Lecture 2 -- Blood Supply, Meninges & Cerebrospinal Fluid
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the three layers of the meninges?
Dura Mater (Thick, fibrinous layer), Arachnoid Mater (Thin, transparent), Pia Mater (Thin, delicate membrane)
Which meningeal layer is closest to the CNS tissue?
Pia Mater
What are the two folds formed by the separation of the dura mater?
Falx cerebri (in the longitudinal fissure) and Tentorium cerebelli (in the transverse fissure)
Which cranial nerve innervates the dura mater, making it pain-sensitive?
CN V (Trigeminal)
What is contained within the venous sinuses found in the dura mater?
Blood
What is the potential space beneath the dura mater called?
Subdural space
Which layer of blood vessels do pia mater merges to?
Tunica adventitia
What does the subarachnoid space contain?
CSF and blood vessels
Which meningeal layer is highly vascular and has dense nerve innervation? Which isn't?
Pia Mater is highly vascular BUT arachnoid mater is avascular with little innervation.
What embryonic tissue gives rise to the dura mater?
Axial mesoderm → mesenchyme → ectomeninx → dura mater
What embryonic tissue gives rise to the arachnoid and pia mater?
Ectoderm → Neural crest cells → Endomeninx → Arachnoid + pia mater
What is the space between the dura mater and the vertebrae called?
Epidural space
What is the epidural space filled with?
Fat and connective tissue
Which meningeal layer is most impermeable anaesthesia?
Arachnoid mater
Which layer of the meninges is the most permeable to anaesthesia?
Dura mater
Where is the landmark for injecting the anaesthesia?
Cul-de-sac → The space where the dura mater continuous while arachnoid and pia mater stop
What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Physical protection of CSF tissue
Circulation of nutrients or neurotransmitters
Stable environment
Volume buffer → If the neural tissue is increasing in size, the CSF is remaining constant → It might cause damage → The amount of CSF may have slightly deviation, avoiding the damage of tissue
Where is CSF found?
Circulates through subarachnoid space, ventricle of brain and central spinal canal
What substances do CSF contain?
Cell-free
Protein-free
Low amino-acid content
Low and stable K+
Low glucose content
Where are the ventricles derived from?
Lateral ventricles → Telencephalic vesicles
Third ventricle → Central cavity of telencephalon + diencephalon
Mesencephalic aqueduct → Mesencephalic vesicle
Fourth ventricle → Rhombencephalon
What is the main source of CSF production?
Choroid plexi
Where are the choroid plexi located?
Main: Roof of the third ventricle
Secondary choroid plexus: Roof of the fourth ventricle
CSF secreted from third ventricle → mesencephalic duct → Fourth ventricle → 1. Drain out to the sub-arachnoid space through the holes in fourth ventricle/ 2. Con’t travel along the central canal → Spinal cord
What type of cells line the ventricles and central canal, aiding CSF circulation?
Ependymal cells
How do ependymal cells contribute to CSF production?
Pump solutes into the CSF, drawing water in by osmosis → Because of the continuous production of water, more and more CSF is produced
How do lipid-soluble substances enter CSF?
Pass readily across
How do water-soluble substances enter CSF?
Via actively transported
How does CSF drain into venous sinuses?
Through arachnoid granulations
How does choroid plexus develop?
Two protection of tela choroidea, which is the region of precursor of pia mater, which adheres to underlying ependyma, invaginate into the roof of the four ventricle in nyelencephalon
+ Roof plate of cranial diencephalon invaginated into 3rd ventricle
+Grooves form in the ventromedial cerebral hemisphere = Choroid fissures → Pia mater covering these grooves invaginate into lateral ventricles
Where can CSF be collected from?
Cerebellomedullary cistern (Alatanto-occipital space) and lumbar cistern (L5-L6 lumbar space)
What two structures form the blood-brain barrier?
Foot processes of astrocytes and tight junctions between endothelial cells
What is the function of the blood-brain barrier?
