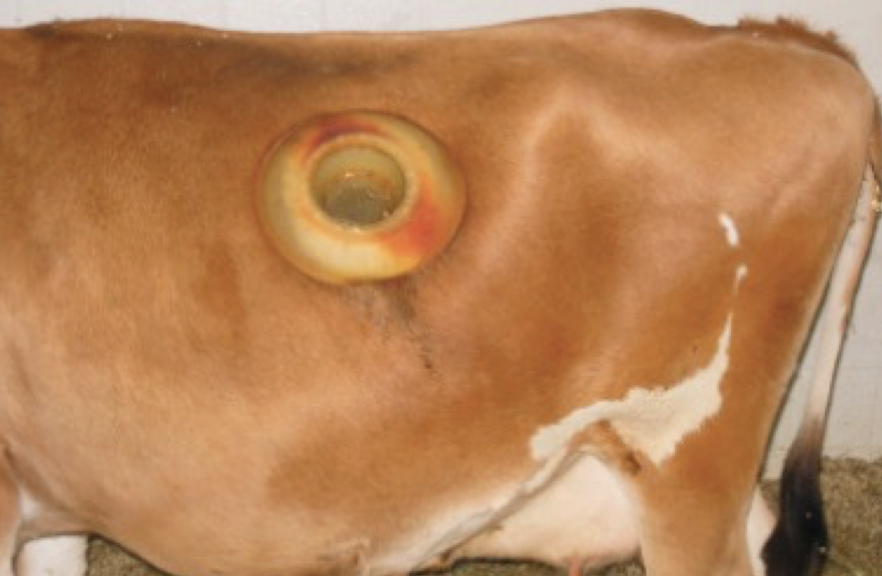
Bovine Abdominal Surgical approaches
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover major concepts and surgical techniques discussed in the Bovine Abdominal Surgery lecture, helping to reinforce key information for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the main surgical approaches discussed in bovine abdominal surgery?
Flank, paramedian, ventral midline.
What structures can be accessed from the left side during a flank celiotomy?
Rumen, reticulum, spleen, diaphragm, reproductive tract, bladder, left kidney, abomasum.
What structures can be accessed from the right side during a flank celiotomy?
access pyloric part of abomasum, small & large intestine, reproductive tract, urinary bladder, kidneys
What are the landmarks for a flank paralumbar fossa celiotomy incision?
6-8cm (~hand width) ventral to transverse processes and 4-6cm caudal to last rib. Dorsoventral direction for approx 25cm
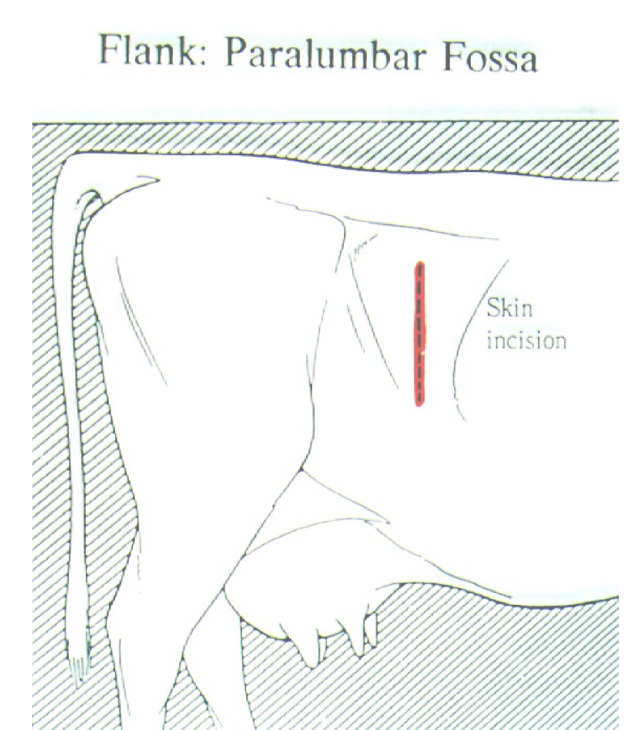
What side of the cow do we go for a C-section more caudal and lower in flank?
L side
What determines the incision location for a pyloropexy on the right side?
It should be closer to the last rib.
What layers are encountered during a flank paralumbar fossa celiotomy?
Skin, subcutaneous fat, external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, transversus abdominis, and peritoneum.


