The Heart and Circulatory System Overview
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
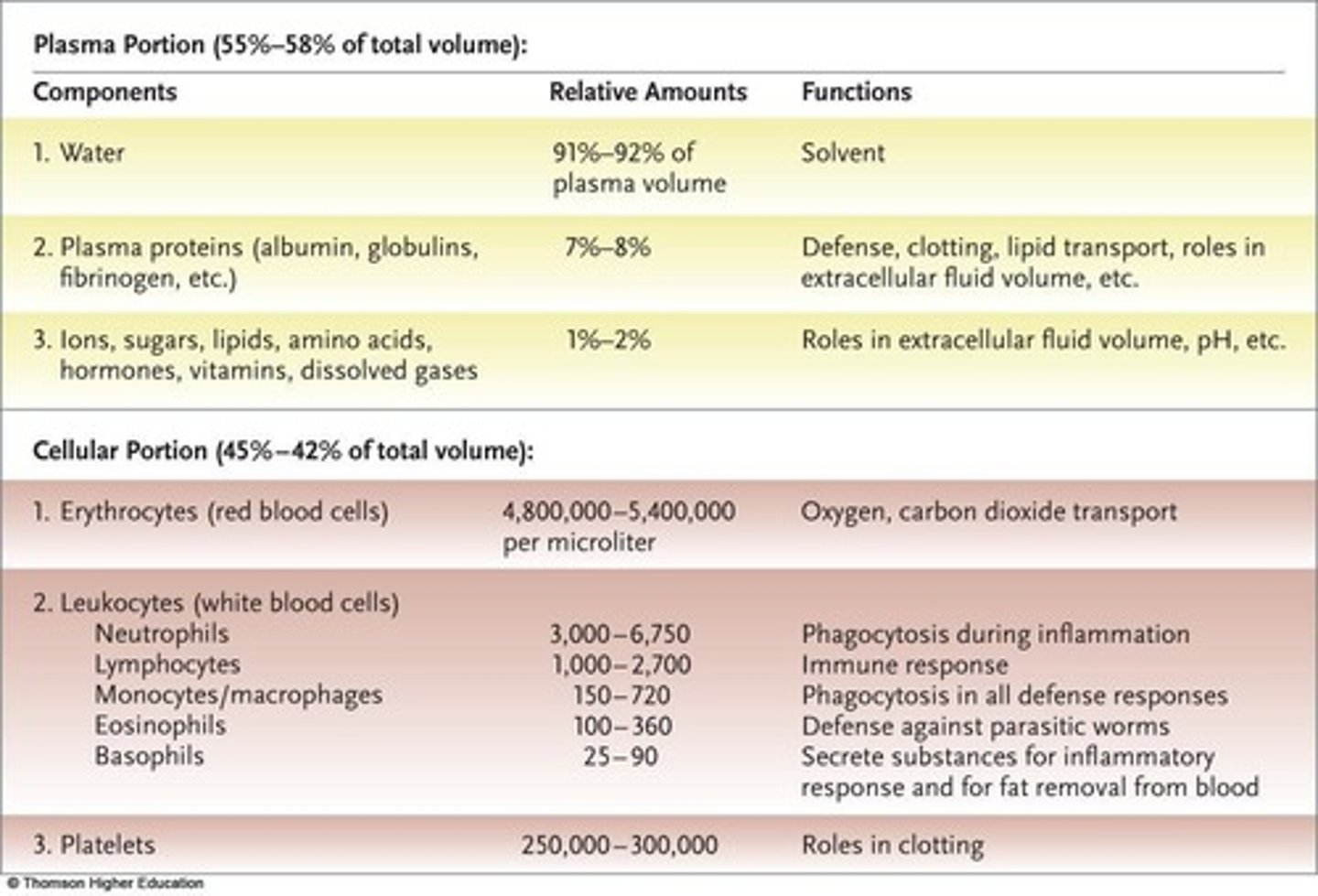
Plasma
Aqueous solution of proteins, ions, and gases.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that carry oxygen.
