Transport in plants adaptations OCR A level biology
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Xerophyte
A plant adapated to reduce water loss in arid conditions
What is transpiration
How does light intensity affect transpiration?
This increases transpiration
Light stimulates stomata to open in order to take in CO2 gas exchange - for photosynhtesis
Larger surface area for evaporation of water
How does temperature affect transpiration?
Water moelcues gain kinetic energy
Move faster increasing evaporation - water gas
Humidity
This decreases water potential
How does wind affect transpiration?
This increase transpiration
Wind will blow away water molecules away near stomata
Steep conc gradient - for increased diffusion
Thick waxy cuticle
Waterproof reduce water loss by evaporation
Longitudinally rolled leaves
Protects lower epidermis.
traps moisture to increase humidity - more water vapour inside tube
Decreases water vapour conc gradient - reducing - water loss by diffusion
Reduces diffusion of water out stomata
Stomata
Fewer stomata to reduce water loss
Stomata location
Stomata are in pits trapping moist air - increase humidity
Reduces water potential gradient
Reduce loss of water vapour
Spongey mesophyll
Very dense with few air spaces
Less surface for evaporation of water
Trichomes
Trap moist air near leaf surface
Reduces water potential gradient
Less water loss via transpiration
Stomata opening
Stomata only open at night to absorb carbon dioxide
Reduces water loss in day time
Roots of xerophyctes
Roots are very extensive
To abosrb rainfall
Cacti
Cacti are succulents
Store water in their stems which are ribbed and can expand when water is available
Why do large multi cellular plants need a transport system
Diffusion is not fast enough
Small surface area to volume rattio
Transport of named substance. e.g. sucrose
Long distance from external surface to cells
Explain the benefit of internal transports systems
Surface area to volume ratio is too small
Diffusion from outer surface is not sufficient'
Ensures molecules like sucrose, and water reach all tissues
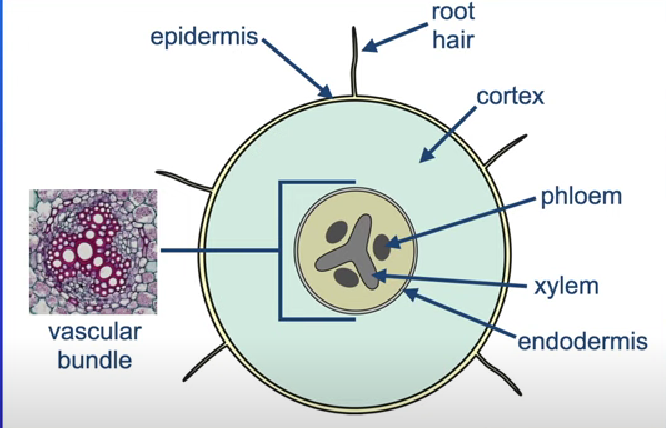
PLANT ROOT
Xylem vessels are mechanicly strong and are always closer to center to provide support
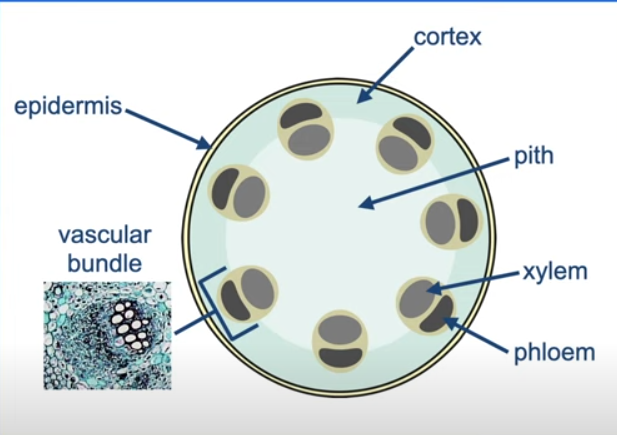
PLANT STEM
Vascular bundles arrange in a ring around edge to withstand bending
Pith made of parenchyma cells
Phloem edge
Xylem closer to center
What type of cell is the cambium made of?
Meristem cells
For what molecule does a plant need nitrogen/phosphorus
DNA
How does the casparian strip prevent ions
The strip is impermeable to water
Forces water to pass through cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer repels ions
Why can water from hydrogen bonds with nitrate?
Water is polar
Nitrate is a charged ion
Process in cell surface membrane of root
Mineral ions are absorbed through active transport using ATP
This decreases water potential in roots
Water diffuses by osmosis from high to low water potential
How to observe leaf stalks
Cut a transverse cross section
Dye the leaf stalk
Walls of xylem vessel in hydrophyte
less lignin in walls
Walls of xylem vessels in xerophyte
More lignified walls
Similarities between xylem and phloem
Both lack nuclei
Both made up of cells joined end to end
Both complex tissues made of multiple cells
Differences between xylem and phloem
Phloem has companion cells xylem doesn’t
Xylem is lignified phloem is not
Xylem has a wider lumen than phloem
Phloem has sieve plates xylem does not
Xylem has vessels phloem does not
Xylem has pits phloem doesn’t
Xylem has not cytoplasm or organelles phloem does
Why do some plants like mosses not need a xylem
High surface area to volume ratio
Function of pits
Lateral movement of water
Companion cell
Mitochondria - respire - energy for active loading
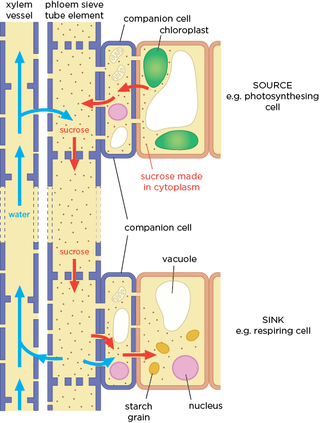
Translocation
Movement of assimilates around plants
Translocation process
Companion cell uses ATP to pump hydrogen ions to source cell
Increases Hydrogen concentration is source cell - diffuses down conc gradient
However must also be transported with sucrose through cotransporter protein
Higher sucrose concentration in companion cell - moves down gradient through plasmodesmata into sieve tube
Decreases water potential in sieve tube
Water moves via osmosis into sieve tube from xylem to phloem high to low water potential increasing hydrostatic pressure
Mass flow - moves assimilates down the sieve tubes to sinks
Sucrose diffuses out the phloem to companion cells down conc gradient
Water potential increases moves via osmosis back to xylem
Sucrose diffuses into sieve cells through plasmodesmata
Roots of hydrocytes
Very short - not extensive
Water does not need to be absorbed as frequently
How does water move against gravity?
Cohesion - tension theory
Water is cohesive due to partially negative O2 and partially positive H
This creates H bonds making water stick together
This creates a continuous column of water
Water is adhesive to the lignin in xylem walls
narrower xylem larger SA of water in contact - faster rate of transpiration
How does root pressure affect movement of water?
As water
Transpiration
Water evaporates out of stomata - reducing volume of liquid - decreasing pressure
Water moves in to fill space pulling water up xylem
Water stuck in a column - H bonds cohesive - water is replaced as it transpires
Water adheres to lignin in xylem this pulls walls inwards as water rises upwards
Narrower more adhesion + root pressure —> pushes water up