Chapter 13 Equilibrium and Human Movement KNES 361
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is torque?
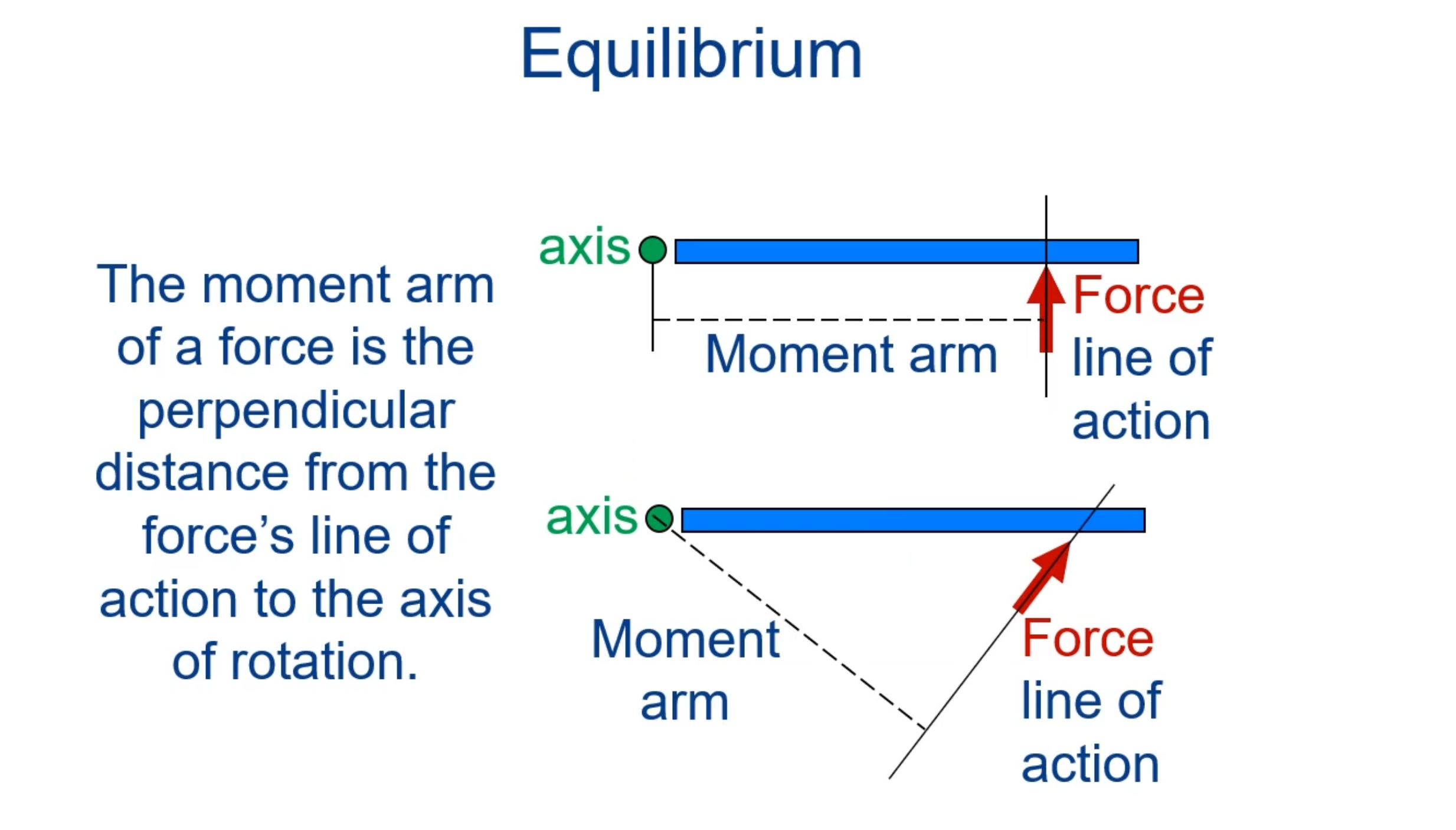
The rotary effect of a force about an axis of rotation
Measured as the product of force and the force moment arm (AKA torque arm, force arm)
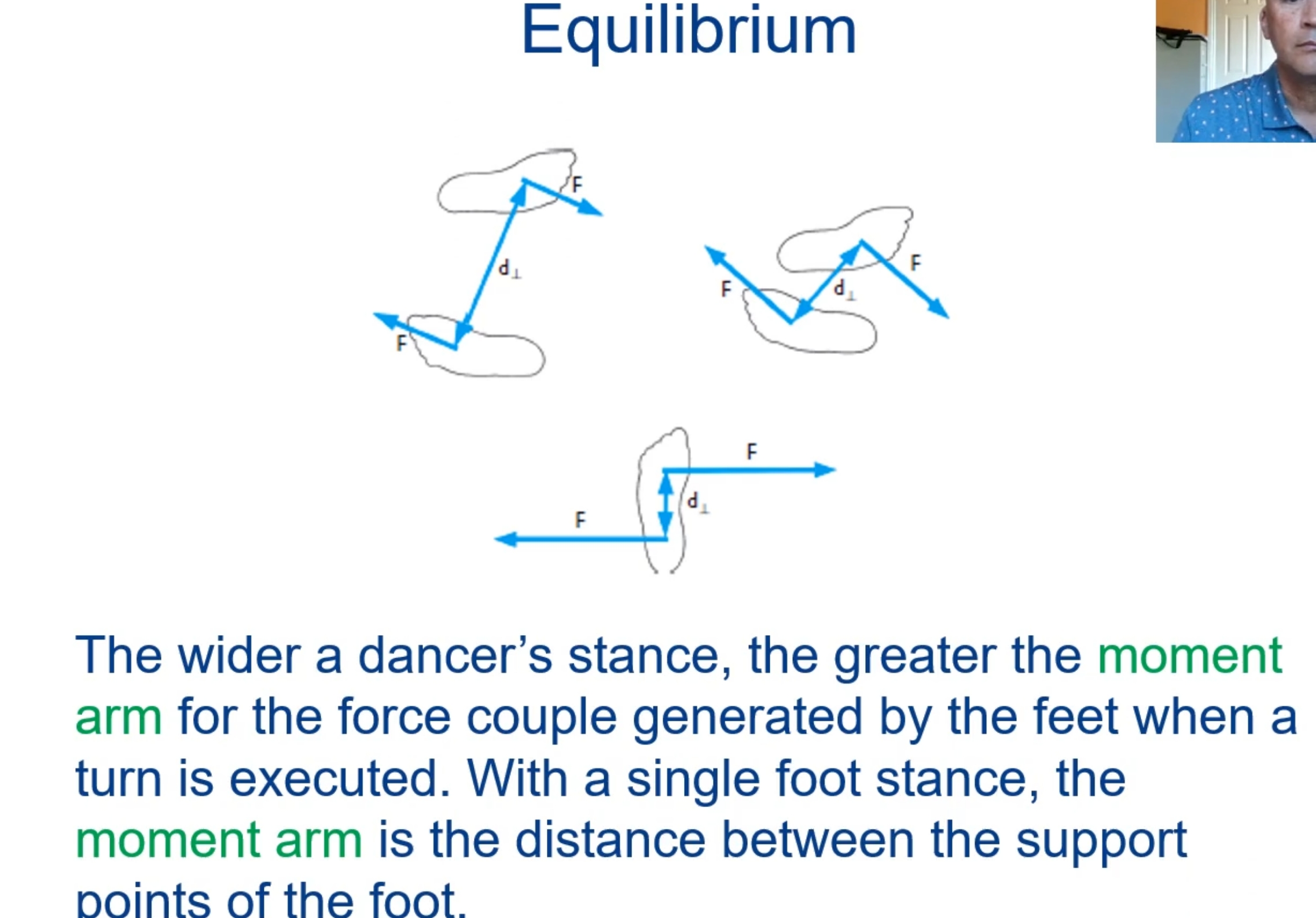
The shortest (perpendicular) distance between a force line of action and an axis of rotation
Where do torques occur within the human body?
