PAS 601 Anemia/Hemoglobinopathies
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
anemia
What is the most common blood disorder?
iron deficiency anemia
What is the most common anemia?
MCV <80
Microcytic
MCV >100
Macrocytic
MCV 80-100
Normocytic
TICS—Thalassemia, Iron deficiency, anemia of Chronic disease, and Sideroblastic anemia
What are the microcytic anemias?
chronic blood loss
What is the most common etiology of iron deficiency anemia in adults?
- chronic blood loss
- parasites
- lack of dietary iron
- inability to absorb iron
- pregnancy
What can cause iron deficiency anemia?
meat, eggs, leafy green vegetables and iron-fortified foods
What are sources of dietary iron?
Celiac disease, Helicobacter pylori, inflammatory bowel disease, surgical resection
What can cause an inability to absorb iron?
- fatigue, lightheadedness, palpitations, exercise intolerance, exertional dyspnea, and weakness
- cheilitis
- koilonychia
- glossitis
- pica (clay, dirt)
- phagophagia (ice)
What are the symptoms of iron deficiency anemia?
- MVC < 80
- low serum ferritin (<12 ng/mL)
- low serum iron
- low transferrin
- high TIBC (total iron binding capacity)
- high RDW
What is seen on labs in iron deficiency anemia?
Hypochromic, microcytic, iron deficiency anemia
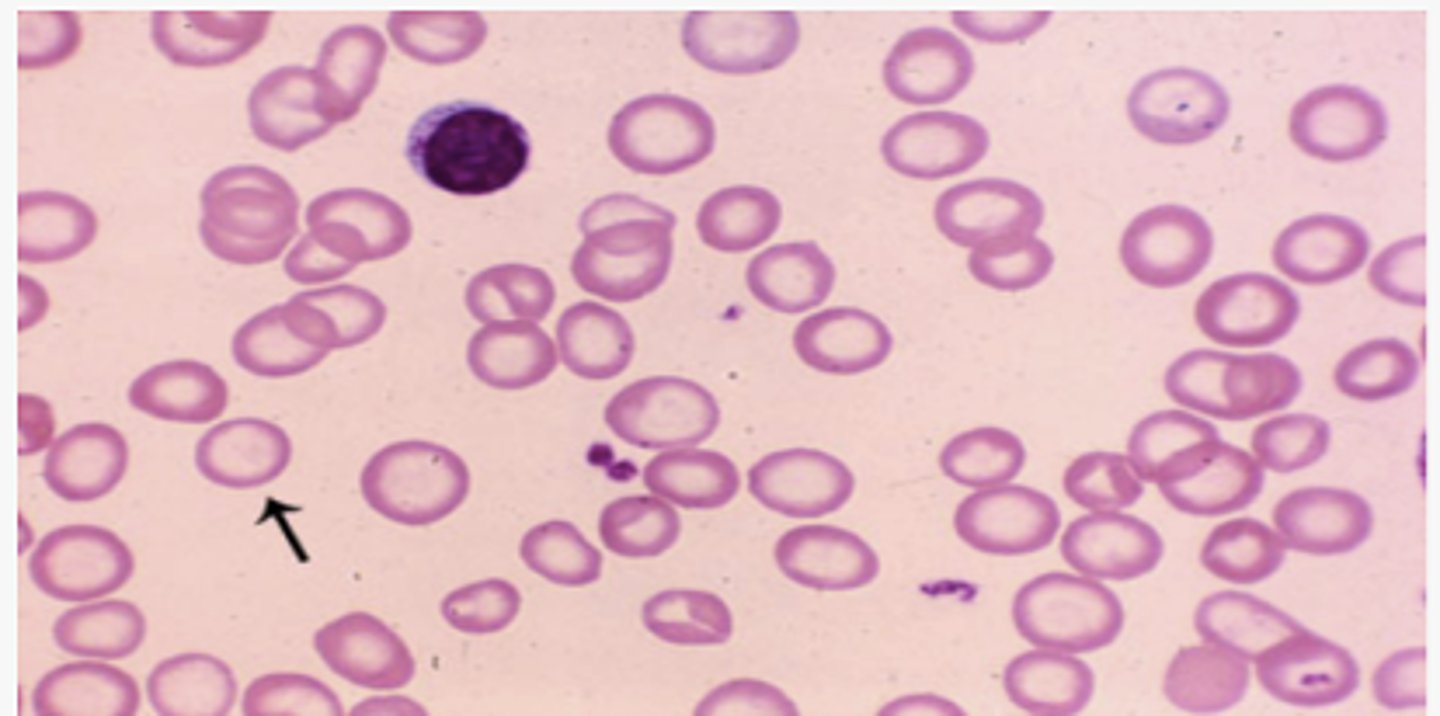
- Poikilocytosis (variation in shape)
- Anisocytosis (variation in size)

- target cells
- nucleated RBCs
What is seen on peripheral smear in severe IDA?
