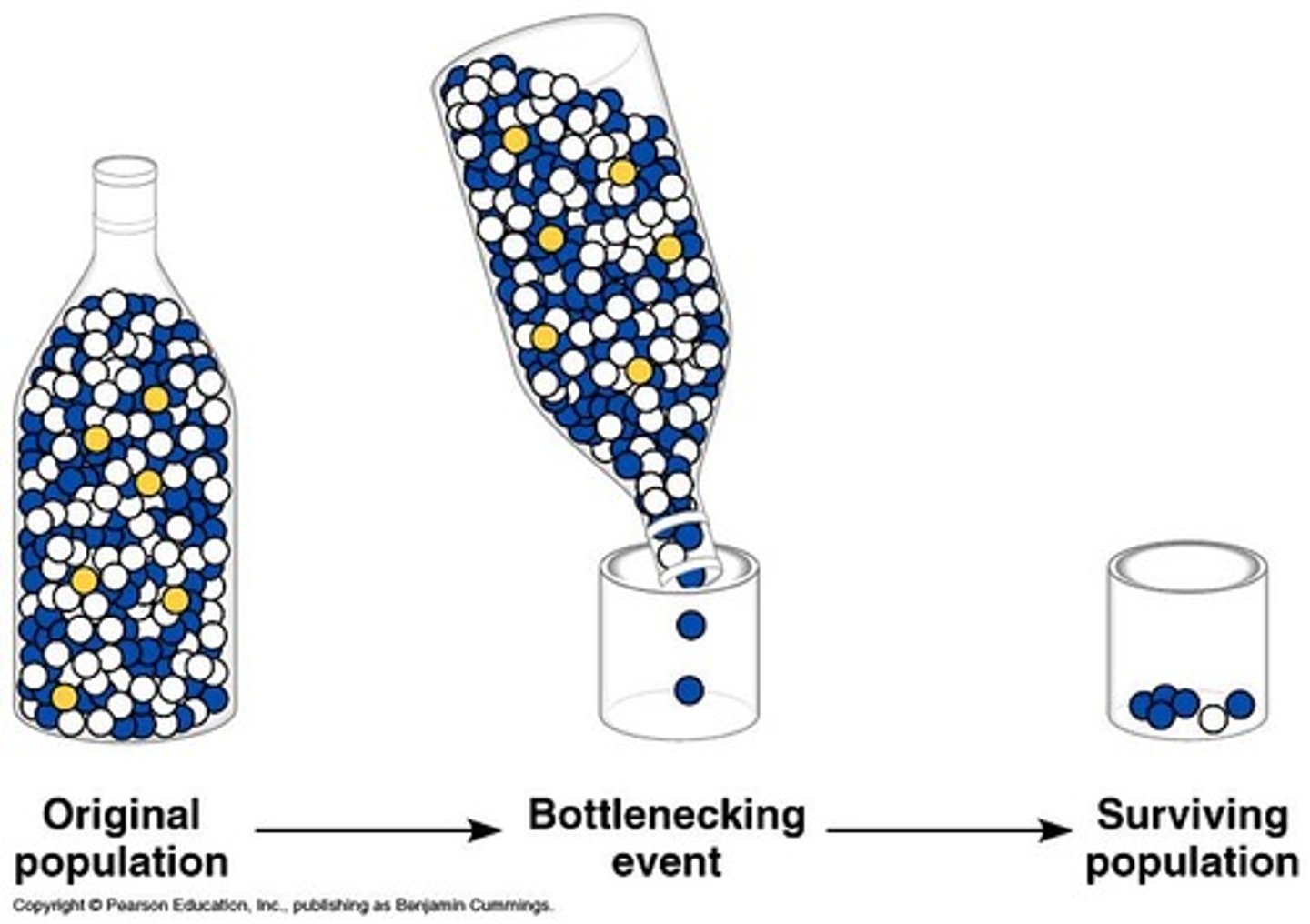
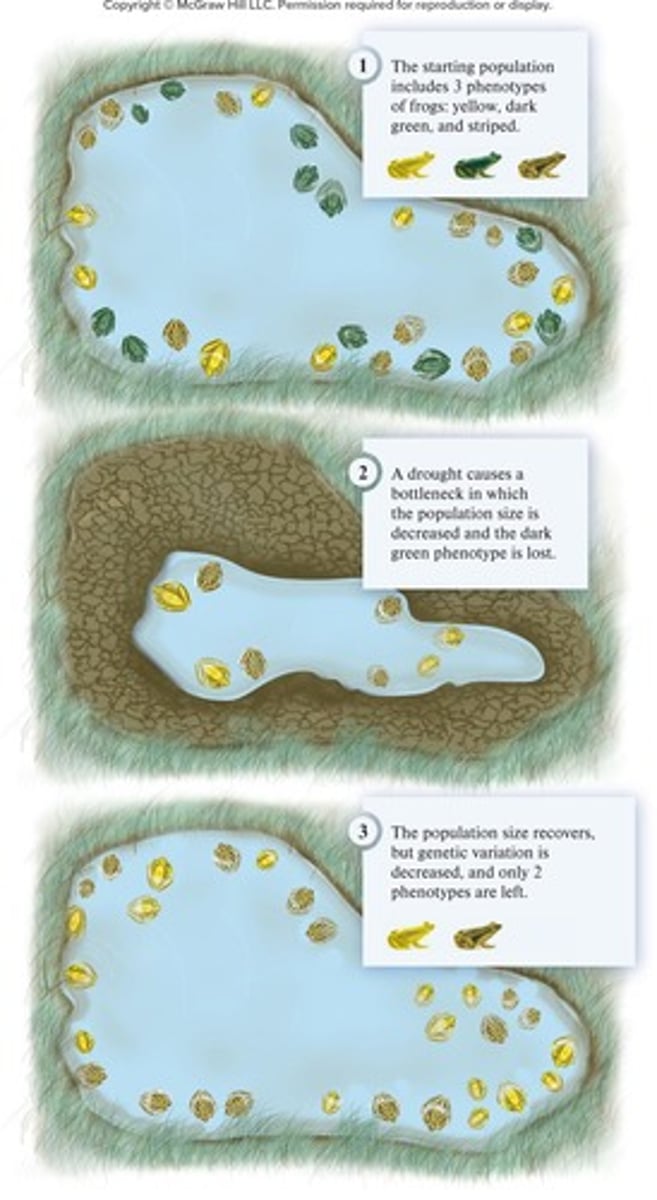
Bottleneck effect
A type of genetic drift that occurs when a population's size is significantly