ADH2 Exam 2: HF
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What can HF result in? (3)
decreased CO
Myocardial hypertrophy
abnormal thickening of heart muscle
Pulmonary and systemic congestion
What are the causes of HF?? (6)
MI
HTN
dysrhythmias
Valvular disease
Cardiomyopathy
disease of heart muscle
Pericarditis
swelling of sac around heart
viral infx
or MI
General lifestyle changes to prevent HF? (7)
what vax should u get?
Quit smoking
Limit alc
Exercise
Low Sodium diet
Weight control
Control HTN, DM. HLD
Get flu and pneumonia vax

Key sign of L.S HF? (6)
PULMONARY congestion!!
dyspnea
orthopnea (trouble breathing when laying flat—supine)
crackles
s3 sound
pink frothy sputum
altered LOC (lack O2 to brain)

Key sign R.S HF?? (6)
SYSTEMIC Congestion!!—rest of body
JVD
dependent edema
ascites
hepatomegaly
weight gain
nocturia
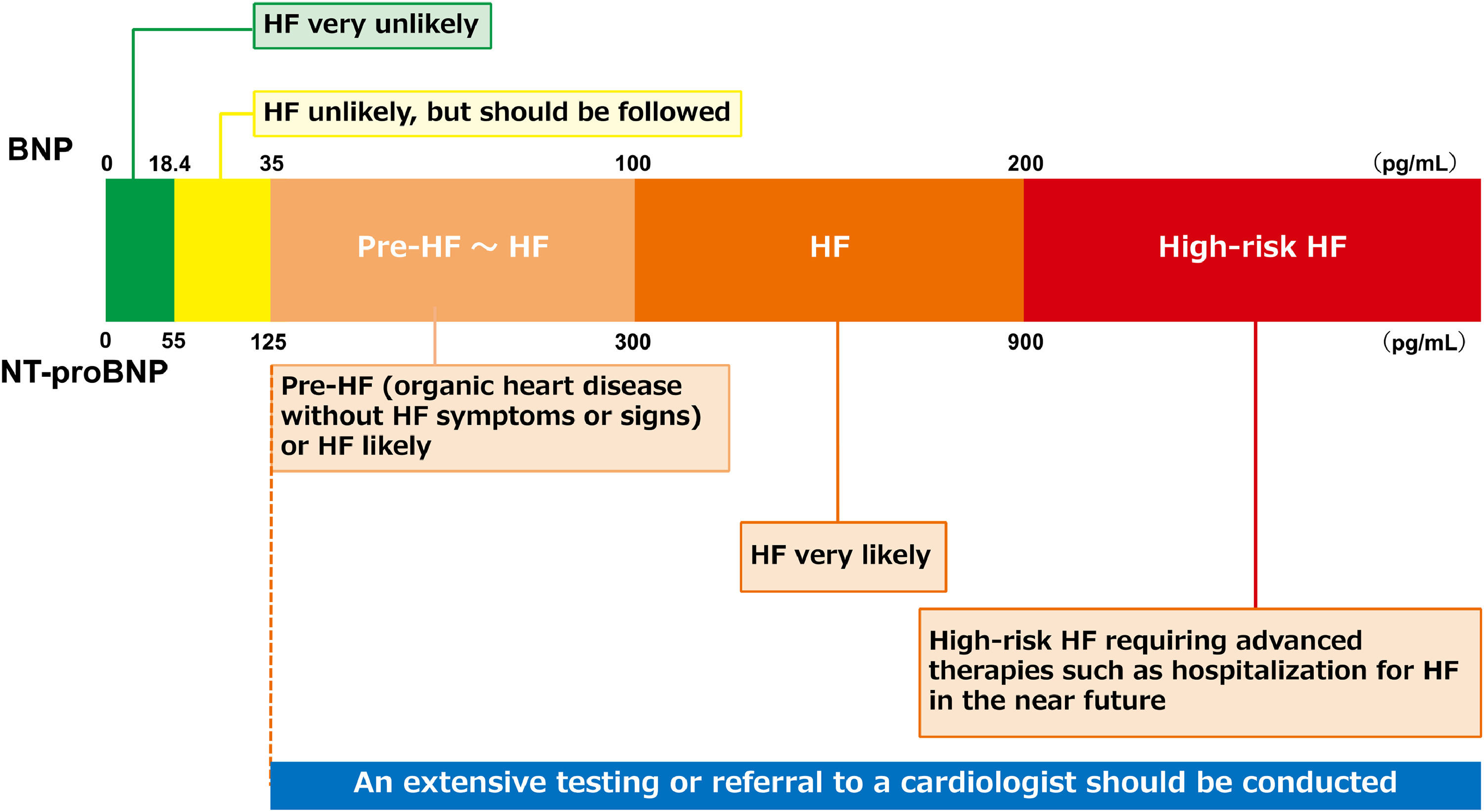
What are the PRIMARY HF Diagnostic tests?? (3)
BNP!!
