Chemistry - 2.3 Rates of Reaction:
1/31
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What does the ‘Rate of reaction’ tell us?
How quickly a chemical reaction happens
What can be measured during a reaction?
How much product is formed in a certain time
How much of a reactant is used up in a certain amount of time
What is the equation of the rate and what are the units?
Rate = 1/Time
Units = S-1
What are the 6 controlling factors that affect the rate of a reaction?
Temperature
Concentration of a liquid
Surface Area of a solid
Pressure of a gas
Light intensity
The addition of a catalyst
When is a gas produced?
When an acid reacts with a metal or a metal carbonate:
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Acid + Metal Carbonate → Salt + Water + CO2
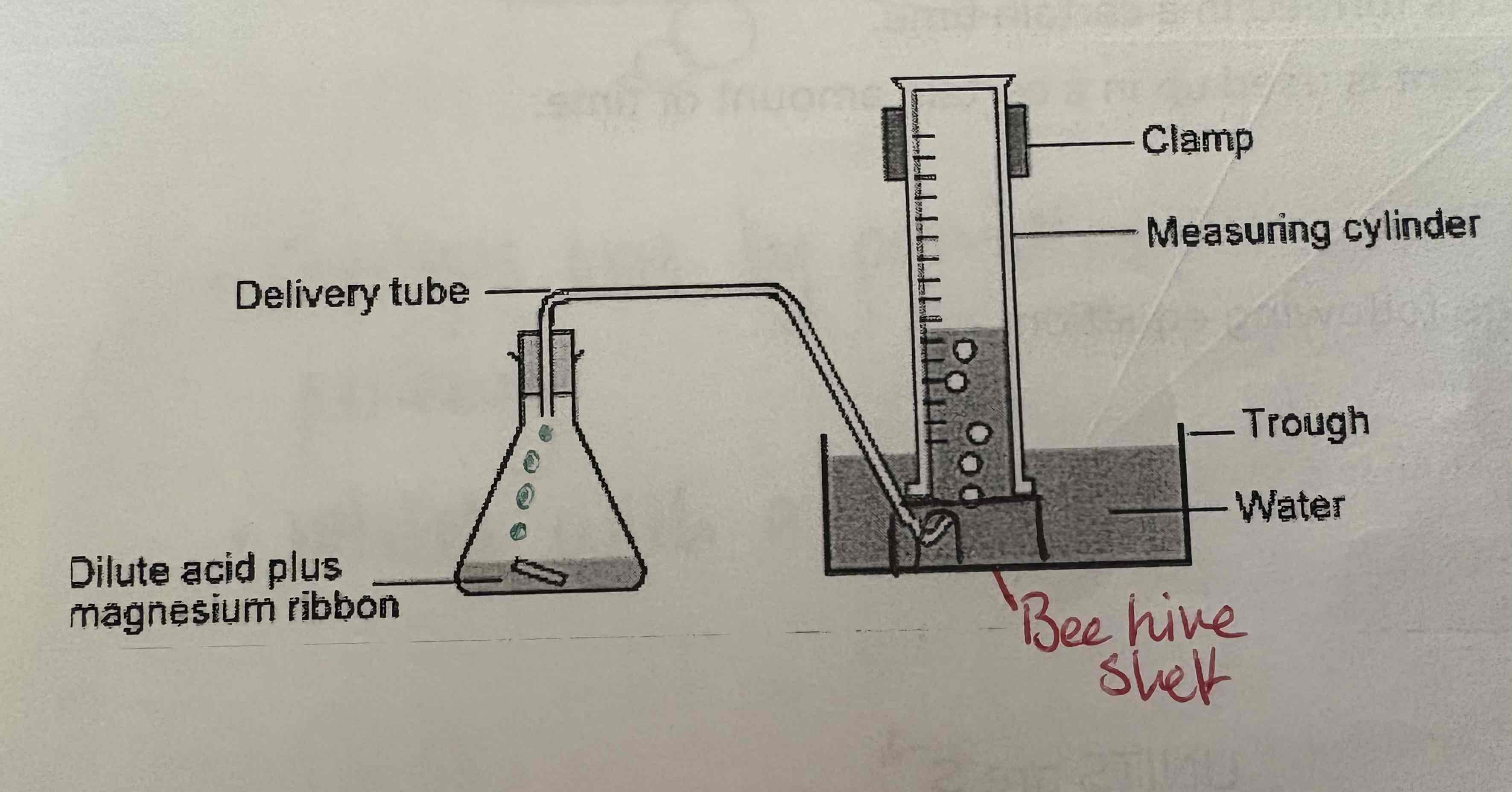
What can be used to measure gas released during a reaction?
Gas syringe clamped onto retort stand
Inverted measuring cylinder, beehive shelf, and a trough of water
When is measuring of gas in a reaction over?
