Unit 4 "Transoceanic Interconnections" AP World History
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit four of AP world history Key Terms to study for the AP test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
primogeniture laws (4.1)
Theme: Economics
Not all sons of the wealthy could own land because primogeniture laws gave all of each estate to the eldest son
Omani-European rivalry (4.1)
Theme: Economics
The Omani-European rivalry was one reason for Christopher Columbus’s search for a new route to India. , Europeans faced competition from Middle Eastern traders based in kingdoms such as Oman. For example, the Portuguese set up forts in Oman but were repeatedly challenged by attempts to remove them
astronomical chart (4.1)
Theme: Technology
An astronomical chart is any map of the stars and galaxies. Mariners relied on these maps to guide ships’ direction, especially before the introduction of the compass, using the skies to help them determine their location.
cartography (4.1)
Theme: Technology
mapmaking, and knowledge of current and wind patterns also improved navigation.
maritime empires (4.1)
Theme: Government
Empires based on navies and sea travel
mercantilism (4.2)
Theme: Economics
Europeans generally measured the wealth of a country in how much gold and silver it had accumulated. For this reason, countries set policies designed to sell as many goods as they could to other countries-in order to maximize the amount of gold and silver coming into the country-and to buy as few as possible from other countries-to minimize the flow of precious metals out of the country.
trading post empire (4.2)
Theme: Economics
one based on small outposts, rather than control of large territories. The Portuguese also restricted Indian Ocean trade to those who were willing to buy permits, The aims of the fort construction were to establish a monopoly
Manila (4.2)
Theme: Economics
became a Spanish commercial center in the area, attracting Chinese merchants and others. Because of the Portuguese and Spanish occupations, many Filipinos became Christians.
galleons (4.2)
Theme: Technology
heavily armed Spanish ships
Christopher Columbus (4.2)
Theme: Government
credited with discovering the “ New World” he gained support from spanish monarchs to voyage across the Atlantic. increase the interest in discovery, and the English, French, and Dutch supported later exploration.
Bartholomew Diaz (4.2)
Theme: Government
sailed around the southern tip of Africa, the Cape of Good Hope
Vasco Da Gama (4.2)
Theme: Government
sailed farther east than Diaz, landing in India.There he claimed territory as part of Portugal’s empire. The Portuguese ports in India were a key step in expanding Portugal’s trade in the Indian Ocean and with points farther east.
Ferdinand Magellan (4.2)
Theme: Government
one of the ships in his feet made it around the world, proving that the earth could be circumnavigated.
northwest passage (4.2)
Theme: Government
a route through or around North America that would lead to East Asia and the precious trade in spices and luxury goods.
Jacques Cartier (4.2)
Theme: Government
sailed from the Atlantic Ocean into the St. Lawrence River at today’s northern U.S. border. He did not find a new route to Asia, but he did claim part of what is now Canada for France.
Samuel de Champlain (4.2)
Theme: Government
realized there were valuable goods and rich resources available in the Americas, so there was no need to go beyond to Asia.
John Cabot (4.2)
Theme: Government
the English king sent an explorer named John Cabot to America to look for a northwest passage. Cabot claimed lands from Newfoundland south to the Chesapeake Bay.
Henry Hudson (4.2)
Theme: Government
the Dutch sent Henry Hudson to explore the East Coast of North America. Among other feats, he sailed up what became known as the Hudson River to see if it led to Asia. He was disappointed in finding no northwest passage
Quebec (4.2)
Theme: Government
French hoped to find gold. Instead, they found a land rich in furs and other natural resources, they established a town and trading post that they named Quebec.
