Archer: Pediatrics
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
apgar
apperance, pulse, grimace, activity, respiration
scored from 0-2
max score is 10
APGAR: apperance
0 points-blue/pale
1 point-pink body
2 points- pink
APGAR: Pulse
0- absent
1- below 100
2- above 100
when do you do APGAR
1 mins and 5 mins
newborn HR normal
100-160
newborn respirations
50-70
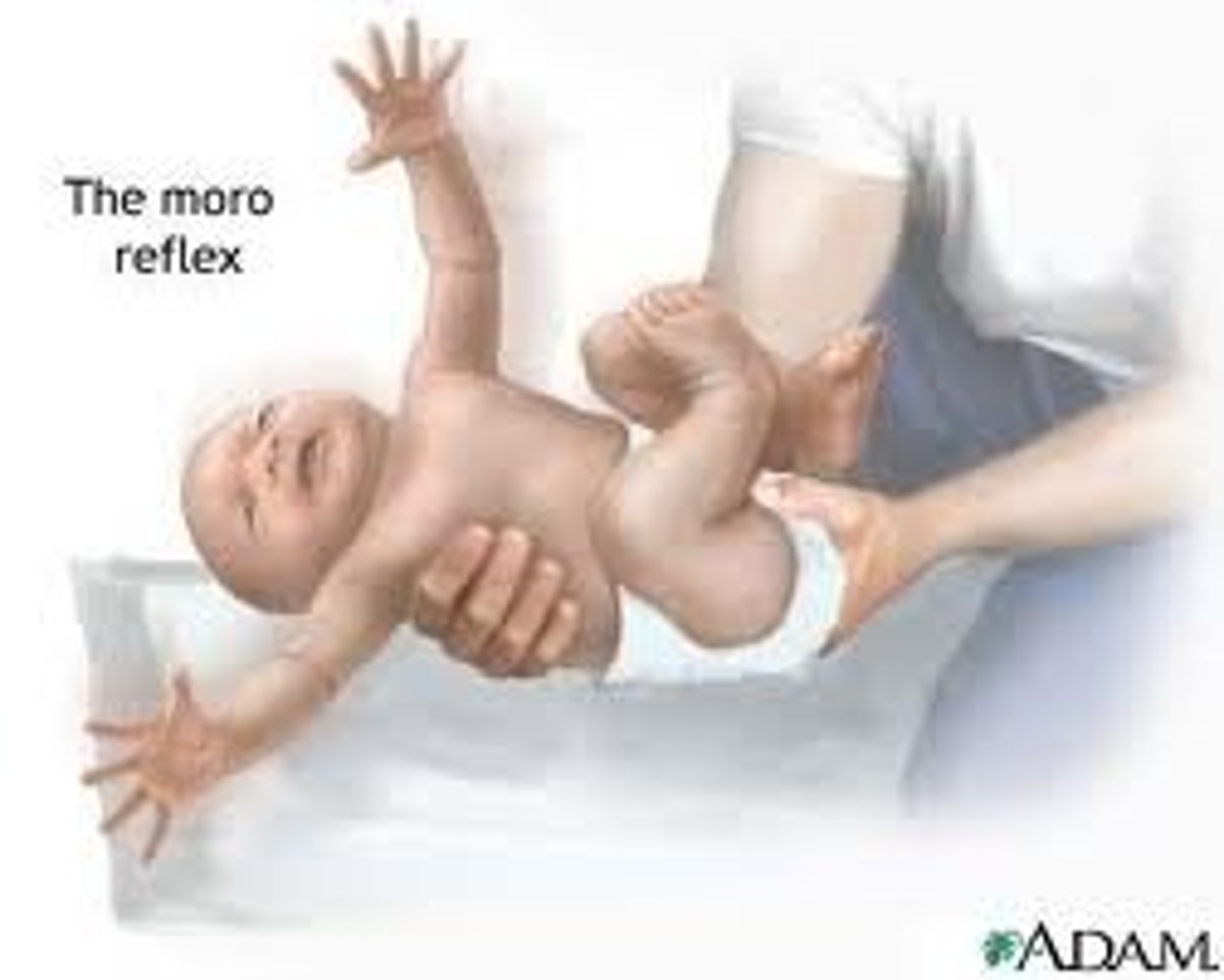
Moro reflex
startle reflex
rooting relfex
Reflex in baby's to open their mouths to feed when touched near the mouth.