When two volume readings are the same. Showing no more gas is being released due to one reactant being used up
Describe the apparatus of measurement of Gas:
See image:
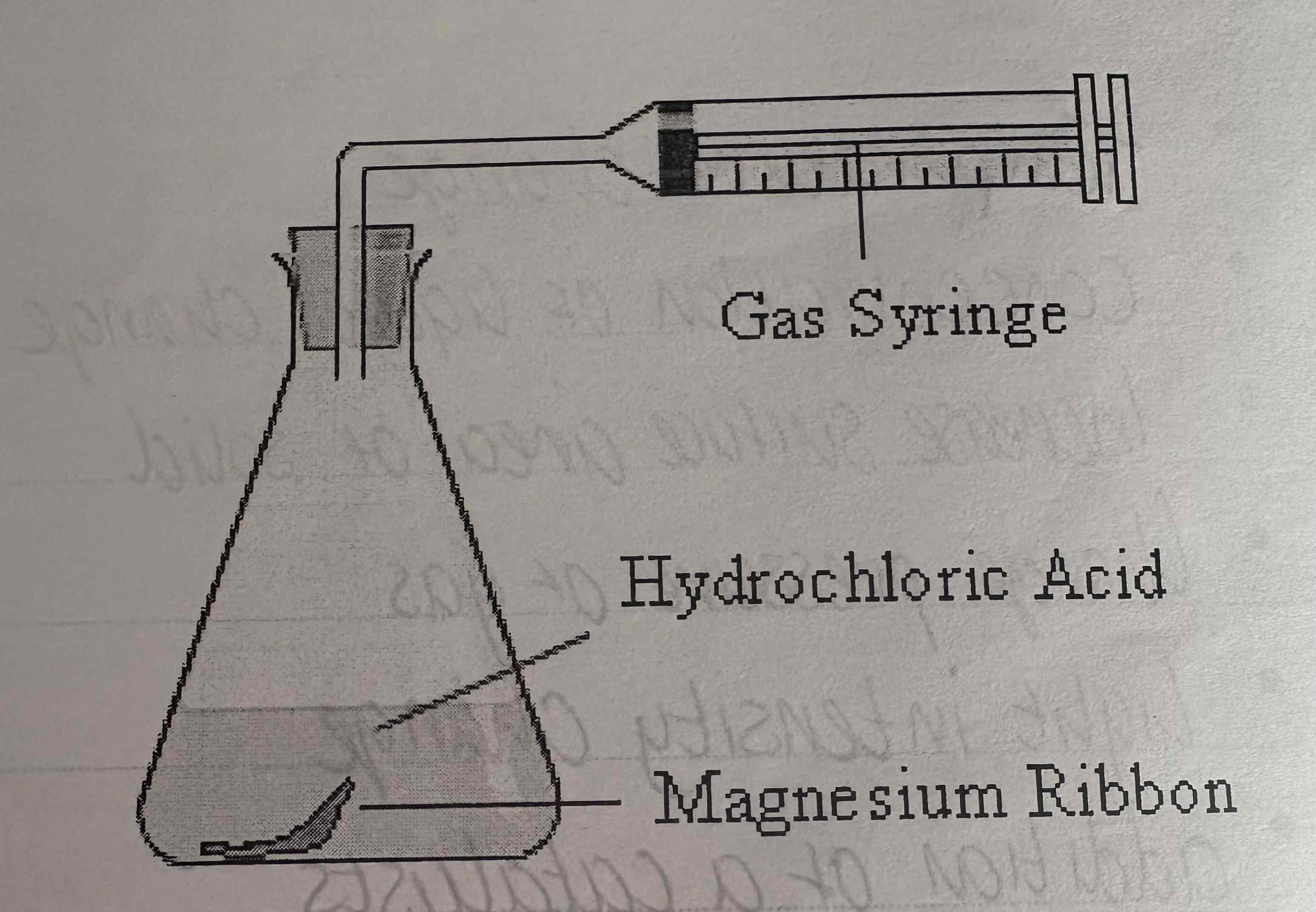
Describe the apparatus of measuring the change in given unit of time:
See image:
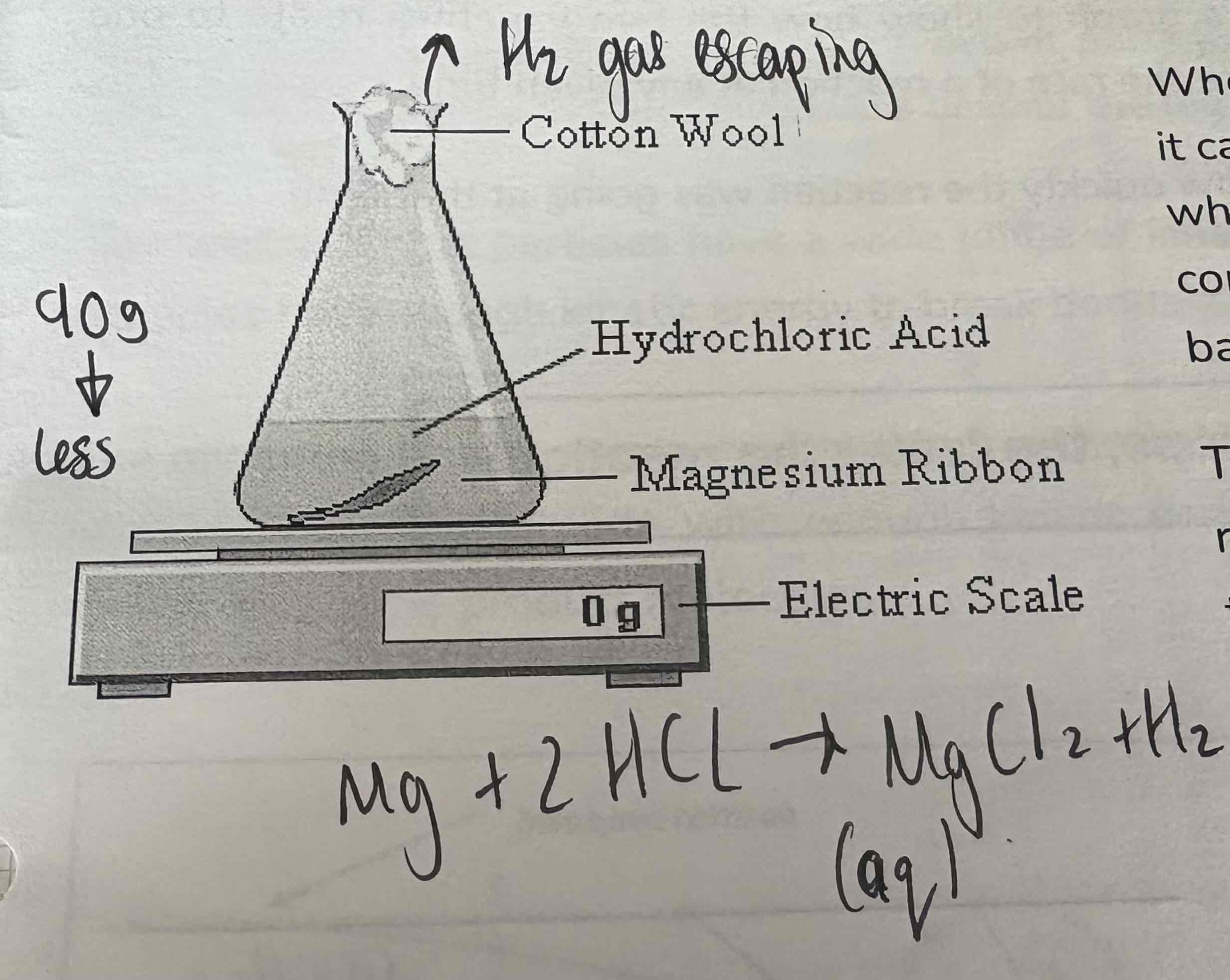
What happens in a measurement of change in mass?