- target cells
- nucleated RBCs
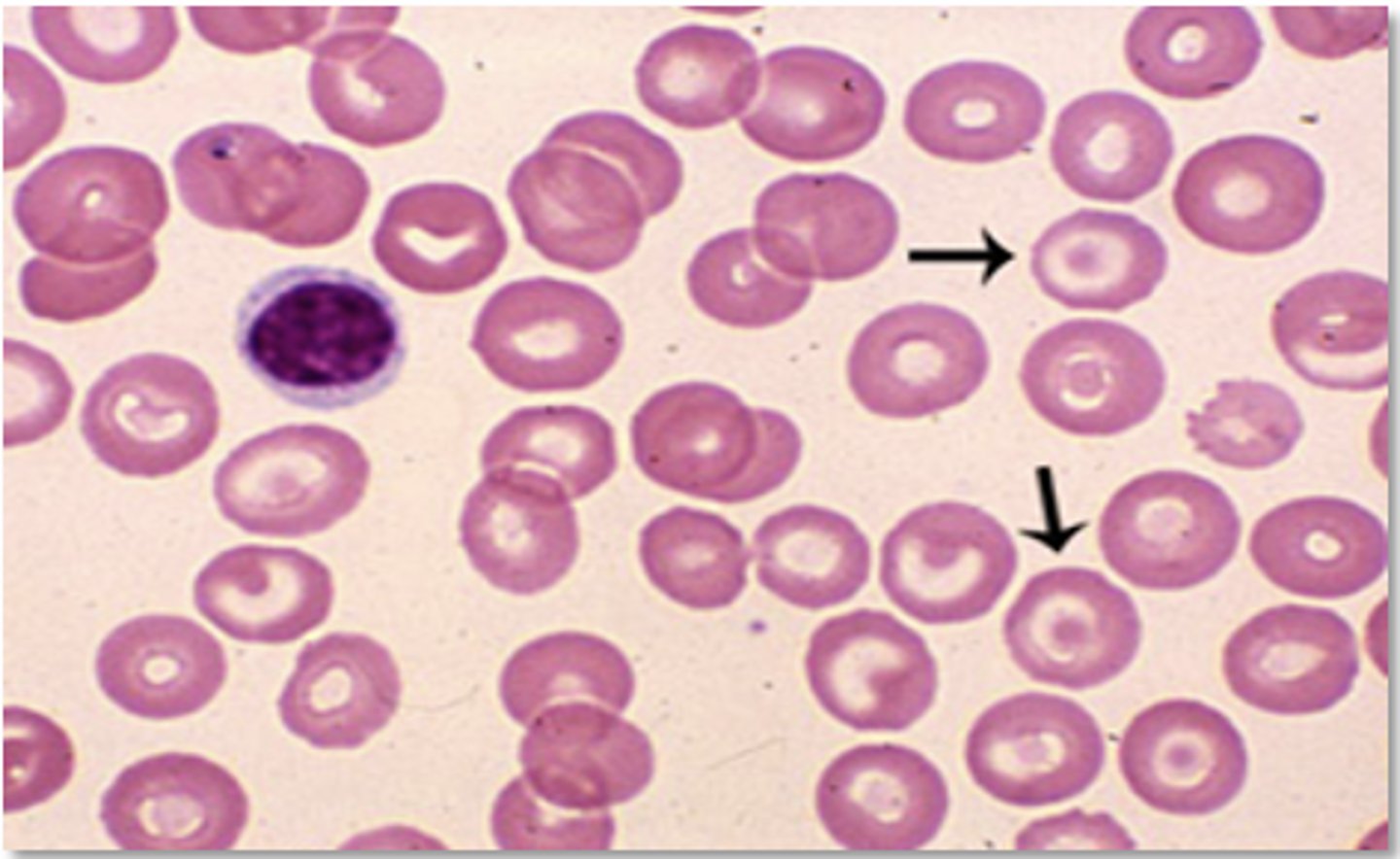
Ferrous Sulfate
How is iron deficiency anemia treated?
