BCM. 31 Dark Reactions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms

does not fix carbon - it converts the 6 oxidised carbons of 2 pyruvate to the 6 reduced carbons of 1 glucose
conversion of glucose-P to glucose is performed by another phosphatase (this is important if glucose itself needs to be made
3 if you include hexokinase - but glucose phosphate is really the ‘start’ point for glycolysis - it is glucose-P that is polymerised into polysaccharides, it is glucose-P that is the product of the Calvin cycle, it is glucose-P that is produced by the breakdown of storage carbohydrates e.g. glycogen and starch
the main sinks for fixed carbon in plants are cellulose and starch - these do consume additional ATP in their manufacture
cellulose synthase in plant cell membranes catalyses the addition of UDP glucose to cellulose, giving UDP and cellulosen+1
The UDP-glucose is made by reacting glucose-P with UTP, with release of PPi (which is then immediately hydrolysed) and UDP (which is regenerated to UTP using ATP). A very similar set of reactions is needed to make starch or glycogen, with the same overall energetics.
The overall reaction for all of these glucans is the sum of these four reactions
Glc-P + UTP => UDP-Glc + PPi
PPi => 2 Pi
UDP-Glc + glucann => glucann+1 + UDP
UDP + ATP => UTP + ADP
====================
Glc-P + ATP + glucann => glucann+1 + ADP + 2Pi
====================
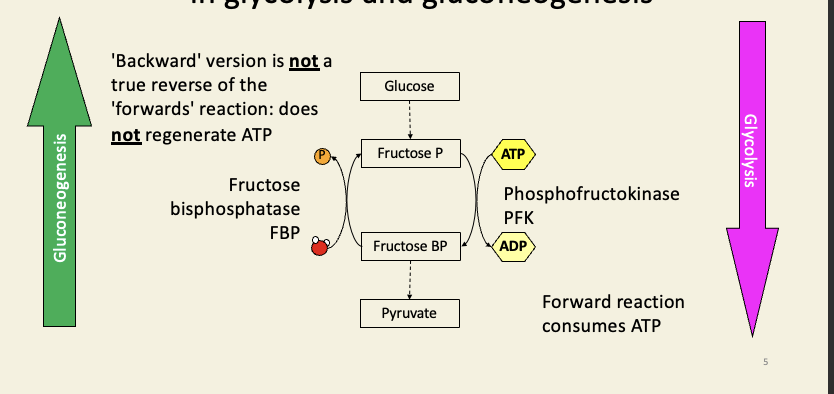
PFK and FBP catalyse different reactions in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
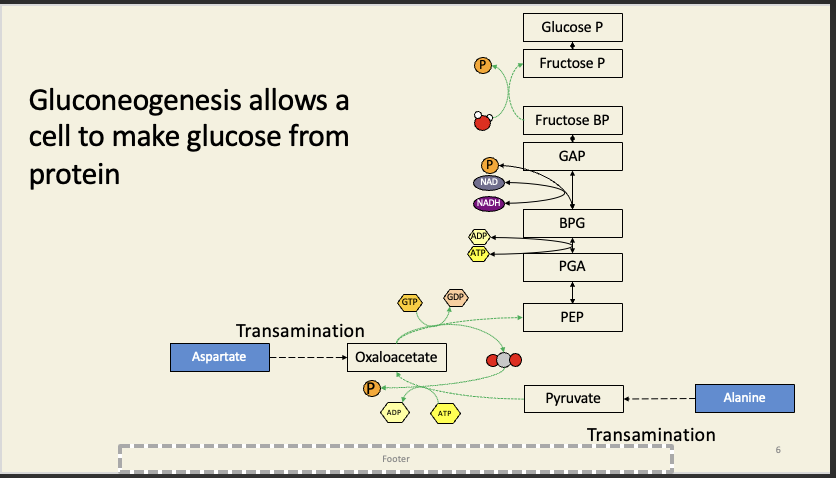
But not lipids. If you feed lipids into Krebs, they go in before the two decarboxylation steps, so the two carbons you add are released as CO2, which means there's no 'profit' and hence no net flow of carbon out of Krebs to gluconeogenesis.