Maintains CSF in a steady state by reducing vascular permeability
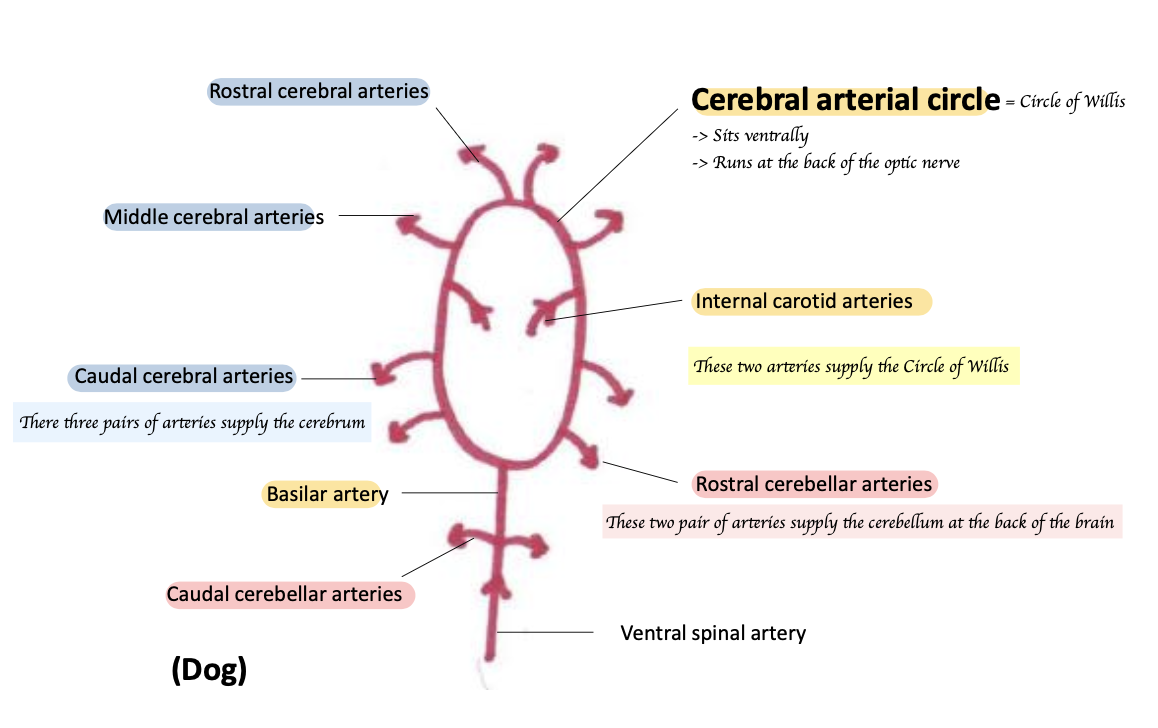
Describes the circle of Willis in dog.

Name three pairs of arteries that supply the cerebrum in dogs.
Rostral cerebral, middle cerebral, caudal cerebral arteries
Name two pairs of arteries that supply the cerebellum.
Rostral cerebellar arteries and caudal cerebellar arteries
