economics section 4
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
the role of the government
to improve the general welfare of its people
collect tax revenue in order to fund its expenditure on essential services (healthcare, infrastructure and national security)
operate at 3 levels : local,national,international. ( may be part of trading block like EU )
local role of government
The central or federal government collects taxes to fund local services ( e.g garbage collection, street lighting, libraries, schools, hospitals and public parks. )
Central government gives local government funding to spend on public and merit goods
national role of government
The central government makes decisions about how to achieve its macroeconomic aims
Make decisions on the following policy areas:
Fiscal: taxation
Monetary: interest rate and money supply
Supply-side: minimum wage and regulation of firms
Environment: protection
international role of government
Modern economies need to trade with other countries.
Trade blocs promote free trade and mobility of factors of production.
If there is no free trade between countries then tariffs and quotas may be imposed on goods traded.
tariff vs quota definitions
tariff - a tax or duty to be paid on a particular class of imports and exports
quota - a government-imposed quantitative limit on the amount of a particular product allowed into the country
macroeconomic aims of government
economic growth
full employment
stable prices/low inflation
balance of payments and stability
redistribution of income and wealth
economic growth definition
Economic growth refers to an increase in a country’s real domestic product (GDP) over time.
GDP definition
a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries.
GDP is used to measure the economic health of a country or region
unemployment + unemployment rate definitions
unemployment - when someone is willing and able to work but does not have a paid job.
unemployment rate - the percentage of people in the labour force who are unemployed.
(not everyone who is of working age is willing and able to work)
why is full employment good?
compliments economic growth.
Higher employment tends to lead to greater GDP.
formula :
(number of unemployed people/number of people in the labour force) x 100
more employed people → government spends less of welfare benefits
Stable prices/low inflation (info about inflation)
Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level in an economy.
Inflation is measured using the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Most governments set a target inflation rate between 1-3%
deflation definition
decrease in the general price level of goods and services; occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0%.
deflation due to people spending less → businesses make less → increases unemployment + reduces government tax revenue
Balance of payments definition
Financial record of a country’s transactions with the rest of the world for a given time period (usually one year).
( when country is not balanced - deficit or surplus )
redistribution of income
Aims to achieve greater equality in the distribution of income in an economy.
This is achieved through taxation, for example, progressive taxation charges a higher percentage tax as an individual’s income rises.
full employment vs stable prices
people have more money to spend when they are employed
demand pull inflation - demand in economy rises faster than supply
cost pull inflation - harder for firms to attract skilled workers → wage inflation
economic growth vs balance of payments + stability
if economic growth is caused by consumer spending → deficit in balance of payments and stability due to expenditure on imports
if economic growth causes deflation → countries exports cheaper
full employment vs balance of payments and stability
more people become employed → more people wealthier → more people buy imports (imported inflation)
cost push inflation → more expensive exports
inflation → currency depreciates → cheaper exports
economic growth vs stable prices
cut in interest rates/increase in money supply → inflation due to more people having more money to spend
More jobs + wealthier people → buy more things → demand pull inflation.
Harder to attract workers → cost push inflation
income tax definition
a direct tax levied on personal incomes.
( e.g wages, salaries, dividends, rent )
in most countries this is the main source of tax revenue
corporation tax definition
tax on the profits of businesses
sales tax
an indirect tax such as VAT. which is charged on an individual’s spending
excise duties
indirect inland taxes imposed on demerit goods and services
customs duties
indirect cross border taxes on foreign imports
capital gains tax
a direct tax on the earnings made from investments such as buying shares private property
inheritance tax
a direct tax on the transfer of income and wealth when passed on to another person
stamp duty
a progressive tax paid on the sale of commercial or residential property
carbon tax
tax imposed on vehicle manufacturers or firms that produce excessive carbon emissions
windfall tax
a tax charged on individuals and firms that gain an unexpected one off amount of money. e.g person winning a lottery
principles of taxation / qualities of good tax
Equitable: based on the ability to pay
Economical: easy and cheap to collect
Efficient: achieve aims without side effects
Convenient: method of payment should be easy
Certain: taxpayer should know when and how to pay
Flexible: adapt to a change in the economic environment
impact of taxation on : price and quantity, economic growth, inflation, business location
price and quantity - sales tax will shift the demand curve to the left and reduce the quantity being sold.
