4. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Evidence for wave-nature of particles
Define probability distribution
Wave particle duality
Classical vs Quantal Descriptions of Nature
Define ψ² and explain its interpretation
Calculate energy of a particle in a 1D box
How PIB energy changes based on mass, length, and principle quantum number
Define phase of a wavefunction
Define Zero-Point Energy and explain its physical interpretation
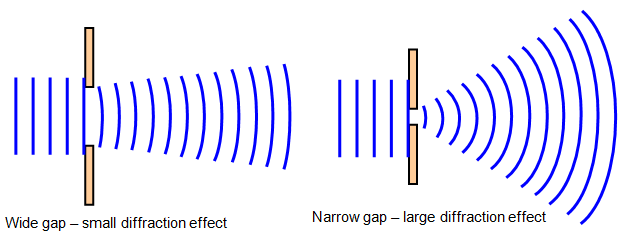
Wave Diffraction
The bending and spreading of waves around obstacles or through openings
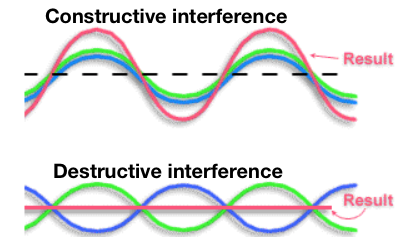
Wave Interference
When two or more waves interact causing the amplitude of the resulting wave to be greater (constructive interference) or smaller (destructive interference) than the individual waves
De Broglie Equation
λ = h/mv
λ = wavelength (m)
h= Planck’s Constant: 6.626×10⁻³⁴
m= Mass of the particle (kg)
V= Velocity of the particle (m/s)
Use: when you need to determine the wavelength of a moving object
Transverse Wave Characteristics
Amplitude: difference between midpoint and wave crest
Wavelength: length of one complete cycle
Frequency: Number of complete cycles per unit time
Speed of Wave Travel
λ = v/f
λ = The wavelength (m)
v= velocity (m/s)
f = frequency (s^-1, Hz)
Nodes
When the oscillation amplitude of a standing wave equals zero. They are areas where the phases change.
Calculating energy of a classic particle in a box
E = (1/2) mv²
The Schrödinger Equation
-(h²/8π²m) (d²Ψ(x)/dx²) + V(x)Ψ(x) = EΨ(x)
Where:
h= Planck’s Constant: 6.626×10⁻³⁴
m = the particle mass
x = the particle position
V = the potential energY
The Schrödinger Equation For Quantum Particle in a Box
-(h²/8π²m) (d²/dx²)Ψ = EΨ
Complete Wave-function for a Particle in a One-Dimensional Box
Ψn(x) = √(2/L) sin (nπx/L)
Calculating for the Energy of a Particle
En = (h²n²)/8mL²
As the value of n increases, the energy increases. N is restricted to positive integers so there can only be specific values, meaning it’s quantized.
The Ground State
n=1 where there is the lowest possible energy. The lowest energy of a confined quantum particle must always be > than zero. These particles are never at rest.
Zero-Point Energy
The difference between the ground state energy (n=1) and zero.
En = (h²)/8mL²
Excited States
When energy is higher than the ground state. There are infinitely many.
Change of energy between energy levels
ΔE = Ef - Ei = (h²)/8mL² (n²f - n²i)