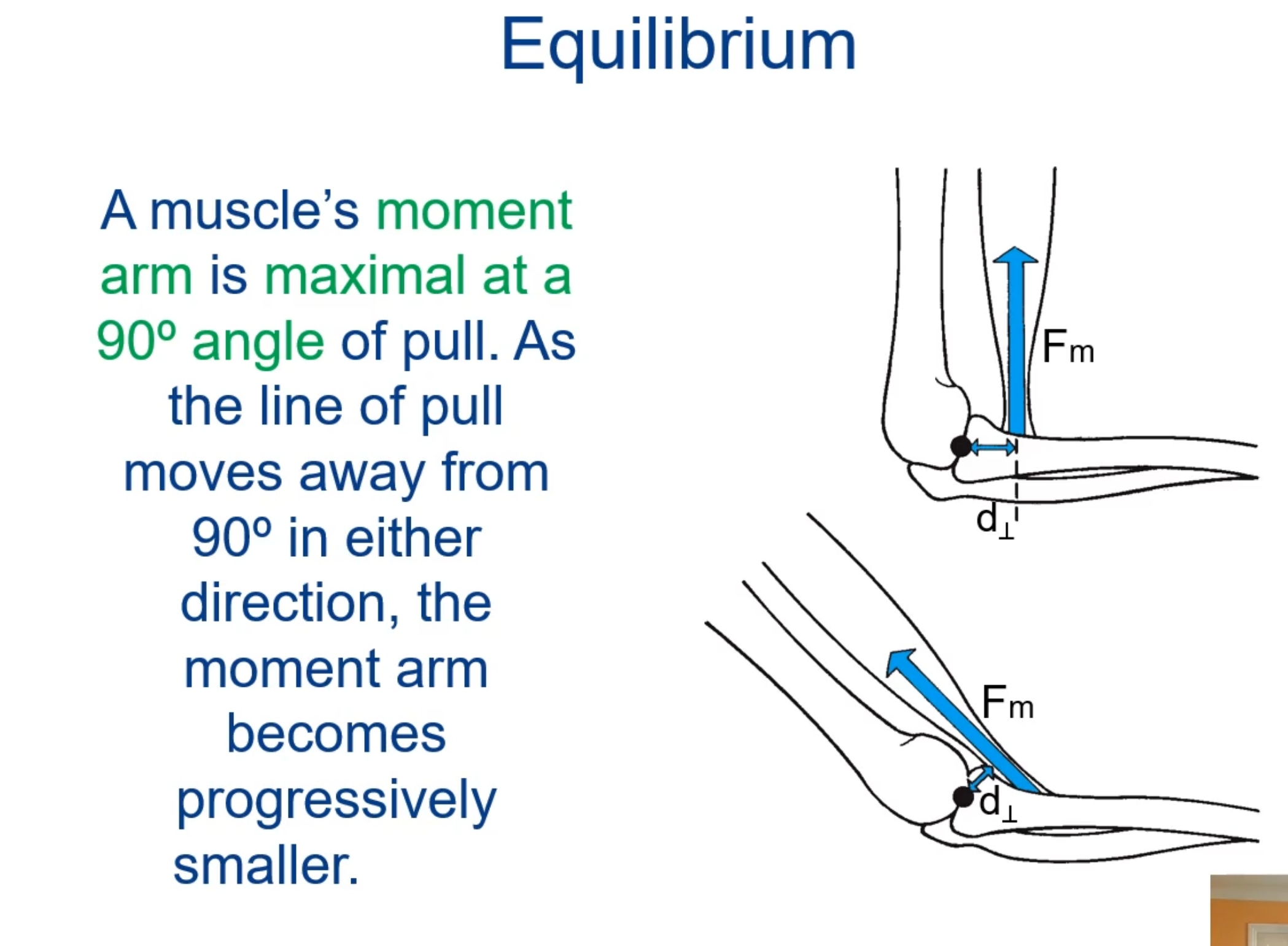
The product of muscle tension and muscle moment arm produces a torque at the joint crossed by the muscle


What is a lever?
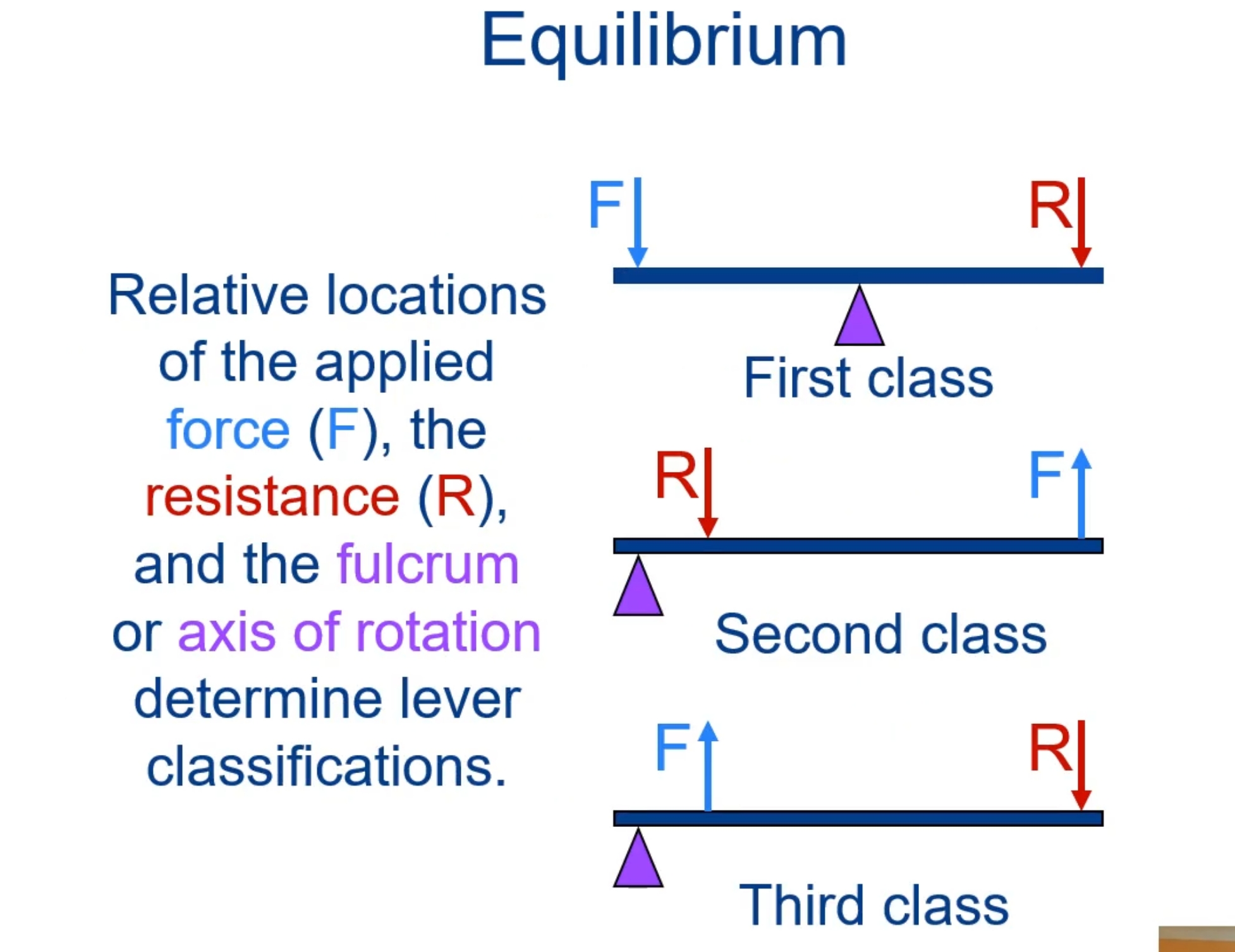