sucking reflex
when you stroke a hungry infant's lips, he will start sucking
Babinski reflex
Reflex in which a newborn fans out the toes when the sole of the foot is touched
disappears in 12 months
when do fontanelles close
anterior- closes between 6-18 months
posterior-closes by 2 months
children have what in cardiac
children have an extra wooshing heart sound
normal to hear murmurs
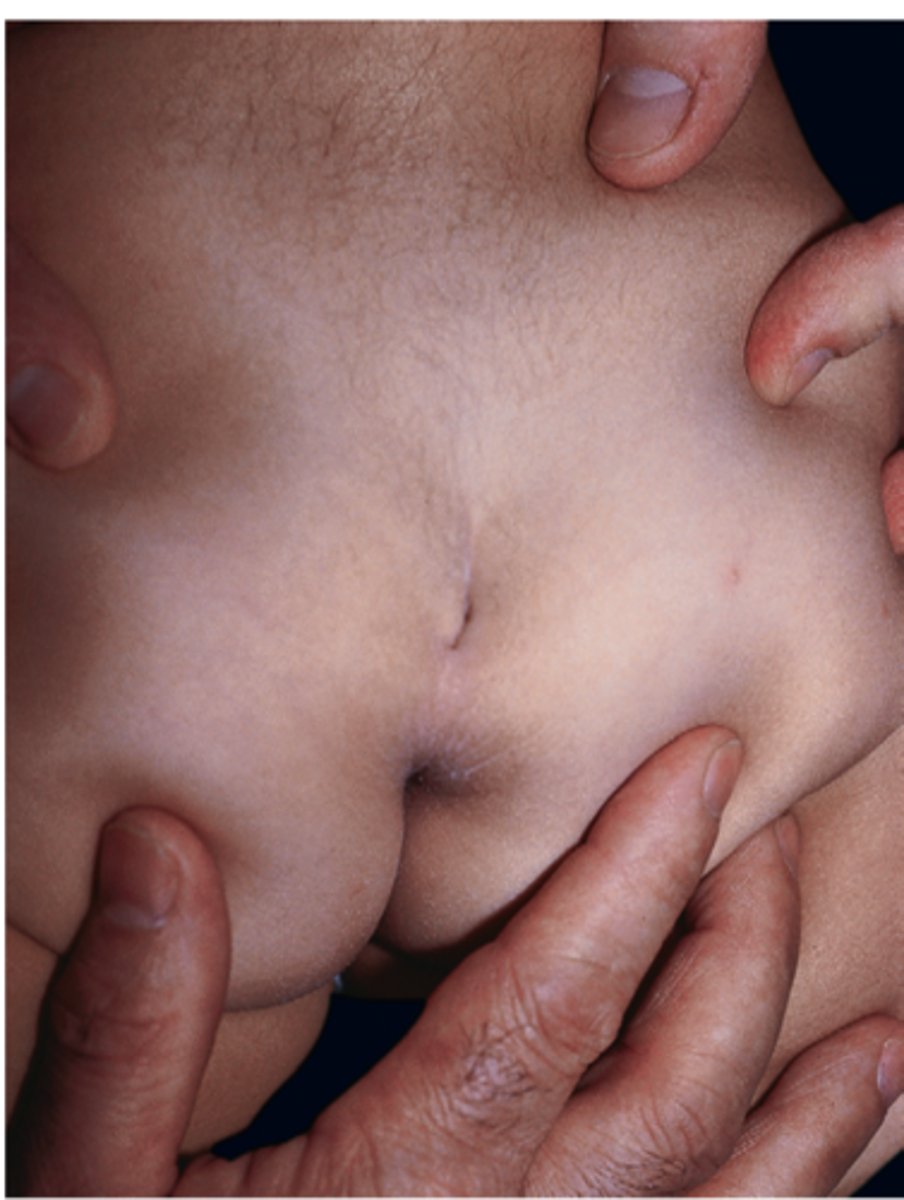
sacral dimple
opening in the skin over the distal spine
might have neuro issues
interventions for meconium aspiration
suction the mouth first immediately after birth
may meed intubation
What indicates meconium aspiration
seeing the meconium
fouls smelling aminotic fluid
discoloration of cord
discoloration of nail/ tongue on infant
physiological jaundice
normal that appears in first 2-3 days of life
pathological jaundice
occurs within 24 hrs of life
could be issues with liver or ABO incompatibility
kernicterus
a type of brain damage that results from high level sof bilirubin in the blood
how to prevent kernicturus
phototherapy that breaks down bilirubin
cover their eyes and genitals (sensitive skin)
this breaks down bilirubin but it does not get rid of it so we need to feed often
fetal circulation lungs
mom is doing oxygenation, no need for blood to go to lungs
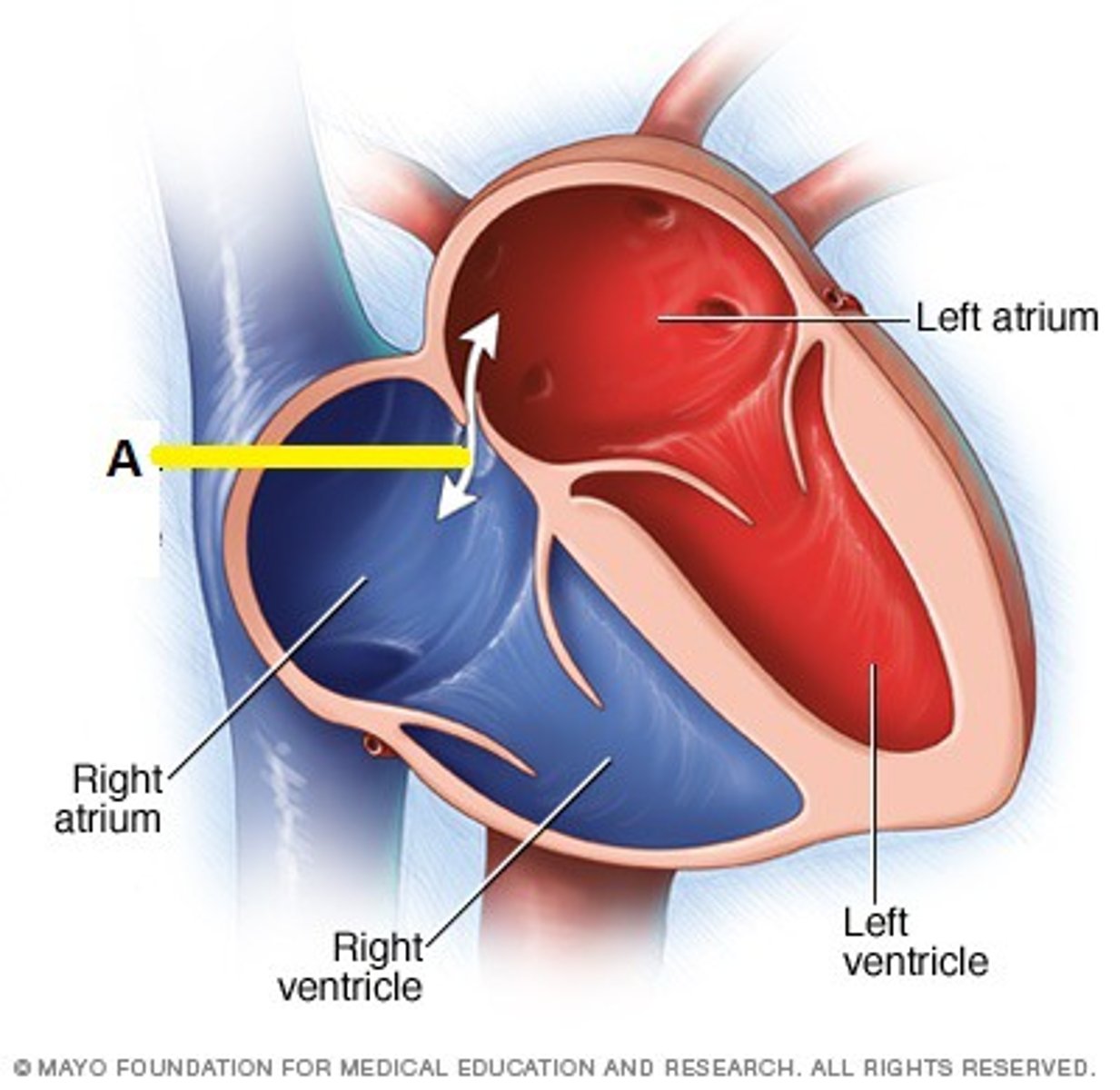
foramen ovale
connects the two atria in the fetal heart
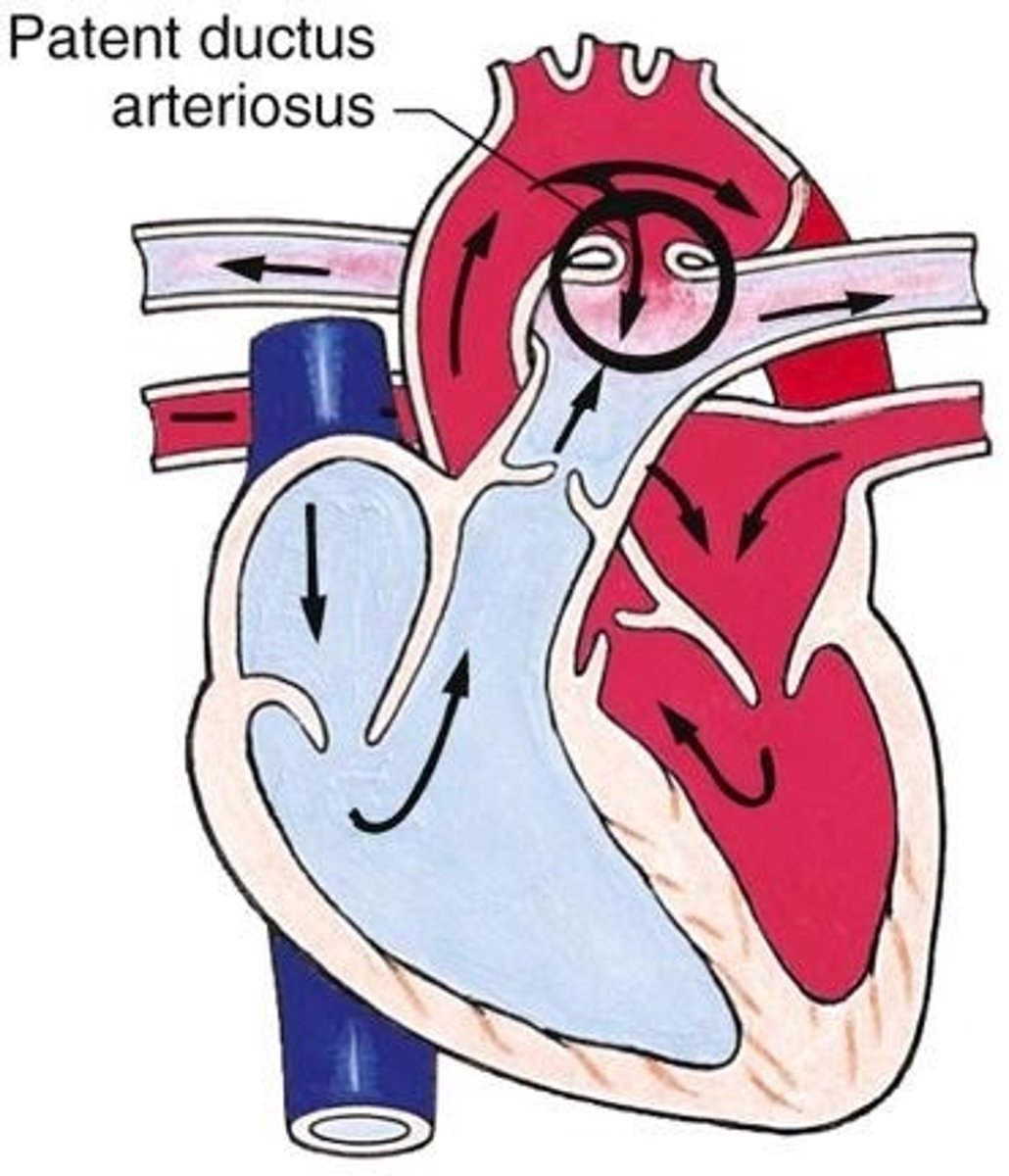
ductus arteriosus