New France (4.2)
Theme: Government
the French colony in North America,
Jamestown (4.2)
Theme: Government
English Colony in North America
New Amsterdam (4.2)
Theme: Government
Dutch settlement which today is known as New York City
Disease smallpox (4.3)
Theme: Environment
a disease , When Europeans, who were largely immune after millennia of exposure in Afro-Eurasia, had face-to-face contact with indigenous populations, they infected these populations with the deadly disease.
horse (4.3)
Theme: Environment
Europeans brought to the Americas, the horse, transformed the culture of the American Indians living in the Plains region. Helped Native American tribes.
conquistadores (4.3)
Theme: Government
Spanish soldiers, brought smallpox to the Western Hemisphere
maize, cacao, okra, rice, sugarcane (4.3)
Theme: Environment
Europeans took home corn, tomatoes, potatoes, beans, peppers and cacao seeds. African brought okra and rice, sugarcane and tobacco were cash crops (crops grown to sell and not for subsistence)
creole (4.3)
Theme: Culture
West African language combined with European languages (English, Spanish, French, or Portuguese)
gumbo (4.3)
Theme: Culture
The dish known as gumbo, popular in the southern United States, has roots in African cooking.
Columbian Exchange (4.3)
Theme: Economy
the Eastern and Western Hemispheres became linked in a new way, sharing disease, foods, and animals. For the role Christopher Columbus played in establishing the link, these interactions became known as the Columbian Exchange.
transatlantic slave trade (4.3)
Theme: Economy
The transactions of slave for labor between The Eastern and Western Hemisphere
engenhos (4.3)
Theme: Economy
Sugar plantations processed so much sugar that they were referred to as engenhos
cash crop (4.3)
Theme: Economy
such as sugar and tobacco. Cash crops are grown for sale rather than subsistence.
African Diaspora (4.3)
Theme: Society
dispersion of Africans out of Africa
Asante Empire and Kingdom of the Kongo (4.4)
Theme: Government
Their participation in trade led to an increase in their influence.
Ming Dynasty (4.4)
Theme: Government
tried to limit outside influence on China by restricting trade. The Ming prohibited private foreign trade, destroyed some dockyards, limited the size of ships that could be built, and began reconstructing the Great Wall. These changes were part of a broader pattern of conservatism under the Ming to undo the influence of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty that ruled China before them. For example, the Ming reemphasized the importance of Confucianism and reinvigorated the traditional exam system.
Aztec Empire and Incan Empire (4.4)
Theme: Government
each included 10 million to 15 million people. However, the spread of European diseases caused their populations to plummet. Both empires collapsed quickly when attacked by Spanish forces.
New Spain (4.4)
Theme: Government
Spain’s new colony where the aztecs and Incans used to be
Francisco Pizarro (4.4)
Theme: Government
a conquistador who attacked the Inca and captured their ruler, Pizarro offered to release Atahualpa if the Inca would fill a large room with gold.
Mexico City (4.4)
Theme: Government
Spain’s colonial capital where they destroyed the Aztecs
Atahualpa (4.4)
Theme: Government
Incan ruler who was held for ransom but killed anyways
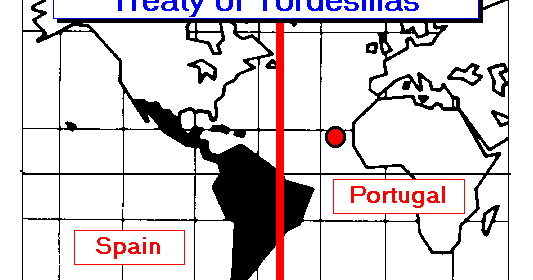
Treaty of Tordesillas (4.4)
Theme: Government
Spain and Portugal divided the Americas between them. Spain reserved all lands to the west of a meridian that went through eastern South America. Portugal reserved all lands east of this line. This arrangement put Brazil under Portugal’s rule, while Spain claimed the rest of the Americas.