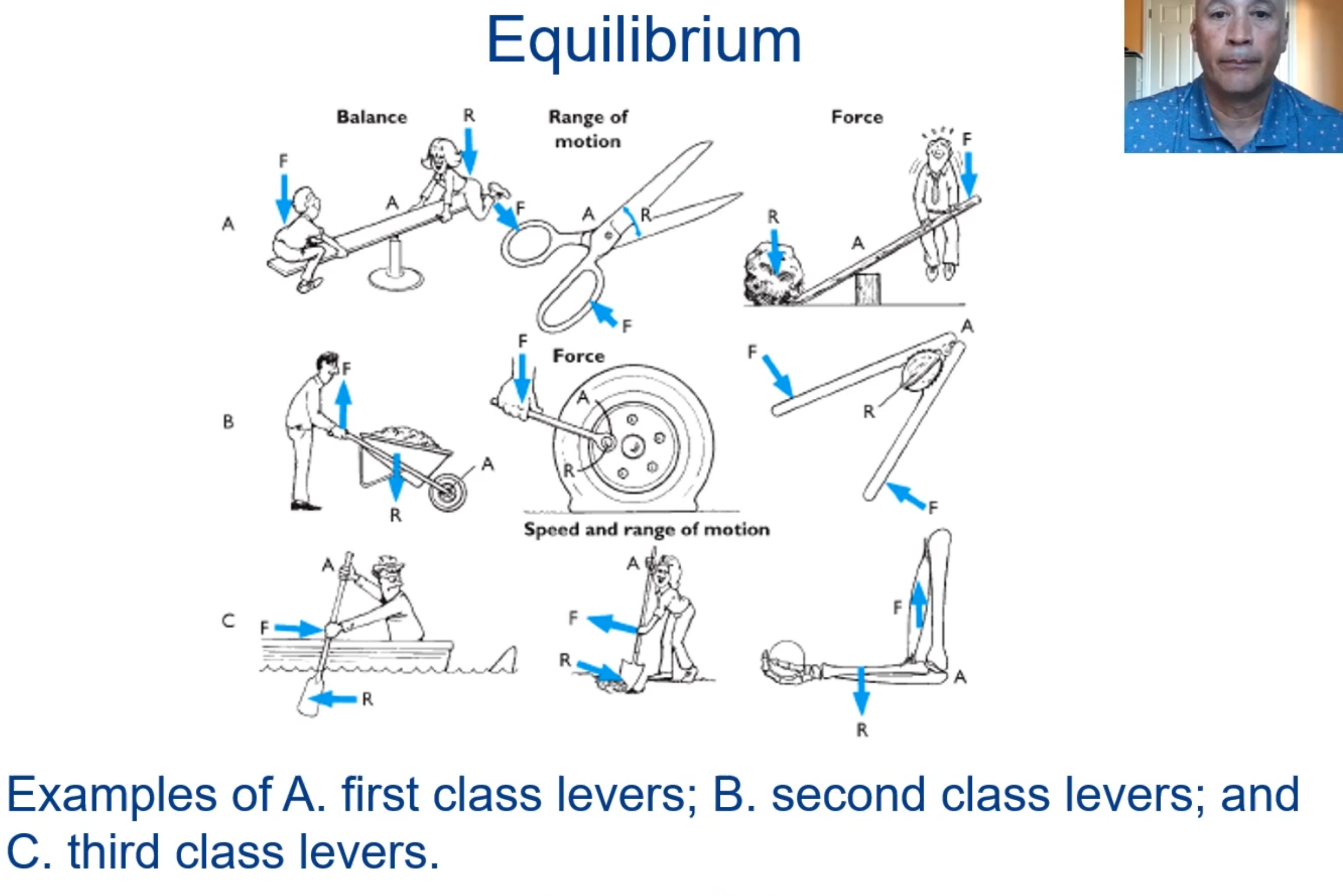
A simple machine consisting of a relatively rigid bar-like body that can be made to rotate about an axis or on a fulcrum.
There is first-, second- and third-class levers