When gas is produced, it can escape through the cotton wool. This leads to a loss in mass. This is then recorded and placed on a mass against time graph.
What is another function of cotton wool when measuring the change in mass?
Allows gas to escape
Prevents liquid spray during reaction from escaping flask
Describe the apparatus of the formation of a precipitate:
See image:
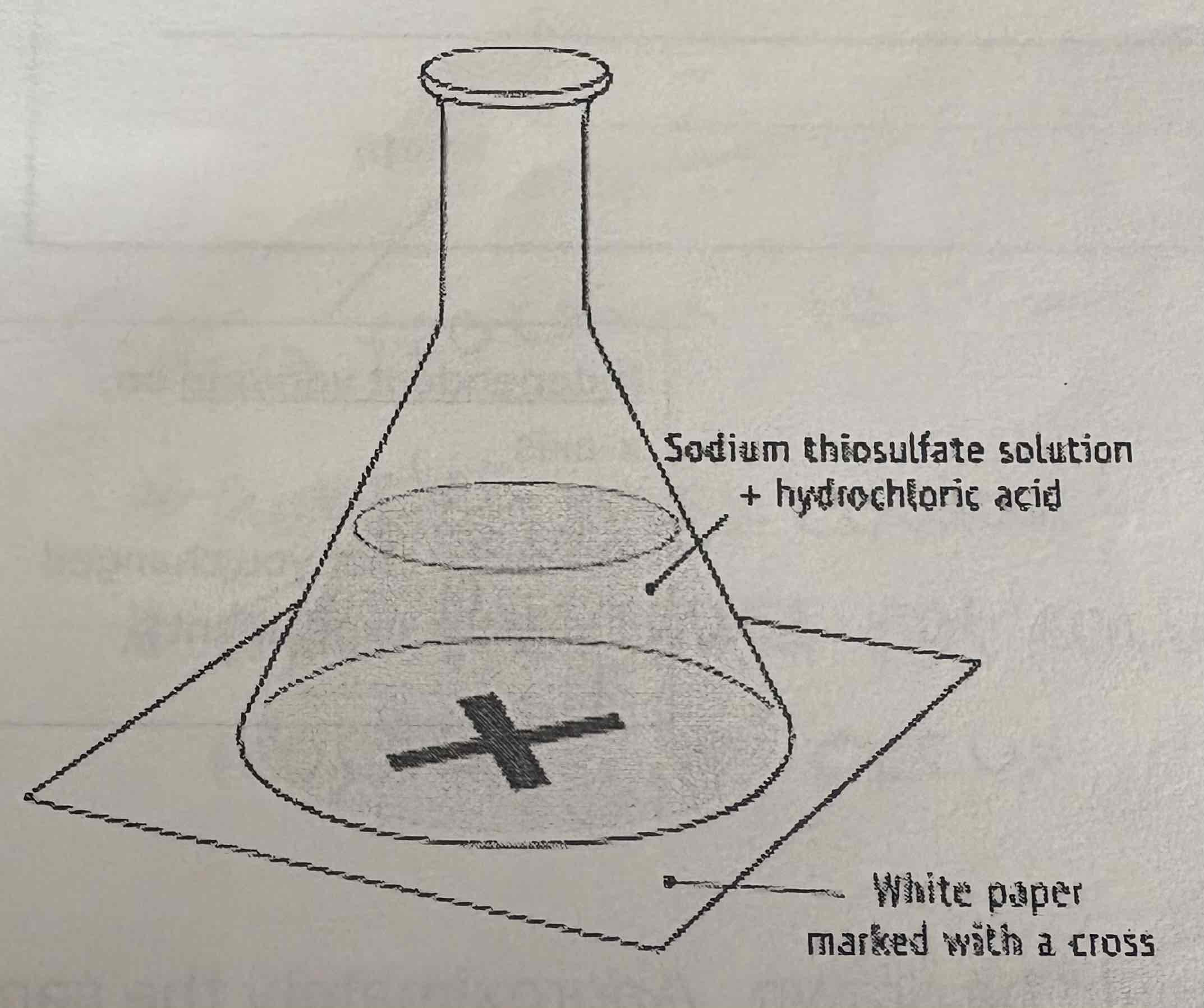
Why is the rate of precipitation investigated?
Sometimes, when two aqueous solutions are mixed, a precipitate (a solid) forms
How is the rate of a precipitation reaction recorded?
The time is recorded from when the second reactant solution is added until the precipitate forms and obscures the cross when directly viewing downwards
What are graphs used for when measuring rates of reaction?
To measure the rate of reaction at any given time
What does the gradient of a line show when measuring rates of reactions?