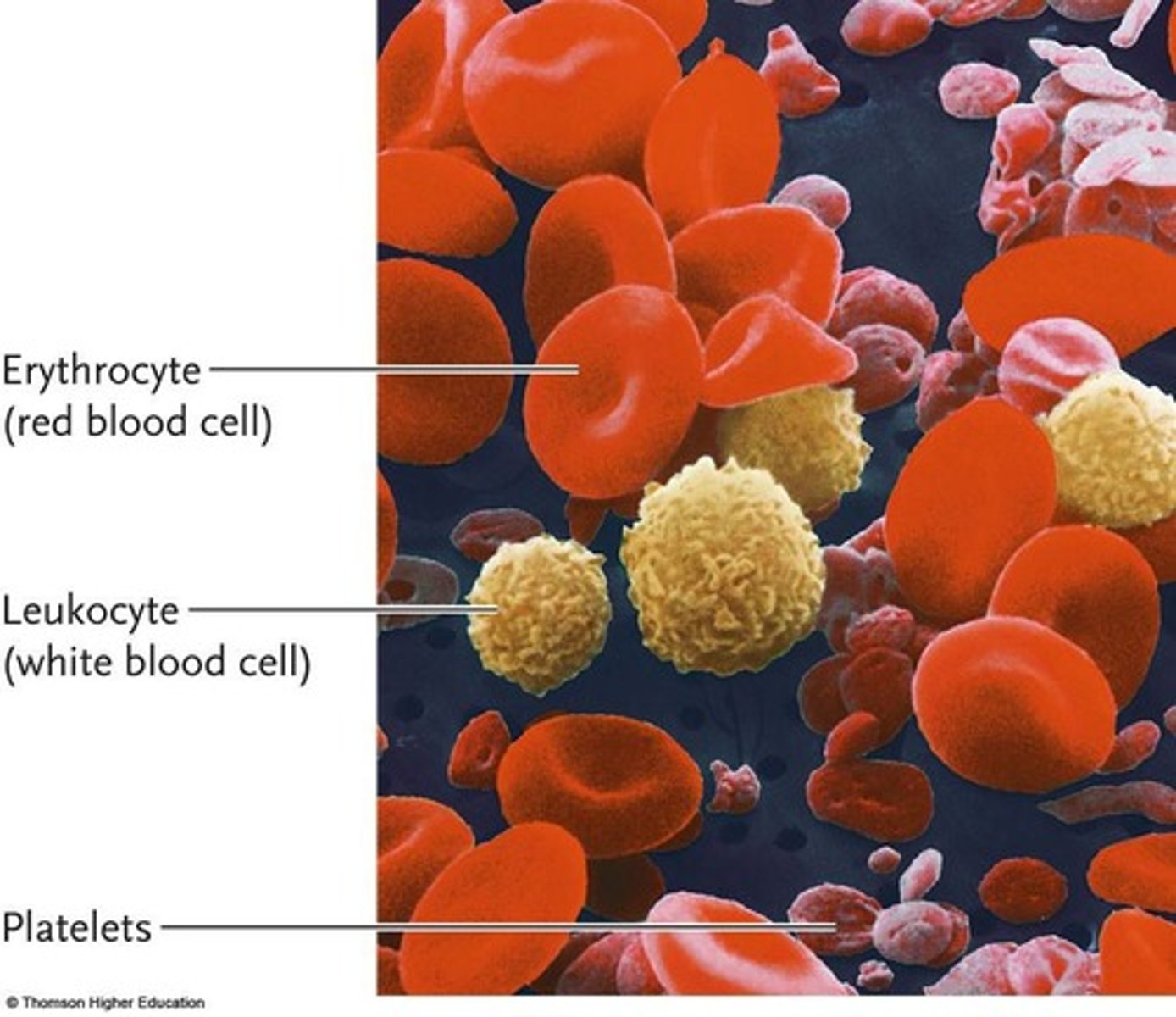
Leukocytes
White blood cells defending against pathogens.
Platelets
Cell fragments that induce blood clotting.
Hematocrit
Volume percentage of red blood cells in blood.
Anemia
Condition of abnormally low hematocrit.
Cardiac Muscle
Muscle tissue making up the heart.