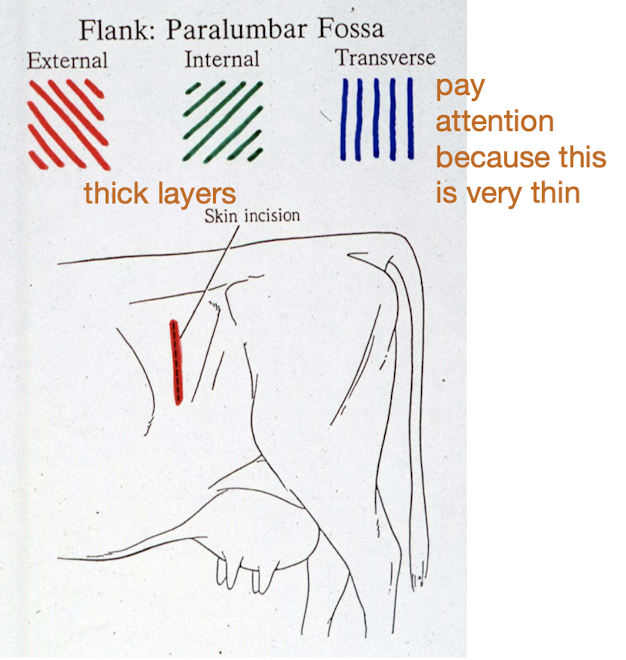
What are the 4 layers we need to close for a paralumbar fossa celiotomy?
Peritoneum & transversus abdominis
Internal abdominal oblique
External abdominal oblique
Skin
What pattern and size suture do we use to close each layer of the peritoneum & transverse abdominis, internal abdominal oblique, external abdominal oblique?
simple continuous #2 absorbable
What is a common closure method for the skin after a flank celiotomy?
Ford interlocking pattern with #1 nonabsorbable sutures.
What are the advantages of the flank approach?
Good for exploration and viscera are in their normal position.
Where do we cut in for the right paracostal approach?
Parallel and caudal to last rib (5-10 cm in adults)
Aponeurosis of external abdominal
oblique
muscular layer of internal
abdominal oblique dorsally, and
aponeurotic portion ventrally
Transversus abdominis and peritoneum together, tented
Advantages and disadvantages of Mid to Low flank incision

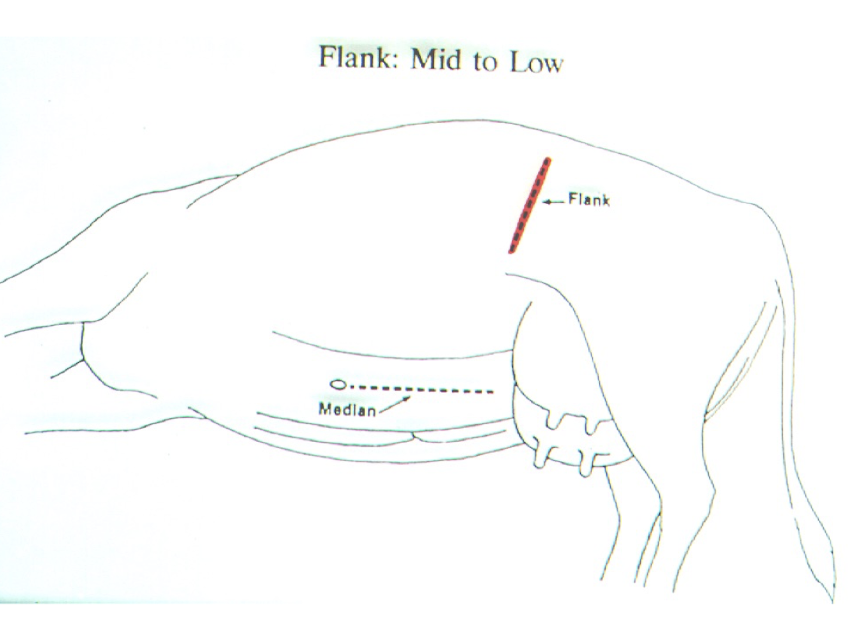
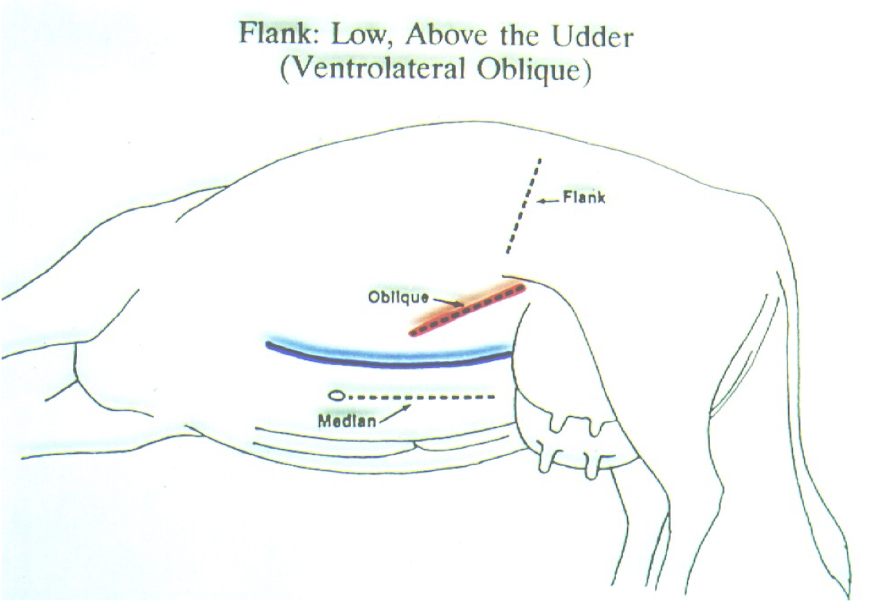
When can we use ventrolateral oblique incision?
C section in recumbent animals
oblique incision (30-40 cm)
Ventral to flank fold, dorsal to udder
extends cranioventrally
MARK MILK VEIN STANDING
What is the primary indication for a right paramedian celiotomy?
Correction of abomasal displacement or volvulus