How quickly the reaction was going at that time
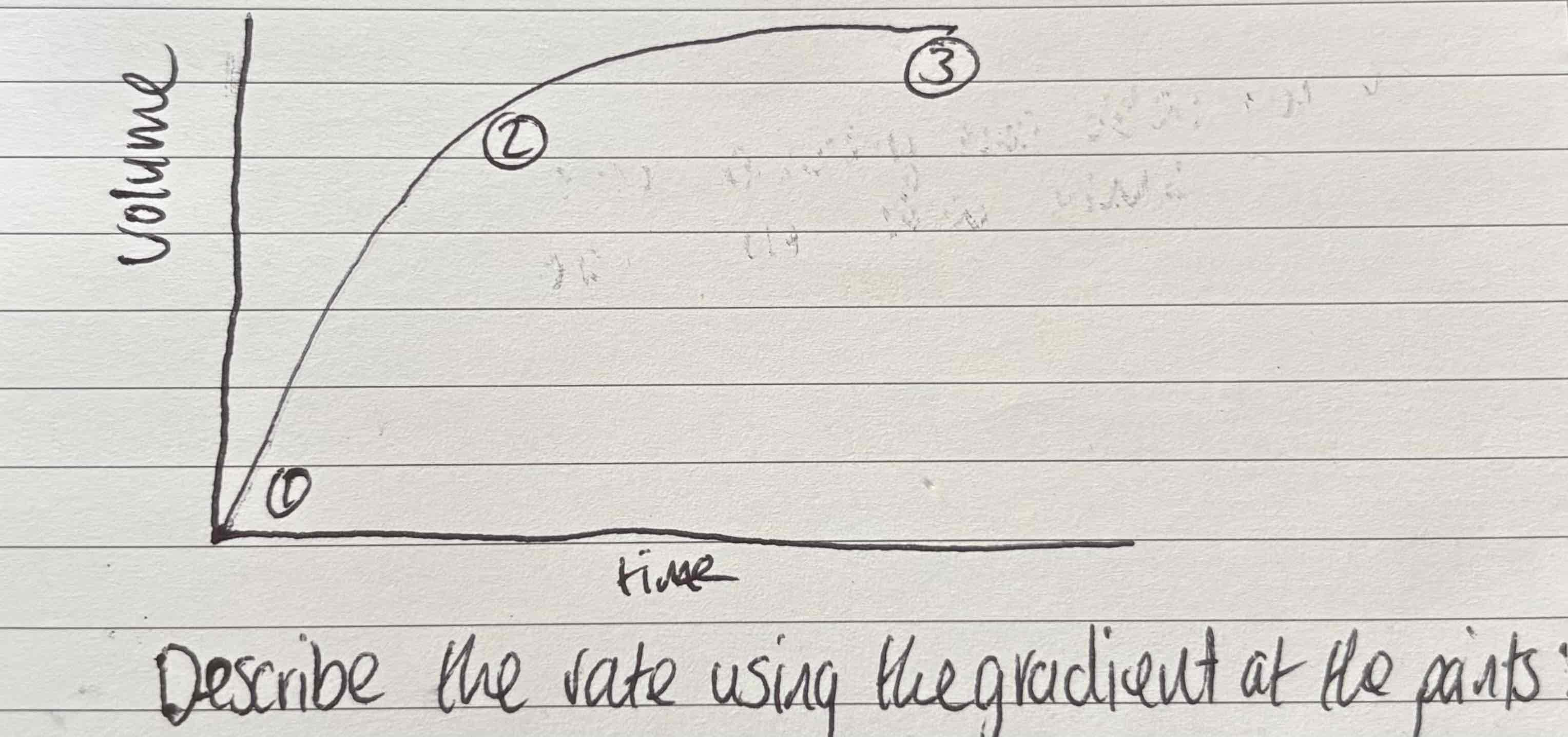
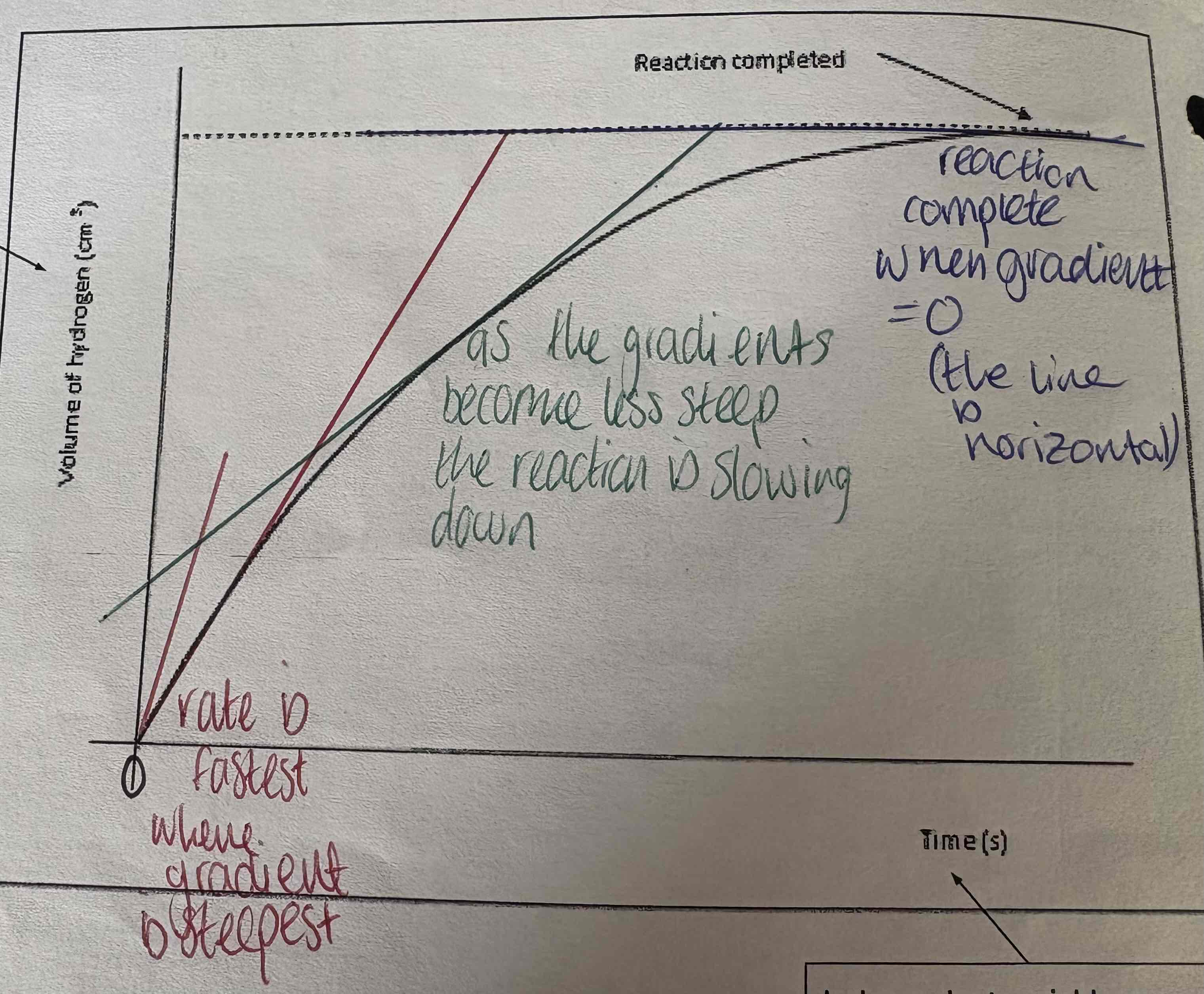
Describe the points of this graph:
Rate is fastest as gradient is steepest
Gradient is becoming less steep and therefore rate is slowing down