< 100 safe
elevated = HF
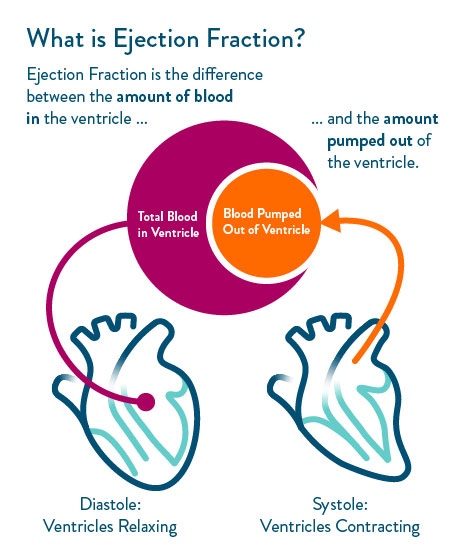
Echocardiogram
shows EF
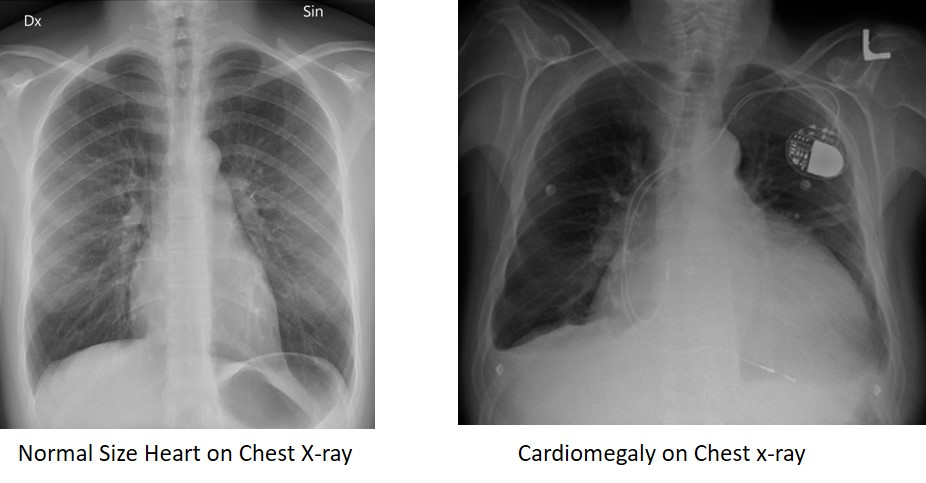
Chest Xray
Supportive HF dx test: (3)
HEMOdynamics
CVP (Central Venous Pressure): R. heart PREload/volume
PAP: (Pulmonary Artery Pressure): pulmonary circulation, RV AFTERload
PAWP: (Pulmonary Artery Wedge Pressure): L. Atrial pressure, LV PREload
What are the EF ranges? (3)
Normal
55-70%
<40% means reduced EF→ systolic HF (weak pump)
>40% but with poor filling means preserved EF → diastolic HF (stiff ventricle, poor filling NOT Pumping tho)
**lower the number, the less blood being ejected from heart in each beat
What does chest xray show in HF? (2)
Cardiomegaly
enlarged heart
Pulmonary congestion
HF 3 general categories of nursing care:
airway/O2 (2)
monitoring (5)
management/support (2)
Airway and O2:
High fowlers
give O2 as prescribed
Monitoring
VS
Hemodynamics (CVP, PAP, PAWP)
Daily weights
Strict I/O
Labs: BNP, electrolytes
Management/ Support
fluid and sodium restriction
energy conservation
5 classes of HF meds and the prototypes:
Diuretics
Loop (furosemide)
Thiazide
K-Sparing (spironolactone)
ACE inhibitors, ARBs, nitrates
Digoxin
BB
metoprolol
carvedilol
Anticoags
warfarin
Meds that decrease PREload?