Hispaniola (4.4)
Theme: Government
the name Columbus gave the island now occupied by Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
silver
Theme: Economy
the discovery of silver in Mexico and Peru revived economic fortunes
indentured servitude (4.4)
Theme: Economy
arrangements through which servants contracted to work for a specified period of years in exchange for passage.
chattel slavery (4.4)
Theme: Economy
a system in which individuals were considered as property to be bought and sold.
encomienda (4.4)
Theme: Economy
the Spanish established a system called the encomienda to gain access to gold and other resources of the Americas. Encomenderos, compelled indigenous people to work for them in exchange for food and shelter, as landowners required of serfs in Europe’s manorial system.
encomenderos (4.4)
Theme: Economy
landowners who had indigenous people work for them for food and shelter
coercive labor system (4.4)
Theme: Economy
was notorious for its brutality, people used chattel slavery with force
hacienda system (4.4)
Theme: Economy
landowners used coerced labor to work the fields
mit’a system (4.4)
Theme: Economy
young men were required to devote a certain amount of labor to public works projects, into a coerced labor system
Middle Passage (4.4)
Theme: Economy
The grueling journey across the Atlantic was known as the Middle Passage, because it was the middle part of the captives’ journey. Many captured Africans attempted rebellions at sea, but most uprisings were crushed.
capital (4.5)
Theme: Economy
material wealth available to produce more wealth
Commercial Revolution (4.5)
Theme: Economy
The Commercial Revolution affected all regions of the world and resulted from four key factors: the development of European overseas colonies- the opening of new ocean trade routes-population growth and inflation, caused partly by the pressure of the increasing population and partly by the increased amount of gold and silver that was mined and put in circulation.
Price Revolution (4.5)
Theme: Economy
The high rate of inflation, or general rise in prices, is called the Price Revolution.
joint-stock companies (4.5)
Theme: Economy
owned by investors who bought stock or shares in them
limited liability (4.5)
Theme: Economy
the principle that an investor was not responsible for a company’s debts or other liabilities beyond the amount of an investment, made investing safer
East India Company (4.5)
Theme: Economy
British stock company
(Dutch East India Company (4.5)
Theme: Economy
Dutch stock company
triangular trade (4.5)
Theme: Economy
A trade route including Africa, North America and Europe that was largely used to transport slaves and goods
syncretism (4.5)
Theme: Culture
the combining of different religious beliefs and practices.
polygyny (4.5)
Theme: Culture
the taking of more than one wife, ocurred because most slaves taken were men and Europeans needed a higher slave population.
Santéria (4.5)
Theme: Culture
Santería means “the way of the saints.” Originally an African faith, it became popular in Cuba and then traveled throughout Latin America and to North America.
Vodun (4.5)
Theme: Culture
Vodun means “spirit” or “deity.” This belief system originated with African peoples of Dahomey, .ongo, and Yoruba who were enslaved and living in Saint-Domingue, which is now Haiti.
Candomblé (4.5)
Theme: Culture
Candomblé means “dance to honor the gods.” It is a combination of Yoruba, Fon, and Bantu beliefs from different parts of Africa. It developed in Brazil.
Virgin of Guadalupe (4.5)
Theme: Culture
In Mexico, a cult developed around the dark-complexioned Virgin of Guadalupe, who was revered for her ability to perform miracles.
viceroys (4.5)
Theme: Government
administrators and representatives of the Spanish crown.
audiencias (4.5)
Theme: Government
royal courts, to which Spanish settlers could appeal viceroys’ decisions or policies.
Dahomey and Oyo (4.5)
Theme: Government
African socities that became richer from selling their captives to Europeans
Yemelyan Pugachev (4.6)
Theme: Government
began a peasant rebellion, leaving the peasants without ties or recourse to the state.
Metacom’s War (4.6)
Theme: Society
was the final major effort of the indigenous people to drive the British from New England.
Pugachev Rebellion (4.6)
Theme: Society
caused Catherine to increase her oppression of the peasants in return for the support of the nobles to help her avoid future revolts.