What arteries supply the Circle of Willis in dogs?
Internal carotid and basilar arteries
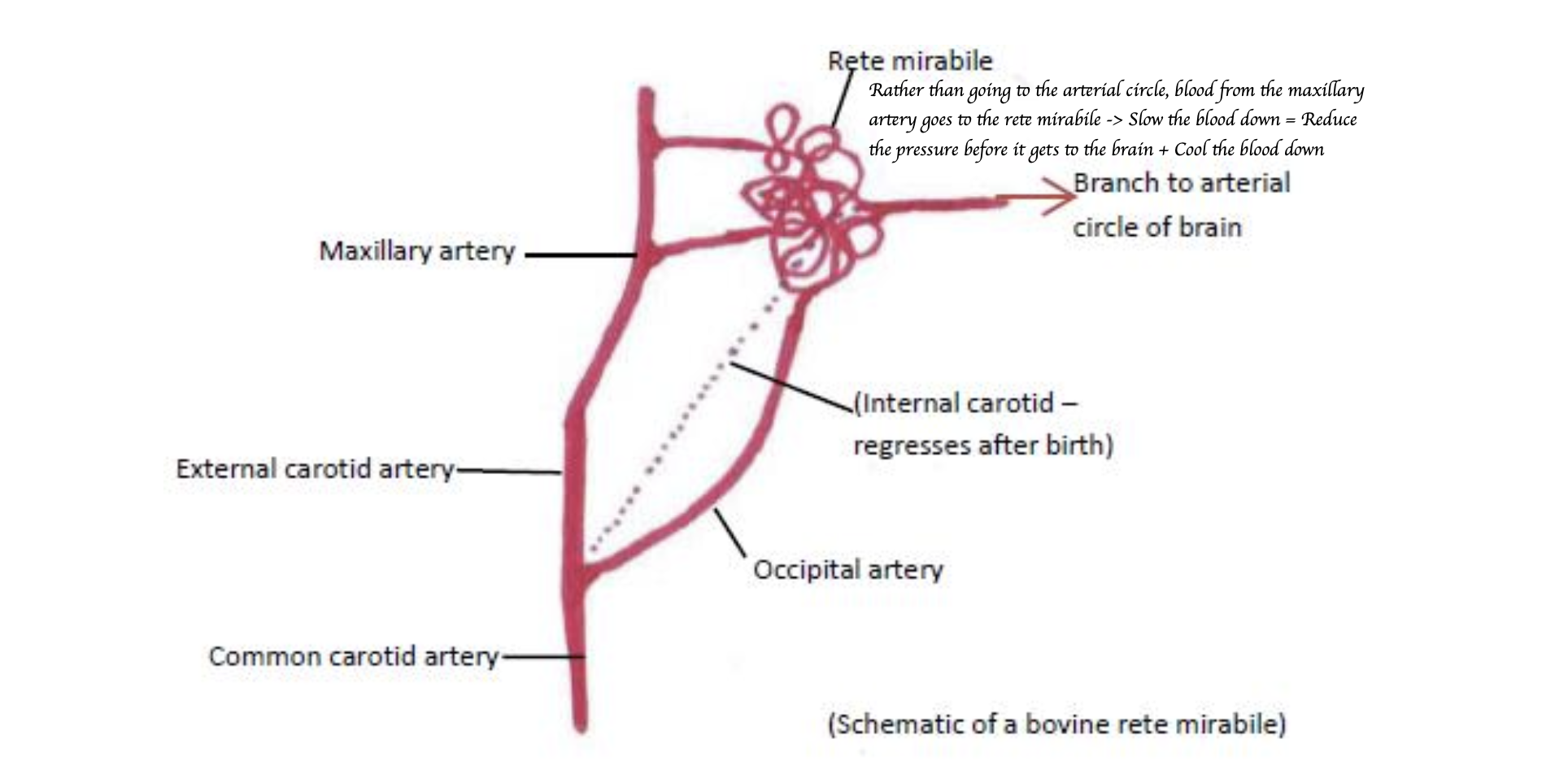
What is the rete mirabile?
Network of blood vessels that slow down and cool blood before it reaches the brain
Which arteries primarily supply blood to the brain in dogs and horses?
Internal carotid and basilar arteries.
