chemistry of the atmosphere topic 9
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what was first billion years of earths history like, early atmosphere was…, what did volcanic activity also release
first billion years of earth’s history were pretty explosive - the surface was covered in volcanoes that erupted & released lots of gases. We think this was how early atmosphere was formed
early atmosphere was probably mostly carbon dioxide, w virtually no oxygen. Quite like Mars & venus today
volcanic activity also released nitrogen, which built up in atmosphere over time, as well as water vapour & small amounts of methane & ammonia
how did oceans form, how was carbon dioxide removed from the early atmosphere & where did it go, what did green plants/algae & marine animals do as they evolved, what happened to the carbon these organisms took in
when water vapour in atmosphere condensed it formed oceans
lots of carbon dioxide was removed from early atmosphere as it dissolved in oceans. The dissolved carbon dioxide went through series of reactions to form carbonate precipitates that formed sediments on seabed
Green plants & algae evolved & absorbed some of carbon dioxide so they could carry out photosynthesis. Later marine animals evolved. Their shells & skeletons contained carbonates from oceans
some of the carbon these organisms took in from atmosphere & oceans became locked up in rocks & fossil fuels after organisms died
how r sedimentary rocks, oil & gas formed & what do they keep in, what r fossil fuels, whats formed from deposits of plankton & what do they form, whats coal, whats limestone
When plants, plankton & marine animals die, they fall to the seabed & get buried by layers of sediment. Over millions of years they become compressed & form sedimentary rocks, oil, gas - trapping carbon within them & helping to keep carbon dioxide levels in atmosphere reduced
coal, crude oil, natural gas r made by this process r called fossil fuels
crude oil & natural gas r formed from deposits of plankton. These fossil fuels form reservoirs under seabed when they get trapped in rocks
Coal is a sedimentary rock made from thick plant deposits
Limestone is sedimentary rock. Mostly made of calcium carbonate deposits from shells & skeletons of marine organisms
how was oxygen produced, what first evolved, as oxygen levels built up…, what the composition of atmosphere today
as well as absorbing carbon dioxide in atmosphere, green plants & algae produced oxygen by photosynthesis - when plants use light to convert carbon dioxide & water into sugars:
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
algae evolved first (~2.7 B years ago), over next B years or so green plants evolved
as oxygen levels built up in atmosphere over time more complex life (animals) could evolve
eventually (~200M years ago) atmosphere reached composition similar to what it is today → ~80% nitrogen, 20% oxygen & small amounts of other gases (each make up >1%), mainly carbon dioxide, noble gases & water vapour

what do greenhouse gases do (atmosphere), whats the greenhouse effect
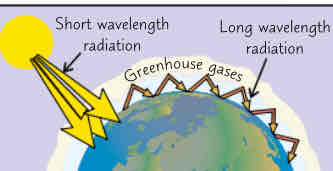
greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, water vapour) act like insulating layer in earths atmosphere, this amongst other factors allows earth to be warm enough to support life
all particles absorb certain frequencies of radiation. Greenhouse gases dont absorb the incoming short wavelength radiation from sun - but absorb long wavelength radiation that gets reflected back off earth. Then they re-radiate it in all directions including back towards earth. Longwave radiation is thermal radiation so it results in warming of surface if earth → greenhouse effect
what r 4 forms of human activity that affect amount of greenhouse gases in atmosphere
deforestation → fewer trees mean less CO_2 is removed from atmosphere via photosynthesis
burning fossil fuels → carbon that was ‘locked up’ in these fossil fuels is released as CO_2
Agriculture → more farm animals more methane through their digestive processes
Creating waste → more landfill sites & more waste from agriculture means more CO_2 & methane released by decomposition of waste
whats causing the avg temp of earths surface to rise, how do u know evidence is reliable, whys it hard to make model thats not oversimplified, what has this led to
earths temp varies naturally but recently average temp of earths surface has been increasing. Scientists agree that extra carbon dioxide from human activity is causing this increase & will lead to climate change
evidence for this has been peer-reviewed so u know the info out there is reliable
unfortunately, its hard to fully understand Earths climate - because its so complex & theres many variables that its very hard to make model that isnt oversimplified