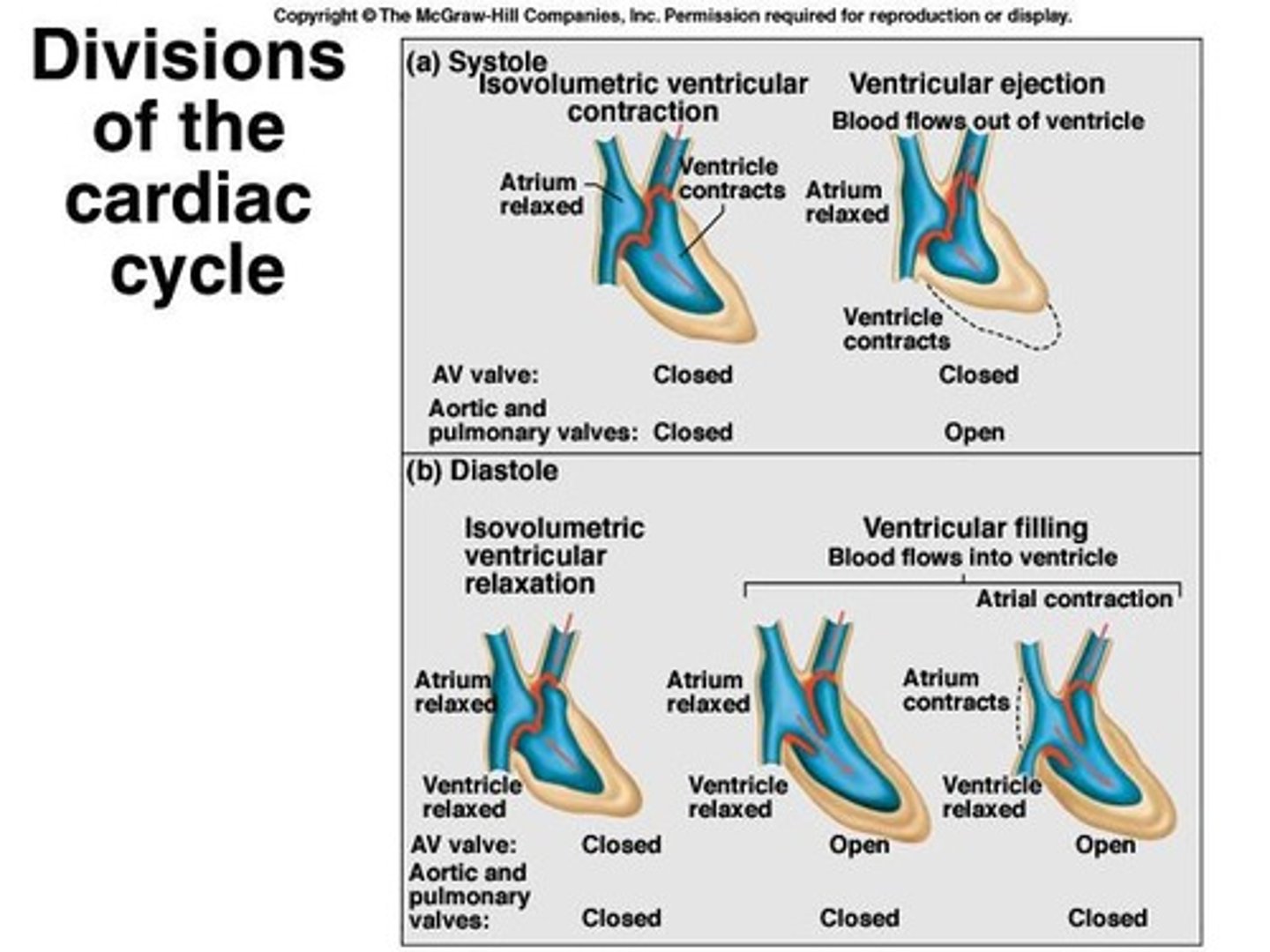
Systole
Phase of ventricle contraction.
Diastole
Phase of ventricle relaxation.
Cardiac Cycle
Sequence of systole and diastole.
Stroke Volume
Amount of blood ejected per heartbeat.
Cardiac Output
Blood pumped by the heart per minute.
