Exam II Biology Review
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/154
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes questions from Mastering Biology, lecture guide, and other information that is needed to be known for EXAM II.
Last updated 7:52 PM on 2/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
1
New cards
Two
How many **fatty acids** are in a phospholipid?
2
New cards
Negative charge to interact with water and place to attach another small charged molecule.
What functional feature(s) does the phosphate group contribute to the structure of a phospholipid?
3
New cards
Hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions with water
What holds **phospholipids** together in a bilayer formation?
4
New cards
A fat molecule is less soluble in water because it has three non-polar fatty acids and no polar or charged head like a phospholipid has.
What type of molecule is ***less*** soluble in water--a fat or a phospholipid? Why?
5
New cards
Hydrogenated vegetable oil is solid at room temperature, whereas non-hydrogenated vegetable oil is liquid.
Hydrogenated vegetable oil is the primary ingredient in margarine. How does hydrogenated vegetable oil **differ** from nonhydrogenated vegetable oil?
6
New cards
1. The diverse proteins found in and attached to membranes perform many important functions.
2. Because membranes are fluid, membrane proteins and phospholipids can drift about in the membrane.
3. The framework of a membrane is a bilayer of phospholipids with their hydrophilic heads facing the aqueous environment inside and outside of the cell and their hydrophobic tails clustered in the center.
Biologists use the fluid mosaic model to describe membrane structure. **What statements about the fluid mosaic structure of a membrane are correct? Select the** ***three*** **correct statements.**
7
New cards
The similarity of the drug molecule to other molecules that are transported into the target cells
You are working on a team that is designing a new drug. For this drug to work, it must enter the cytoplasm of specific target cells.
**What would be a factor that determines whether the molecule selectively enters the target cells?**
**What would be a factor that determines whether the molecule selectively enters the target cells?**
8
New cards
Phosphate Group
A phospholipid has a "head" made up of a glycerol molecule attached to a single ___________________, which is attached to another small molecule.
9
New cards
Choline Group
Phospholipids vary in the small molecules attached to the phosphate group. The phospholipid shown in the figure has a **_______________** attached to phosphate.
10
New cards
Hydrophilic
Because the phosphate group and its attachments are either charged or polar, the phospholipid head is **_______________**, which means it has an affinity for water.
11
New cards
Fatty Acid
A phospholipid also has two "tails" made up of two **_______________** molecules, which consist of a carboxyl group with a long hydrocarbon chain attached.
12
New cards
Hydrophobic
Because the C-H bonds in the fatty acid tails are relatively non-polar, the phospholipid tails are **_______________**, which means they are excluded from water.
13
New cards
Non-Polar molecules
\
Ex: Hydrocarbons, O2, & CO2
\
Ex: Hydrocarbons, O2, & CO2
Hydrophobic, can cross easily, & no transport protein required.
14
New cards
Polar molecules
\
Ex: Water & Sugars
\
Ex: Water & Sugars
Hydrophilic, have difficulty crossing the hydrophobic part, and requires a transport protein to cross.
15
New cards
Ions
\
Ex: Na+, Ka+, Ca2+, & Cl-
\
Ex: Na+, Ka+, Ca2+, & Cl-
Hydrophilic, have difficulty crossing the hydrophobic part, and requires a transport protein to cross.
16
New cards
Always
Orange dye moves **independently** of purple dye. When is this true?
17
New cards
Only before equilibrium is reached
Concentration gradients exist that drive diffusion of both dyes. When is this true?
18
New cards
Only before equilibrium is reached
There is a net movement of orange dye from **Side A to Side B**. When is this true?
19
New cards
Never
Purple dye moves only from **Side B to Side A**. When is this true?
20
New cards
Only at equilibrium.
There is **no** net movement of purple dye. When is this true?
21
New cards
Primary Structure
Which **protein structure** cannot be easily broken?
22
New cards
CO2, O2, water, & lipids
What **molecules** can cross the lipid bilayer of a membrane directly, without a transport protein or other mechanism?
23
New cards
Channels
What type **transport protein** allows water molecules & small ions to flow quickly across the membrane, and provide a continuous path across the membrane?
24
New cards
Carriers
What type of **transport protein** primarily transports small polar organic molecules, and undergoes a change in shape to transport solutes across the membrane?
25
New cards
3 Na+
How much **sodium** is released in a Sodium Potassium pump?
26
New cards
2 K+
How much **potassium** is pumped in a Sodium Potassium pump?