Some lipids can feed in via succinyl CoA (after the decarboxylation steps), but whether this is physiologically important is still contentious.
Plants can use a short-cut through the cycle (the glyoxylate cycle) to convert lipids to glucose: this is done in specialised peroxisomes called glyoxysomes, which are found in seedlings, which use stored fats to make glucose for cell wall synthesis.
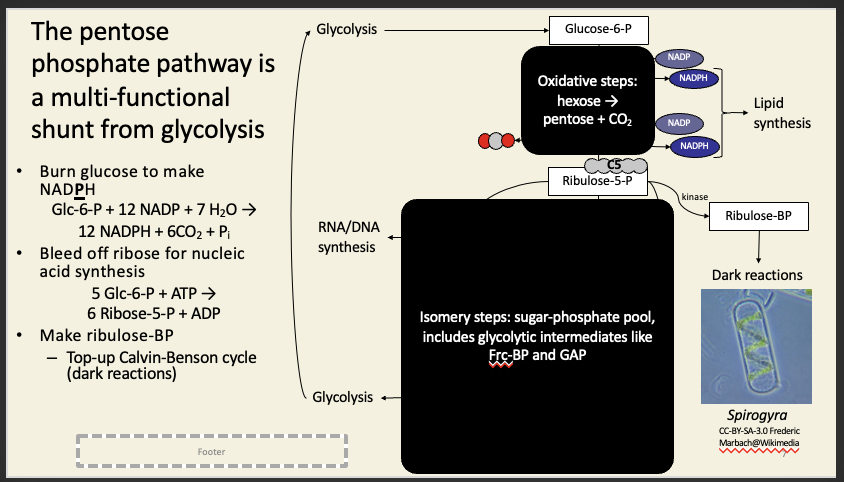