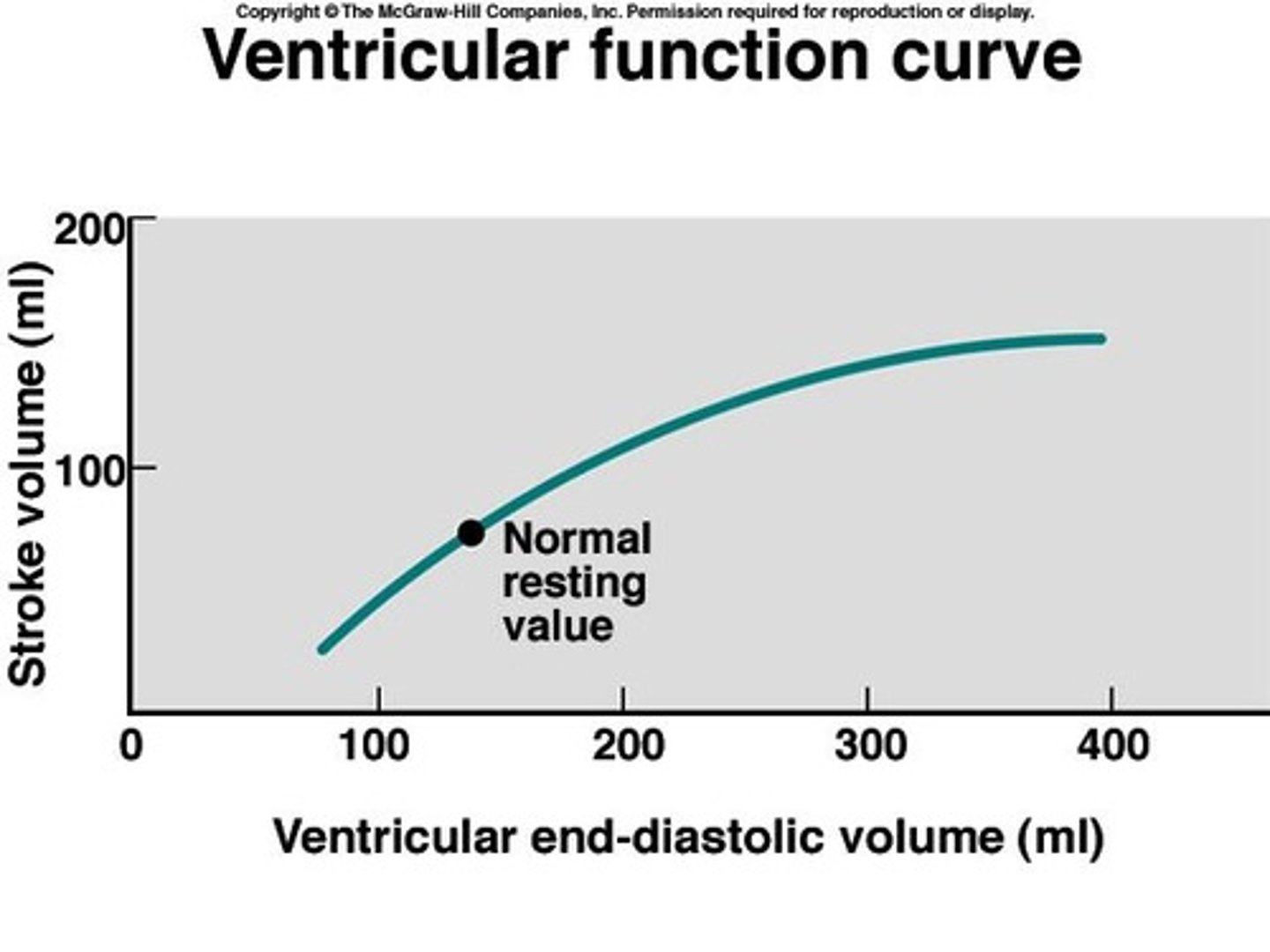
Preload
Ventricular stretch at end of diastole.
Afterload
Resistance heart must overcome to eject blood.
Pulmonary Circuit
Circuit transporting blood to and from lungs.
Systemic Circuit
Circuit transporting blood to and from body.
AV Valves
Valves between atria and ventricles.
SL Valves
Valves between ventricles and arteries.
Blood Pressure
Pressure exerted by circulating blood.
