Clouds
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Clouds and Fog Formation
● Cloud type is dependant on stability and moisture content.
● In order to get clouds or fog the water vapour must change into a liquid (water droplets) or solid (ice crystals) to form.
➢ In other words for clouds to form the air must become saturated.
● There are a number of ways that this can happen:
➢ By lowering the air temperature to the dew point temperature, most common is by rising air (lifting process).
➢ By adding water vapour into the air.
➢ By mixing warm moist air with cold air
Cloud coverage
● Cloud coverage is reported in oktas or eighths of the celestial dome.
● For weather reports these are broken up into five basic categories:
➢ SKC: Clear Sky.
➢ FEW: 1/8 to 2/8 of the sky covered.
➢ SCT: Scattered, 3/8 to 4/8 of the sky covered.
➢ BKN: Broken, 5/8 to less than 8/8 covered.
➢ OVC: Overcast, 8/8 covered.
Ceilings
● A ceiling is said to exist whenever the sky is either BKN or OVC.
○ Remember, in this case the cloud coverage is equal to or greater than 5/8ths of the sky covered.
○ VFR pilots are NOT permitted to fly above a BKN or OVC layer.
○ (Unless they have a VFR OTT rating )
● A ceiling will also be defined by a Vertical Visibility (VV) on a METAR or in a TAF.
○ Example: VV001=Ceiling obscured at 100 feet
● Ceilings are depicted on the GFA with a scalloped border
Cloud Classification
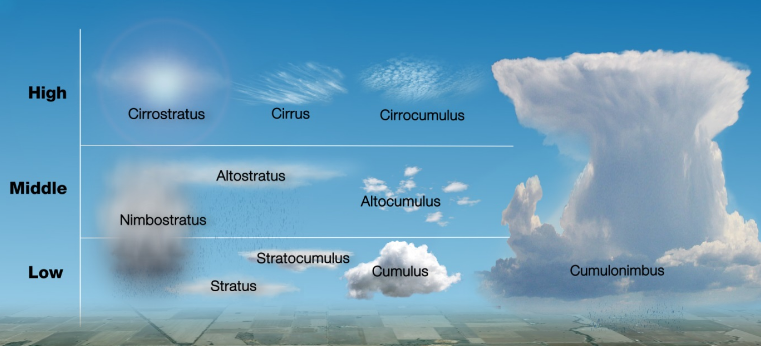
● Clouds are classified into four families based on their height and vertical development, i.e. strati-form or cumuli-form.
● Stratiform develop horizontally and cumuliform family develop vertically.
● Stratus family is associated with fog and low clouds with poor visibility.
● This system of classification describes the approximate altitude and appearance
● High Clouds
● Middle Clouds
● Low Clouds
● Clouds with Vertical Development
High Clouds
● These are clouds found at altitudes between 20000 ft and 40000 ft.
● They include:
➢ Cirrus (CI)
➢ Cirrostratus (CS)
➢ Cirrocumlulus (CC)
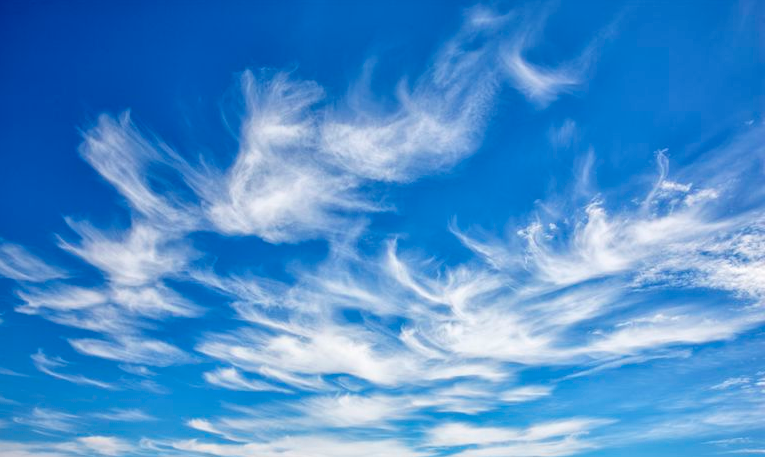