The oxidative steps of PPP produces NADPH and CO2. This is a critical link between hexose and pentose metabolisms, and NADPH can be used for e.g. lipid synthesis.
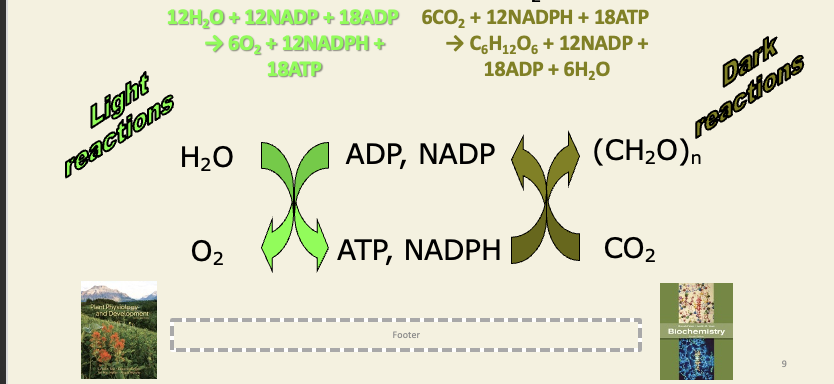
Dark reactions consume NADPH and ATP from light reactions to fix C02

2D chromatography achieves better separation by using two solvents
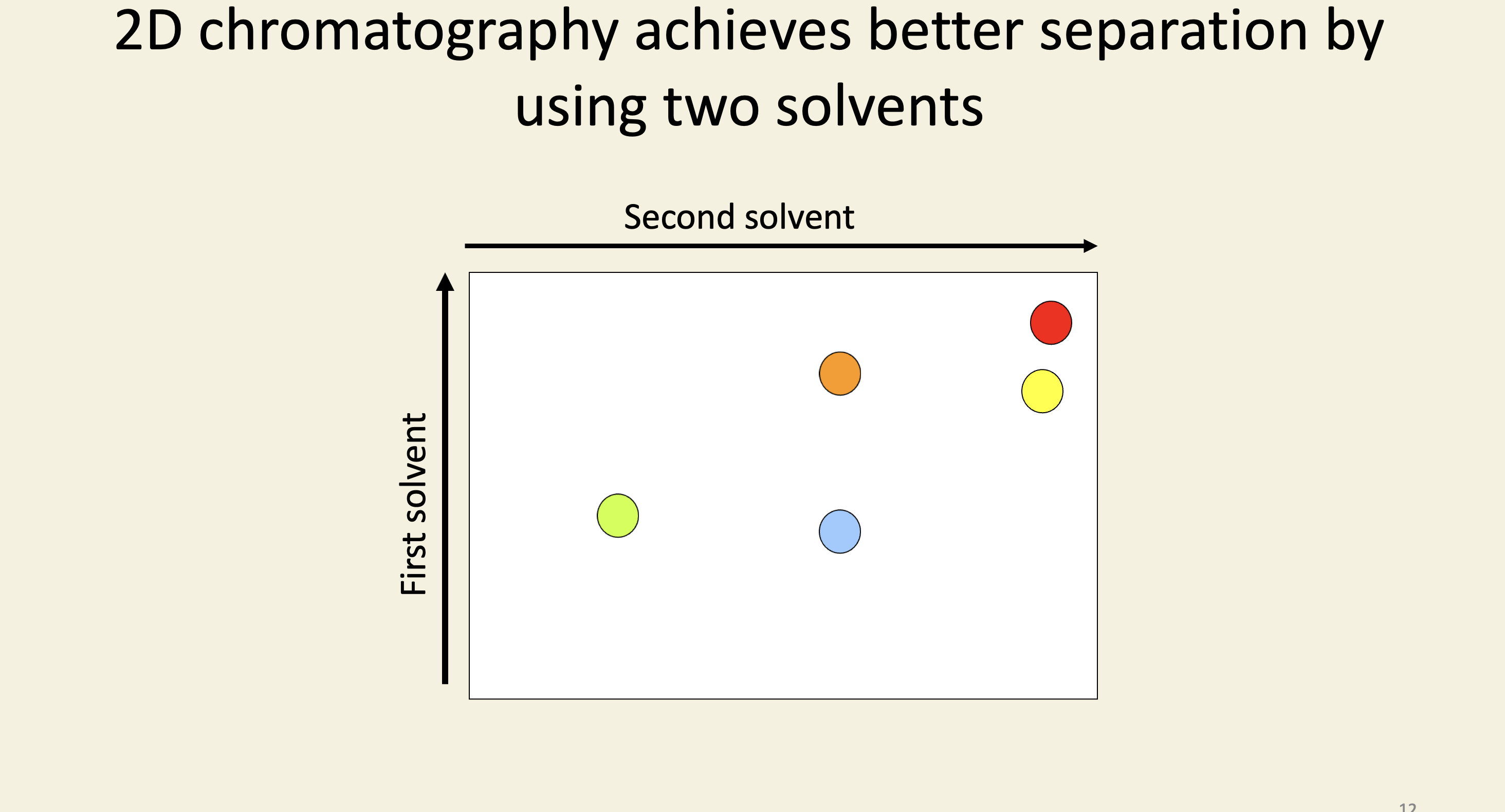
Photosynthetic products were detected by autoradiography of the chromatograms