economic growth - taxation tends to decrease incentives to work and produce.
inflation - Increase in taxation → reduce spending. Decrease in taxation fuels inflationary pressure.
business location - Rate of corporation and income tax may affect the location of multinational businesses.
impact of taxation on : distribution of wealth, tax avoidance, tax evasion
distribution of wealth - Taxes can be used to help redistribute income and wealth from the rich to the poor.
tax avoidance - the legal act of not paying taxes (e.g, non-smokers to not pay a tobacco tax.)
tax evasion - illegal act of non-payment of taxes due ( e.g, a business under-declaring its level of profits. )
expansionary vs contractionary fiscal policy
expansionary - used to stimulate the economy by increasing government spending and/or lowering taxes.
contractionary - used to reduce the level of economic activity by decreasing government spending and/or raising taxes.
effects of fiscal policy on macroeconomic aims
economic growth - government expenditure on infrastructure helps to boost investment in the economy.
low inflation - lower taxes and higher foreign direct investment can boost productive capacity which helps to keep general price level low.
redistribution of income - use of progressive taxes and government spending helps to redistribute income and wealth in the economy.
full employment - cuts in income tax may cause people to seek employment and work harder.
balance of payments - low rates of taxation → domestic firms competitive, government subsidies on domestic industries → improve international competitiveness.
budget deficit
occurs when expenses exceed revenue and indicate the financial health of a country.
Certain unanticipated events and policies may cause budget deficits.
Countries can counter budget deficits by raising taxes and cutting spending.
Monetary policy measures
change in interest rates : influence level of economic activity
change in money supply : influence economic activity (e.g allowing commercial banks to lend more money to boost consumption)
changes in foreign exchange rates : has direct impact on domestic money supply (e.g domestic customers need to purchase foreign currency to buy imports)
expansionary vs contractionary monetary policy
expansionary - aims to boost economic activity by mainly lowering interest rates
contractionary - reduce overspending and limit investment in the economy mainly by increasing interest rates which decreases economic activity
effects of monetary policy on macroeconomic aims
Economic growth - lowering interest rates will reduce the cost of borrowing and should boost consumption
low unemployment - lower interest rates → economic growth → more spending + investment → creates more jobs
low inflation - more investment + spending due to economic growth → increase productive capacity so more can be produced without having to incur higher prices
balance of payments + stability - a lower exchange rate will tend to improve the financial competitiveness of a country. ( lower exchange rate lowers the price of a country’s goods for consumers in other countries but raises the prices of imported goods and services for domestic consumers)
limitations of monetary policy
lags in the reaction to changes in interest rates
economic activity is not only dependent on interest rates other factors such as consumer and business confidence levels may impact GDP.
supply side policies definition
Long-term strategies aimed at increasing the productive capacity of the economy by improving the quality and/or quantity of the factors of production.
effect of supply side policies on PPC curves
With more and improved factors of production, the economy can produce more goods and services.