Cirrus (CI)
● High and Wispy.
● Typically found at heights greater than 20 000 feet.
● Generally occur in high pressure systems, and fair weather.
● They will point in the direction of air movement at their elevation.
● Mainly composed of ice crystals.
● A ragged windswept appearance of the Cirrus Clouds is always an indication of very strong winds or jet streams

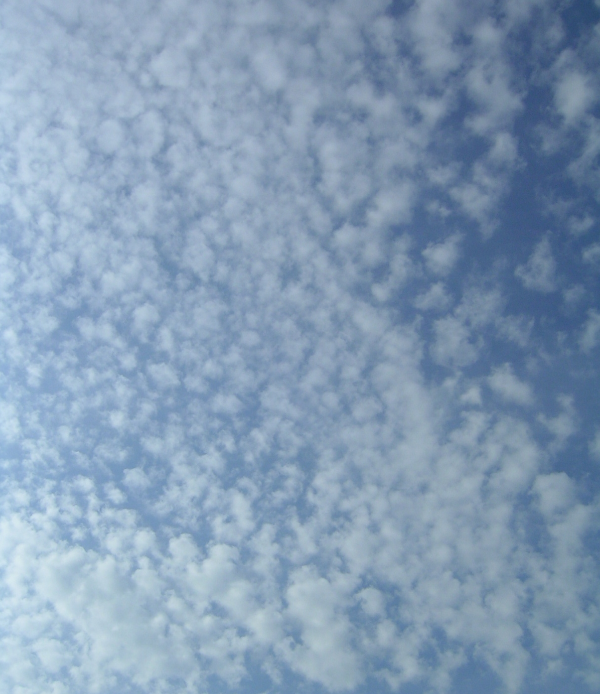
Cirrostratus (CS)
● Sheet-like high-level clouds composed of ice crystals
● Cirrostratus clouds tend to thicken as a warm front approaches signifying an increased production of ice crystals

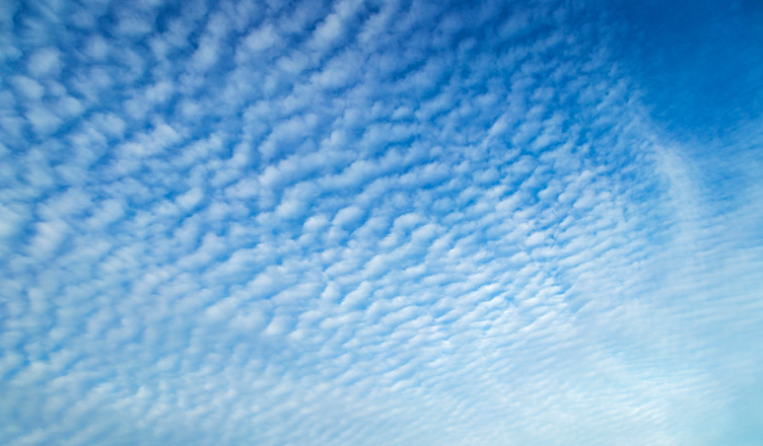
Cirrocumulus (CC)
● Somewhat rare.
● Appears as a white sheet with a pebbly pattern.
● Characterized by high ice crystals
Middle Clouds
● Found at altitudes between 6500 ft to 20000 ft.
● Types:
➢ Altostratus (AS)
➢ Altocumulus (AC)
➢ Altocumulus Castellanus (ACC)
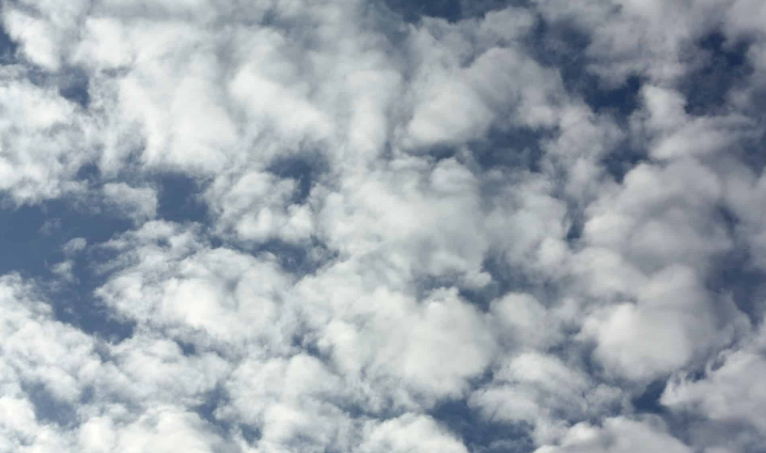