Pueblo Revolt (4.6)
Theme: Society
The Pueblo and Apache, two indigenous groups, fought colonizers who were trying to force religious conversions. The indigenous people killed about 400 Spaniards, drove the rest out of the area, and destroyed churches. The Spanish reconquered the area
Maroon wars (4.6)
Theme: Society
Enslaved people in the Caribbean and former Spanish territories in the Americas fought to gain freedom in what were known as Maroon wars
Gloucester County (4.6)
Theme: Society
In this rebellion, enslaved Africans and white indentured servants conspired together to demand their freedom from the governor. Authorities found out about their plot, ambushed them, and arrested them.
Glorious Revolution (4.6)
Theme: Society
strengthened the power of Parliament, which passed a law forbidding Catholics to rule England.
Mehmed II (4.7)
Theme: Government
invited jews into the Ottoman empire, however he taxed them for being Jewish,couldn’t hold top positions in the empire and only lived in certain areas of the empire
Akbar the Great (4.7)
Theme: Government
To help keep his huge, fractious empire together, Akbar, like Ottoman rulers, was tolerant of all religions. He ended the jizya tax. He gave grants of land and money to Hindus and Muslims, provided funds to build a Catholic church, and supported Sikhism.
Roxelana (4.7)
Theme: Government
became unusually powerful in the Ottoman Empire. When she was a young girl, Crimean raiders stole Roxelana from her home in Eastern Europe and sold her into slavery in the Ottoman Empire. She was forced to convert to Islam and entered the harem of Suleiman the Magnificent, sultan of the empire. Suleiman married Roxelana, which was highly unusual. She went from being enslaved to commissioning ambitious public works projects.
Qing Dynasty (4.7)
Theme: Government
The dynasty after the Ming ruled by the Manchu people
Manchu (4.7)
Theme: Government
people from Manchuria ruled over the majority Han Chinese and other ethnic groups. he Manchu were ethnically and culturally distinct from the people they ruled. However, they were less tolerant than the Mongol leaders, and they resolved to make their culture dominant in China.
Li Chengdong (4.7)
Theme: Government
orchestrated three separate massacres in the city of Jaiding within one month. By the end of those four weeks, there was hardly a person left alive in the city.
Liu Liangzuo (4.7)
Theme: Government
massacred the entire population of Jiangyin, killing between 74,000 and 100,000 people.
Louis XIV (4.7)
Theme: Government
A failed uprising in France convinced Louis XIV that he must keep power from the common people and the nobility.
Ivan IV (4.7)
Theme: Government
e. Boyars of Novgorod opposed the expansionist policies of Ivan IV, known as “Ivan the Terrible” for murdering his own son, among other crimes. After Ivan s forces defeated Novgorod, Ivan confiscated the lands of his boyar opponents. He forced them and their families to move to Moscow, where he could keep them under surveillance.
timar (4.7)
Theme: Society
a system in which the sultan granted land or tax revenues to those he favored. The sultan also used timar to reward soldiers and keep them loyal.
harem (4.7)
Theme: Society
a residence where a powerful man’s wives and concubines lived.
boyar (4.7)
Theme: Society
topped the Russian social pyramid
nobility (4.7)
Theme: Society
The nobility made up a small minority of the population but owned most of the land. They maintained their power through a system in which lands and titles passed down from one generation to the next through a system of inheritance.
peninsulares criollo castas mestizos mulattos zambos (4.7)
Theme: Society
peninsulares, those who were born on the Iberian peninsula, Next down the pyramid were the criollos, those of European descent born in the Americas. mestizos, those of mixed European and indigenous ancestry, followed by mulattoes, those of mixed European and African ancestry, and zambos, those of mixed indigenous and African ancestry
Barbary pirates (4.7)
Theme: Economics
those who plied the seas near North Africa along the Barbary Coast. captured other Europeans in the Mediterranean and then sold them to the sultan or other high-ranking officials.
impressed (4.7)
Theme: Economics
forced into service, in the navy as enslaved galley workers.
Sephardic Jew (4.7)
Theme: Culture
Jews who trace their heritage back to Spain became known as Sephardic Jews.
Ashkenazi Jew (4.7)
Theme: Culture
Jews from central and eastern Europe became known as Ashkenazi Jews