Waves
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
What is a wave?
A wave is an oscillation or vibration that transfers energy or information
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The amplitude of a wave is the distance from the middle to the top of a wave
What is the frequency of a wave?
The frequency of a wave is the number of waves that travel past a point every second
What is the wavelength?
The wavelength is the distance from the top of one wave to the top of the next wave
What is a transverse wave?
A transverse wave is a wave where the oscillation is at 90° to the direction of the wave
What is oscillation?
Oscillation is the repetitive motion of particles or systems which create waves
What is a longitudinal wave?
A longitudinal wave is a wave where the oscillation is in the direction of travel for the wave
Which type of wave is sound?
Sound is a longitudinal wave
What is the period of a wave and what is it measured in?
The period of a wave is the time taken for one complete cycle of a wave. It is measured in seconds
How do we calculate the period of a wave?
We calculate the period of the wave using the formula: 1/Frequency
How do we calculate wave speed?
Speed = Distance / Time OR Speed = Wavelength X Frequency
How do we calculate frequency using a ripple tank?
We calculate frequency by using a ripple tank by: Using a stop clock. Count the number of waves passing a point in a fixed time period. Divide the time by the number of waves to determine the time for one wave. Use the formula: Frequency = 1/Time. Alternatively, read the frequency off the oscillator.
How do we calculate the wavelength using a ripple tank?
We calculate the wavelength by using a ripple tank in the steps: Use a camera to freeze the image. Use a metre ruler to measure the distance between two wavefronts. Count the number of waves between the wavefronts. Divide distance by the number of waves to determine the wavelength.
What is a wavefront?
A wavefront is an imaginary surface that represents the points of a wave that are vibrating in unison at a specific moment in time.
What is a ripple tank?
A ripple tank is a shallow glass tank of water used to demonstrate the basic properties of waves.
What is the frequency measured in?
Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz)
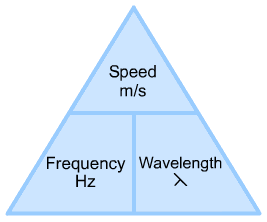
What is this?
This is the triangle formula of Speed, frequency and wavelength.
What is absorbed
Absorbed is to take in
What is the angle of incidence?
The angle of incidence is the angle between an incoming light ray and the normal.
What is the angle of reflection?
The angle of reflection is the angle between the normal and the ray of light leaving a mirror
What is the angle of refraction?
The angle of refraction is the angle between the normal and a ray of light that has been refracted
What is compression?
Compression is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are closest together
What is the units for measuring the loudness of a sound?
The units for measured the loudness of a sound is Decibels (dB)
What is an echo
An echo is where we hear sound again when it reflects off a surface. The reflected sound is called an echo.
What is electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic radiation is waves that start in space and carry electromagnetic energy.
What are gamma rays?
Gamma rays are the highest frequency wave in the E/M spectrum
What is an E/M spectrum
An E/M spectrum is short for an electromagnetic spectrum
What are hertz (Hz)
Hertz (Hz) are the units for frequency. 1 Hertz means 1 wave per second
What is infrared?
Infrared is a low frequency radiation used for heating and thermal imaging cameras
What are thermal imaging cameras
Thermal imaging cameras are devices that detects and displays infrared radiation emitted by objects and living beings.
What is intensity?
Intensity is the loudness or volume of a sound.
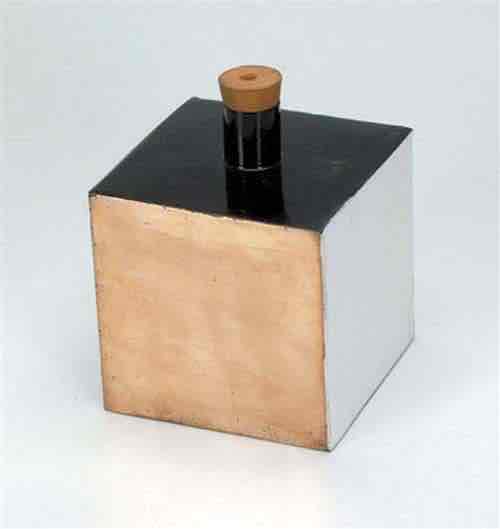

What is a leslie cube?
A leslie cube is a block with 4 different surfaces used to show which surfaces absorb or reflect infrared radiation
What is a medium?
A medium is any substance through which something travels is called a medium
What are microwaves?
Microwaves are a low frequency wave used in cooking and communication
What is an oscillation?
An oscillation is a backwards and forwards motion
What is an oscilloscope?
An oscilloscope is an instrument that shows a picture of a wave on screen
What is the pitch?
The pitch is how high or low a note sounds.
What is a prism?
A prism is a 3rd glass shape used to split white light
What are radiowaves?
Radiowaves are the lowest frequency wave in the E/M spectrum
What is rarefraction?
Rarefraction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart
What is a ray?
