earth science and astronomy
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
solar wind
stream of high-energy particles sent into space which causes the light displays
aurora borealis
if seen from the Northern Hemisphere
aurora Australis
Southern Hemisphere
prominences
storms that look like huge arches extending outward the Sun’s surface that could last for several days
solar flares
more intense than prominences and last for only about 15 minutes
sunspots
dark, cooler parts of the Sun’s surface caused by changes in the sun’s magnetic field
sun
the only in the solar system; a ball of hot plasma that serves as the source of heat and light; holds 99.8% of the mass of the solar system
mercury
smallest planet; closest to the sun; no atmosphere
venus
– hottest planet in the solar system; slowest rotation among the solar system’s planets; Earth’s “twin sister”
earth
only known planet in the universe that supports life; within the “Goldilocks zone” maintaining water to remain liquid
mars
the red planet, its reddishness resulting from abundant presence of iron oxide
jupiter
– largest planet in the solar system; a gas giant mainly composed of hydrogen and helium; famous for its “Great Red Spot”
saturn
also a gas giant; known for its “ring system”
uranus
a gas giant; methane ice responsible for its bluish color; coldest planet
neptune
gas giant; farthest planet from the sun; only planet not visible to the naked eye
pluto
dwarf planet; a year in ——— is equal to 248 Earth years
248
one pluto year is equal —- earth years
earth’s moon
Earth’s only natural satellite; brightest object in the night sky
asteroids
“minor planets”; rocky objects that orbit the sun
jupiter saturn uranus neptune
planets that are gas giants
meteoroid
smaller than asteroids; “space rocks”
meteor
meteoroids entering the Earth’s atmosphere at high speed burning up; also referred to as “shooting stars”
meteorite
a fragment of an asteroid, comet, or meteoroid that survived its passage through the atmosphere and reached the Earth’s surface
polaris
north star; the tip of Little Dipper’s “handle”
sirius
brightest star in the night sky; “Dog Star”
ursa major
Big Bear; contains the Big Dipper
ursa minor
Little Bear; contains the Little Dipper
canis major
Big Dog; contains Sirius
canis minor
– Little Dog
orion
The Hunter
tres marias
form the belt of the constellation Orion
proxima centauri
closest star to Eart but too small to be seen in the night sky
alpha centauri
closest star to the Earth that is visible in the night sky
pegasus
The Winged Horse
light year
the distance light travels in one year
milky way
the galaxy where the solar system belongs in
supernova
explosion of a big star
black hole
areas in space with a very strong gravitational field that even light cannot escape
new moon
the moon is positioned between the Earth and the Sun, with the illuminated side facing away from Earth
waxing crescent
where a thin sliver of the moon's surface becomes visible and appears to be growing larger
first quarter
where the moon appears half illuminated, specifically the right side in the Northern Hemisphere
waxing gibbous
moon that is more than half illuminated and is increasing in illumination, moving towards a full moon
full moon
occurs when the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, resulting in the entire near side of the Moon being illuminated and visible from Earth
waning gibbous
the moon phase when it is more than half illuminated but less than fully illuminated, and the illuminated portion is decreasing in size
third quarter
a phase in the moon's cycle where half of the lunar surface appears illuminated from Earth, specifically the left half in the Northern Hemisphere and the right half in the Southern Hemisphere
waning crescent
the last visible phase of the moon before it becomes a new moon
new moon waxing crescent first quarter waxing gibbous full moon waning gibbous third quarter waning crescent
phases of the moon
spring tides
strongest tides; occurs when the sun, Earth, and moon line up (every full moon and new moon); the sun and the moon’s gravities add up
neap tides
moderate tides; occur when the positions of the sun, Earth, and moon produces a right angle. Related concept: moon, winds, and earthquakes all can cause water waves; cause tidal waves, normal waves, and tsunamis respectively.
crust mantle core
what are the compositional layers
crust
outermost layer
mantle
composed of aluminum and silicates
core
mainly composed of iron and nickel
lithosphere asthenosphere mesosphere outer core inner core
the mechanical layers
lithosphere
includes the crust and top of mantle
asthenosphere
“plastic layer” where mantle flows easily
mesosphere
includes the lower mantle, where the mantle flows slower than the asthenosphere
outer core
– iron and nickel composition; liquid layer; produces the Earth’s magnetic field
inner core
– iron and nickel composition; different with outer core since it is solid due to intense pressure
10 to 70km
continental crust thickness
5 to 7km
oceanic crust thickness
2900km
core thickness
10 to 200km
range of lithospheric thickness
660km
the depth of the upper mantle boundary beneath Earth's surface.
5150km
the depth of the outer core boundary beneath Earth's surface.
6396km
the average radius of Earth.
mantle outer core inner core crust
thickest to thinnest layer of the earth
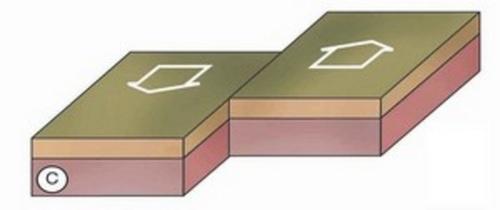
transform plate boundary
area where two plates slide past each other horizontally; causes earthquakes
divergent plate boundary
area on Earth where plates move away from one another;occurs at mid-oceanic ridges
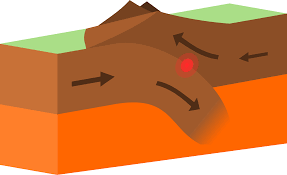
convergent plate boundary
area on Earth where lithospheric plates collide together/move toward each other
transform plate boundary
convergent plate boundary
divergent plate boundary

continental continental
– occurs between two continental plates where their collision results in little to no subduction; creates mountains
oceanic continental
occurs between an oceanic plate and continental plate; the oceanic plate subducts beneath the less dense continental plate; creates volcanic ranges
oceanic oceanic
occurs between two oceanic plates; the older (and cooler) plate subducts beneath the younger one; forms an island arc; the Philippines is an example of an island arc
continental continental
forms mountains
oceanic continental
forms volcanic arcs.
oceanic oceanic
forms island arcs
magnitude
the size of the earthquakes; measured using the Richter Scale
richter scale
magnitude is measured using the
focus
a point at some depth in the crust where the earthquake originates
epicenter
the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus
p waves
longitudinal waves; seismic wave that can travel within the Earth’s surface and can pass through all kinds of medium: solid, liquid, and gas. faster than the other wave
s waves
transverse waves; can pass through solids; side-to-side shaking of the surface
love waves
surface waves moving parallel to the Earth’s surface; perpendicular to the wave propagation direction
rayleigh waves
surface waves moving in elliptical, rolling motion
igneous
rocks that are formed by the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
metamorphic
rocks that are subjected to heat and pressure
sedimentary
rocks formed by the accumulation of deposits of rocks fragments, minerals, and/or fossils
rock
a naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals
weathering
breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces
erosion
transport of sediment from one place to another
deposition
dropping/settling of sediment by factors such as ice, wind, water, and/or gravity.
Talc Gypsum Calcite Fluorite Apatite Orthoclase Quartz Topaz Corundum Diamond
mohs scale of hardness
Fossils
are preserved remains of plants and animals found in rock, soil, or amber
paleontology
the study of ancient and prehistoric life through fossils
trace fossils
preserved evidences of movement and activity of an organism that lived in the past such as tracks and burrows.
continental drift theory
proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912
continental drift theory
suggests that continents are once united in a supercontinent called Pangaea but drifted apart until they arrived at their relative position right now.