Reaction is done, gradient = 0
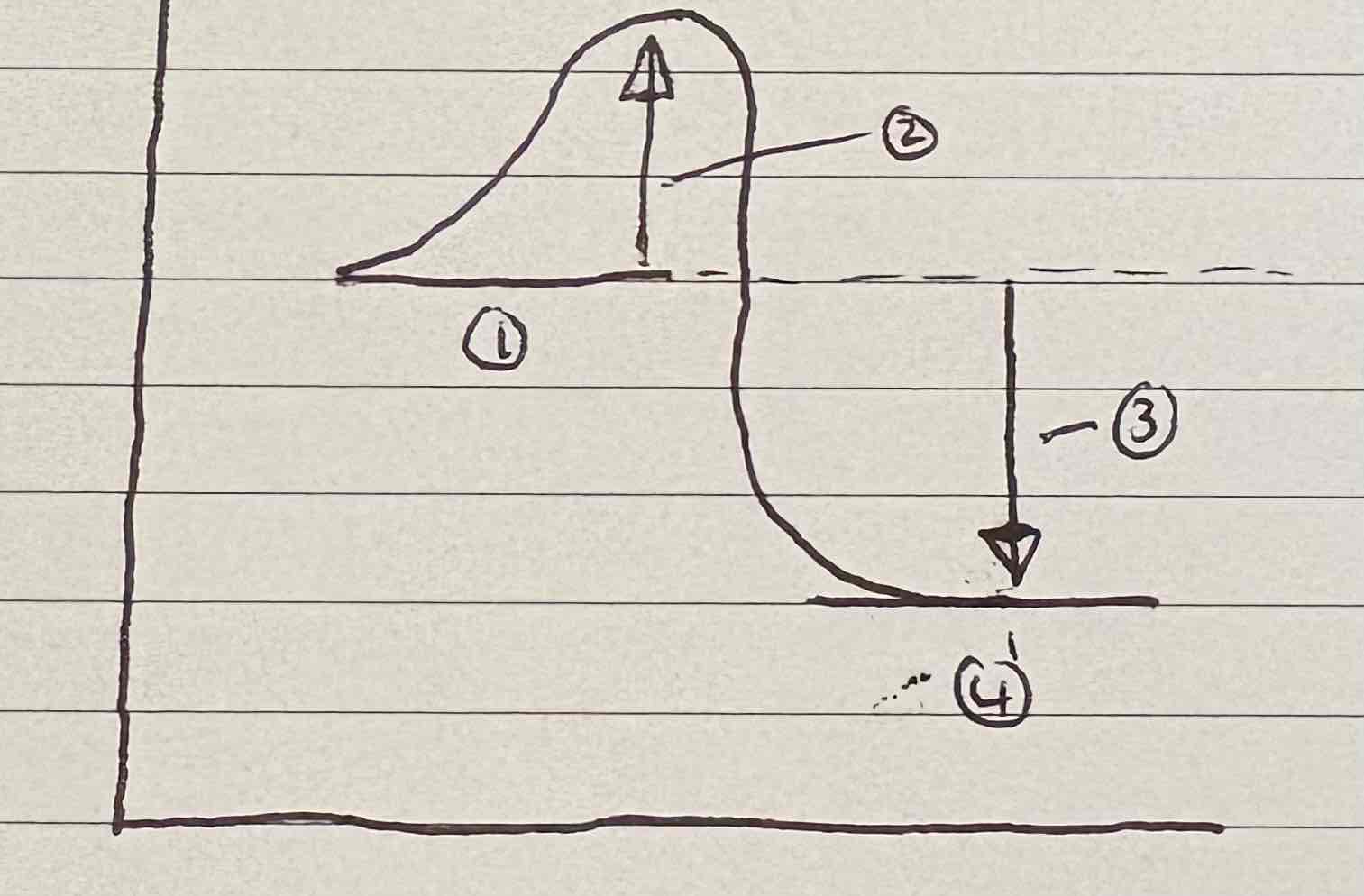
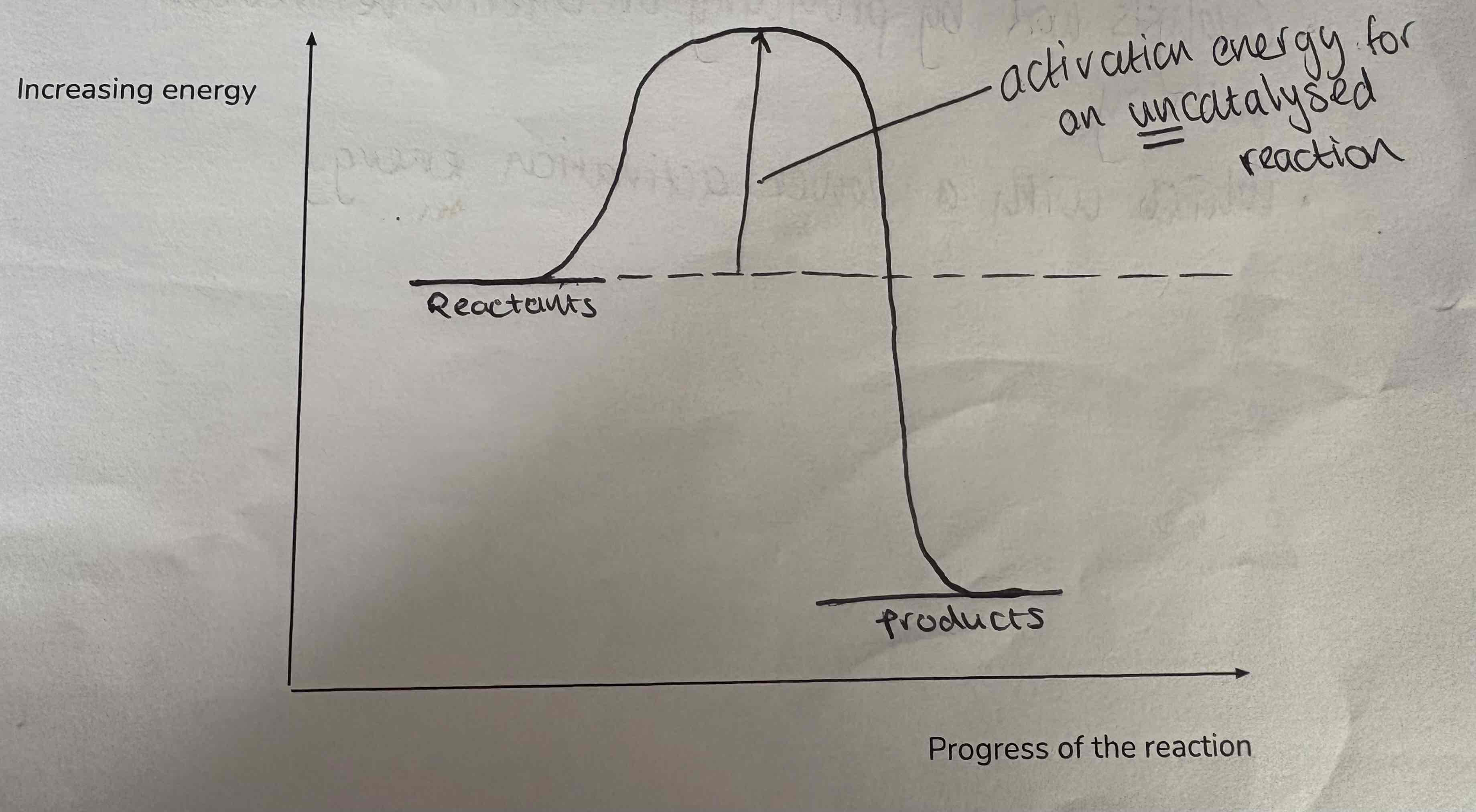
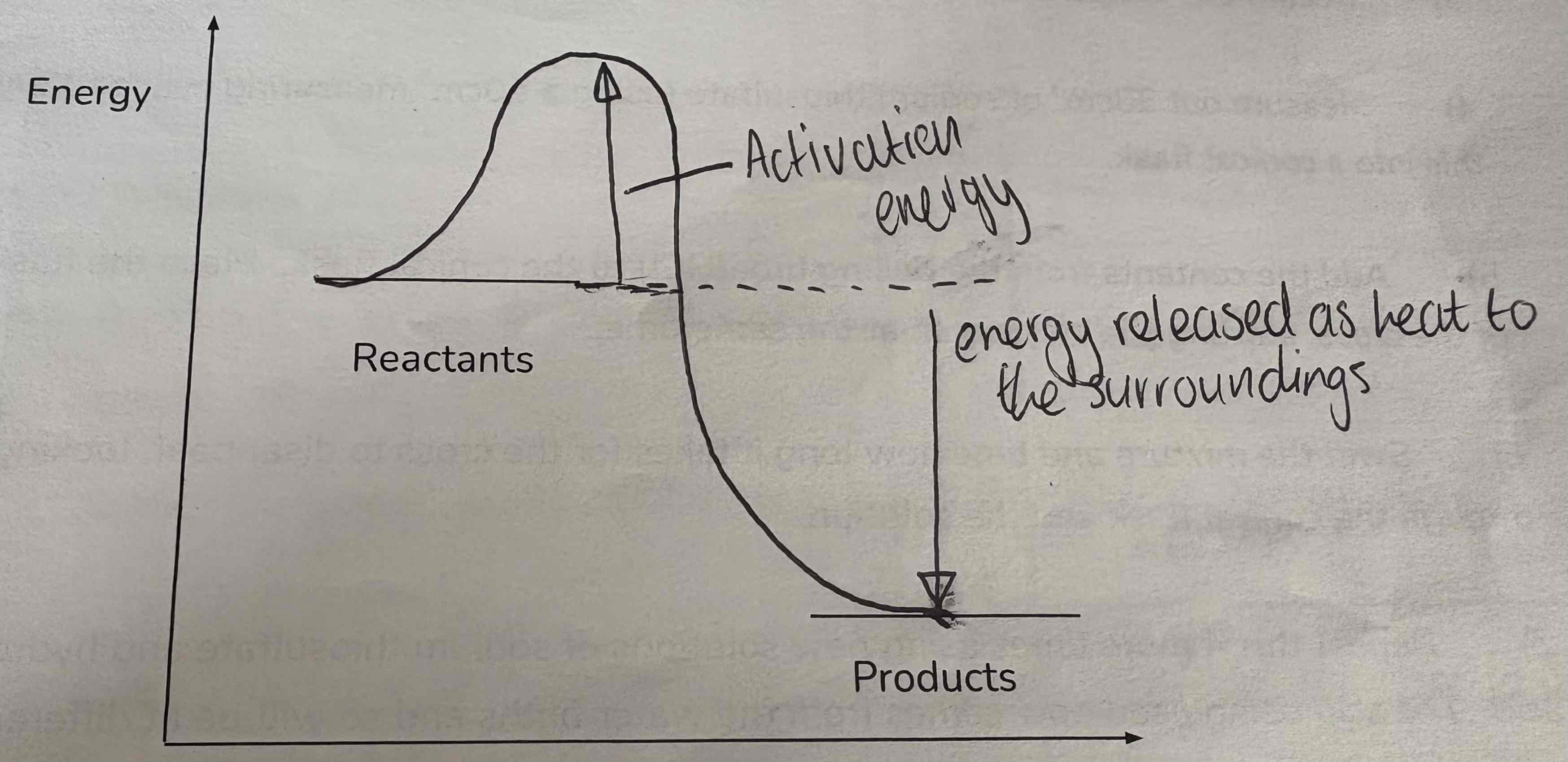
Label this diagram:
Reactants
Activation energy
Energy released as heat to surroundings