What is mechanical advantage?
The ratio of the moment arm of the force (force arm) to the moment arm of the resistance (resistance arm) for a given lever
MA= FA / RA
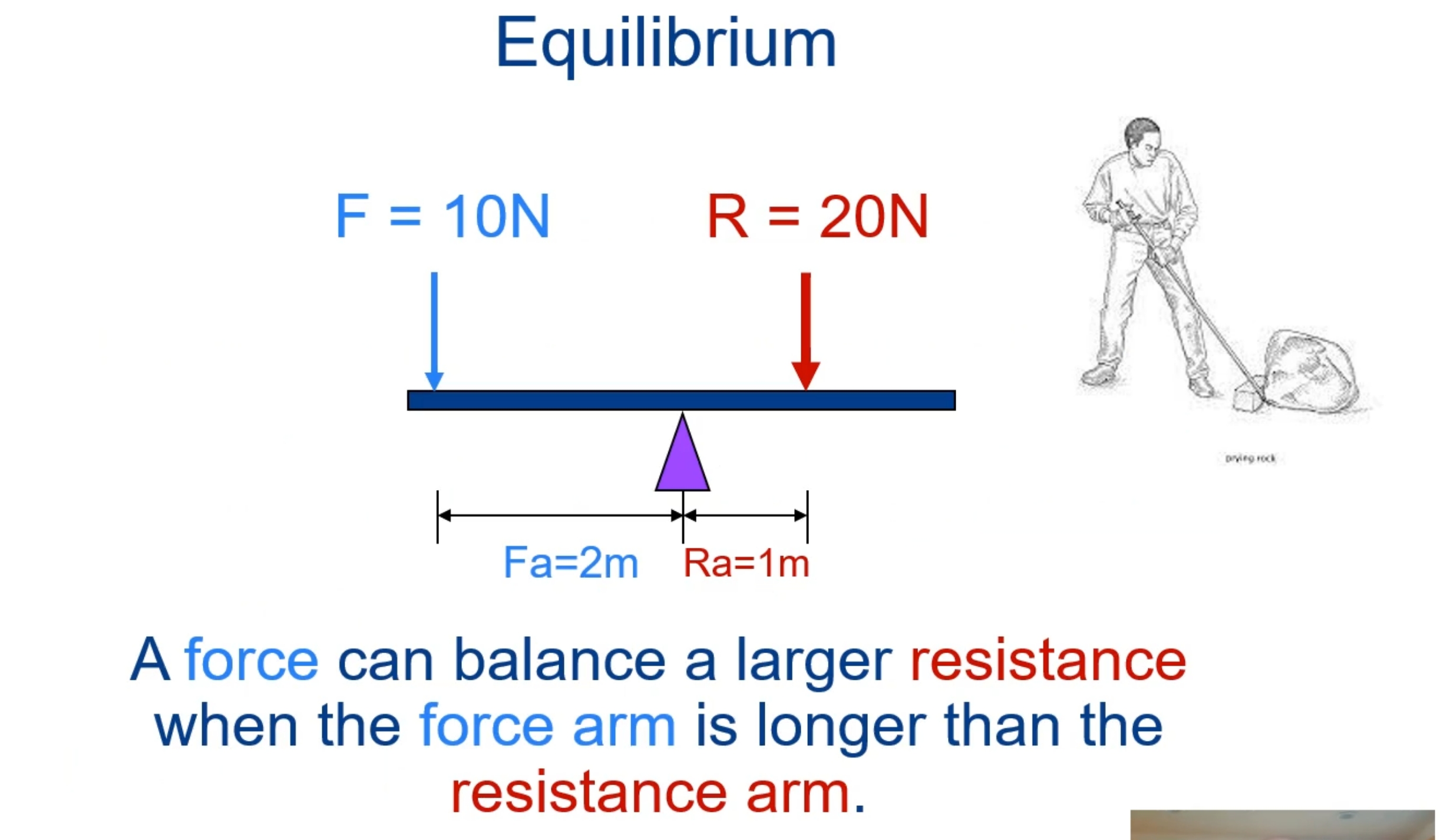