Erythrocyte Lifespan
Approximately 4 months in circulation.
Blood Volume
Average 4-5 liters in humans.
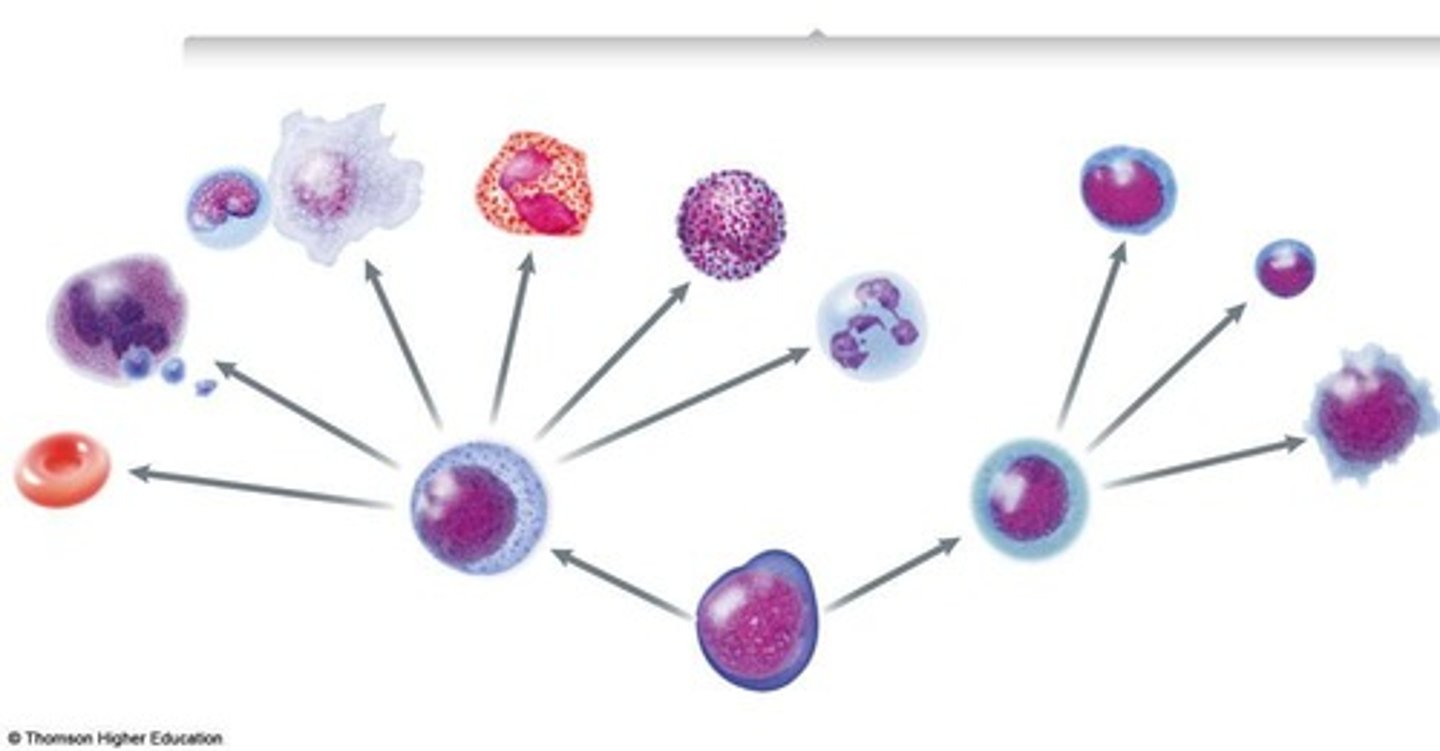
Multi-potent Stem Cells
Cells that differentiate into blood cell types.
Cardiac Muscle Stretch
Influences strength of contraction.
Cardiac Cycle Phases
Includes systole and diastole phases.
Blood Flow Equation
F = DP/R, where F is flow.
Resistance in Blood Vessels
Impacts blood flow based on vessel diameter.
Normal Systolic Pressure
Ranges from 110-140 mmHg at rest.
Normal Diastolic Pressure
Ranges from 60-90 mmHg at rest.