GI distress
What is the most common complication of oral iron therapy?
beans, lentils or red meat
What foods should be eaten to increase dietary iron?
ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
What increases the bioavailability of iron?
red blood cell transfusion
What is used when IDA is symptomatic, cardiovascular instability, continued blood loss; used to stabilize a patient?
Group of disorders where hemoglobin synthesis is decreased due to inability to synthesize heme → iron inside RBC is inadequately used to make hemoglobin despite normal amounts of iron → iron accumulates in mitochondria giving it a ringed appearance (ringed sideroblasts)
What is sideroblastic anemia?
- subtype of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
- chronic alcoholism
- lead poisoning
- copper deficiency
- isoniazid & chloramphenicol
- chronic infection/inflammation
What is the etiology of sideroblastic anemia?
- bronzing of the skin
- arthropathies
- glucose intolerance
- myocardial dysfunction
What can be seen in sideroblastic if undetected for prolonged period?
- high RDW
- MCV low or normal
- high serum iron
- high transferrin saturation
- high ferritin
What are lab findings in sideroblastic anemia?
- dimorphic RBCs (microcytic + normal)
- pappenheimer bodies
- basophilic stippling in lead poisoning
What is seen on peripheral smear in sideroblastic anemia?
bone marrow biopsy
How is sideroblastic anemia dx confirmed?
- ringed sideroblasts
- pappenheimer bodies
- increased iron stores
What is seen on bone marrow biopsy in sideroblastic anemia?
pappenheimer bodies
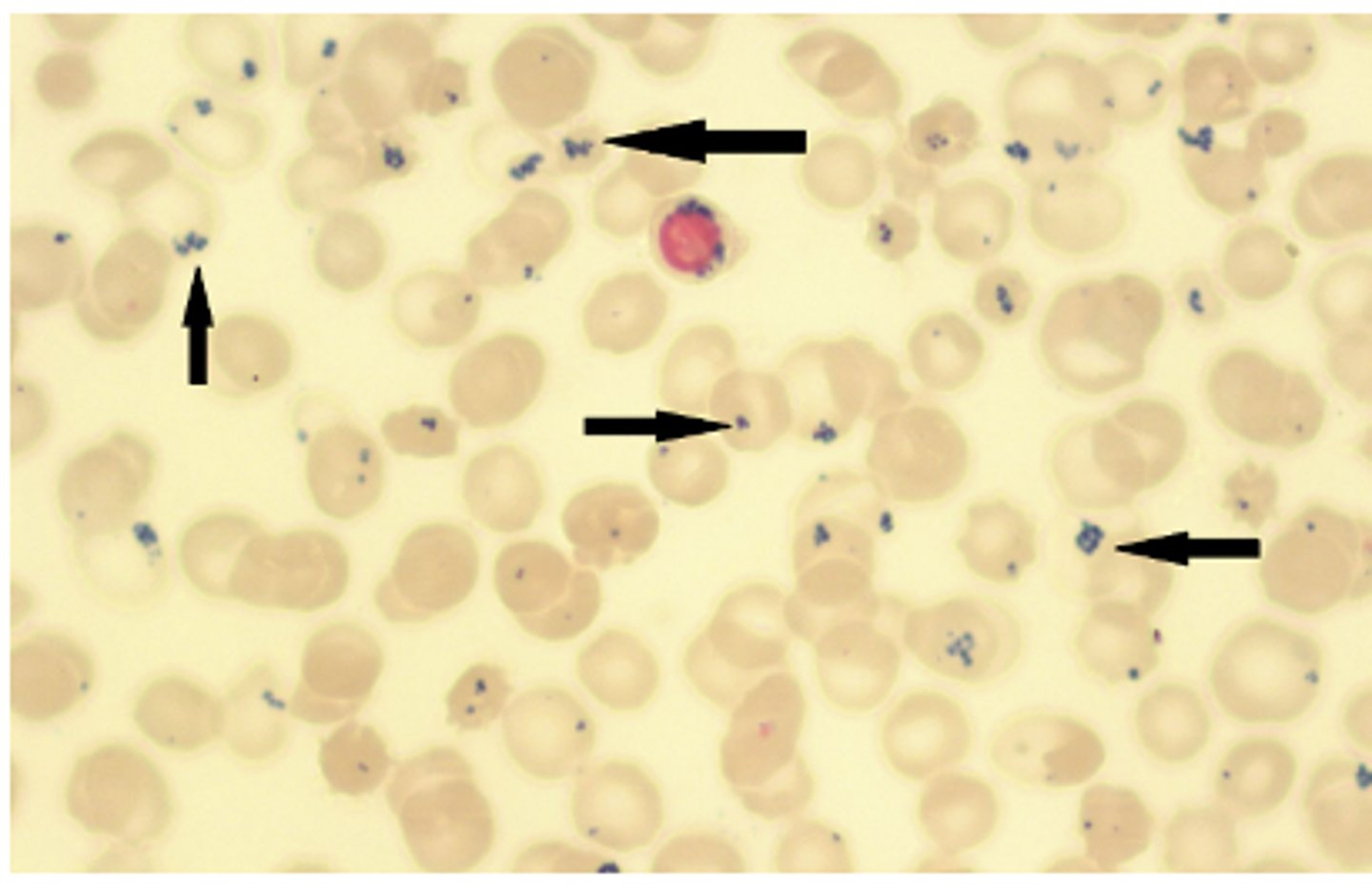
ringed sideroblasts
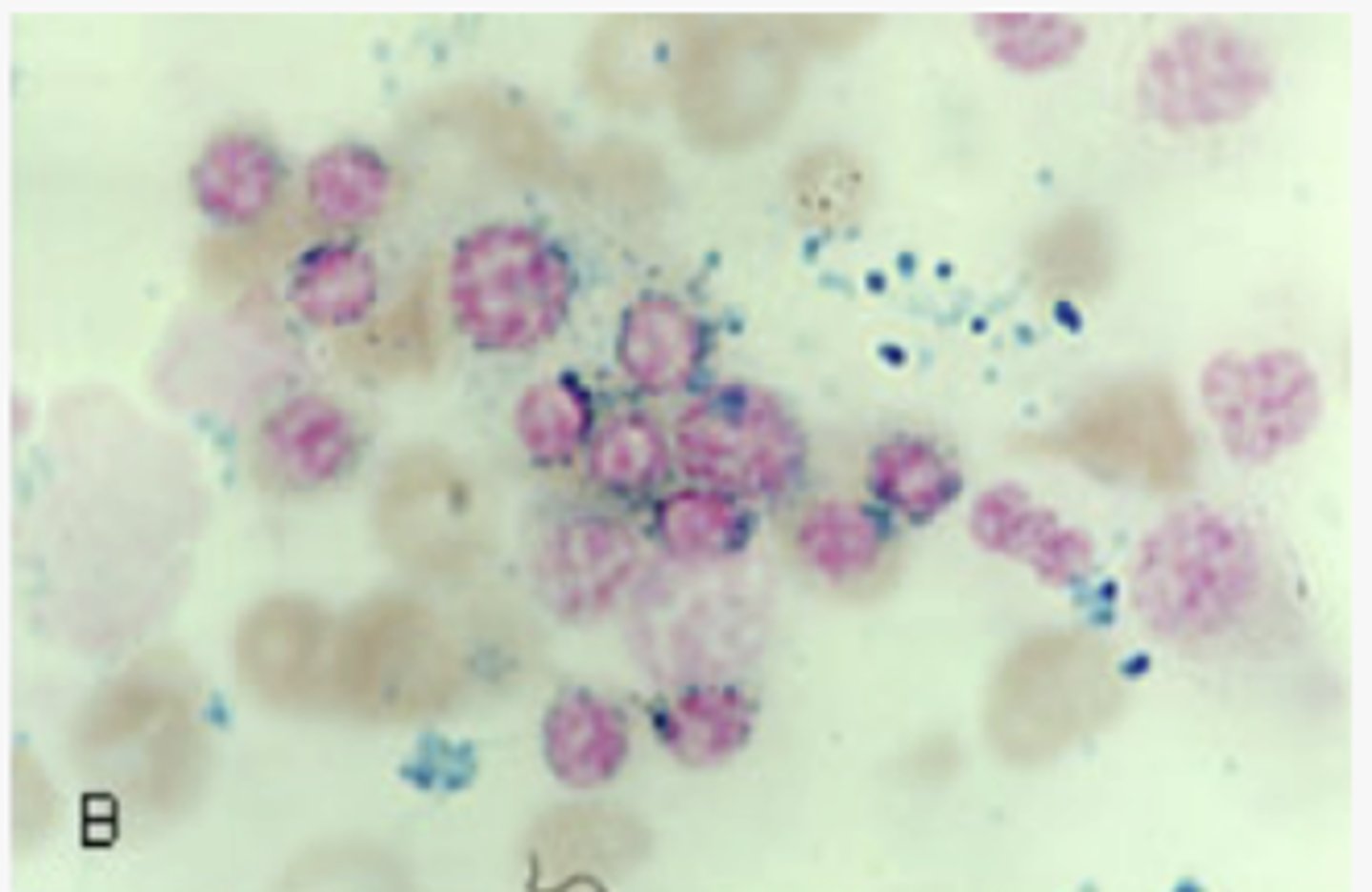
- supplementation of pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)
- removal of offending agent
- blood transfusion if severe
How is sideroblastic anemia tx?
