Equilibrium Constants
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Keq= [Products]/[Reactants]
For example, the formula of:
Fe3+(aq) + SCN-⇋ FeSCN2+(aq)
Keq=[FeSCN2+]/[Fe3+][SCN-]
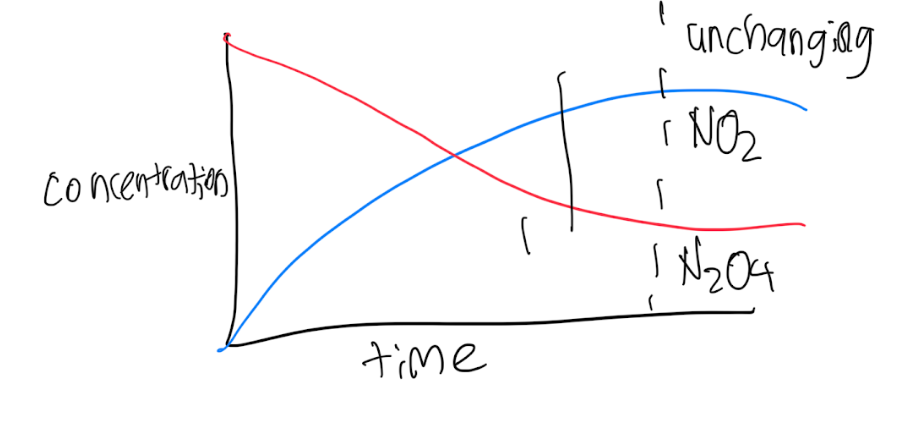
N2O4(g)—> 2NO2(g)
forward rate=Kt[N2O4]
2NO2(s)—>N2O4(g)
reverse rate=Kr[NO2]2
N2O4(g)⇋ 2NO2(g)
rate forward=rate reverse
Kf[N2O4]=Kr[NO2]²
Kf/Kr=[NO2]²/[N2O4] Law of mass action equation
Q=[NO2]²/[N2O4]
Q is reaction quotient
At equilibrium “eq”
Q=Kf/Kr=[NO2]²eq/[N2O4]eq=Keq
Keq =equilibrium constant
aA+bB⇋ cC+dD
Q=[C]c[D]D/[A]a[B]b Law of mass action
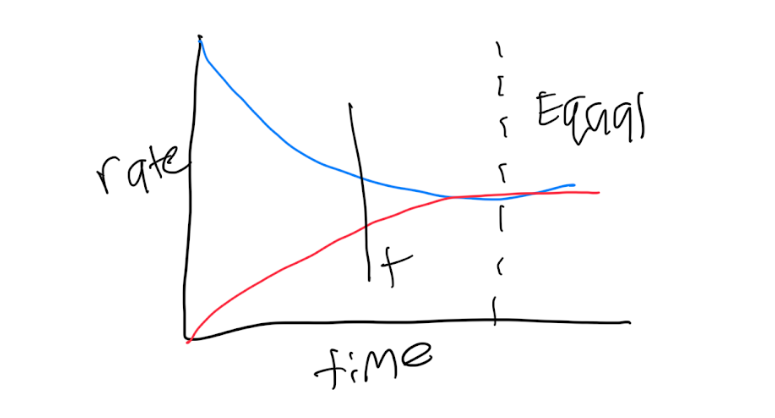
Equilibrium occurs when the forward rate is equal to the reverse rate
Equilibrium is dynamic - there is still reaction happening. It’s just balanced
O3⇋ O+O2
H2O⇋ H+ OH-
Fe + O2 —> Fe2+3 O2
Magnitude of Keq
CO(aq)+CI2 (g) = COCI2(g)
Keq=[COCI2]/[CO][CI2]=4.56×10^9
K>1 greater products than reactants
K<1 greater reactants than products.
COCI2(g)=CO(aq)+CI2 (g)
Keq=[CO][CI2]/[COCI2]=2.142×10^-10=1/Keq=1/4.56×10^9
If you reverse the direction the Keq is inverse
N2O4(g)=2NO2(g)
Keq1=[NO2]²/[N2O4]
2N2O=4NO2(g)
Keq2=[NO2]4/[N2O4]2
Keq2=Keq12
If a reaction is multiplied by a constant then the Keq is raised to that power.
2NOBR(g)=2NO(g)+Br2(g) Keq1
Br2(g)+CI2(g)=2BrCl(g) Keq2
2NOBr(g)+Cl2(g)=2NO(g)+2BrCl Keq3
Keq3=Keq2=Keq1
If you add reactions together Keq is equal to individual Keq multiplied
Ka
The acid-dissociation constant. The equlibrium constant related to weak acids.
Kb
Base dissociation constant. The equlibrium constant related to weak bases.
General Form
HA ⇋ H+ + A-
For ex:) HCI → H+ + Cl-
Table of Acid with Ka and pKa Values (7 you need to know)
Acid HA A-
Hydroiodic HI I-
Hydrobromic HBr Br-
Perchloric HCIO4 CIO4-
Hydrochloric HCI Cl-
Chloric HCIO3 CIO3-
Sulfuric(1) H2SO4 HSO4-
Nitric HNO3 NO3-
pH=-log[H-]
The pH is a method of reporting hydrogen ion concentration.
pH is 7
Acidic pH is below 7
Basic pH is above 7
Only the digits after the decimal point are sig figs in logarithms