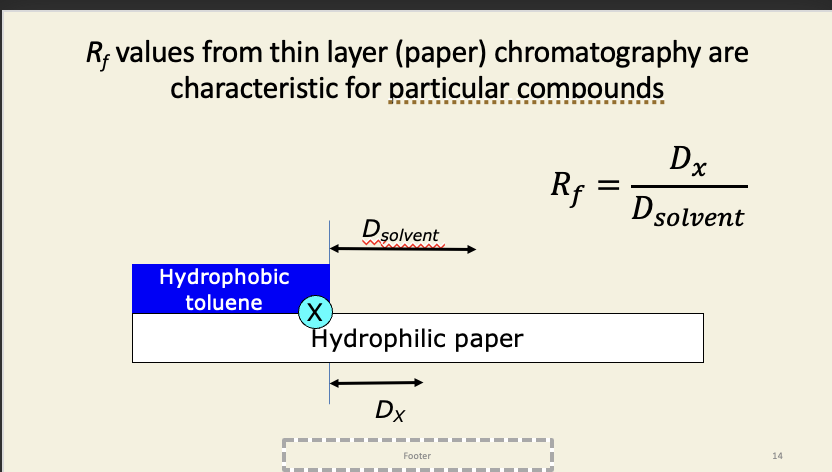
Spots were eluted from the paper and identified
After 5 s of photosynthesis, 90% of radioactivity was in COOH of PGA
After 30 s, the other two carbons also became labelled → acceptor molecule regenerated from its products
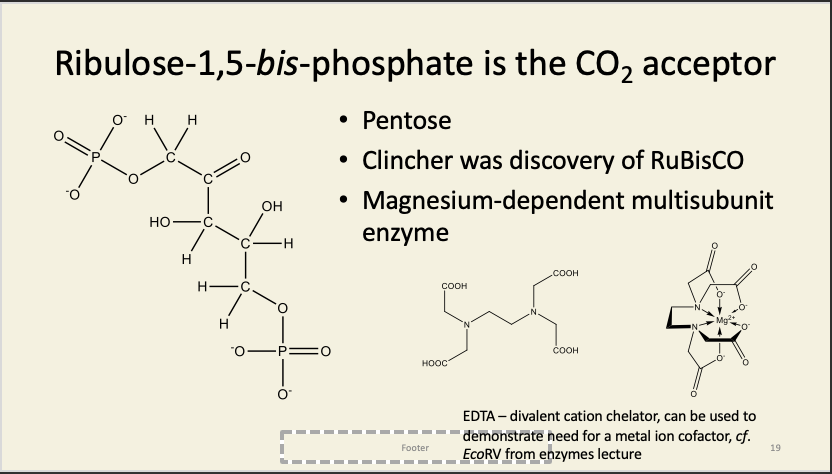
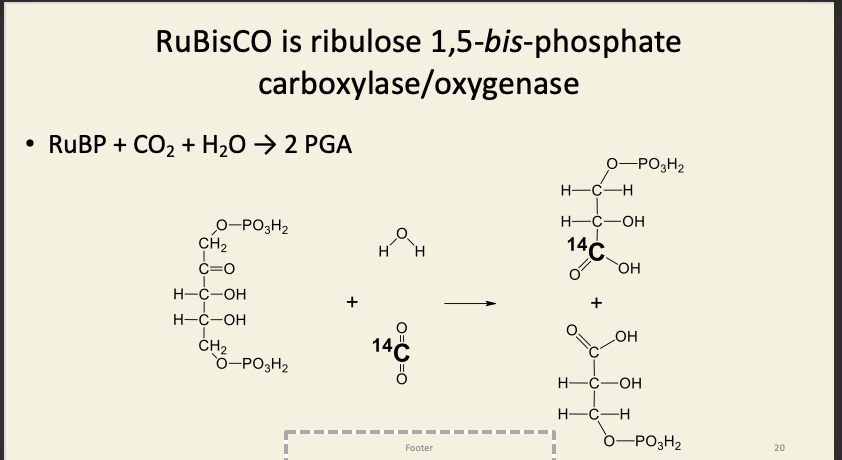
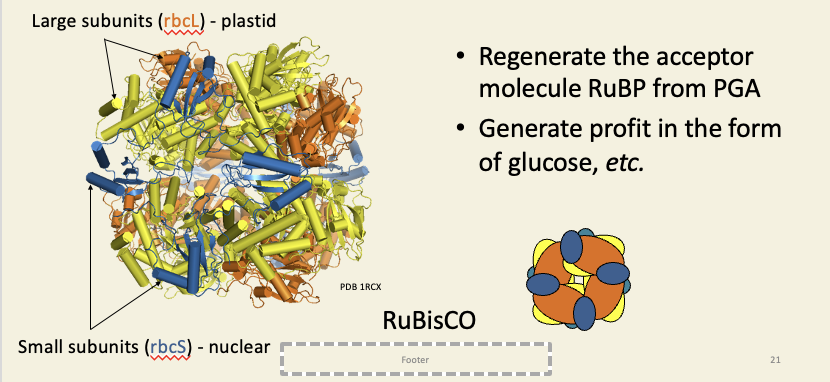
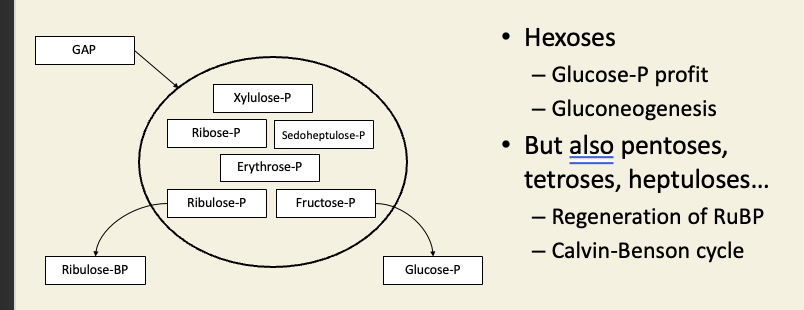
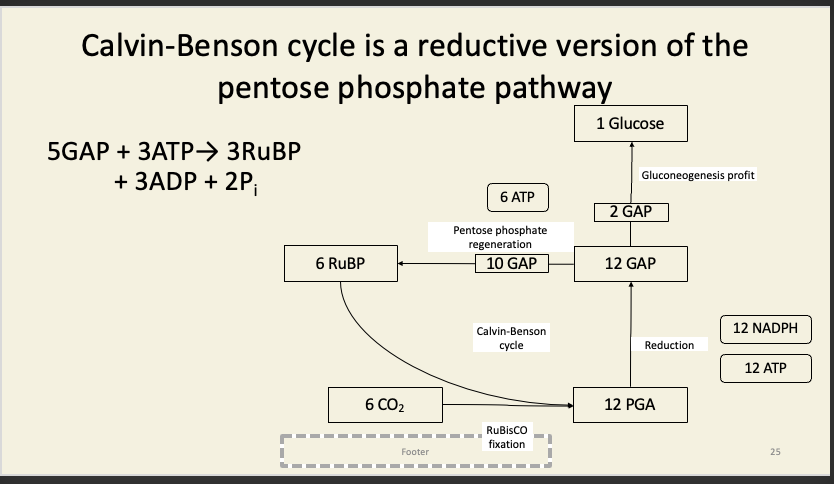