27
New cards
1. The diffusion of Na+ ions into the cell is facilitated by the Na+ concentration gradient across the plasma membrane.
2. The diffusion of K+ ions out of the cell is impeded by the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane.
3. The electrochemical gradient is larger for Na+ than for K+.
**What are the driving forces for diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions through their respective channels?**
28
New cards
1. Secretes large molecules out of the cell.
2. Increases the surface area of the plasma membrane.
3. Requires fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane.
What describes **Exocytosis**?
29
New cards
1. Forms vesicles from inward folding of the plasma membrane.
2. Decreases the surface area of the plasma membrane.
What describes **Endocytosis**?
30
New cards
1. Transported substances never physically cross the plasma membrane.
2. Requires cellular energy.
How are **Exocytosis** and **Endocytosis** similar?
31
New cards
Water flows into the cell to the same extent that it flows out of the cell.
What happens in an **isotonic** solution?
32
New cards
Water flows into the cell, which causes it to swell and potentially burst (lyse).
What happens in a **hypotonic** solution?
33
New cards
Water flows out of the cell, which causes it to shrink.
What happens in a **hypertonic** solution?
34
New cards
True
With the Sodium potassium, the sodium and potassium ions are transported against their concentration gradients.
True or False?
True or False?
35
New cards
into ... membranous vesicles
**Endocytosis** moves materials _____ a cell via _____.
36
New cards
The cell is engulfing extracellular fluid.
You can recognize the process of **pinocytosis** when _____.
37
New cards
Phagocytosis
A white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is an example of _____.
38
New cards
The cell engulfs a large particle.
What happens in **phagocytosis**?
39
New cards
“Cell Drinking”
**Pinocytosis** is also known as what?
40
New cards
Inward
What does the prefix “endo” mean?
41
New cards
Dehydration
What is another name for a condensation reaction?
42
New cards
Hydrolysis
What is the name of the process during which a bond between two monomers is broken?
43
New cards
Amino Acid
Protein polymers are made up of **_______________** monomers.
44
New cards
Nucleotide
Nucleic acid polymers are made up of **_____________** monomers.
45
New cards
Simple Sugar
Carbohydrate polymers are made up of **______________** monomers.
46
New cards
Structural
Arrow A is indicating a(n) _____ protein.
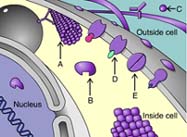
47
New cards
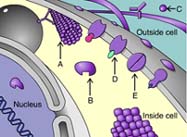
Receptor
Arrow D is indicating a _____ protein.
48
New cards
Ovalbumin
Which of these does NOT contain a structural protein?
a) Ligaments
b) Ovalbumin
c) Spider Silk
d) Muscles
e) Tendons
a) Ligaments
b) Ovalbumin
c) Spider Silk
d) Muscles
e) Tendons
49
New cards
Immune
Defensive proteins are manufactured by the _____ system.
50
New cards
Amino Acids
Proteins are polymers of _____.
51
New cards
Peptide
What type of bond joins the monomers in a protein's primary structure?
52
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
The secondary structure of a protein results from _____.
53
New cards
Peptide Bonds
Tertiary structure is NOT directly dependent on _____.
54
New cards
Tertiary
____________ structure is achieved when a protein folds into a compact, three-dimensional shape stabilized by interactions between side-chain R groups of amino acids.
55
New cards
Quaternary
________________ structure is the result of two or more protein subunits assembling to form a larger, biologically active protein complex.
56
New cards
Secondary
______________ structure describes the alpha-helices and beta-sheets that are formed by hydrogen bonding between backbone atoms located near each other in the polypeptide chain.
57
New cards
Primary
___________ structure is the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
58
New cards
True
The primary structure of a protein is the order of amino acids in a polypeptide, as coded for in the DNA of a gene.
True or False?
True or False?
59
New cards
The new amino acid would not form the same interactions with hydrophobic R groups, and the protein's shape would likely be affected.
What could happen if a mutation in a gene caused a hydrophobic amino acid in a polypeptide to be replaced by a hydrophilic amino acid?
60
New cards
Alzheimer’s is a neurological disease with loss of memory and motor skills.
What statement best describes Alzheimer’s disease?
61
New cards
True
There is a correlation between beta-amyloid plaques and the severity of Alzheimer’s disease.
True or False?
True or False?
62
New cards
Region C
Look at the graph of reaction rate versus substrate concentration for an enzyme.