Altocumulus (AC)
● These are puffy “cotton ball” type clouds.
● On a warm and humid summer morning they may be followed by thunderstorms as the day progresses.
● Icing is usually present in the cloud above the freezing level and will be especially heavy near the top of the cloud

Nimbostratus (ST)
● Low layer cloud. Smooth air.
● Resembles fog but does not rest on the ground.
● No waves or patterns, “grey.

Altostratus (AS)
● Layer cloud with no definite pattern.
● Steely or bluish in color.
● Sometimes the sun or moon can be seen dimly through.
● Altostratus clouds make the sun seem to appear to be behind heavily frosted glass.
● Incapable of producing heavy precipitation but often cause light drizzle

Alto Cumulus Castellanus (ACC)
● Created from instability associated with air flows having marked vertical shear and weak thermal stratification
Low Clouds
● These are clouds found at altitudes between the surface to 6500 ft.
● Types:
➢ Stratus (ST)
➢ Nimbostratus (NS)
➢ Stratocumulus (SC)
➢ Stratus Fractus (SF)
➢ Cumulus Fractus (CF)

Stratus (ST)
● Stratus clouds are known for drizzle or freezing drizzle.
● Updrafts associated with Stratus clouds are very weak so that the larger droplets in the cloud tend to settle earthward.
● As they sink they strike and coalesce with other droplets and grow.
● Finally they sink out of the cloud base as drizzle

Nimbostratus (NS)
● Dark, low-level clouds often accompanied by steady, light to moderate continuous precip.
● Low clouds are primarily composed of water droplets since their bases generally lie below 6 500 feet.
● The prefix ‘nimbus’ indicates precipitation

Stratocumulus (SC)
● Low, lumpy layer of clouds.
● Sometimes accompanied by weak intensity precipitation.
● Precipitation with varying intensity, from light to heavy showers.
● Main producer of drizzle.

Stratus Fractus (SF)
● Stratus cloud that has been torn by wind into fragments.
● Drizzle may fall from these clouds

Cumulus Fractus (CF)
● Stratocumulus torn by wind .
● These can be differentiated from Stratus Fractus by their more rounded tops

Cumulus (CU) Fair Weather
● Appearance of floating cotton or "popcorn popping" and have a lifetime of 5-40 minutes.
● Indicates the presence of significant vertical currents at low levels without precip.
● With the proper conditions, harmless fair weather cumulus can later develop into TCU and then CB
Clouds of Vertical Development
● Cumulus (CU).
● Towering Cumulus (TCU).
● Cumulonimbus (CB).
● Alto Cumulus Castellanus (ACC).
● Have high proportion of supercooled water while developing.
● As the cell ceases to grow ice crystals will be found.
● In new growth CBs for example, icing will be severe.
● Horizontal extent of icing is minimal
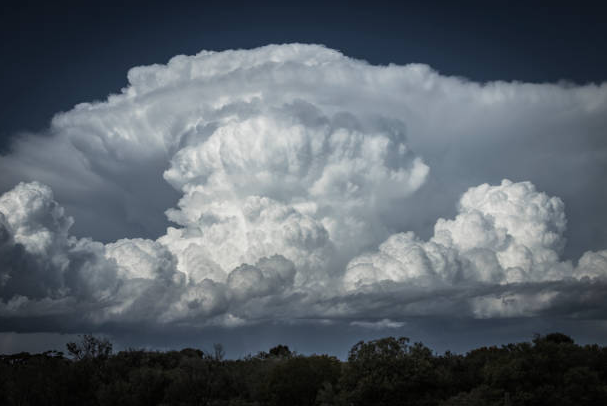

Towering Cumulus (TCU)
● Growing cumulus cloud.
● On the way to becoming a Cumulonimbus
Cumulonimbus (CB)
● Violent vertical currents that at times are in excess of 50 KT and contain the greatest turbulence.
● Depending on the height of the troposphere and the buoyancy of the updraft, the tops of cumulonimbus clouds can reach up to 60 000 feet.