a blood vessel in a fetus that bypasses pulmonary circulation by connecting the pulmonary artery directly to the ascending aorta
atresia
does not develop
ductal dependent
dependent on ductus arteriosis for shunting
left to right shunt
causes pulmonary circulation but not cyanosis
because remember the left part has highest pressure so the rests of the body is still gettiong some sort of blood flow
risk factors for heart sunts
maternal infection
maternal diabetes
drug and alc use
advacned maternal age
right to left shunt
shunt causes cyanosis
patent ductus arteriosus assessmet findings
machine like murmur
treatment for PDA
surgery
indomethacin or ibuprofen (antiprostiglandins that clsoe these ductus)
alprostadil
medicaiton that can be administered to keep PDA open in certain heart defects
can allow blood to get out to the body when otherwise couldn't
Artrial septal defect
opening between the atria
will hear murmur
tx surgery or if small can close on its own
child will have DOE fatigue and poor weight gain
ventricular septal defect
opening between two ventricles, typical s/s of HF begin at 2-8 weeks
LOUD MURMUR ADN CHF
tx- CHF TX AND BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITICS PROPHYLACTICS
CHF management
diuretics, ACE inhibitors, b-blockers
atrioventricular canal defect
opening betwene the atria and ventricles (ASD VSD and single AV valve)
mur,ur + heart failure s/s + failure to thrive
tx- tx for CHF and. bacterial prophy;actics