In which region does the reaction rate remain constant?
In which region does the reaction rate remain constant?
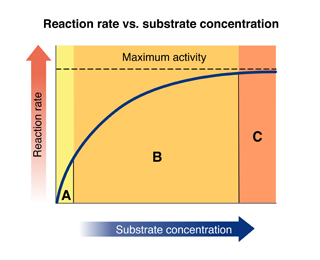
63
New cards
Region C
Refer again to the graph.
In which region is the enzyme saturated with substrate?
In which region is the enzyme saturated with substrate?
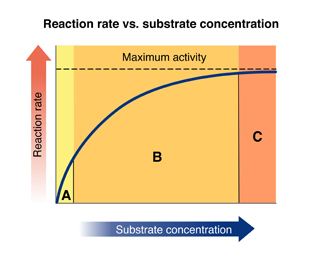
64
New cards
Increase the substrate concentration.
Consider a situation in which the enzyme is operating at optimum temperature and pHpH, and has been saturated with substrate. What is your best option for increasing the rate of the reaction?
65
New cards
Competitive
A _______________ inhibitor has a structure that is so similar to the substrate that it can bond to the enzyme just like the substrate.
66
New cards
Non-Competitive
A _________________ inhibitor binds to a site on the enzyme that is not the active site.
67
New cards
Irreversible
Usually a(n) ________________ inhibitor forms a covalent bond with an amino acid side group within the active site, which prevents the substrate from entering the active site or prevents catalytic activity.
68
New cards
Active Site
The competitive inhibitor competes with the substrate for the **______________** on the enzyme.
69
New cards
Shape
When the noncompetitive inhibitor is bonded to the enzyme, the ___________ of the **enzyme** is distorted.
70
New cards
Substrate
Enzyme inhibitors disrupt normal interactions between an enzyme and its **___________.**
71
New cards
The enzyme is inactive at this point. New enzyme must be added to regain enzyme activity.
You have added an irreversible inhibitor to a sample of enzyme and substrate. At this point, the reaction has stopped completely.
**What can you do to regain the activity of the enzyme?**
**What can you do to regain the activity of the enzyme?**
72
New cards
Add more substrate; it will outcompete the inhibitor and increase the reaction rate.
You have an enzymatic reaction proceeding at the optimum pH and optimum temperature. You add a competitive inhibitor to the reaction and notice that the reaction slows down.
**What can you do to speed the reaction up again?**
**What can you do to speed the reaction up again?**
73
New cards
Denatured
An enzyme is **_____________** when it loses its native conformation and its biological activity.
74
New cards
Catalyst
An enzyme is considered a **__________** because it speeds up chemical reactions without being used up.
75
New cards
Specific
An enzyme is considered **__________** because of its ability to recognize the shape of a particular molecule.
76
New cards
Cofactor
A **___________**, such as a vitamin, binds to an enzyme and plays a role in catalysis.
77
New cards
Complex
When properly aligned, the enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate (ES) **___________.**
78
New cards
Active Site
A substrate binds to an enzyme at the **______________**, where the reaction occurs.
79
New cards
Substrate
In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called a **___________.**
80
New cards
A similar shape exists between a pocket on the surface of the enzyme and a functional group on the substrate.
What would *unlikely* to contribute to the substrate specificity of an enzyme?
81
New cards
increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Enzymes are described as catalysts, which means that they __________.
82
New cards
The compound is a competitive inhibitor.
The binding of a compound to an enzyme is observed to slow down or stop the rate of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. Increasing the substrate concentration reduces the inhibitory effects of this compound. What could account for this observation?
83
New cards
Plasma Membrane
What cell structure allows selective permeability between a cell and its external environment?
84
New cards
True
Phospholipids form a selectively permeable structure.
True or False?
True or False?
85
New cards
True
The fluid aspect of the membrane is due to the lateral and rotational movement of phospholipids, and embedded proteins account for the mosaic aspect.
True or False?
True or False?
86
New cards
Wedged between phospholipid molecules in the interior of the membrane
Under the fluid mosaic model, where in the plasma membrane would cholesterol most likely be found?
87
New cards
Energy, carbon, and nitrogen storage
What functional process is not a consequence of the association of proteins with biological membranes?
88
New cards
True
Membrane carbohydrates function primarily in cell-cell recognition. True or False?
89
New cards
On the outside (external) surface of the membrane
Where in the fluid mosaic model of the membrane would **carbohydrates** be found?