Products
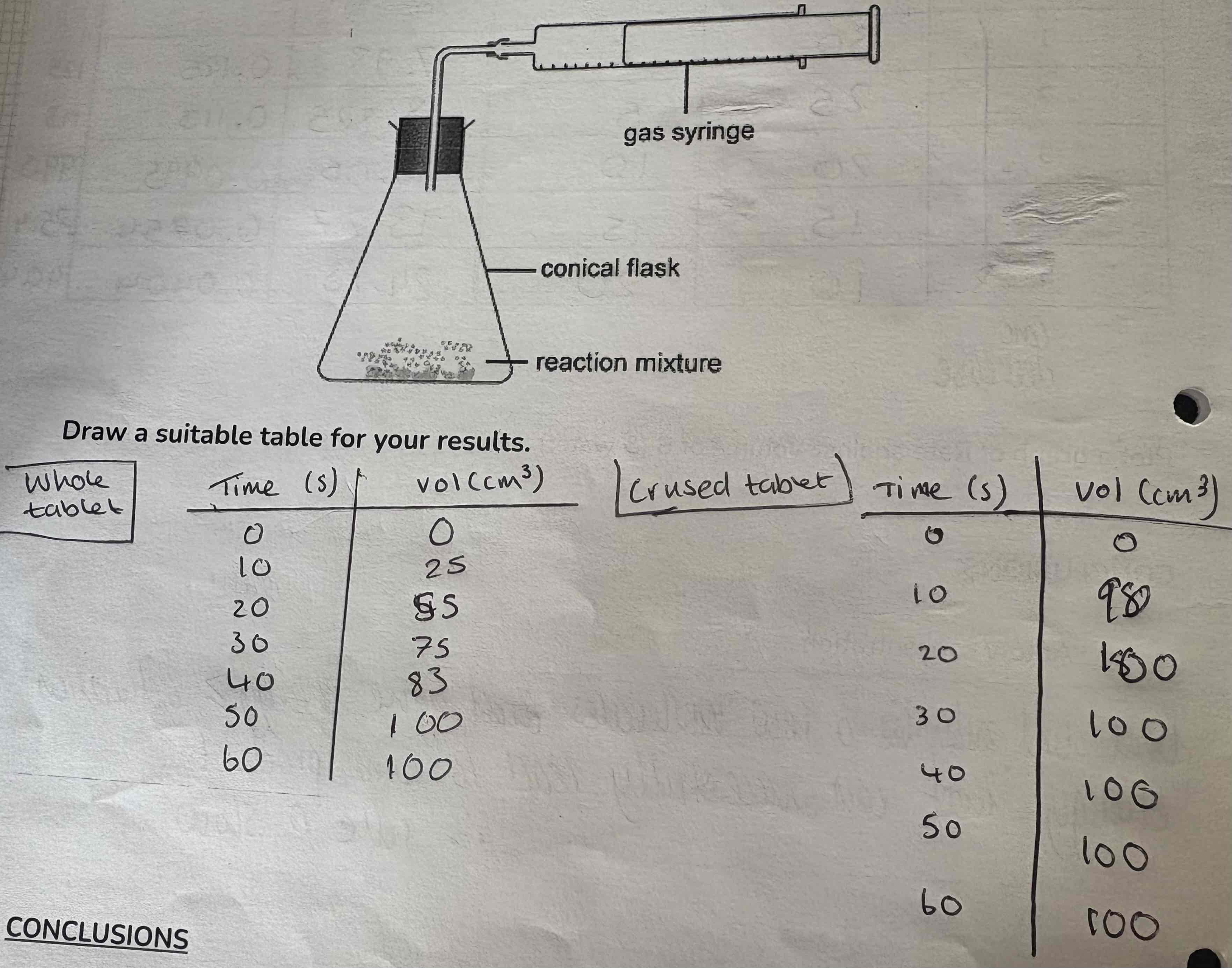
How is this apparatus used?
Time how long it takes to collect a known volume of gas as the Vitamin C tablet dissolves in water
Crush it up and re-time
Why do some reactions not occur even though a collision occurs?
Only a fraction of the particles have enough kinetic energy to break bonds and bring about chemical change
What is activation energy?
The minimum kinetic energy required
What 2 things must happen for a reaction to occur?