This can be shown with an outward shift in a country’s PPC
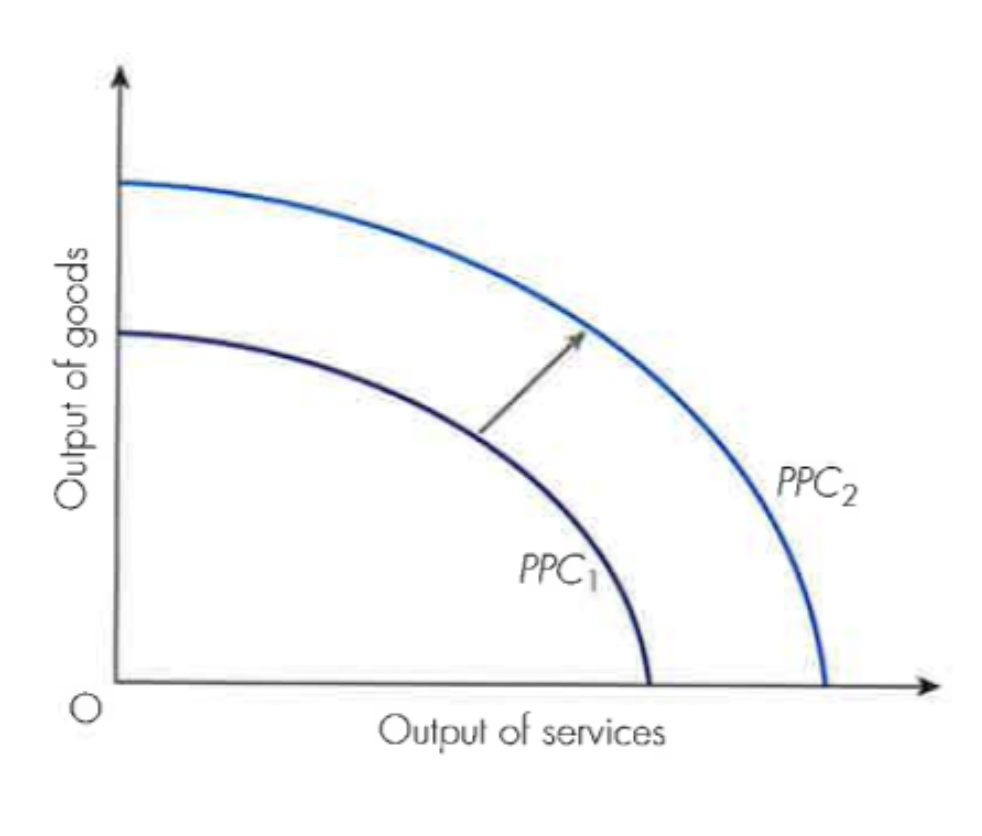
education and training and healthcare supply side policy
Increasing government spending on education and retraining raises the quality of the workforce.
Increasing government spending on healthcare so that worker productivity improves.
labour market reforms examples supply side policy
Decreasing trade union power / Decreasing minimum wages : wages can be decreased encourages firms to hire more workers as they are cheaper
Increased government spending on improving occupational mobility
deregulation supply side policy
This is the process of removing government controls/laws from markets in order to increase competition.
Regulation increases costs of production for firms and deregulation decreases costs which may result in greater supply.
improving incentives to work and invest supply side policy
Restructuring the unemployment benefits system to incentivise the unemployed to seek work.
Increased government spending on innovation increases the supply of potential jobs in the economy.
Direct support to firms (subsidies) increases output and promotes international competitiveness.
lower direct taxes
Reducing income/corporation tax rates incentivises workers to work harder (they keep more money for themselves).
Also provides firms with extra funds which they can use to invest in new machinery/technology
privatisation supply side policy
Government firms are usually so big that private enterprise refrains from trying to compete with them.
Privatisation encourages new firms to enter the market and compete, thus increasing the total supply in the economy.
effects of supply side policy on macroeconomic aims
economic growth - can increase economic growth by increasing the productive capacity
full employment - increase in an economy’s productive capacity → increase national output → creating jobs. + education and training can help frictional + structural unemployment
low inflation - increase in the productive capacity preventing general price levels to go out of control
balance of payments - increase in the productive capacity without pressure on prices → international competitiveness should improve → more export earnings
redistribution of income - education and training + greater incentives to work → benefit low income workers more
criticisms of supply side policy
it does not take into account factors such as inflation, interest rates, and unemployment levels.