infections, cancer, chronic kidney disease, autoimmune diseases (RA, SLE, vasculitis, sarcoidosis, IBD), heart failure, obesity
What is anemia of chronic disease caused by?
hepcidin
What does the liver increase production of in response to chronic inflammation?
prevention of iron store release --> decreases iron in circulation
What does increased hepcidin in anemia of chronic disease lead to?
serum ferritin normal or increased
What lab finding is seen in anemia of chronic disease that differentiates it from iron deficiency anemia?
- tx underlying disease
- blood transfusion
- synthetic erythropoietin
How is anemia of chronic disease tx?
tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension
How does acute blood loss manifest?
hemodilution and a lowered Hct
A shift of water from the interstitial fluid compartment into the plasma leads to:
group of disorders in which RBCs are destroyed
What is hemolytic anemia?
RBCs lyse in the circulation releasing hemoglobin into the plasma
What is intravascular hemolytic anemia?
RBCs phagocytized by macrophages in spleen and liver
What is extravascular hemolytic anemia?
- Defects in red blood cell membrane: hereditary spherocytosis, eliptocytosis 🡪 more prone to hemolysis
- Defects in hemoglobin production (sickle cell disease, thalassemia)
- Defective red blood cell metabolism (G6PD deficiency)
What are intrinsic causes of hemolytic anemia?
- Autoimmune diseases like autoimmune hemolytic anemia, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis
- Infections, e.g., Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection (cold agglutinin disease)