Particles must collide
They must collide with enough energy for a reaction to occur
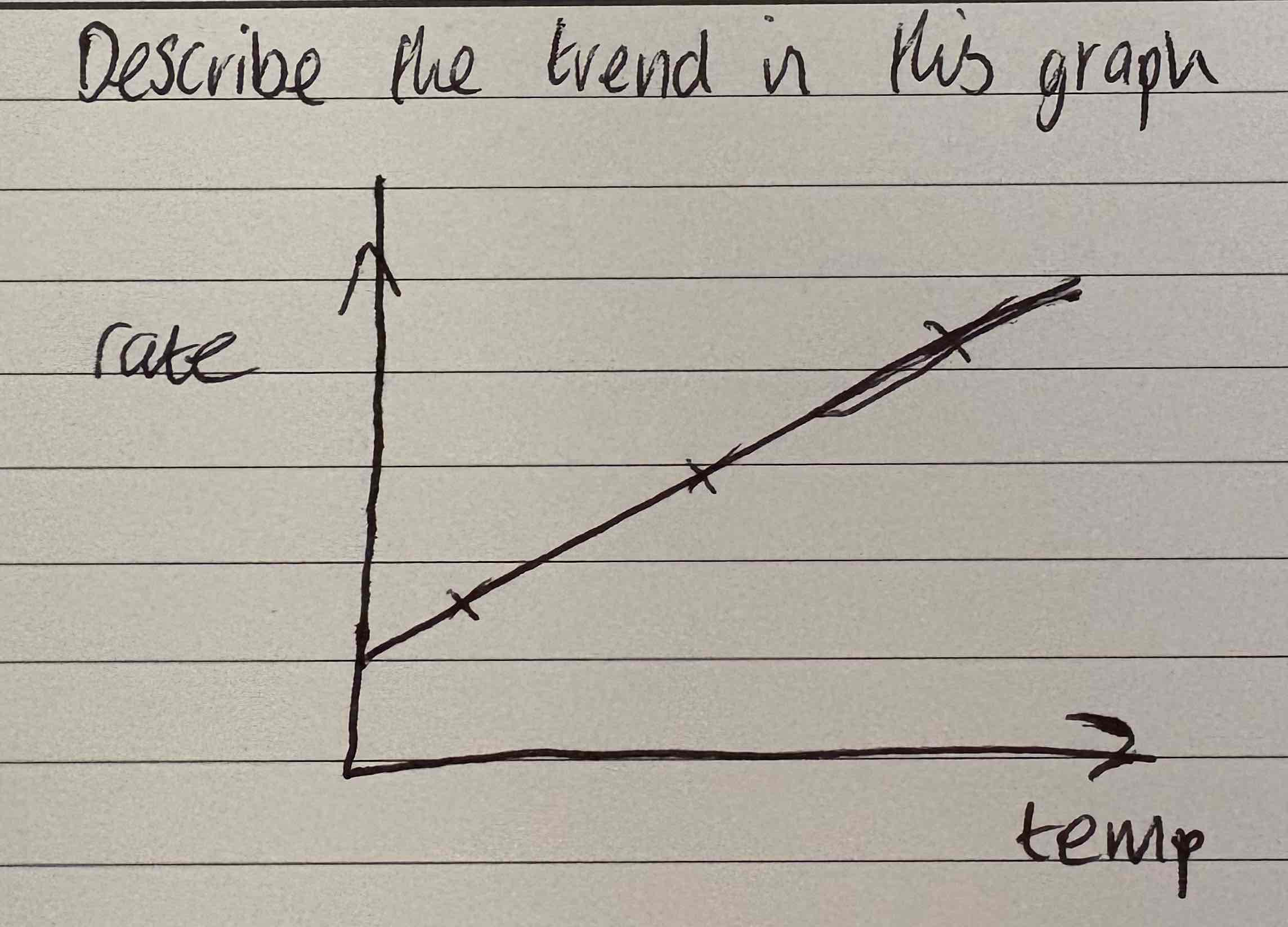
Describe the trend in this graph:
As the temp goes up, the rate goes up
How to measure the affect of temp in rates of reactions?
10cm3 of HCL into 5 boiling tubes into 4 water baths of different temps (30, 40, 50, 60) and leave 1 on the desk on rack
Record temp of the one not in water bath and right down - this is the control without affect of heat
30cm3 of Sodium Thiosulfate into comical flask. Add HCL, 4 separate times an calculate the time of how long it takes to cover up the x below the flask
What are the conclusions of the affect of temp on a reaction?
During low temps:
At low temps:
Molecules will only have a small amount of energy and so move about slowly
Only a few of them will have energy >= activation energy for that reaction
Only a few successful collisions occur per second and the rate is slow
Affect of temp on reaction as temp increases:
As temp increases:
The molecules gain energy and move around more rapidly
More molecules now have energy greater tan activation energy
More collisions occur, more of which are successful per second and so the rate of reaction increases
How does concentration affect the rate of reaction and how would you investigate this?
30cm3 of B into a conical flask then add 30cm3 of A
Time how long A + B take to turn down
Repeat but decrease amount of B by 5cm3 and replace with 5cm3 of water
What is the conclusion of the affect or low concentration in reaction?
At low concentration, there will only be a few molecules that have energy greater than the activation energy that can be successfully react to form products and so rate is slow
How does the concentration increase the affect rate of reaction?
There will be more molecule with energy greater than activation energy present in the same volume of liquid
Therefore, there is an increase in the chance of a successful collision in a given unit of time and the rate increases
What is the affect of Surface Area in the rate of a reaction?
Increasing SA, increases the rate of reaction
More particles are exposed to the other reactant when the surface area is increased
This leads to more successful collisions in a given unit of time and so the rate increases
What is a catalyst?
A substance that will increase the rate of reaction without undergoing any permanent change
e.g. Manganese Dioxide (black powder), MnO2 helps breakdown of Hydrogen Peroxide
e.g. Iron is used in the production of Ammonia from N2 to H2
e.g. Enzymes - biological catalysts - some breakdown food
How do catalysts speed up rate of reaction?
For a reaction to occur there must be sufficient energy to overcome activation energy
Catalysts reduce activation energy required and so increase successful collisions which in turn form products and the reaction in faster