Some critics argue that supply-side policies do not always lead to increased demand for goods and services.
tax cuts alone cannot achieve truly sustainable long-term growth outcomes.
implications of supply side policy
have been successful in terms of increased production – but this has not always translated into higher levels of prosperity for all.
Its emphasis on deregulation may lead to financial instability in times of crisis.
Also, its reliance on tax cuts as a mechanism for stimulating growth may exacerbate income inequality over time.
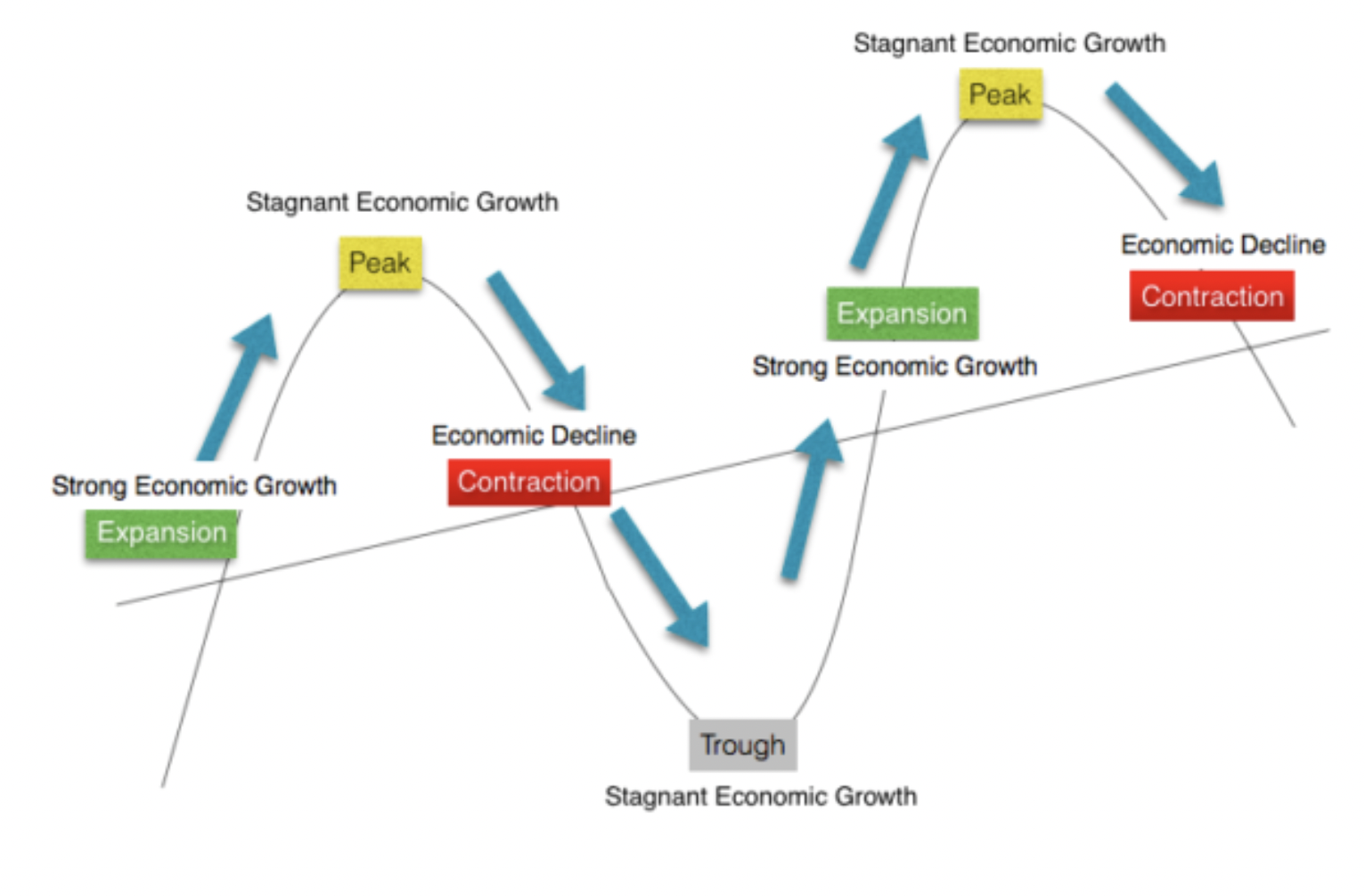
Business cycle
describes the fluctuations in the economic activity of a country over time creating a long term trend of economic growth in an economy
how to calculate GDP
GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
consumption + investment + government spendings + ( export earnings - import expenditure)
nominal GDP definition
measures the monetary value of goods and services produced within a country during a given period of time
consumption definition
the value of all private household consumption within a country
investment expenditure definition
the sum of capital spending by all businesses within a country
net exports definition
the monetary value of the difference between a countries exports and imports
GDP per head
average value of annual GDP per capita
causes + consequences of economic growth
factor endowments - high quantity and quality of a country’s factors of production → can can specialise production on large scale → can export special products at a lower price
labour force - higher skills + mobility of a country’s workforce → greater the economic growth is going to be.
labour productivity - increase in labour productivity → increases countries competitiveness → higher economic growth
investment expenditure - increase in investment boosts a country’s GDP. Help increase a country’s productive capacity in the long run. investment into capital can boost labour productivity. → makes a country more competitive
positive consequences of economic growth
improved standards of living - higher income levels → can spend more money. helps eliminate absolute poverty
employment - economic growth → higher employment, helps raise consumption + invest into capital → sustain economic growth
tax revenue - higher levels of spending → more tax revenue
negative consequences of economic growth
environmental consequences - economic growth can cause pollution,congestion,land erosion which can impact people’s wellbeing and quality of life in the long run.
risk of inflation - demand pull inflation.
inequalities in income + wealth
resource depletion - economic growth often involves using the earth’s scarce resources at rates which are not sustainable. e.g deforestation