Which arteries primarily supply blood to the brain in sheep and cats?
Maxillary arteries via rete mirabile
Which arteries primarily supply blood to the brain in cows?
Maxillary and vertebral arteries via two rete mirabile
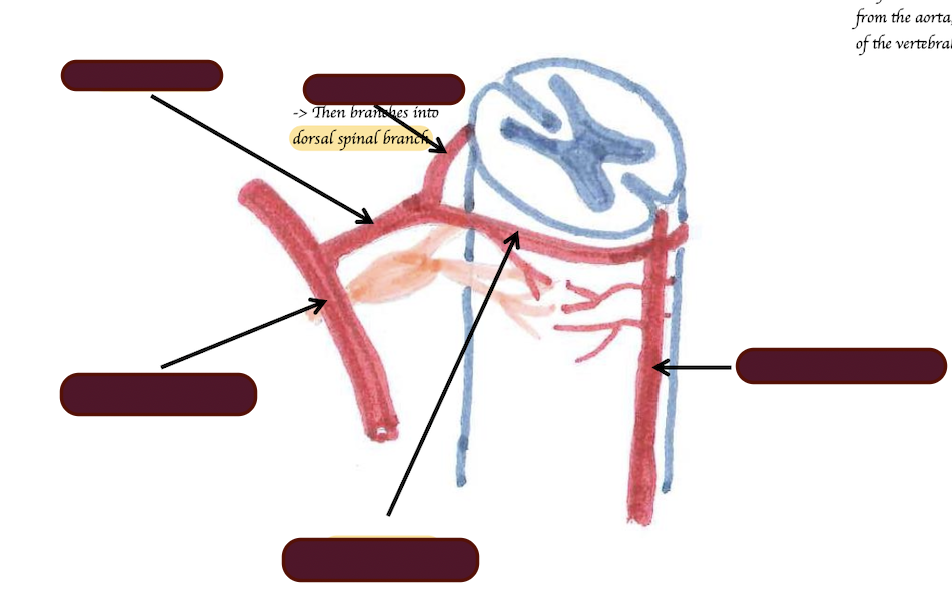
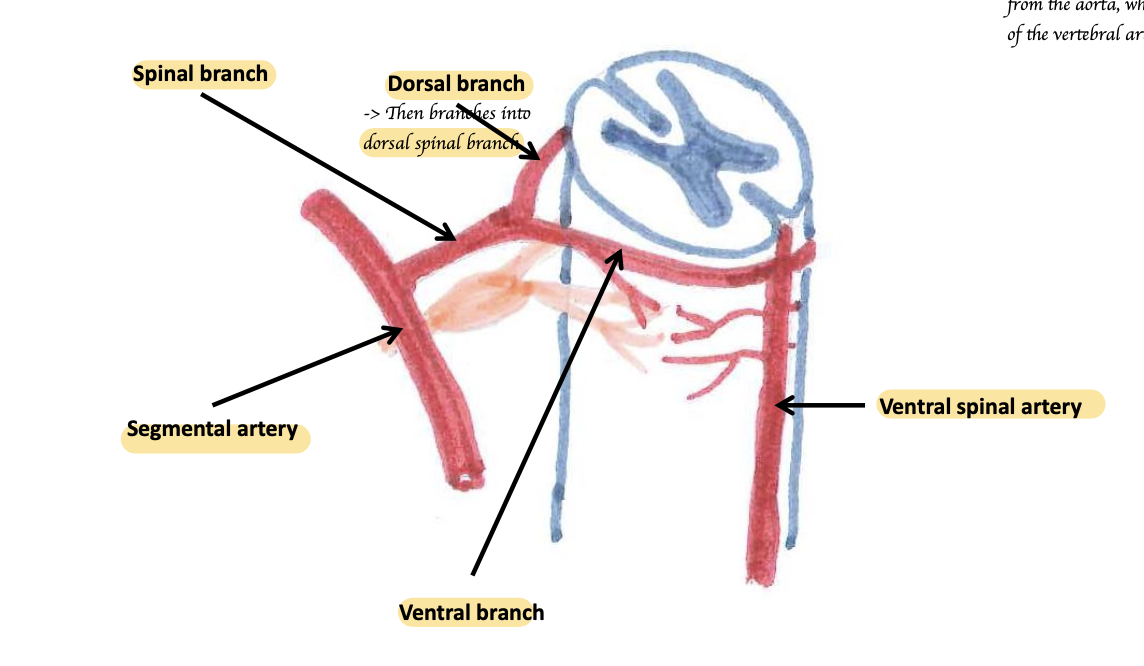
Inter-arterial anastomoses and collateral circulation is limited in the CNS. What are the consequences?