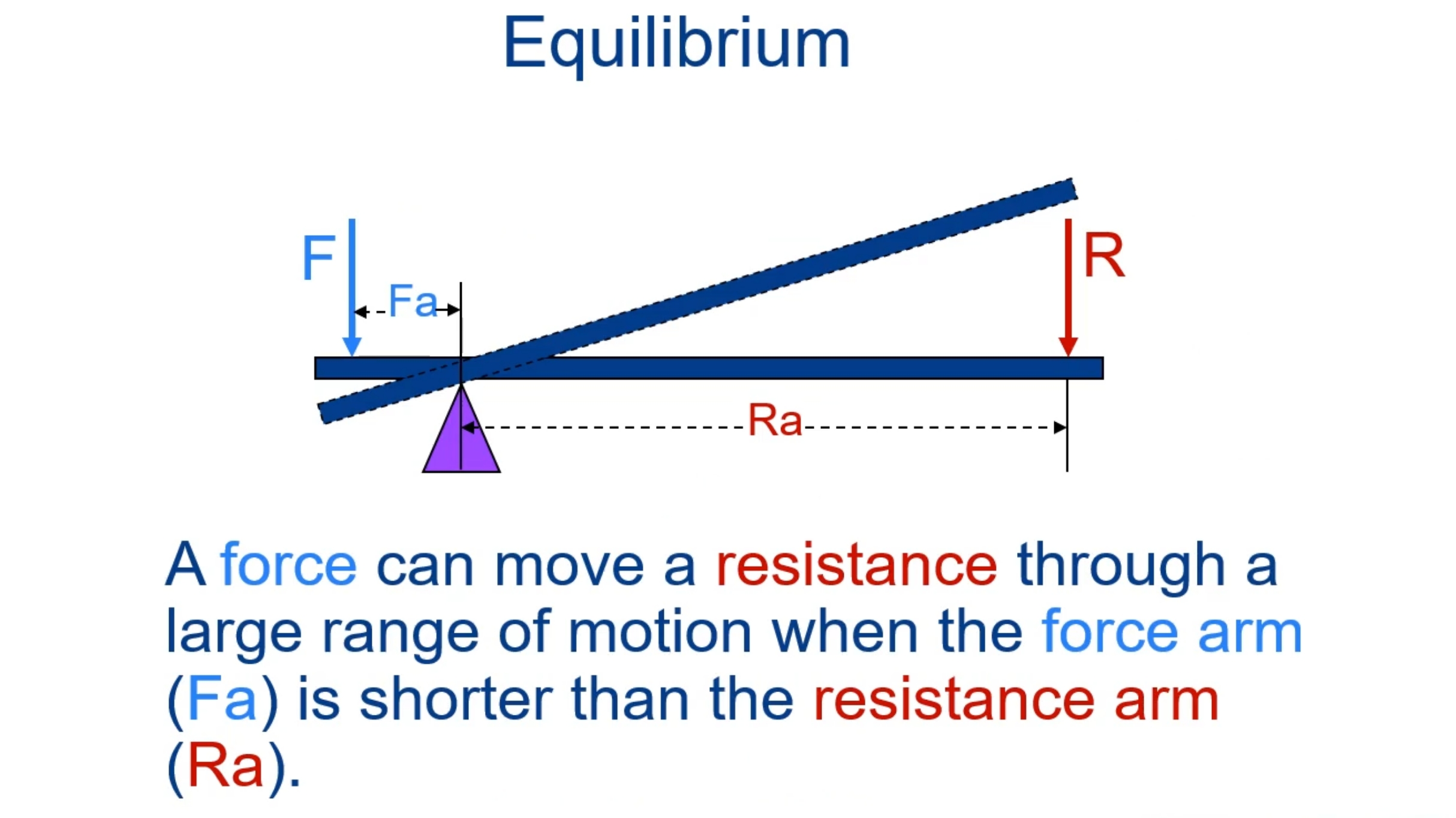
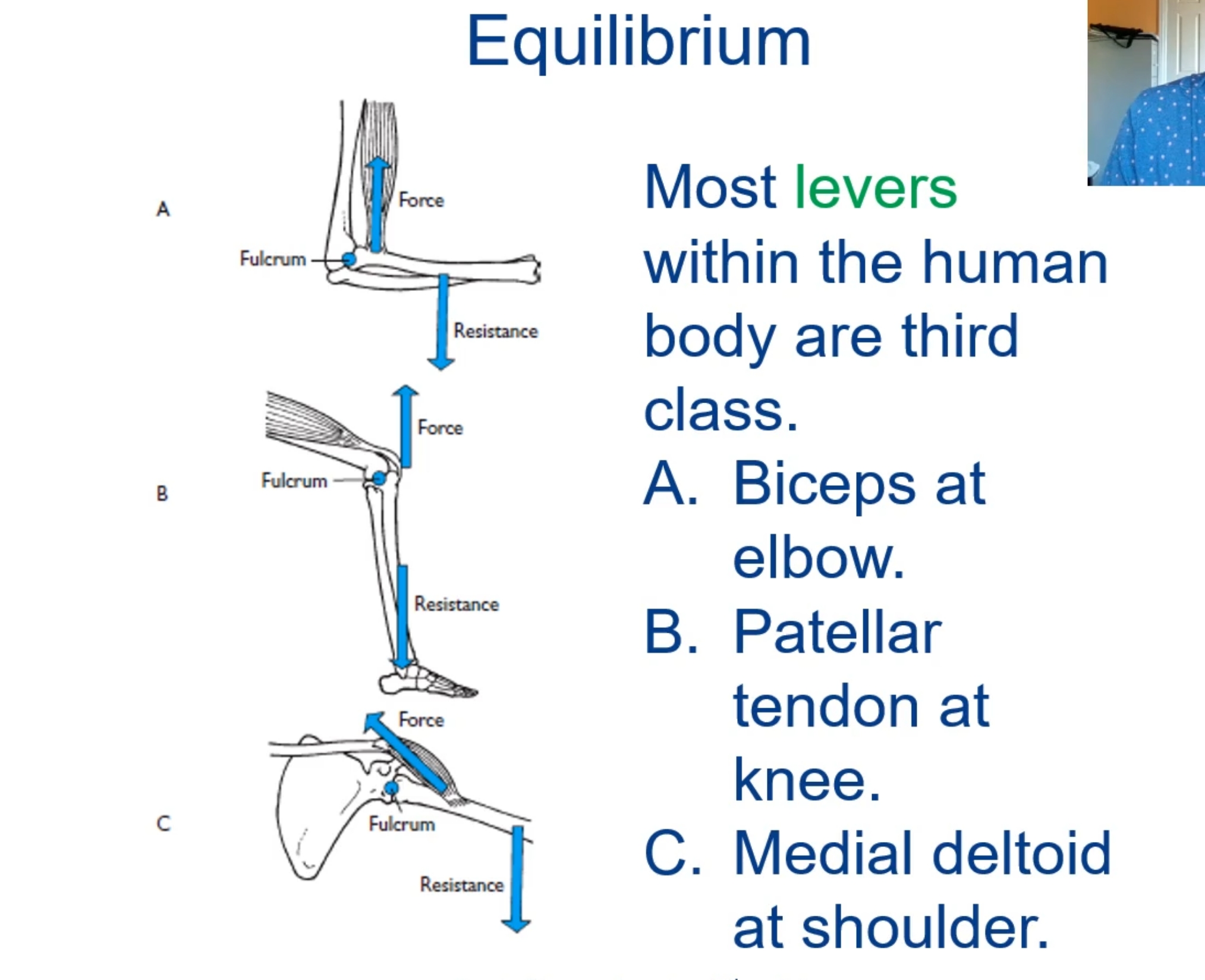
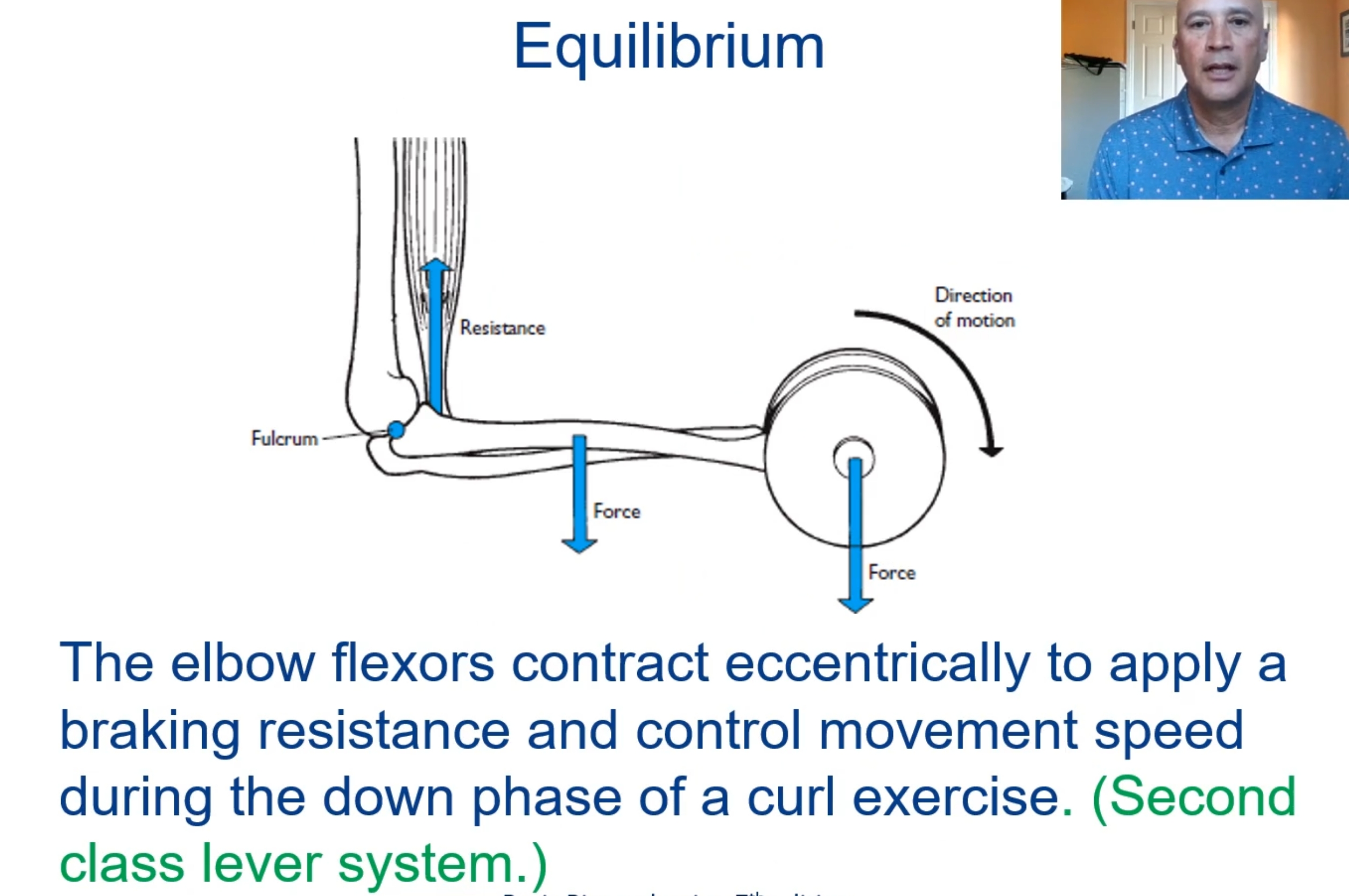
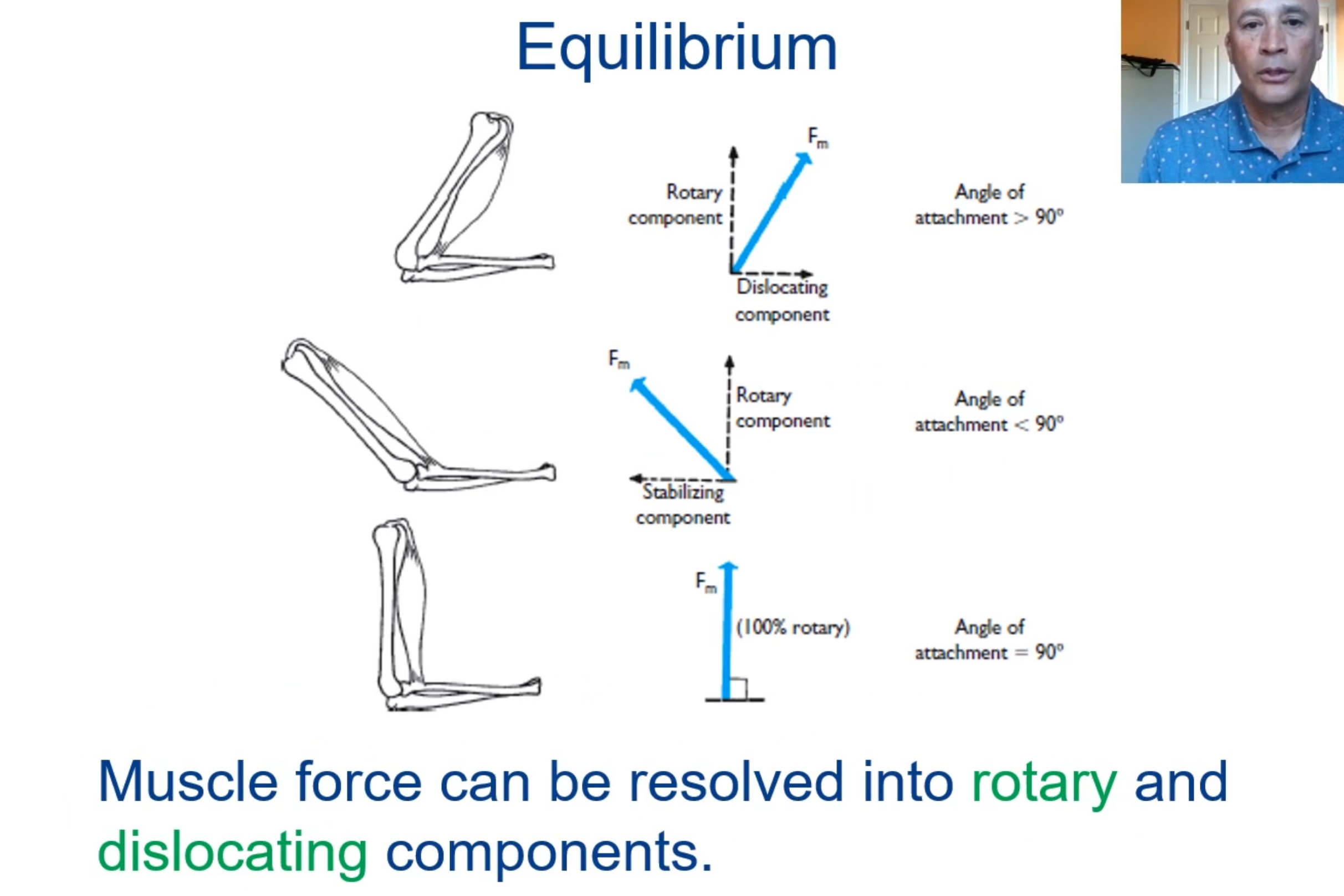
What is static equilibrium?