policies to promote economic growth
fiscal policy - use of taxation to control the levels of economic activity. demand is too low → decrease taxes/increase government expenditure → economic growth
monetary policy - when demand is too low → lower interest rates → fund consumer expenditure + business investments → economic growth
supply side policy - increase a country’s productive capacity by increasing competition, innovation and productivity which boost economic growth
employment vs unemployment definitions
Employment: economic use of labour as a factor of production
Unemployment: people of working age willing and able to work that can’t find jobs.
formal sector employment definition
refers to officially recorded employment where workers pay income tax and contribute to a country’s official GDP.
female participation rate definition
measures the proportion of women who are active in the labour force.
claimant count definition
measures the number of people out of work claiming unemployment benefits.
labour force survey definition
uses the International Labour Organization household-based survey to collect work related statistics.
why does the government care about employment?
high employment → raises standards of living
promotes economic growth
increases tax revenue
spending of welfare benefits falls → decreases opportunity cost + financial burden of government
prevents brain drain where highly skilled workers leave the country
reduces income + wealth inequalities
changing patterns and levels of employment - employment sector, Delayed entry to the workforce, Ageing population, Flexible working patterns
employment sector - country develops → less people working in the primary sector
Delayed entry to the workforce - more people study to tertiary education → average age of employees entering workforce rises
Ageing population - firms are willing to higher older people
Flexible working patterns - firms need to be flexible in order to be internationally competitive (e.g allowing staff to work from home)
changing patterns and levels of employment - Formal sector employment, Female participation rates, Public sector employment
Formal sector employment - employment increases → more people working in formal sector
Female participation rates - changes in social attitudes increases female participation rate which increases with higher employment
Public sector employment - higher employment + more market economy → less people working in public sector
cyclical unemployment
Caused by lack of demand which causes a fall in national income.
Also known as demand-deficient unemployment, is the most severe type of unemployment and is experienced during economic downturn (recessions and slumps).