this has led to speculation, particularly in media - where stories may br biased/ only some of info given
4 predictions about climate change that have dangerous consequences
higher global temps r causing the polar ice caps to melt - causing sea levels to rise. If sea levels keep rising, this will lead to increased flooding in coastal areas & coastal erosion
changes in rainfall patterns (amounts, timing, distribution) r causing some regions to get too much/ too little water. This along w changes in temp may affect ability of certain regions to produce food
the frequency & severity of storms may also increase
changes in temp & amount of water available in diff habitats r affecting wild species, leading to changes in their distribution
whats carbon footprint, measuring total carbon footprint…, why is this, why r rough calculations good
Carbon footprints → measure of amount of CO_2 & other greenhouse gases released over full life cycle of something (service, product, event)
measuring total carbon footprint of smthing can be really hard/ impossible
because there r so many diff factors to consider - emissions released as result of sourcing all parts, emissions when actually used & dispose of it
rough calculation can give good idea of what worst emitters r so pple can avoid them in future
5 ways of reducing carbon footprint
renewable energy sources/ nuclear energy could be used instead of fossil fuels
using more efficient processes could conserve energy & cut waste. Lots of waste decomposes to release methane so this will reduce methane emissions
governments could tax companies/ individuals based amount of greenhouse gases they emit
governments can put cap on emissions of all greenhouse gases that companies make then sell licenses for emissions up to that cap
technology that captures CO_2 produced by burning fossil fuels before its released into atmosphere - can be stored deep underground in cracks in rock such as old oil wells
4 reasons making reductions is difficult
still lots of work to be done on alternative technologies that result in lower CO_2 emissions
lots of governments r also worried making these changes will impact economic growth of communities - could be bad for pples well-being. Important for countries that r still developing
not everyones on board - hard to make international agreements to reduce emissions, most countries wont sacrifice economic development if others wont do same
individuals in developed countries need make changes to their lifestyle but might be hard to get pple to make change if they dont want to & if isnt enough education provided about why changes r necessary & how to make them
fossil fuels contain.. & during combustion.., whats complete combustion, whats incomplete combustion & what happens
fossil fuels (crude oil, coal) contain hydrocarbons. During combustion carbon & hydrogen in these compounds r oxidised so carbon dioxide & water vapour r released into atmosphere
when theres plenty of oxygen all fuel burns → complete combustion
if theres not enough oxygen, some fuel doesnt burn → incomplete combustion. Under these conditions solid particles (particulates) of soot (carbon) & unburnt fuel r released & carbon monoxide can be produced as well as carbon dioxide
2 problems particulates in air can cause
if particulates r inhaled, they can get stuck in lungs & cause damage. Can lead to respiratory problems
they’re bad for environment - they themselves/ clouds they help produce, reflect sunlight back into space. Means less light reaches earth causing global dimming
problem carbon monoxide causes & whys it dangerous
really dangerous because can stop our blood from doing its proper job of carrying oxygen around body
does this by binding to haemoglobin in blood that normally carries O_2 - so less oxygen is able to be transported round body
lack of oxygen in blood can lead to fainting, coma, death
doesnt have any colour or smell so its very hard to detect, this makes it even more dangerous
how is sulfur dioxide & nitrogen oxides formed, whats complete combustion happens when these gases mix w clouds, whats does acid rain do (3), what do sulfur dioxide & nitrogen oxides do when breathed in
sulfur dioxide (SO_2) is released during combustion of fossil fuels (coal) that contain sulfur impurities - sulfur in fuel becomes oxidised
nitrogen oxides r created from reaction between nitrogen & oxygen in air, caused by heat of burning (can happen in internal combustion engines of cars)
when these gases mix w clouds they form dilute sulfuric/ nitric acid. This then falls as acid rain
acid rain kills plants & damages buildings & statues. makes metal corrode
sulfur dioxide & nitrogen oxides can be bad for human health - cause respiratory problems if breathed in