Diuretics (loop, thiazide, K-sparing)
furosemide
spironolactone
rapid relief of fluid overload, P. Edma
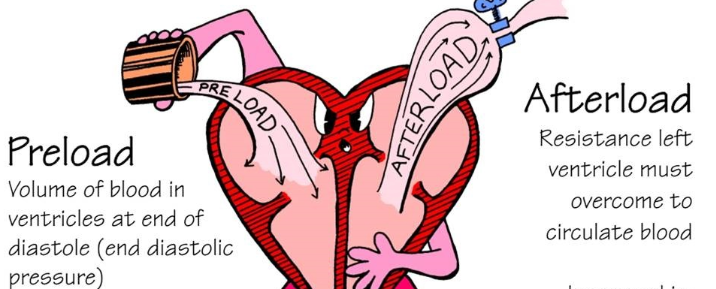
Meds decrease AFTERload? (3)
ACE inhibitors (captopril)
ARBs (losartan)
Nitrates
Med improving contractility:
Digoxin!!
Dig toxicity (early and late)
Early: GI issues (NVD; anorexia)
Late: Vision changes
yellow, green halos
dysrhythmias
0.2-2 ng
What meds decrease WORKLOAD
and why?
BB
- Metoprolol etc
decreases HR and BP, allowing heart to fill better
*start low and slow, may worsen symptoms if titrated too quickly!!!
What are major complications of HF?? (4)
Pulmonary Edema
fluid OVERload
impaired gas exchange
Cardiogenic shock
severe pump FAILURE!! → hypotension
poor perfusion
Dysrhythmias
a. fib
ventricular dysrhythmias
Organ dysfunction
renal and liver failure from chronic poor perfusion!
Pulmonary edema HF complication findings: (8)
Severe dyspnea
orthopnea
cyanosis
anxiety
crackles
pink frothy sputum
cough
tachycardia
Management of Pulmonary edema: (6)
High fowlers
O2
Possible intubation
IV diuretics (furosemide)
would need bed pan/ catheter
Morphine (decreases preload and anxiety)
Vasodilators as ordered (nitro)
breath easier
HF basic pt education (3 categories):
diet/fluid (3)
self-monitoring (2)
meds/lifestyle (2)
also, what med to avoid?
report how much weight gain?
Diet/ fluids—duh
Low sodium diet
fluid restrictions
NO NSAIDS!!!!! (increases sodium and fluid retention)*******
Self-monitoring
daily weight
report >2 lb/day OR >5lb. week gain************
Meds and lifestyle:
balance activity w/ rest
take meds as prescribed
HF key points:
definition
causes (6)
Left v Right
Diagnostics (3)
Nursing care (5)
Meds (5)
Complications (4)
Education (5)
definition: heart muscles pump badly→ decreased CO and congestion!
causes (6)
MI
HTN
valvular disease
Cardiomyopathy
Pericarditis
Dysrhythmias
Left v Right
Left: Lungs (dyspnea, crackles, frothy sputum)
Right: rest of body (ascites, edema, JVD)
Diagnostics (3)
BNP: elevated = HF
ECG: EF <40% systolic; Preserved EF is diastolic)
In systolic HF (reduced EF), the heart is weak and can’t pump enough blood out.
🔹 In diastolic HF (preserved EF), the heart muscle is stiff, so it doesn’t relax and fill properly.
CXR: pulmonary congestion
Nursing care (5)
High fowler
O2
Daily weight
I/O
fluid and Na restriction
Meds (5)
Diuretics (decrease PREload)
ACE/ARBs (decrease AFTERload)
BB (decrease WORKload)
Digoxin (increase contractility)
Anti-coags (if clot risk)
Complications (4)
Pulmonary Edema
Cardiogenic shock
Dysrhythimas
Organ failure
Education (5)
Daily weight
Low sodium diet
fluid restriction
med adherence
report rapid weight gain (> 2lb/day OR >5lb/week)