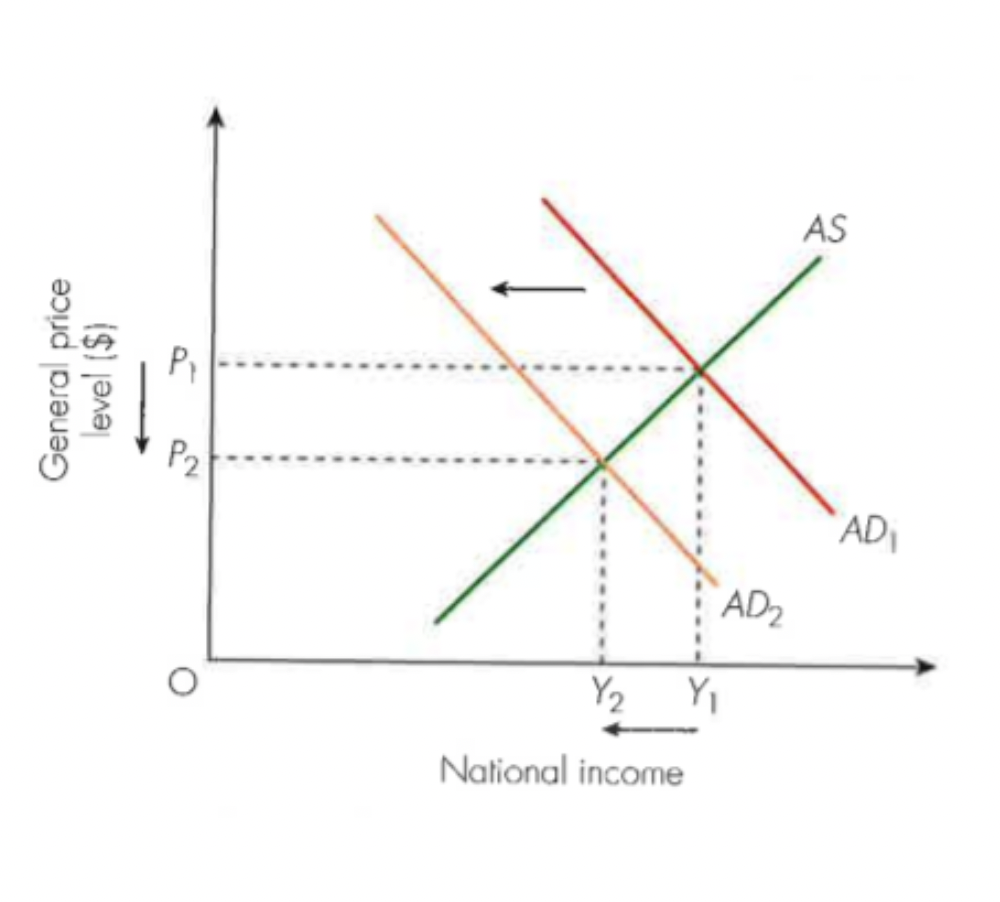
structural unemployment
Occurs when the demand for products produced in a particular industry continually falls often due to foreign competition.
frictional unemployment
Transitional unemployment which occurs when people change jobs
unemployment is due to the time delay between leaving a job and finding a new one.
what unemployment numbers don’t tell us
A low unemployment rate does not necessarily indicate that a country's people are living in favorable, sustainable conditions.