A motionless state in which there is no net force or net torque acting
The conditions of static equilibrum are:
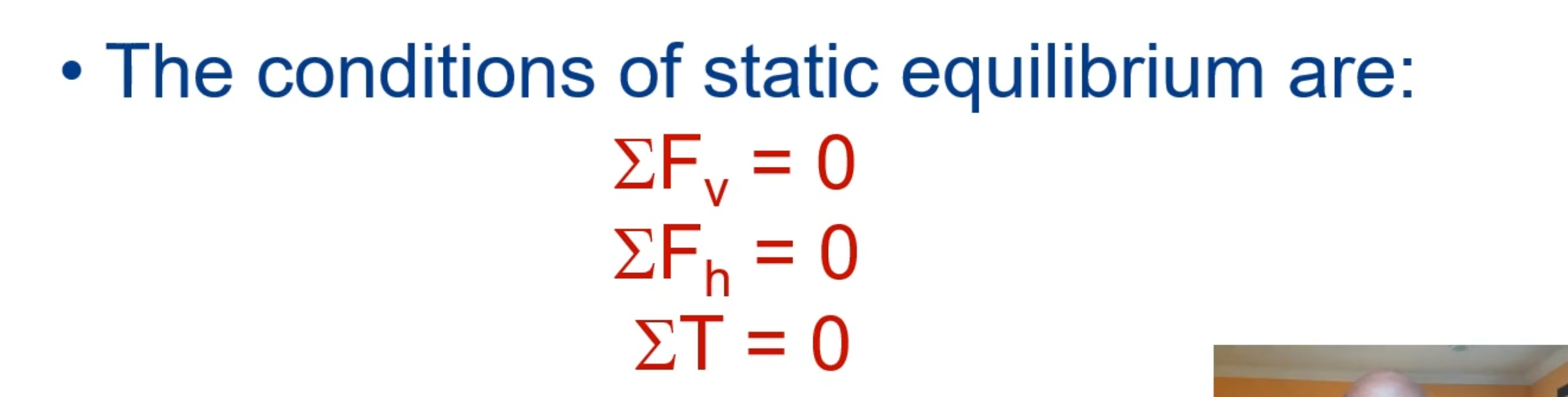
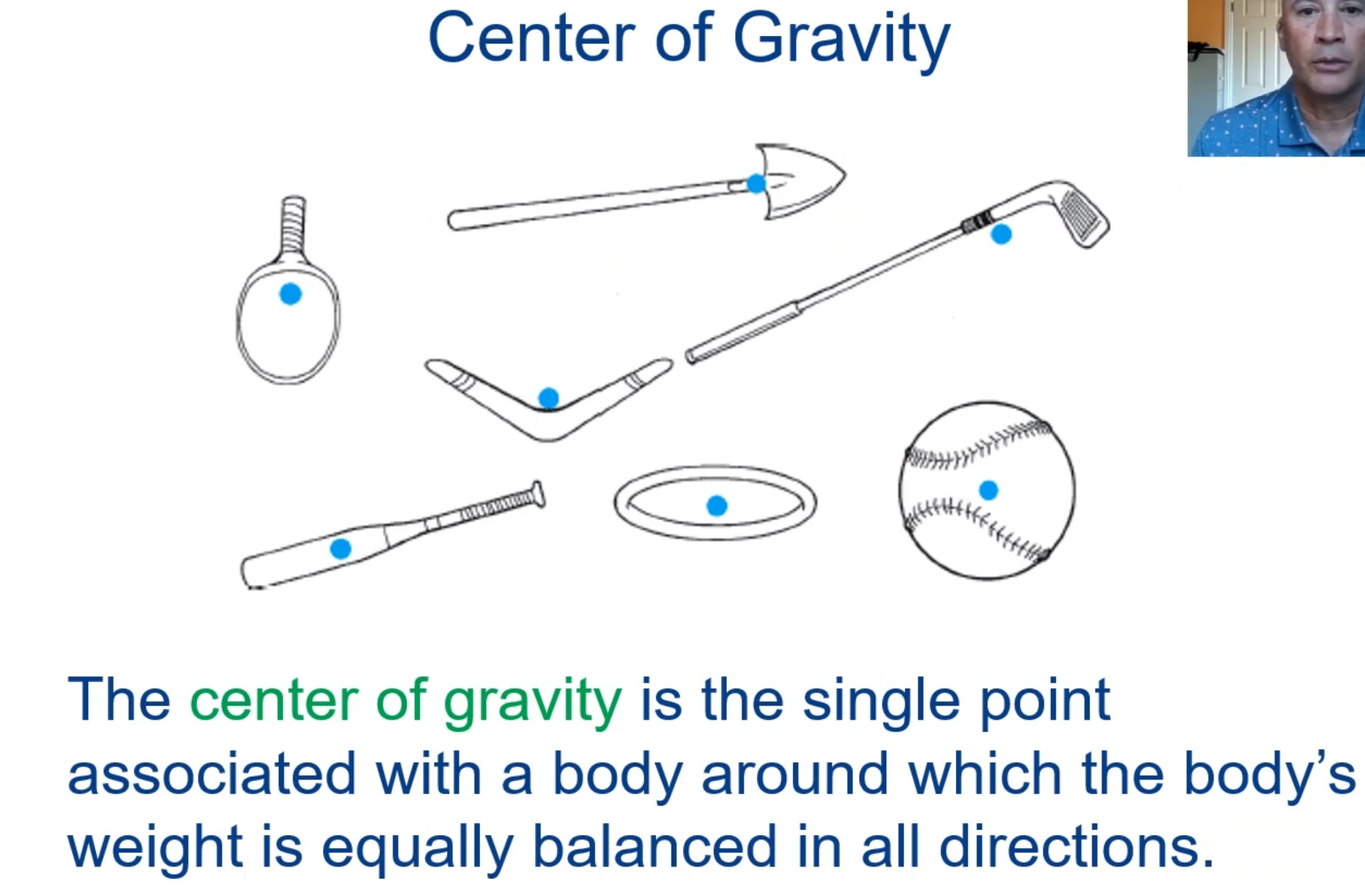
What is the center of gravity?
The point around which a body’s weight is equally balanced in all directions
Also referred to as the centered of mass or mass centroid
(Need not be physically located inside of a body)
Why is the center of gravity of interests in the study of human biomechanics?