- Direct trauma
- Drug-induced
What are extrinsic causes of hemolytic anemia?
acute jaundice or hematuria in the presence of anemia
Suspect acute hemolytic anemia in patients who present with:
- increased reticulocytes
- increased LDH
- decreased haptoglobin
- elevated unconjugated billirubin
What are lab features common to all hemolytic anemias?
schistocytes
What is seen on peripheral smear in all hemolytic anemias?
immune process
If the direct antiglobin test (DAT), aka direct Coombs test is positive, hemolysis is caused by:
hemosiderin
What in the urine indicates chronic intravascular hemolysis?
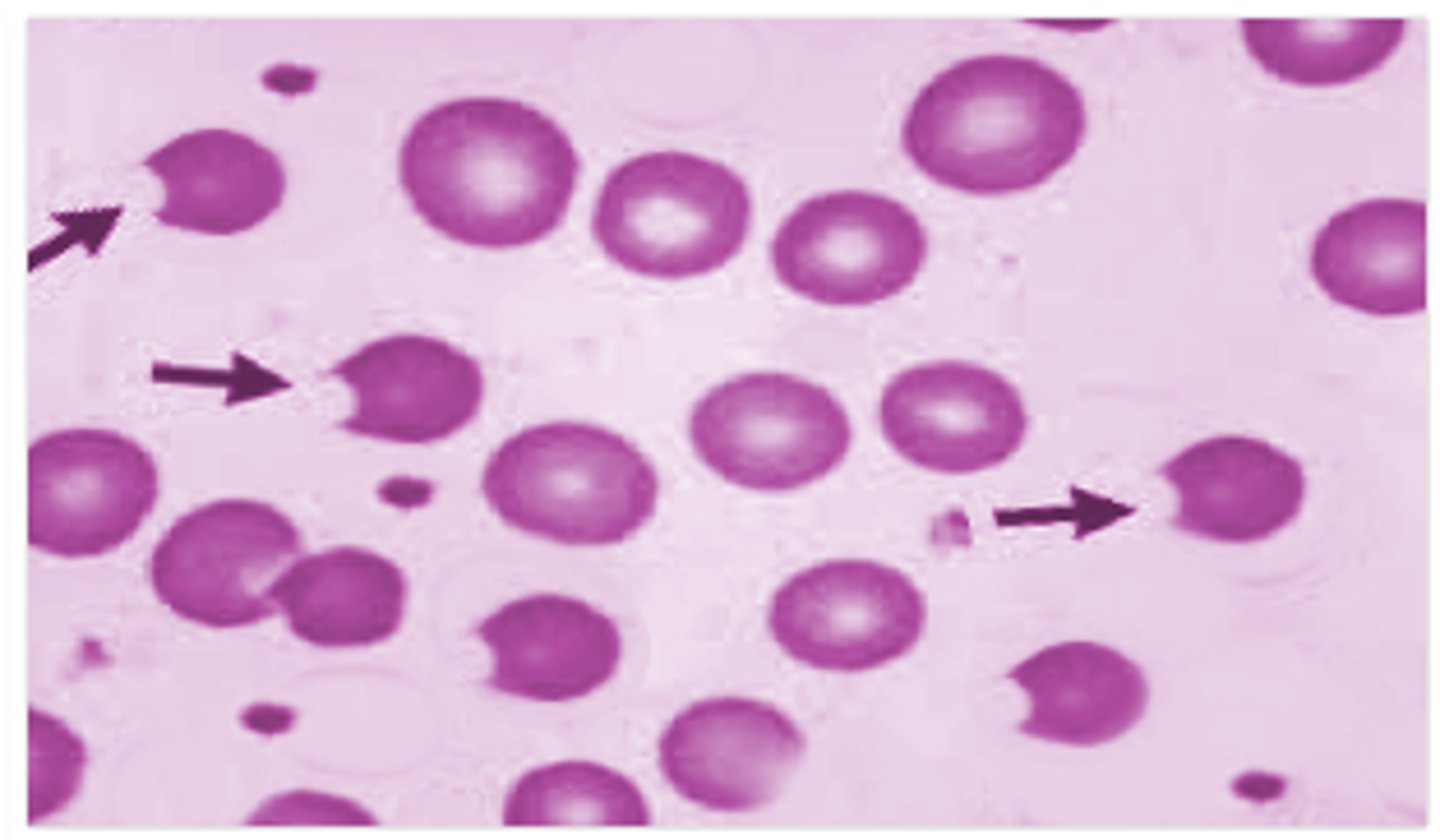
Shistocytes
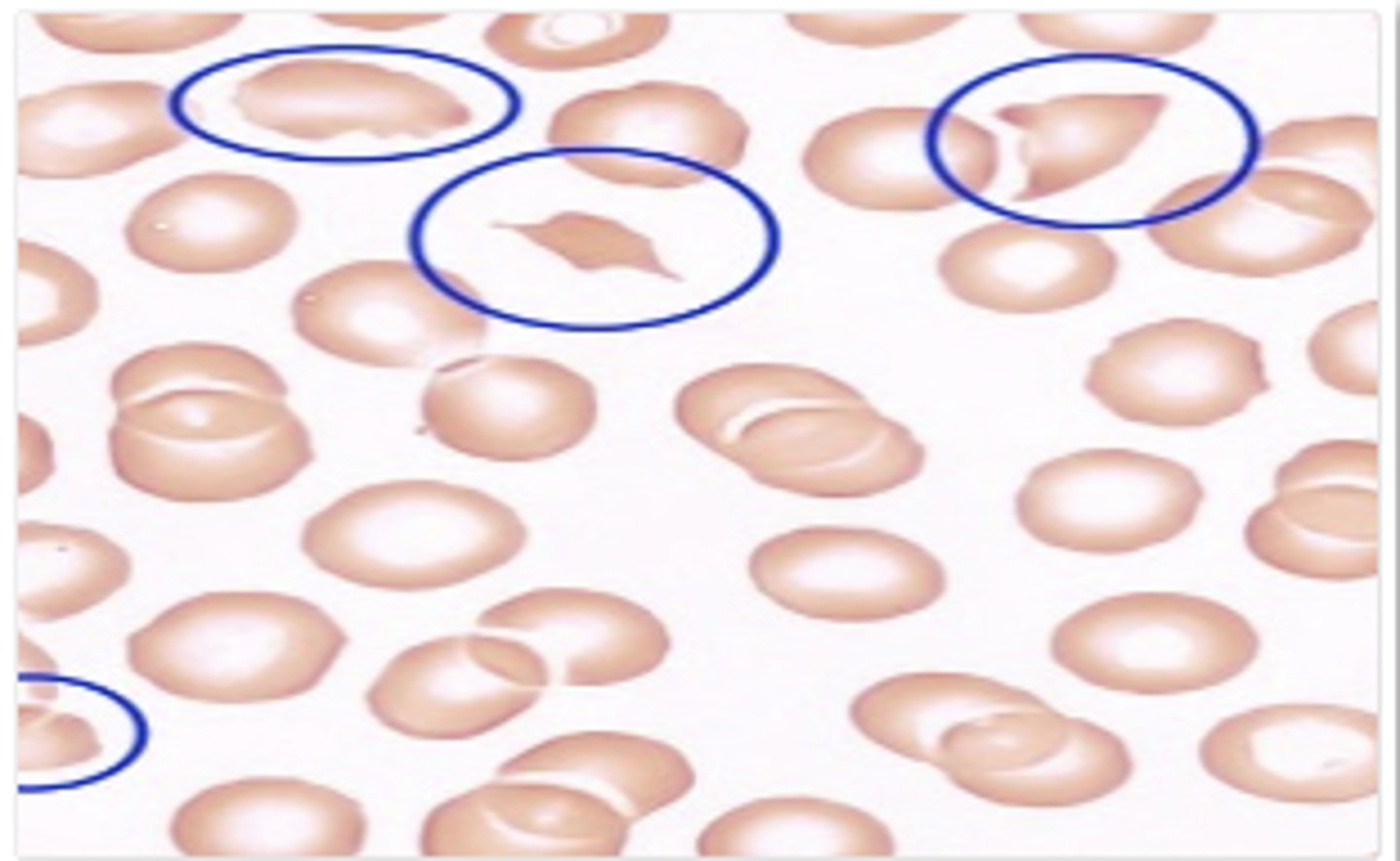
Bite cells
What may be present due to Heinz body removal by the spleen in G6PD deficiency?
Bite cells
- Symptomatic treatment can be given by blood transfusion if there is marked anemia
- In severe immune-related hemolytic anemia, steroid therapy is sometimes necessary
- Splenectomy may be helpful where extravascular hemolysis is predominant (e.g., most of the red blood cells are being removed by the spleen)
What is tx for hemolytic anemia?
Africa, the Mediterranean, the Middle East and South Asia
What population is affected the most by G6PD deficiency?
infections, medications, fava beans
What are triggers for G6PD deficiency?
G6PD deficiency
Suspected when someone develops jaundice, anemia, and hemolysis especially after exposure to triggers
- Hemoglobin rarely falls below 8g/dL
- Reticulocytes
- Increased indirect bilirubin