when surgically repairing a heart defect, what must you do
give antibiotics prophylactically
tetralogy of fallot
defects
large VSD
pulmonary stenosis
right ventricular hypertrophy
overriding aorta
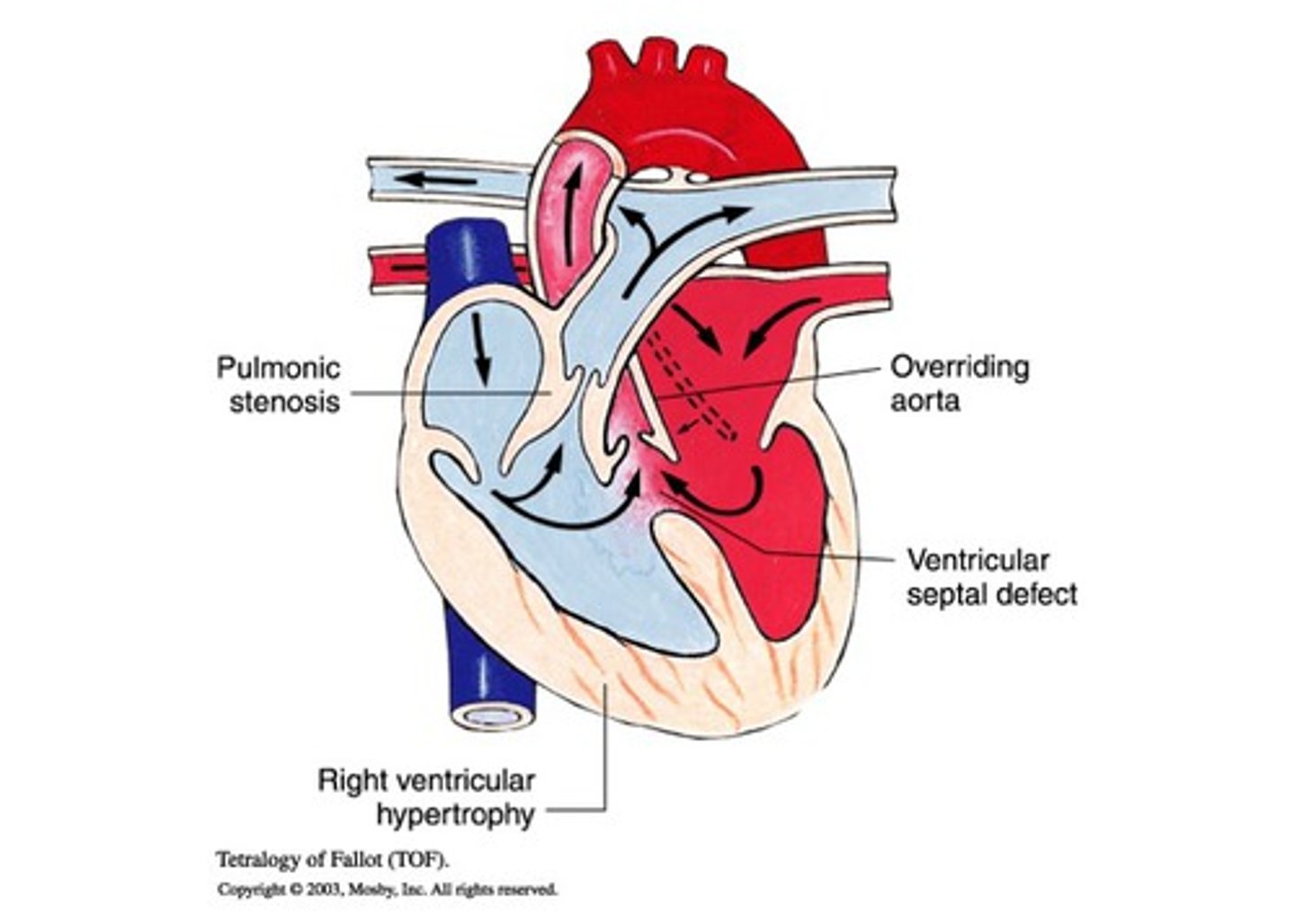
tet spells
begins with irritability and hyperpnea
a drop in systemic vascular resistance incrase the right to left shunt and decreases pulmonary blood flow
hypoxic spells, intense cyansosi that leads to sycnope
tet spell interventions
comoft and calm
kneww to chest
supplemental oxygen
sedation-morphone
volume
tricuspid atresia
the tricuspid valve does not grow
VSD/ASD
hypoplastic RV enlarge mitral valave dn LV
tricuspid atresia treatment
Prostaglandin to maintain patency of PDA, Surgical Repair (rashkind procedure)
transposition of great arteries
the aorta and pulomnary artery are switched\
oxygenated blood is continously circulating through the pulmonary circut and deoxygenated blodo is cirulating through the systemic area
assesment - cyanosis within 1 hour of birth
transposition of great arteries management
prostaglandins to keep ductus arteriosis opne
surgical repair
bacterial endocaridditis for life
hypoplastic left heart syndrome
left sided structures don't develop normally
aorta is small
what happens to baby with hypoplastic left heart syndrome
cardiogenic shock is common
cyanosis when DA closes
assessment findings for hypoplastic left heart syndrome
hepatomegaly, murmur
hypoplastic left heart syndrome immediate interventions
prostagalandins