If the blood supply is comprised in a certain region for some reasons, it is difficult to redirect blood to that region → Stroke can be very traumatic
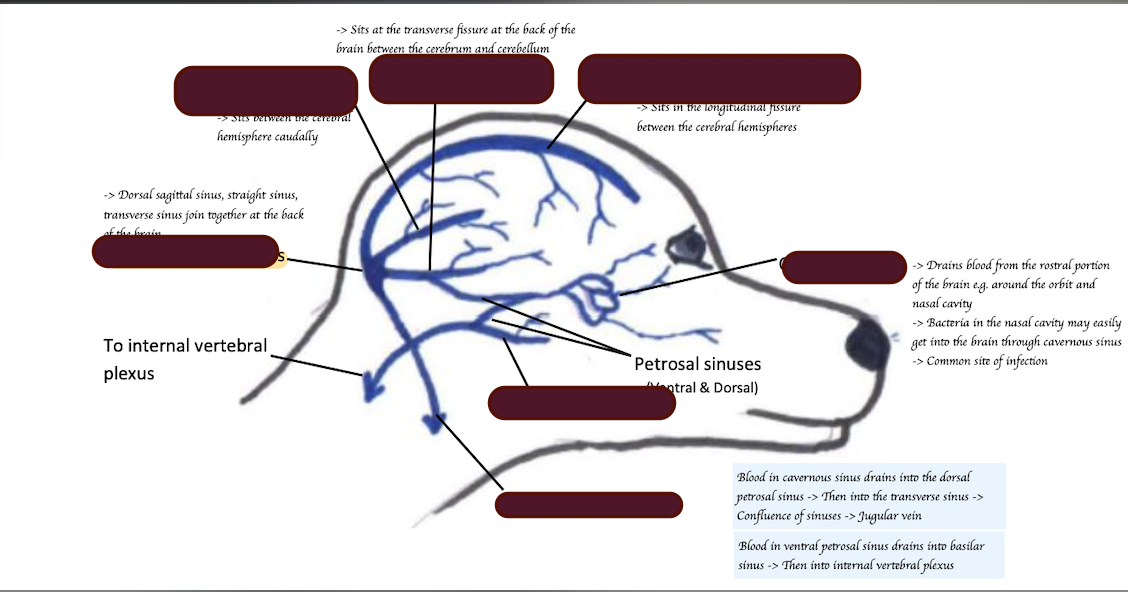
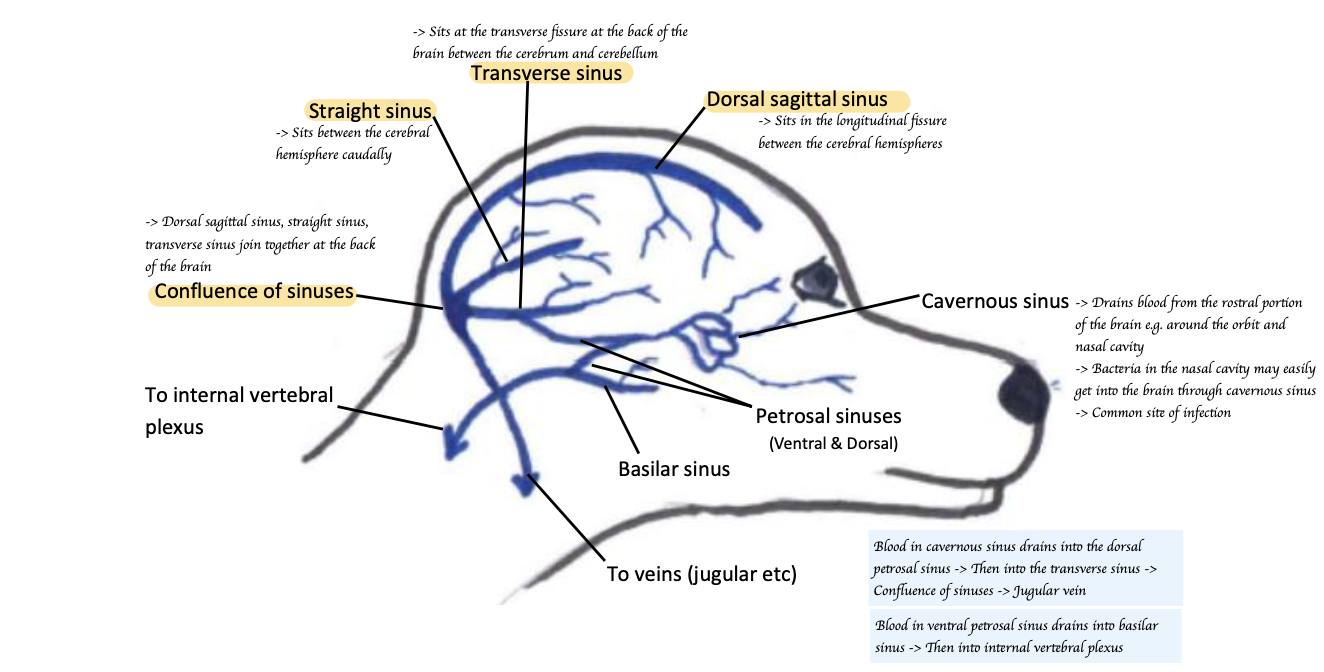
Name three venous sinuses involved in the venous drainage of the brain.
Dorsal sagittal sinus, straight sinus, transverse sinus
Describe the Venus drainage of the brain.