It serves as an index of total body motion
Path of the center of gravity of a runner
The body responds to external forces as if all mass were concentrated at the CG
This is consequently the point at which the weight vector is shown to act in a free-body diagram

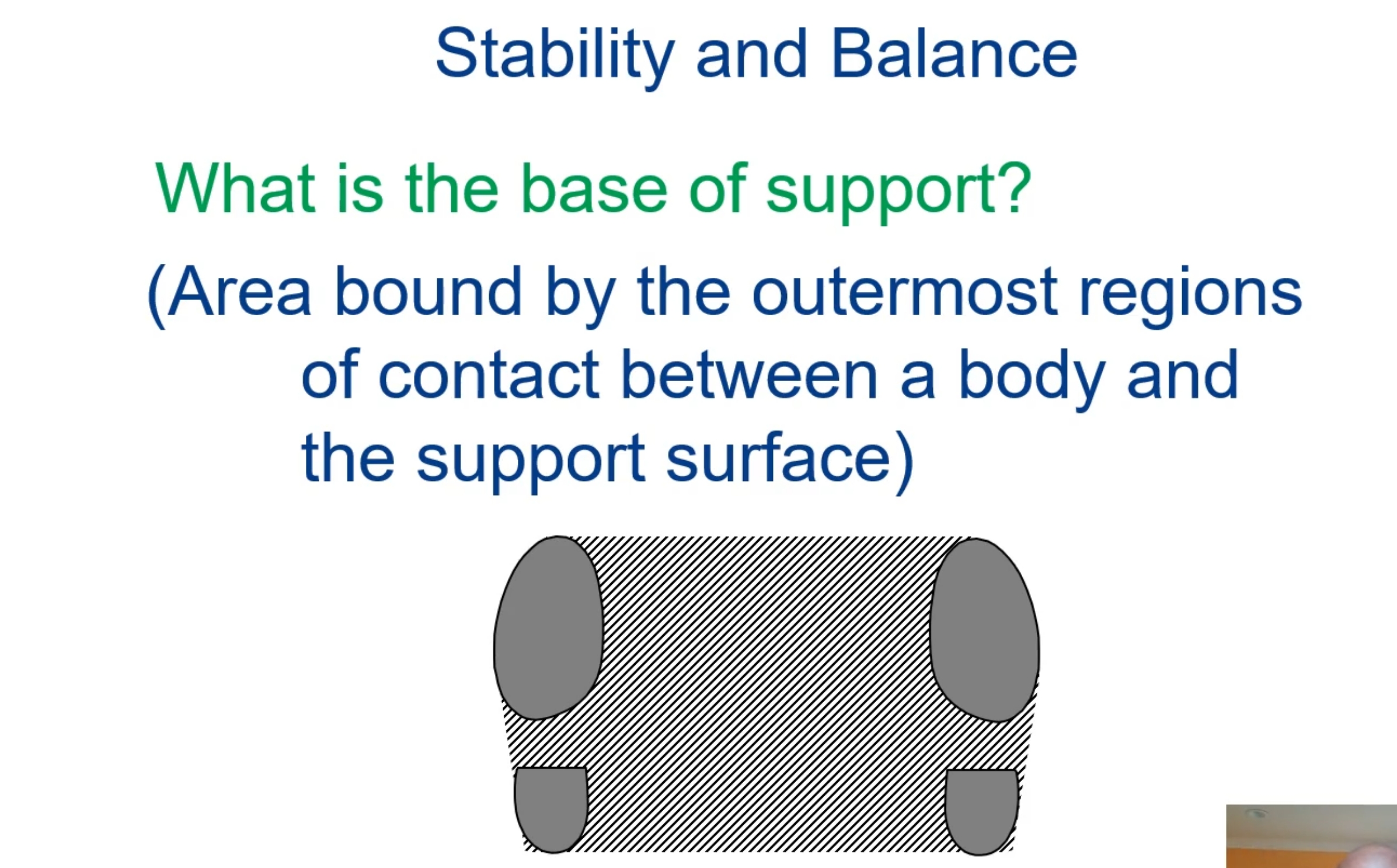
What is Stability?