correct acidemia
inotropes
plan for surgery
hypoplastic left heart syndrome procedures
norwood at birth
glenn at 2 months old
fontan at 2 years old
aortic stenosis
narrowing of the aortic valve
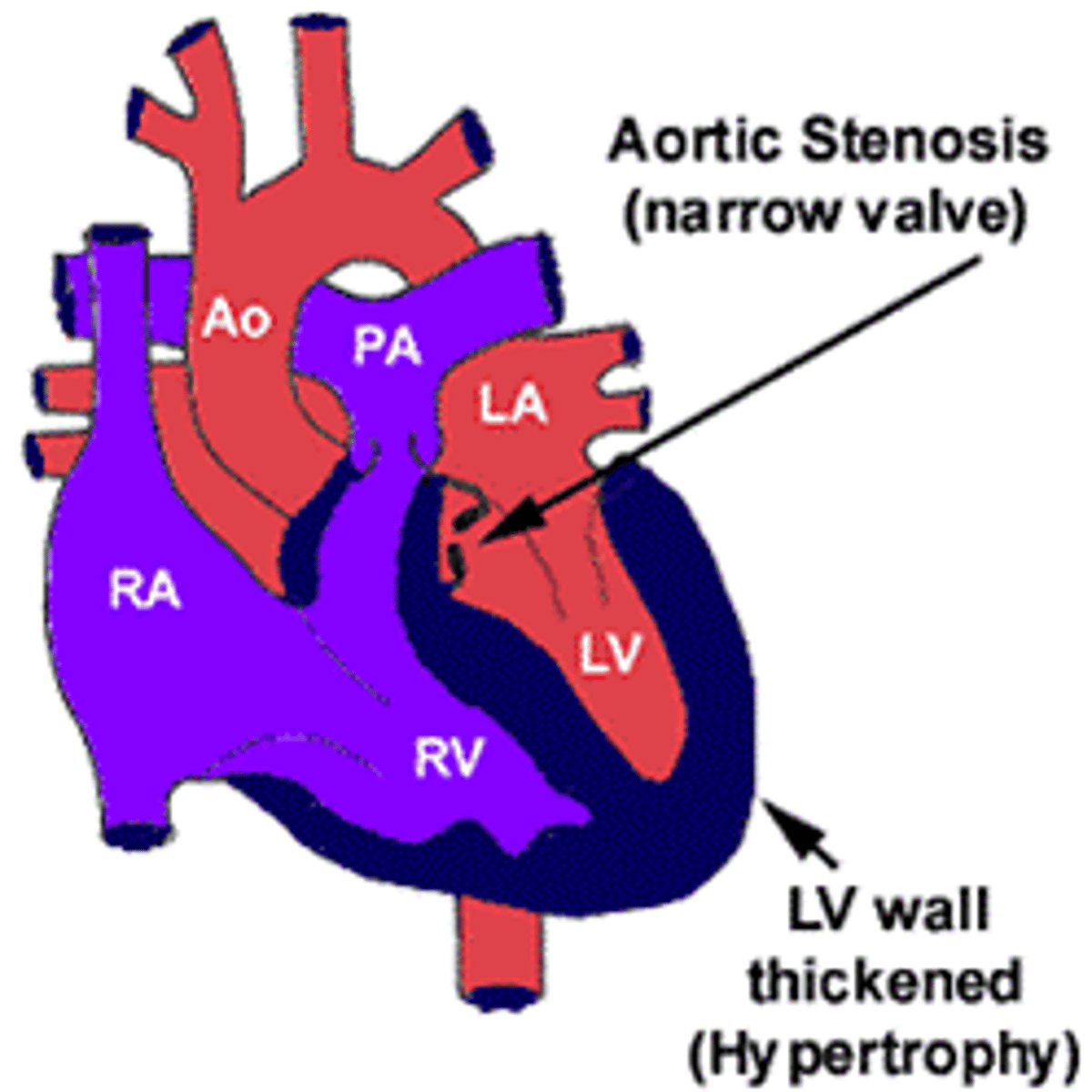
aortic stenosis assessment findings
pronounced apical pulse
thrill
exercise intolerance and syncopal episodes
narrowed pulse pressure
treatment of aortic stenosis
balloon valvuloplasty asap to pevent shock
surgical valve replacement
if sever- avoid exercise
pulmonary stenosis
narrowing of pulmonary artery
leads to RV hypertophy
specific assessment for pulmonary stenosis
dyspnea on exertion
murmur
treatment of pulmonary stenosis
pulmonary valvotomy
moderate to severe stenosis; child should avoid high intensitty activities
coarctation of the aorta defect
narrowing of the aorta
impedes blood flow to lower half of body
symptoms appear quick as soon as the arerious close can progress to hypotension acidosis and shock even death
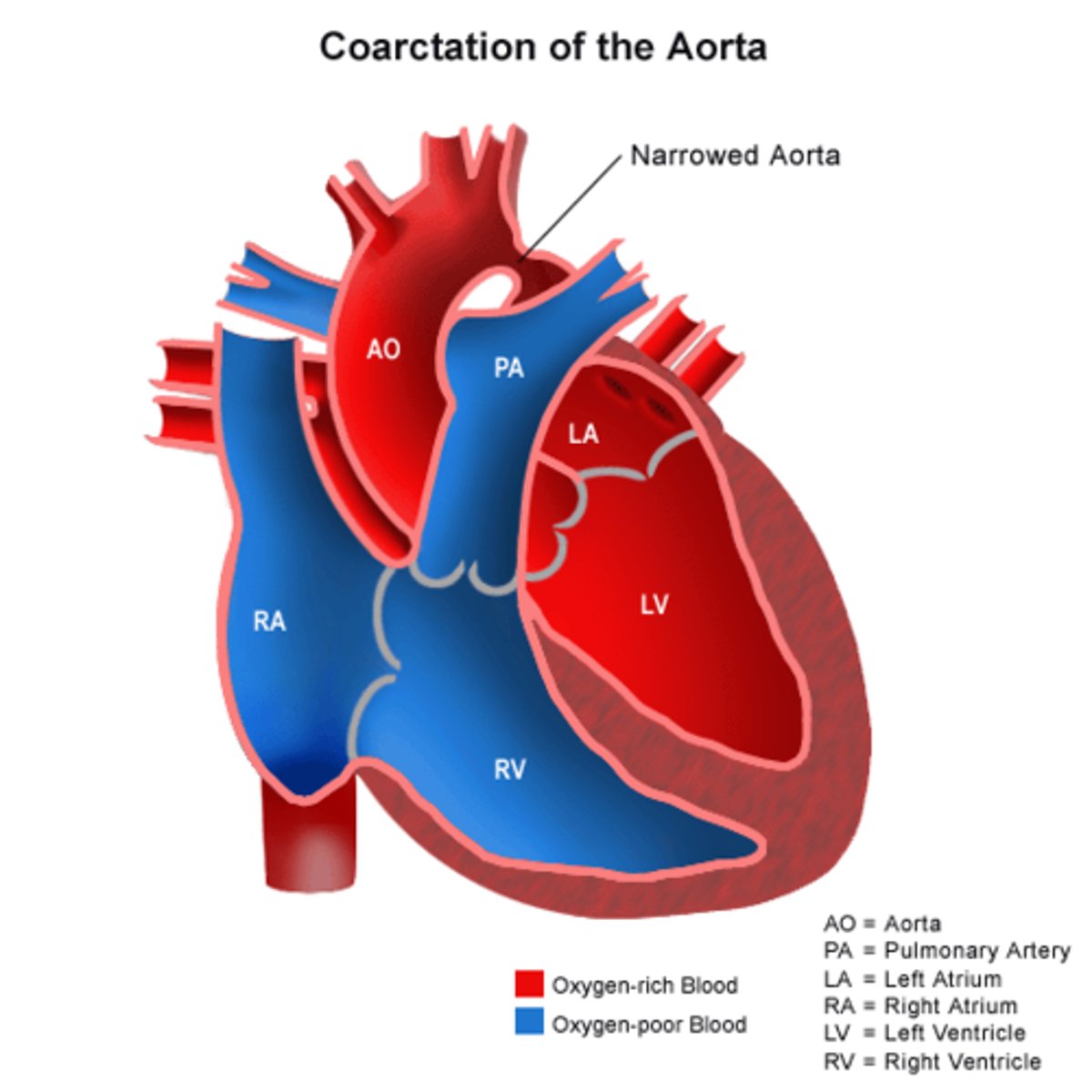
specific findings of coarctation of the aorta
upper extremities- bounding pulses
lower- weak or absent pulses
Coarctation of the aorta treatment
prostaglandins and surgical repair
life time follow up
epiglottitis symptoms
4 ds of epiglottitis
dys[hagia
dysphonia
drooling
distress
interventions of epiglottis
keep child calm
do not irritate throat
tripod positioning
avoid supine postioninf
bronchiolitis
inflammation of bronchiolitis
what is most common cause of bronchiolitis