- Bite cells and Heinz bodies on peripheral smear
- low G6PD enzyme level
What test results are seen in G6PD deficiency?
- Prevention - avoiding/removing triggers
- Blood transfusion if needed
- Dialysis if needed
How is G6PD deficiency tx?
deficiency of vitamin B12 and/or folate
What causes megaloblastic macrocytic anemia?
liver dysfunction, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, certain drugs, reticulocytosis
What causes non-megaloblastic macrocytic anemia?
Inability to absorb vitamin B12 due to absence of intrinsic factor (IF)
What does pernicious anemia cause?
vegans, vegetarians, pernicious anemia
What causes B12 deficiency?
nutrition (poor diet, alcoholism), malabsorption (celiac disease, IBD), increased requirements (pregnancy, breast feeding) and certain medications
What causes folate deficiency?
Normal physiologic response to anemia; because reticulocytes are larger than mature RBCs, their increasing percentage of total RBCs will raise the MCV proportionately
What is reticulocytosis?
- Tingling/numbness in hands and feet
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty walking
What are neuro sx of B12 deficiency?
- hypersegmented neutrophils
- MCV > 100
- B12 < 200
- increased homocysteine
- increased methylmalonic acid
What is seen in B12 def anemia labs?
- hypersegmented neutrophils
- MCV > 100
- serum folate < 3
- increased homocysteine
- normal methylmalonic acid
What is seen in folate def anemia labs?
- Vitamin B12 supplementation
- PO: Methylcobalamin
- increase dietary intake of eggs, chicken, milk, fortified cereals
How is B12 deficiency tx?