A ray is a beam of light
What is reflected?
Reflected is when waves bounce back off a surface
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light due to speed of a wave in different mediums
What is a ripple tank?
A ripple tank is an apparatus used to measure the speed of a wave
What is an apparatus
An apparatus is a machine or device
What are sound waves?
Sound waves are sound energy carries from one place to another
What is a spectrum?
A spectrum is a range of waves
What is speed?
Speed is a measure of how fast something is
What is a strobe light?
A strobe light is a light that flashes, if set the same oscillation as a wave it can give an exact measure of frequency
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies above 20000hz, the upper limit of human hearing
What is ultraviolet
Ultraviolet is a medium frequency wave in the E/M spectrum
What is a vacuum
A vacuum is a completely empty space that contains no particles
What is vibrate?
Vibrate is moving backwards and forwards
What is a visible light?
A visible light is the wave in an E/M spectrum we can see
What is volume?
Volume is the loudness of a sound
What does a wave do?
A wave transfers energy or information
What is white light?
White light is light where all of the colours are reflected
What are xrays?
Xrays are a high frequency wave that is used to view bones inside the body
What are some examples of waves?
Different examples of waves are sound, water, light, microwaves and radiowaves.
What can waves travel through?
Waves can travel through everything
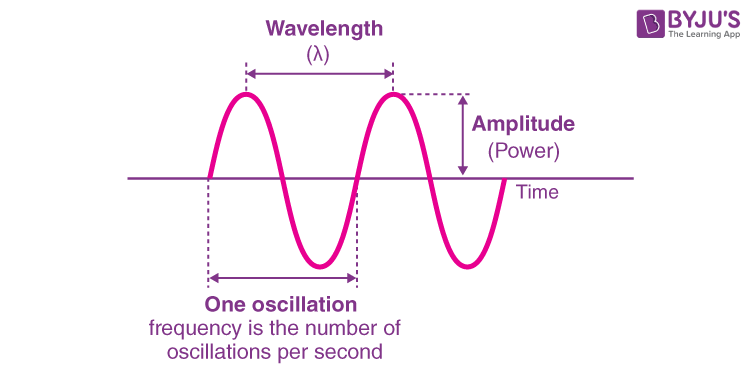
How many waves are in this image?
There are 2 waves in this image
What is the symbol of wavelength?
lambda, λ
How does sound reach our ears?
Sound reaches our ears when an object makes a sound by vibrating. The vibration passes through air by making air molecules vibrate. These vibrations are picked up by the ear
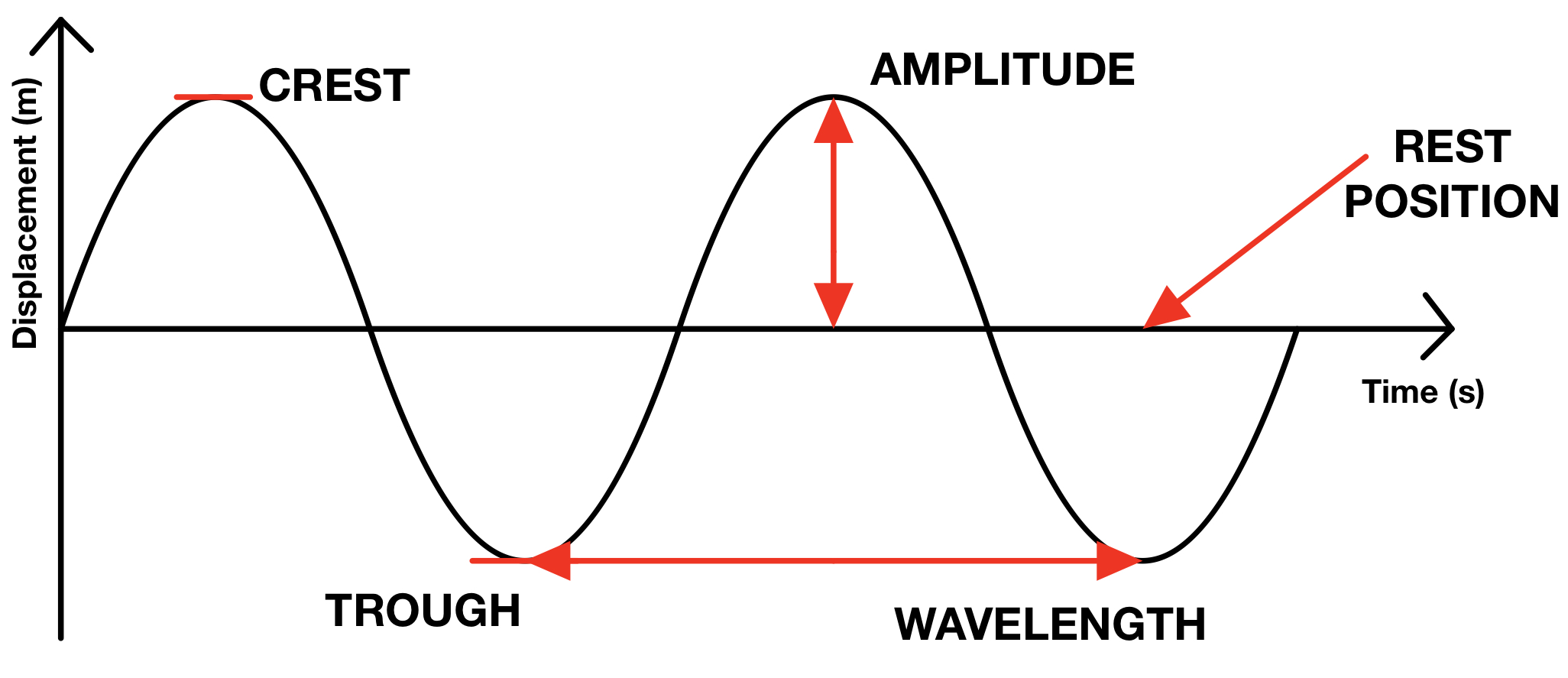
What are examples of transverse waves?