reduced, leading to a loss of genetic diversity.
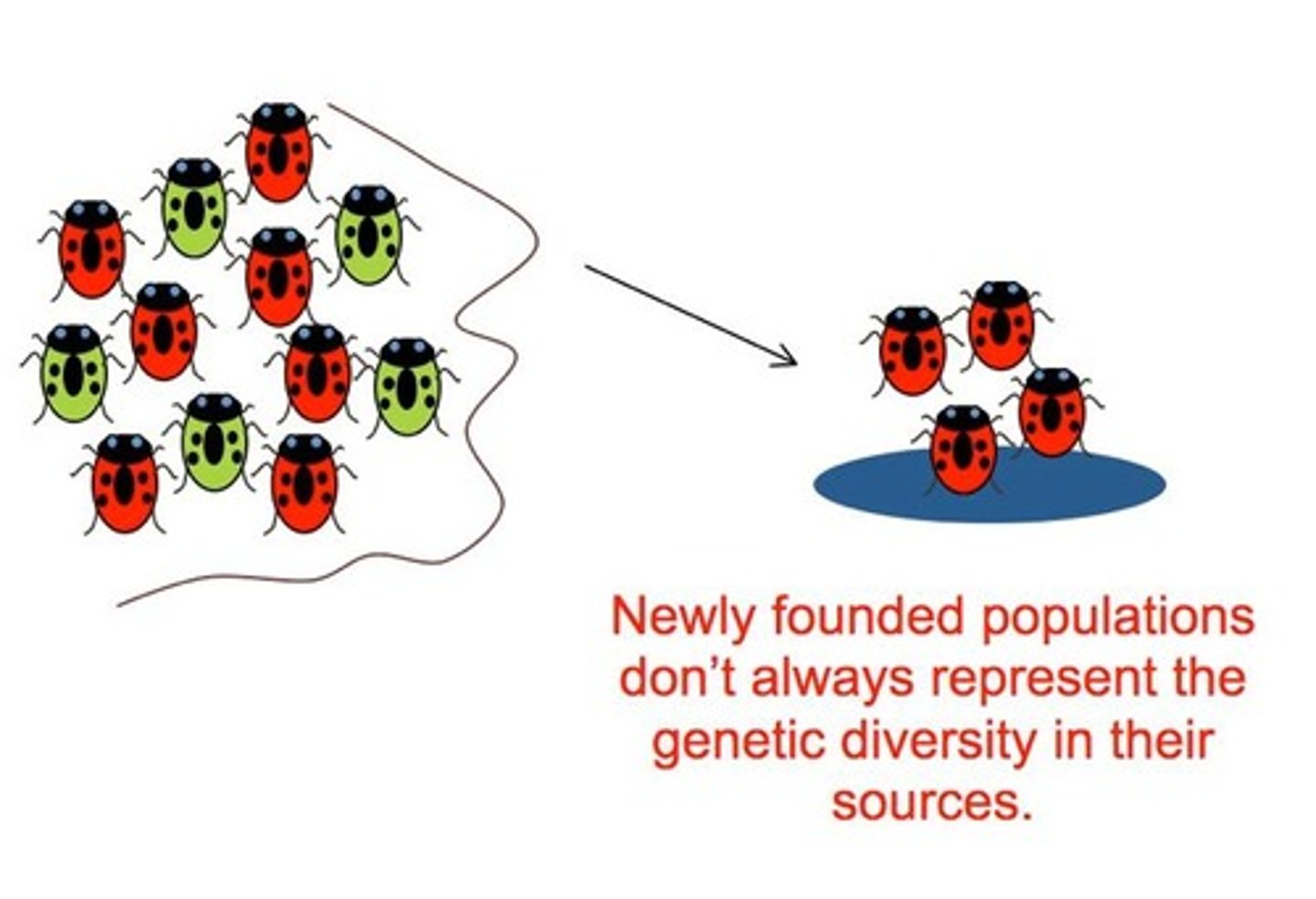
Founder effect
A type of genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals establishes a new population.
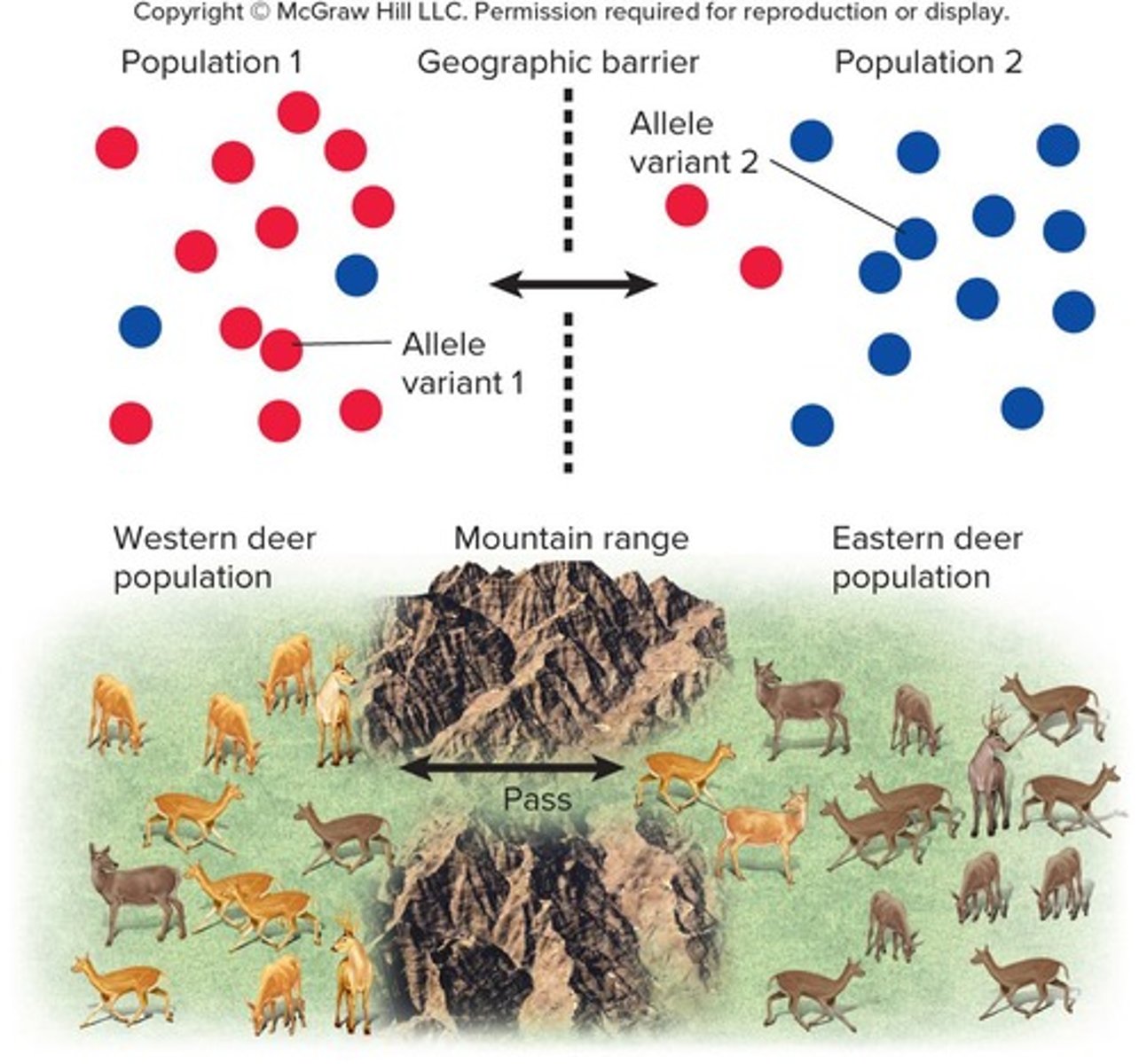
Gene flow
The transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another, often through migration.