RSV
assessment and tx of bronchiolitis
hypoxia, irritability, crackles+wheezing, retractions
tx - oxygentation fluid and nutrition
antipyretics and analgesics
croup
laryngotracheobronchitis
results in inflammation and edema of the larynx and/or trachea
croup assessment findings
hoarse, bark like cough
stridor
chest wall restractions
runny nose,fever
symptoms often worsen at night
croup treatment
corticosteroids
epinephrine (racemic epi)
keep pt calm (can worsen distress)
cystic fibrosis
autosomal recessive disorder
mutation leads to a buildup of excessive mucus in the airways
diagnosis of cystic fibrosis
meconium ileus
-meconium is thicker and stickier than normal
sweat chloride test
-sweat is collected and analyzed for increased level of chloride
assessment findings of cystic fibrosis
excessive mucus
cyanosis
barrel chest
clubbing
steatorrhea
intestinal obstruction
fat soluble vitamin deficiency-ADEK
endocrine-diabetes
salty tasting sweat
males are infertile
treatment for cystic fibrosis
chest phsyiotherapy
vest therapy
monitor for resp infections
bronchodilators
cystic fibrosis diet
high calories, high protein
incrased fluid intake
pancreatic enzymes- given within 30 min og eating every meal and snack
sprinkle capsules on food
nursing intervention for vp shunt
they can have MRI
careful with contact sports
can go in airplane
VP shunt can not be working if what happens
vomitting or headache in morning
cerebral palsy
damage to immature brain