Heart Rate
Number of heartbeats per minute.
CO Formula
CO = SV x HR for cardiac output.
Frank-Starling Mechanism
Increased stretch leads to increased contraction force.
Sympathetic Activity
Increases heart rate and contraction force.
Parasympathetic Activity
Decreases heart rate via vagus nerve stimulation.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter that slows heart rate.
M2 Receptors
Muscarinic receptors that slow heart rate.
Catecholamines
Hormones like norepinephrine and epinephrine.
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter that increases heart rate and contraction.
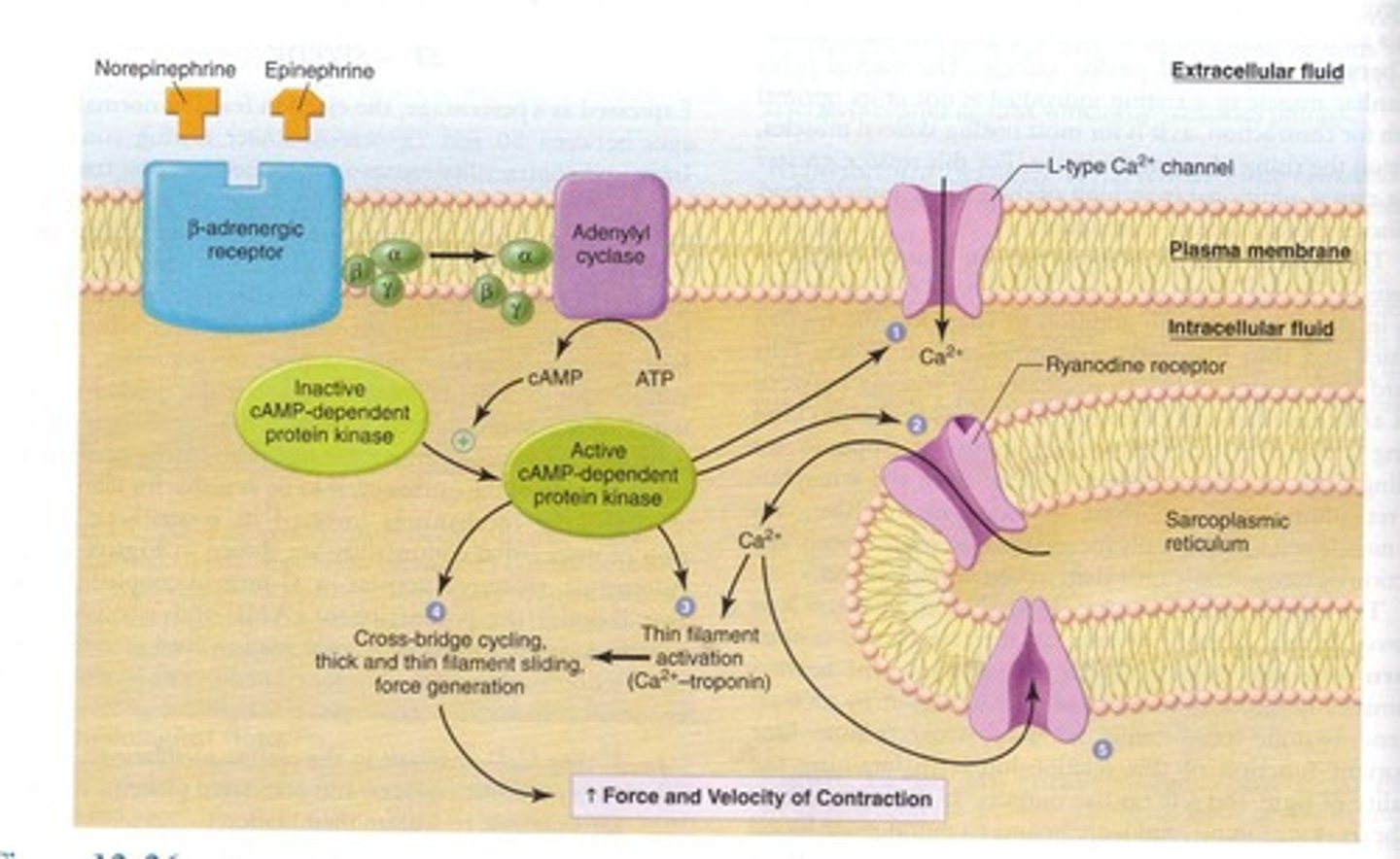
Epinephrine
Hormone that enhances cardiac output and glucose levels.