Nonrandom mating
Mating that is not random, which can affect genetic variation in a population.
Inbreeding
Mating between closely related individuals, which can reduce genetic diversity.
Outbreeding
Mating between unrelated individuals, which can increase genetic diversity.
p2
the predicted frequency of homozygous dominant (EE) people in a population.
2pq
the predicted frequency of heterozygous (Ee) people.
q2
the predicted frequency of homozygous recessive (ee) ones.
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
Relates allele and genotype frequencies under specific assumptions.
Hardy-Weinberg Assumptions
Five rules that must be satisfied: no gene mutations, no migration, random mating, no genetic drift, no natural selection.
Microevolution
the change in the genetic makeup (gene pool) of a population from generation to generation.
Genetic Variation
Introduction of new genetic variation such as mutations to alleles and gene duplication.
Evolutionary Mechanisms
Factors that alter the prevalence of an allele or genotype in a population.
Natural Selection
the process in which individuals with certain heritable traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates.
Reproductive Success
the likelihood of an individual contributing fertile offspring to the next generation.
Directional Selection
shifts the frequency curve for variations in some phenotypic character in one direction or another.
Stabilizing Selection
acts against extreme phenotypes; favors the survival of the more common intermediate variants.
Diversifying Selection
favors the survival of two or more variants of opposite extremes over the intermediate individual.
Balancing Selection
does not favor the survival of one over the other, but maintains genetic diversity.
Sexual Selection
a form of natural selection where individuals with certain traits are more likely to successfully reproduce.
Intrasexual Selection
competition between members of the same sex for mating opportunities.
Intersexual Selection
members of one sex choose their mates from individuals of the other sex based on desirable characteristics.
Genetic Drift
The genetic fluctuation in allele frequencies due to random chance from one generation to the next.
Bottleneck Effect
A sudden change in the environment may drastically reduce the size of a population, killing members unselectively.
Founder Effect
Occurs when a small group of individuals becomes separated or isolated from a larger population and forms a new population in a new location.
Migration
The movement of individuals in or out of a population.
Gene Flow
The transfer of alleles into or out of a population.
Nonrandom Mating
Occurs when the probability that two individuals in a population will mate is not the same for all possible pairs of individuals.
Random Mating
When the probability is the same, individuals are just as likely to mate with distant relatives as with close relatives.
Inbreeding
Individuals are more likely to mate with close relatives than with distant relatives.
Outbreeding
Individuals are more likely to mate with distant relatives than with close relatives.
Tay-Sachs
A disease that is more common in people of Eastern European Jewish and French-Canadian descent.
Sickle Cell Anemia
A disease that is more common in people whose ancestry links back to certain parts of the world, such as Africa and Central and South America.
Genetic Variation
The diversity in gene frequencies within a population.
Population Size
The number of individuals in a population which affects genetic drift and variation.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene that may exist at a specific locus.
Fitness
The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment.
Behavioral Choices
Decisions made by individuals that influence their mating patterns.
Genetic Makeup
The unique combination of alleles that an individual possesses.
Environmental Change
A sudden alteration in the environment that can affect population size and genetic variation.
Genetic Exchange
The transfer of genetic material between populations through migration.
Population Representation
The degree to which a small population reflects the genetic diversity of the original population.
Genetic Diversity
The total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species.
Recessive Alleles
Alleles that do not manifest in the phenotype unless two copies are present.
Ethnic Group
A community of people who share a common cultural background.