What are the advantages of the ventral midline approach?
Good exposure, especially in young calves

What are the indications for performing a rumenotomy?
Metallic foreign objects, traumatic reticulitis, removal of foreign material, rumen impaction, and ingestion of toxic plants.
How is a rumenotomy typically performed?
Through a surgical incision in the left paralumbar fossa with care taken to avoid contamination
Incision caudal to last rib
Abdominal exploration before opening rumen (do clean part of the surgery first)
Caudal & central part first • Abscesses firm & spherical, usually right side of reticulum or cranial to omasum
Palpate for adhesions
How do we cut into the rumen?

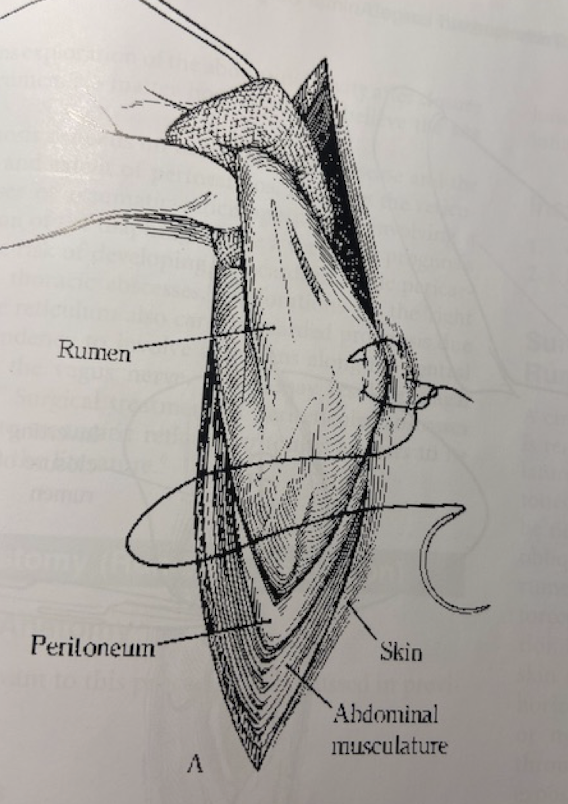
What is the closure technique used for a rumen after a rumenotomy?
Continuous inverting suture pattern with non-absorbable material.

What is a rumenostomy?
A surgical procedure that creates a permanent opening in the rumen, allowing access for drainage or feeding → for chronic vagal indigestion, space occupying lesions, idiopathic