-causes disorder in movement, muscle tone, and posture
assessment findings of cerebral palsy
stiff muscles, spasticity, ataxia, tremors, drooling, dysphagia, developmentally delay, intellectual disabilities
treatment of cerebral palsy
anticonvulsants for seizures, muscle relaxants for spasticity
meningocele
protrustion of spinal fluid-filled meninges through a vertebral defect
myelomeningocele
protrusion of spinal fluid-filled meninges and the spinal cord through a vertebral defect
assessment finding for spina befidida
sacral dimple or tuft of hair
preop for spina bifida
prone position
cover the sac with moist, warm, sterile dressing
no diapering if defect is low-keep the sac clean with a protective barrier
microcephaly
head circumference than normal
assessment findings for microcephaly
impaired cognitive development
delayed motor function
facial distortion
dwarfism
hyperactivity
seizures
treatment for microcephaly
decrease impact neurological complications
cleft lip and cleft palete surgery
cleft lip- 3-6 months
palete- 6-24 months
feedings for cleft palete
specialized long bottle
small, frequent feedings
upright position
burp frequently
may take longer to feed than other children
monitor for aspiration
burp frequently
cleft palate vs cleft lip post positioning
lip-should not be prone because this can disrupt suture line
palate- can be pone post op to drain secretions
cleft lip and palete post op
no oral or nasal suctioning
elbow restraints