Adrenergic Receptors
Receptors for catecholamines affecting heart function.
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal conditions in the body.
Vagus Nerve
Carries parasympathetic signals to the heart.
Ionotropic Receptors
Receptors that form ion channel pores.
Metabotropic Receptors
Receptors linked to ion channels via G proteins.
Baroreceptor Reflex
Regulates blood pressure through heart rate adjustments.

Force of Contraction
Strength of heart muscle contraction during systole.
Sympathetic Nerves
Nerves that stimulate heart from spinal cord.
Norepinephrine Secretion
Released by sympathetic neurons to increase heart function.
Cardiac Muscle Depolarization
Process that triggers heart muscle contraction.
Action Potential
Electrical impulse that initiates heart contraction.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
Molecule that mediates sympathetic effects on heart.
Blood Volume Return
Amount of blood returning to the heart influences stroke volume.
β-adrenergic receptors
Receptors that bind epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Fight or flight response
Physiological reaction to perceived threat.
Calcium release
Increased calcium entry enhances heart contraction.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle that stores calcium in muscle cells.
Troponin
Protein that interacts with calcium to trigger contraction.
Contractility
Strength of heart contraction for given blood volume.
Cardiac output
Volume of blood pumped by heart per minute.
Sympathetic stimulation
Increases heart rate and contractility.
Parasympathetic activity
Reduces heart rate via vagus nerve.
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Pacemaker of the heart generating action potentials.
Auto-rhythmicity
Ability of heart to contract independently.
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Delays signals from atria to ventricles.
Bundle of His
Conducts electrical signals from AV node.
Purkinje fibers
Rapidly spread action potentials in ventricles.
Action potential
Electrical impulse triggering heart muscle contraction.
Calcium channels
Regulate calcium flow into cardiac cells.
L-type calcium channel
Long-lasting channel sustaining action potentials.
T-type calcium channel
Transient channel initiating action potentials.
Funny channels
Mixed sodium-potassium channels activating heart rhythm.
Membrane potential
Electrical charge difference across cell membrane.
Repolarization
Return of membrane potential after depolarization.
Depolarization
Membrane potential becomes less negative, triggers contraction.
Ventricular contraction
Pumping action of ventricles to circulate blood.
Atrial contraction
Filling ventricles with blood before ventricular contraction.
Cardiac muscle cells
Branched cells connected by intercalated discs.
Intercalated discs
Structures allowing ion passage between cardiac cells.
Gap junctions
Connections permitting action potential spread in heart.
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; increases f-channel opening.
Pacemaker Potentials
Electrical signals generated by SA node.
PNa
Permeability to sodium ions in cardiac cells.
PCa
Permeability to calcium ions in cardiac cells.
PK
Permeability to potassium ions in cardiac cells.
Sympathetic Effect
Norepinephrine increases PNa and PCa, speeding depolarization.
Parasympathetic Effect
ACh decreases PNa and PCa, slowing depolarization.
Action Potential (AP)
Electrical impulse in cardiac muscle cells.
Refractory Period
Time during which cardiac cells cannot re-excite.
Tetanus
Sustained muscle contraction not possible in heart.
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Process linking electrical signals to muscle contraction.
T-tubules
Extensions of plasma membrane in muscle cells.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Calcium storage organelle in muscle cells.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Measure of heart's electrical activity on skin.
Electrode Placement
Pads that detect electrical signals from heart.
ECG Leads
Different angles measuring heart's electrical activity.
P Wave
Atrial depolarization lasting 0.08-0.10 seconds.
P-R Interval
Time from atrial to ventricular depolarization, 0.12-0.20 seconds.
QRS Complex
Ventricular depolarization, short duration 0.06-0.10 seconds.
S-T Segment
Plateau phase of ventricular action potentials.
T Wave
Ventricular repolarization phase in ECG.
Q-T Interval
Time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization, 0.20-0.40 seconds.