90
New cards
Carbon Dioxide
\
__Explanation:__ Hydrophobic molecules, such as hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, and oxygen, can dissolve in the membrane and cross it with ease.
\
__Explanation:__ Hydrophobic molecules, such as hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, and oxygen, can dissolve in the membrane and cross it with ease.
Which molecule is most likely to passively diffuse across the plasma membrane?
a) Carbon Dioxide
b) Hemoglobin
c) Glucose
d) DNA
e) Sodium Ion
a) Carbon Dioxide
b) Hemoglobin
c) Glucose
d) DNA
e) Sodium Ion
91
New cards
A large polar molecule
Which would be least likely to diffuse through a plasma membrane without the help of a transport protein?
a) Dissolved gases such as oxygen or carbon dioxide
b) A large polar molecule
c) A large nonpolar molecule
d) A small nonpolar molecule
e) All choices are correct
a) Dissolved gases such as oxygen or carbon dioxide
b) A large polar molecule
c) A large nonpolar molecule
d) A small nonpolar molecule
e) All choices are correct
92
New cards
Proteins embedded in two layers of phospholipid
\
__Explanation:__ With the proteins embedded within two layers of phospholipids, the cell retains its general restriction on the unregulated movement of polar molecules across the membrane, and the proteins provide for selective transport functions.
\
__Explanation:__ With the proteins embedded within two layers of phospholipids, the cell retains its general restriction on the unregulated movement of polar molecules across the membrane, and the proteins provide for selective transport functions.
What structural arrangement of the components in biological membranes is most consistent with membrane’s property of selective permeability?
93
New cards
True
Passive transport permits the solute to move in either direction, but the net movement of the population of solute occurs down the concentration gradient of the molecule.
True or False?
True or False?
94
New cards
B … the diffusion gradient in cell B is steeper.
\
__Explanation:__ As long as a metabolically active cell converts oxygen to water during cellular respiration shortly after it enters, diffusion into the cell will continue because the concentration gradient favors movement in that direction.
\
__Explanation:__ As long as a metabolically active cell converts oxygen to water during cellular respiration shortly after it enters, diffusion into the cell will continue because the concentration gradient favors movement in that direction.
Cells A and B are the same size, shape, and temperature, but cell A is metabolically less active than cell B; cell B is actively converting oxygen to water in cellular respiration. Oxygen will diffuse more rapidly into cell __________ because __________.
95
New cards
True
Diffusion is a passive process of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment.
True or False?
True or False?
96
New cards
1\.0 M
\
__Explanation:__ This is hypertonic to the plant cell. Water will leave the cell, and eventually the plasma membrane will pull away from the cell wall, resulting in plasmolysis.
\
__Explanation:__ This is hypertonic to the plant cell. Water will leave the cell, and eventually the plasma membrane will pull away from the cell wall, resulting in plasmolysis.
The internal solute concentration of a plant cell is about 0.8 *M*. To demonstrate plasmolysis, it would be necessary to suspend the cell in what total concentration of solutes?
97
New cards
Water would leave the cell by osmosis, causing the volume of the cytoplasm to decrease.
\
__Explanation:__ The added salt makes the solution hypertonic compared to the cell. Water will leave the cell by osmosis.
\
__Explanation:__ The added salt makes the solution hypertonic compared to the cell. Water will leave the cell by osmosis.
A single plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution. Salt is then added to the solution. Which would occur fairly quickly as a result of that addition?
98
New cards
Facilitated diffusion of solutes may occur through channel or transport proteins in the membrane.
What describes some aspect of facilitated diffusion?
99
New cards
False
\
__Explanation:__ Facilitated diffusion, like passive diffusion, needs only a concentration gradient--no energy input is required.
\
__Explanation:__ Facilitated diffusion, like passive diffusion, needs only a concentration gradient--no energy input is required.
Facilitated diffusion requires the hydrolysis of ATP.
True or False?
True or False?
100
New cards
A hypertonic sucrose solution
\
__Explanation:__ When a cell is placed in a hypertonic environment, water will leave the cell, causing it to shrink.
\
__Explanation:__ When a cell is placed in a hypertonic environment, water will leave the cell, causing it to shrink.
The red blood cell contain about 2% solutes but almost no sucrose or urea. Sucrose cannot pass through the membrane, but water and urea can. Osmosis would cause red blood cells to shrink most when immersed in what type of solution?