Resistance to disruption of equilibrium
What is balance?
Ability to control equilibrium


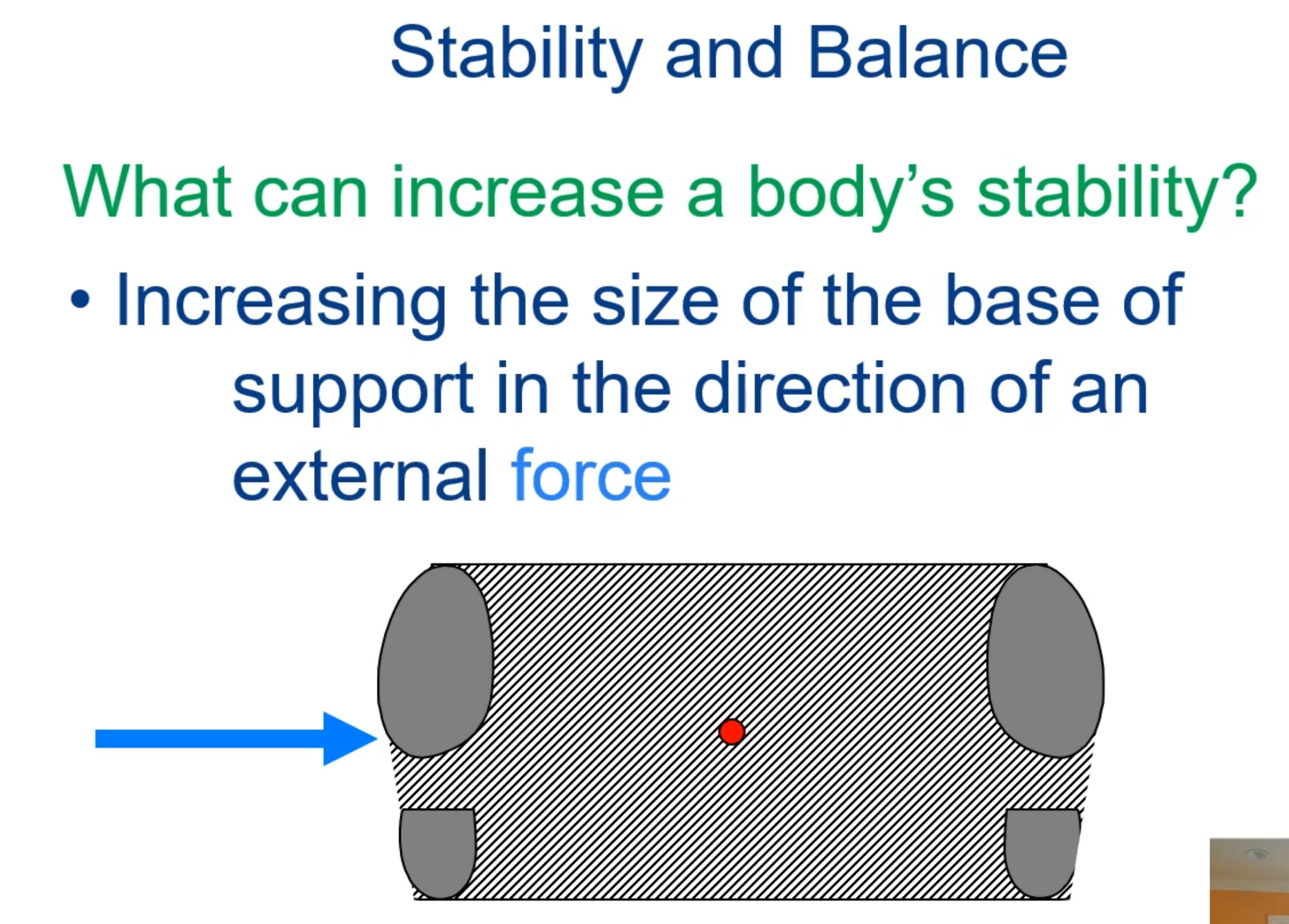
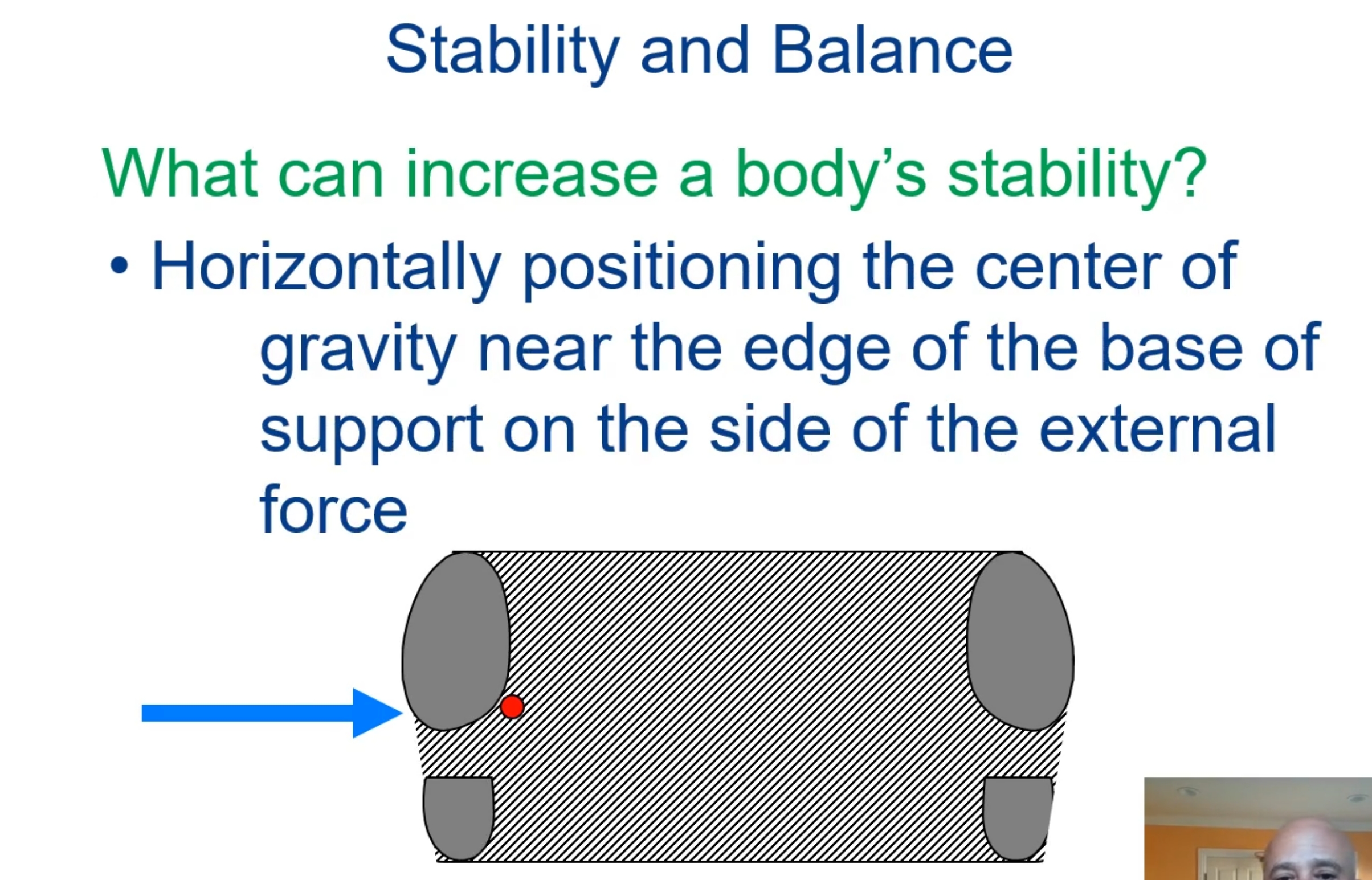
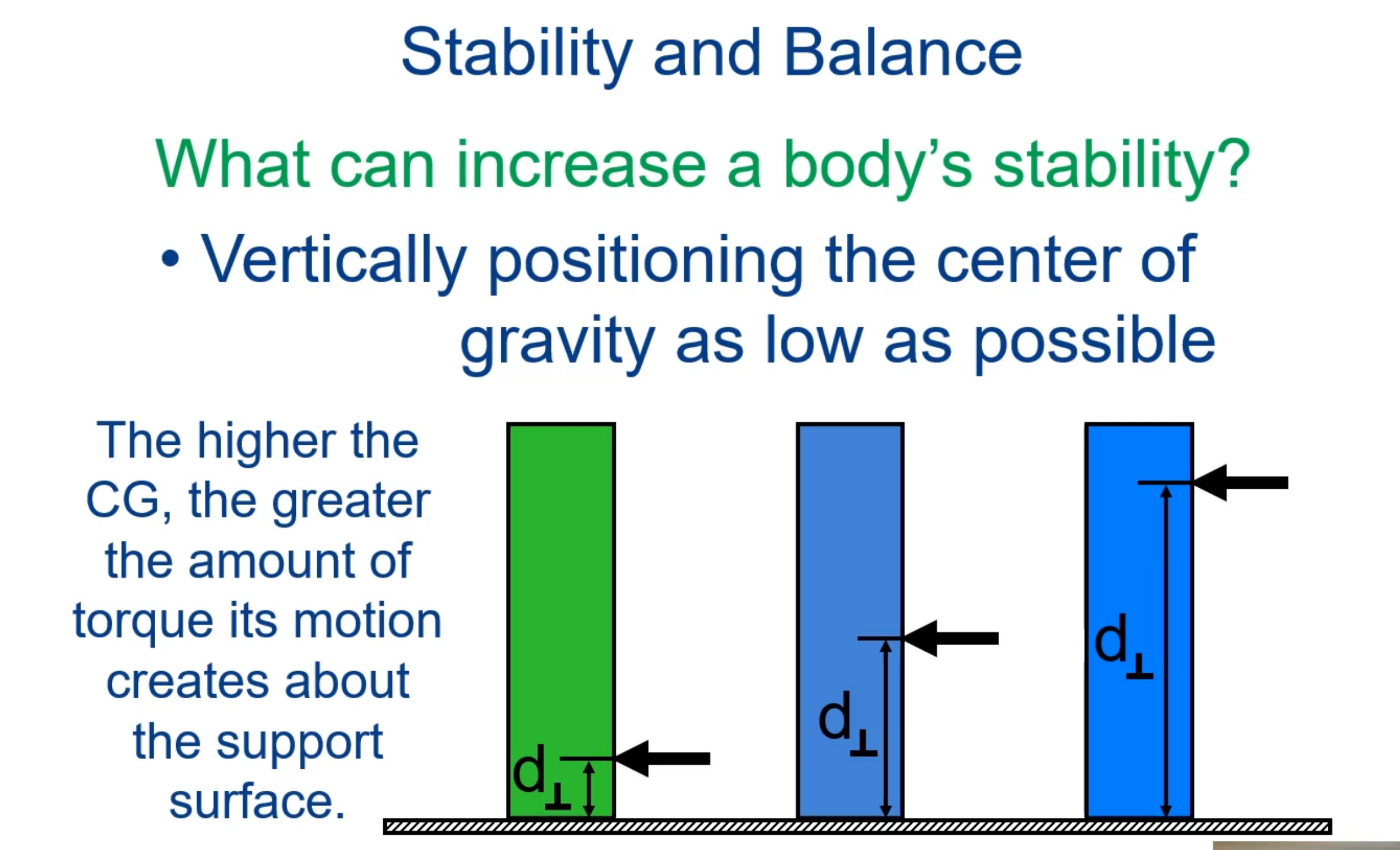
What can increase a body’s stability?
Increasing body mass
Increasing friction between the body and the surfaces of contact