- folic acid supplement
- increase dietary intake of leafy green vegetables, oranges, peanuts, lentils
How is folate deficiency tx?
thalassemias
What hemoglobinopathy occurs from a quantitative change in hemoglobin molecule?
sickle cell
What hemoglobinopathy occurs from a qualitative change in hemoglobin molecule?
SE Asia and China
What population is a thalassemia more common in?
- silent carrier
- no sx
What occurs if 3 of 4 alpha globin genes present?
- a thalassemia minor/trait
- low MCV
- mild anemia
What occurs if 2 of 4 alpha globin genes present?
- Hemoglobin H Disease
(Thalassemia major)
- low MCV
- more marked anemia
- reticulocytosis
What occurs if 1 of 4 alpha globin genes present?
- Hydrops fetalis
- stillborn fetus
- bart's Hgb
What occurs if 0 of 4 alpha globin genes present?
Mediterranean (Italian, Greek)
What population is B thalassemia more common in?
- Beta-thalassemia major (Cooley anemia)
- severe anemia
- transfusion dependent
- bony deformities
- iron overload
What occurs if homozygous for Beta thalassemia?
- Beta-thalassemia intermedia
- chronic anemia
- bony deformities
What occurs if homozygous for a milder form Beta thalassemia?
- Beta-thalassemia minor
- Clinically insignificant microcytic anemia
- modest anemia
What occurs if heterozygous for Beta thalassemia?
- hepatosplenomegaly due to extramedullary hematopoiesis
- medullary expansion, such as prominent or protruding forehead
What are signs and sx of thalassemia?
Increased HbA2, reduced HbA, and probably increased HbF
What is seen on Hgb electrophoresis in B thalessemia?
Adults: normal Newborns: may have HbH or Hb Bart's
What is seen on Hgb electrophoresis in a thalessemia?
normal
RDW is _________ in thalassemia
normal
Ferritin is _________ in thalassemia
- Overload of iron - from the disease itself or from frequent blood transfusions. Results in damage to the heart, liver and endocrine system
- Infection: people with thalassemia have an increased risk of infection. This is especially true if the spleen has been removed.
- Bone deformities: Thalassemia can make the bone marrow expand, which causes bones to widen, especially in the face and skull. Also makes bones thin and brittle, increasing the risk of broken bones.
- Heart problems: congestive heart failure and arrhythmias may be associated with severe thalassemia
- Endocrine complications: impaired growth and hormone deficiencies
What are complications of thalassemia?
- Blood transfusion regimen
- Iron chelation therapy to prevent iron overload
- Lusoatercept - FDA approved for transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia to promote erythroid maturation and decrease transfusion needs
- Allogeneic stem cell transplant is the only available cure for beta-thalassemia major
How is severe thalassemia tx?
Allogeneic stem cell transplant
What is the only available cure for beta-thalassemia major?
8% of Black Americans
The beta S gene is carried in ______________, and 1 of 400 American Black children will be born with sickle cell anemia
- hemoglobin (HgbS)
- hemoglobin C with sickling (HgbSC)
What are the two most common forms of sickle cell hemoglobin?
acidosis, hypoxemia, stressors
What leads to sickling of RBCs?
malaria (P. falciparum)
Sickle cell heterozygotes are protected from:
West Africa and in South and Central America
Where is sickle cell trait most common?
- Symptoms typically appear by 4 months of age
- Pallor, jaundice, bone pain, edema
- Recurrent painful episodes and chronic organ disease secondary to vasoocclusion
What are signs and sx of sickle cell?
encapsulated organisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What infection are sickle cell pts. at increased risk?
- CBC: Hgb 6-8 with high reticulocyte
- peripheral smear: sickled cells (5-50% of RBCs)
- hemoglobin electrophoresis: HgbS, HgbSC
- IEF and HPLC - high sensitivity and specificity for SCD
How is sickle cell dx?
- isoelectric focusing (IEF) analysis
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
What tests have high sensitivity and specificity for SCD?
painful ischemia, necrosis, organ damage
How does vaso-occlusion SCD present?
analgesics (often opioids)
How is vaso-occlusion SCD tx?
- fever, cough, sputum, excruciating pain, dyspnea, hypoxia
- infiltrate on CXR
How does acute chest syndrome SCD present?
analgesics (often opioids)
How is acute chest syndrome SCD tx?