no hard foods, straws, pacifiers
tracheoesophageal fistula
there is an opening between the trachea and the esophagus
esophageal atresia
part of esophagus does not form
cs of esophageal atresia
choking coughing cyanosis
pyloric stenosis
narrowing of the pyloric sphincter that blocks the passage of food from the stomach into the duodenum

pyloric stenosis assessment
non-bilous
projectile vomiting
right after feeeding
infant is still hungry
PALPABLE OLIVE SHAPED MASS
omphalocele
congentital abnormalityt where the abdominal content protrube through the umbilicus while remaining in perotineal sac
complicaitons for omphalocele
hypothermia, dehydration, sepsis
pre-op omphalocele
keep exposed intestine moist
cover with sterile gaize soaked in saline
iv fluids + antibiotics
thermoregulation
post op omphalocele
parenteral feeds
trophic feeds started enterally very gradually
monitor weight
gastroschisis
not in periotenal sac
only intestinal organs
intussusception
telescoping
occurs when part of intestine slips inside other intestines
intussusception assessment
red curant jelly stool
sausage-shaped mass
cyclical abdominal pain
green-bilious emisis
treatment for intussception
enema to attempt to push the intestine back out
hirschsprung's disease
absence at birth of the autonomic ganglia in a segment of the intestinal smooth muscle wall that normally stimulates peristalsis
causes megacolon
hirschsprung disease assessment
ribbon like stool
swollen belly
vomiting
gas