Energy Generation in Mitochondria/Chloroplasts
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Photosynthesis
process using energy in sunlight & CO2 to create the organic materials required of cells
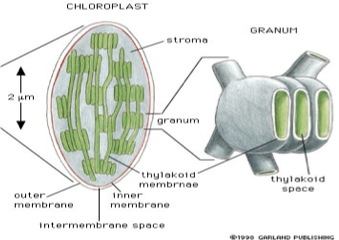
Chloroplasts
special organelle in plants
similar to mitochondria
proton pump creates ATP
Stroma instead of matrix
Has its own RNA, DNA, & ribosomes
electron transport chain is in thylakoid membrane
Photosynthetic e- transfer reactions
sunlight energizes e- in chlorophyll
moves down e- transport chain
e- from H2O makes O2 waste
electrochemical gradient is made in the stroma
makes ATP
generates NADPH from NADP+
Carbon fixation reactions (light-independent)
ATP & NADPH produced in light reaction used as energy
reduces power to take CO2 & convert it to a carb
Chlorophyll
green because it absorbs all but green light
e- gains a higher energy level when wavelength is absorbed
Photosystem
Chlorophylls are in a multiprotein complex
antenna is many molecules of chlorophyll that capture sunlight
Reaction Center
set of proteins in the thylakoid membrane
special chlorophyll molecule that is an irreversible trap for excited e-
transfers e- to a more stable environment
replacement e- comes from splitting water
when 4 e- removed O2 released
The light reaction makes what to synthesize the sugar
ATP & NADPH
Electron from chlorophyll in photosystem 2 is donated to
a primary electron acceptor
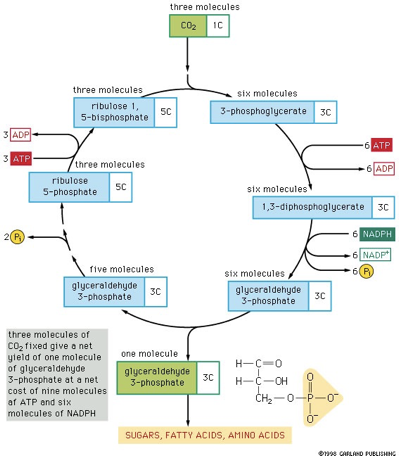
Calvin Cycle goes around how many times?
3
Enzyme that catalyzes most reactions is
rubisco
slow enzyme
large quantity
large compensation need
CO2 joins with ribulose 1.5 bisphosphate by…
carboxylase called rubisco
1 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in Calvin Cycle
is generated & goes to make sugar
large amount of energy goes to regenerate ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate
3 ATP & 2 NADH required per CO2
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
converted to glucose
can be shuttled into glycolytic pathway in the mitochondria
eventually become pyruvate & ATP
excess converted into starch in the stroma