Mammatus
● Powerful cumulonimbus clouds may have appendages protruding from the base of them called Mammatus clouds.
● Mammatus clouds indicate that the atmosphere is extremely unstable.
● Severe weather is imminent.
● Funnel clouds may also be associated, STEER WELL CLEAR!!
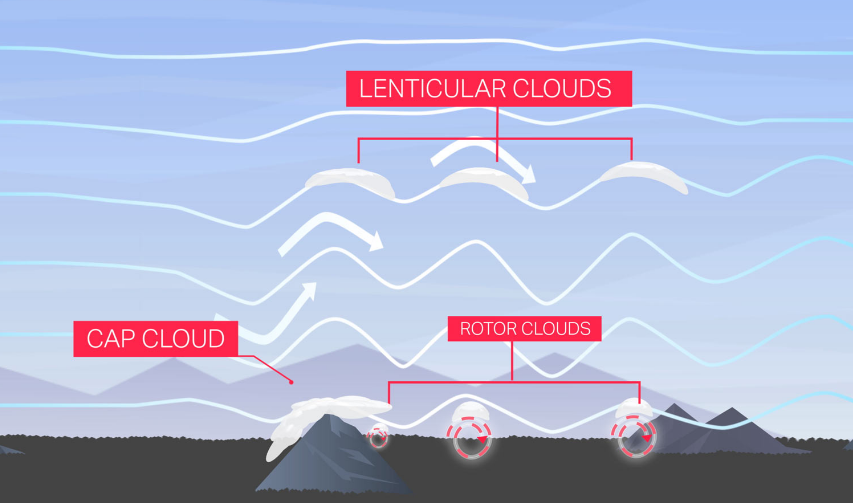
Orographic Clouds
● Developed when air is forced to rise by the earth's topography
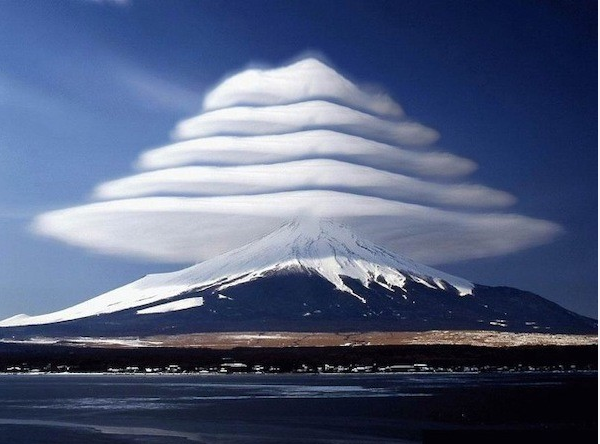
Mountain Wave Clouds
Lenticular Clouds
● Forms in the wave crest very high and hundreds of miles long


Rotor Clouds
● Associated with mountain wave activity.
● Form downwind and below each mountain wave crest.
● These are dissipating and forming at the same time due to the
rotation of the air
Cap Cloud
● Lies over the top of the mountain and extends partially down the leeward slopes, indicating an extremely strong downdraft

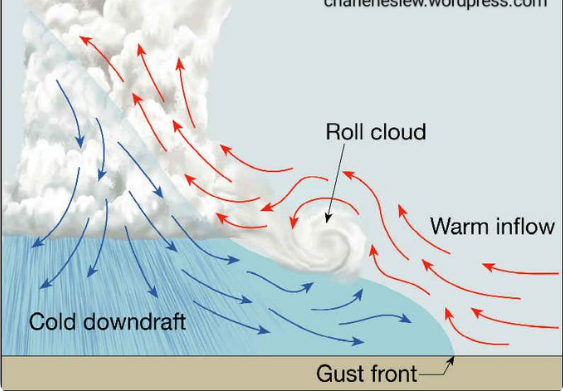
Roll Cloud
● Associated with thunderstorms.
● May form near the main cloud base in the shear area where the downdraft comes out