1.3.2 Externalities
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Define a private cost/private benefit.
The costs/benefits to the individual participating in the economic activity. Demand curve represents MPB and supply curve represents MPC
Define social costs/benefits.
The costs/benefits of the activity to society as a whole.
Define external costs/benefits.
The costs/benefits to a third party not involved in the economic activity.
What is the formula for external costs/ external benefits
EXTERNAL COSTS = PRIVATE COST - SOCIAL COST
EXTERNAL BENEFIT = PRIVATE BENEFIT - SOCIAL BENEFIT
What is a merit good?
A merit good is a good with external benefits, where the benefit to society is greater than the benefit to the individual. These goods tend to be underprovided by the free market.
Define a demerit good.
A demerit good is a good with external costs, where the cost to society is greater than the cost to the individual. They tend to be over-provided by the free market.
What is MPB
is the extra satisfaction gained by the individual from consuming one more of a good and the marginal social benefit
What is MSB?
Is the extra gain to society from the consumption of one more good
What is the MPC?
The marginal private cost (MPC) is the extra cost to the individual from producing one more of the good
What is MSC?
marginal social cost (MSC) is the extra cost to society from the production of one more good.
Draw the negative externality of production diagram.
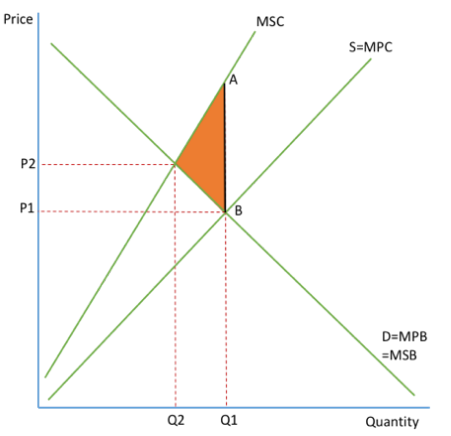
How do negative externalities of production occur?
Negative externalities of production occur when social costs are greater than private costs. The market left to operate freely will ignore the external costs involved in producing a good.
Show the positive externality of consumption diagram.
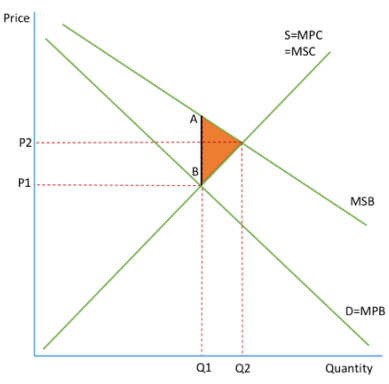
Explain how positive externalities of consumption occur.
Positive externalities of consumption occur when social benefits are greater than social costs. In the diagram, the market left to its own devices will produce where MPB=MPC, it will not consider the benefits to society so will produce Q1P1
The failure of the market to consider the external benefits has led to the misallocation of resources and so there is an underproduction of Q1-Q2.
Why are externalities difficult to work out and what are many externalities caused by?
It is difficult to work out the size of the externality as it tends to be placed on value judgements, since it is difficult to monetise external costs. Many externalities are involved with information gaps, as people are unaware of the full implications of their decisions