consequences of unemployment
individuals who are unemployed may experience stress, depression and other health problems. extreme cases suicide
local community can suffer if there is mass unemployment → increased crime rates + decrease in value of assets
bad for firms → lower levels of consumer spending, investment and profits
government may face higher expenditure on welfare benefits → increase in government debts
reliance of taxpayers to finance welfare benefits
economy as a whole suffers due to not being as internationally competitive
policies to reduce unemployment
fiscal policy - expansionary fiscal policy → higher employment
monetary policy - interest rates falls → encourages borrowing + investment → shifts demand for labour to the right
protectionist measures - tariffs + quotas used to safeguard domestic jobs from international competition
investment in education + training → more people suitable for jobs
reduction in trade union powers → labour is cheaper
incentives can be offered to firms to employ + train people
reducing welfare benefits motivates people to find jobs
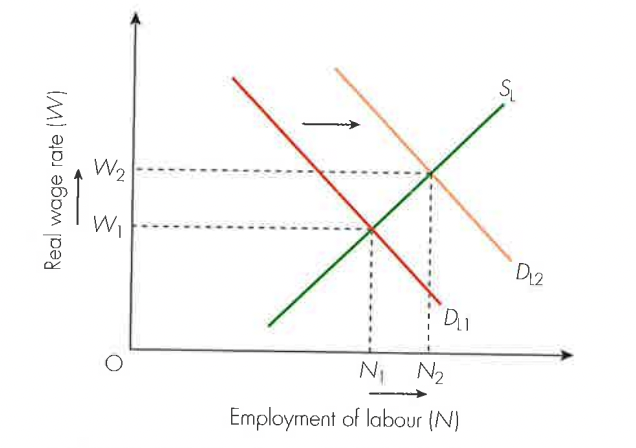
hyperinflation + deflation definitions
hyperinflation - very high rates of inflation that are out of control causing average prices in the economy to rise rapidly.
deflation - the sustained fall in the general price level in an economy over time (negative inflation).
Base year definition
refers to the starting year when calculating a price index.
cost push vs demand pull inflation
cost push - cause of inflation, triggered by higher costs of production, forcing up prices.
demand pull - cause of inflation, triggered by higher levels of demand, driving up the general prices level.
why do governments want to control inflation
because it reduces the value of money and the spending of individuals, governments and firms
demand + supply factors of deflation
Supply factors: Higher levels of supply and services drives down general price level - benign deflation
Demand factors: Lower levels of demand drives down price level due to excess capacity - malign deflation
measuring inflation + deflation
The CPI is a common method to calculate the inflation rate.
It measures the price changes in the basket of goods and services consumed by the average household in the country.
used for international comparisons of inflation rates because it uses a wide sample of the population when assigning statistical weights to the index.
calculating CPI
Collection of the monthly price data of the basket of goods and services.
Assigning the statistical weights representing different patterns of spending.
(current cost of basket/base year cost of basket) x 100
((CPI in year 2 - CPI in year 1)/CPI in year 1) ×100
causes of inflation + deflation
Cost-push inflation
Demand-pull inflation
Monetary causes related to increase in the money supply.
Imported inflation occurs due to higher import prices.
consequences of inflation
Menu costs - impacts price of products sold by business → costly to keep changing prices
Consumers - purchasing power of consumers decreases
Shoe leather costs - fluctuations in price levels → consumers spend more time looking for the best deals → opportunity cost for consumers
Savers - money people have saved is worth less than before
Lenders - money lent out to borrowers is worth less
Borrowers - gain from inflation as money they need to pay is worth less
Fixed income earners - fall in real incomes
Employers - employees are likely to ask for higher wages → higher labour production costs
Business confidence levels - uncertain → lower the amount of planned investment in the economy
consequences of deflation
Unemployment - fall in demand for labour
Bankruptcies - less consumer spending → firms have lower revenues
Debt effect - real cost of borrowing increases due to real interest rate rising
Government debt - tax revenues fall
fall in Consumer confidence
fiscal policy to control inflation + deflation
inflation - general level of demand is too high → contractionary fiscal policy
deflation - cut in direct taxes → higher levels of economic activity
monetary policy to control inflation + deflation
inflation → increase in interest rates
deflation → decrease in interest rates →lowers exchange rate → increase in demand of exports
standards of living
refers to the quality of life of individuals
including income levels, access to healthcare, education, and overall well-being.