All electromagnet waves, water waves, and S Seismic waves
What is the symbol for Period / Time Period
The symbol for Time Period is T
What is the trough of a wave?
The trough of a wave is the lowest part of a wave
What is the crest of a wave?
The crest of a wave is the highest point of a wave
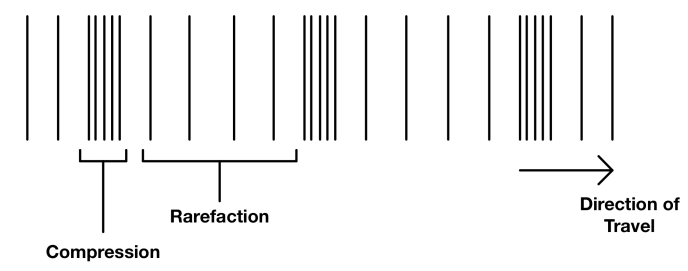
What are examples of longitudinal waves?
Sound waves, P seismic waves
What is another word for frequency
Another word for frequency is pitch
What is another word for amplitude?
Another word for amplitude is volume
What is the speed of typical water waves
The speed of typical water waves is 5m/s
What is the speed of sound in the air?
The speed of sound in the air is 343m/s
What is the symbol for wavespeed?
The symbol for wavespeed is v
What is the speed of light?
The speed of light is 300,000,000 m/s
How do you calculate wave speed using a ripple tank?
Use a stopclock to count the number of waves passing a point in a fixed time. Divide the number of waves by the time to get the frequency. Use a camera to freeze the image. Use a metre ruler to measure the distance between 2 wavefronts. Count the number of waves between wavefronts and divide the distance by the number of waves for wavelength. Now use the formula Speed = Frequency * Wavelength to calculate the wavespeed
How do we calculate the speed of a sound?
We calculate the speed of a sound by standing a long distance apart, measuring the distance, make a sound and time how long it takes to be heard. Use the formula Speed=Distance/Time
What is specular reflection?
Specular reflection is when light reflects from a smooth surface to give a clear image, such as a mirror
What is diffuse scattering?
Diffuse scattering is when light reflects off a rough surface and travels in different directions
What is a normal line?
A normal line is an imaginary line drawn at a right angle to a surface where light hits it
What do we call the ray that shines onto an object
The incident ray, a ray that shines onto an object
What is a reflected ray?
A reflected ray is a ray of light that has reflected off a surface
What is the angle of incidence?
The angle of incidence is the angle between the normal and the incident ray
What is the angle between the normal and the reflected ray called?
The angle of reflection
What is the law of reflection?
The law of reflection is the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence
What is a plane mirror?
A plane mirror is a flat mirror
What is the angle of refraction?
The angle of refraction is the angle between the normal and the refracted ray
Why does light change direction when it enters a different material?
Light changes direction when it enters a different material because it changes speed
What happens when light travels from a less dense to a more dense material?
It refracts towards the normal
What type of waves are the electromagnetic spectrum?
Transverse waves that travel the same speed in a vacuum
Name the waves that make up the E/M spectrum in increasing frequency
The waves that make up the E/M spectrum are called Radiowaves, Microwaves, Infrared, Visible Light, Ultraviolet, Xrays and gamma waves
What are microwaves used for?
Communication and cooking
What is infrared used for?
Infrared is used for thermal imaging and heating
What are the primary colours of light?
The primary colours of light are red, green and blue
What colour do we see if we mix red and green light?
Yellow light
What colour do we see if we mix green and blue light?
Cyan light
What colour do we see if we mix blue and red light?
Magenta
What colour do we see if we mix red, green and blue light?
White
What colour do we see if no light can refract from an object?
Black
What colour of light can a red object reflect
Red
What colours of light can a cyan object reflect?
Green and blue light