Rest of the dark reactions have two purposes

PGA is phosphorylated by ATP and reduced by NADPH to GAP

Last things to appear in pulse-chase were sugar phosphates

Photoinhibition is light-induced damaged to the D1 subunit of PSI.
It is caused by backing-up of electrons in the PQH2 pool, preventing electrons from leaving PS2 – these then causes oxidative damage to the rest of the subunit.
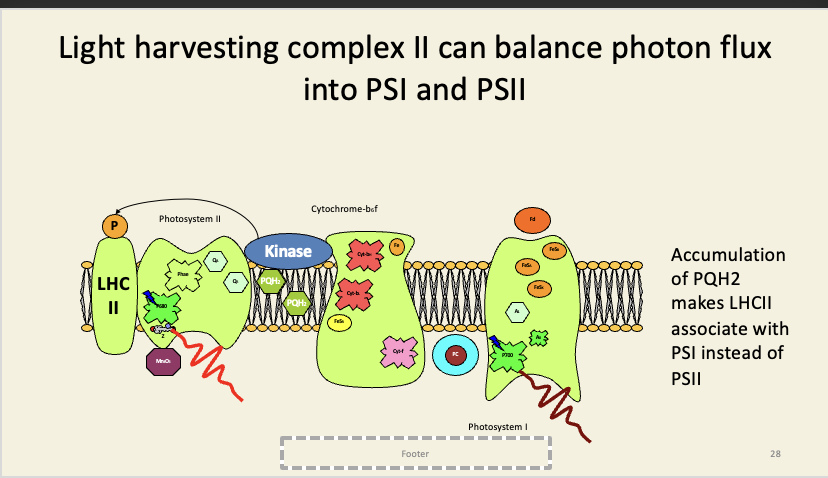
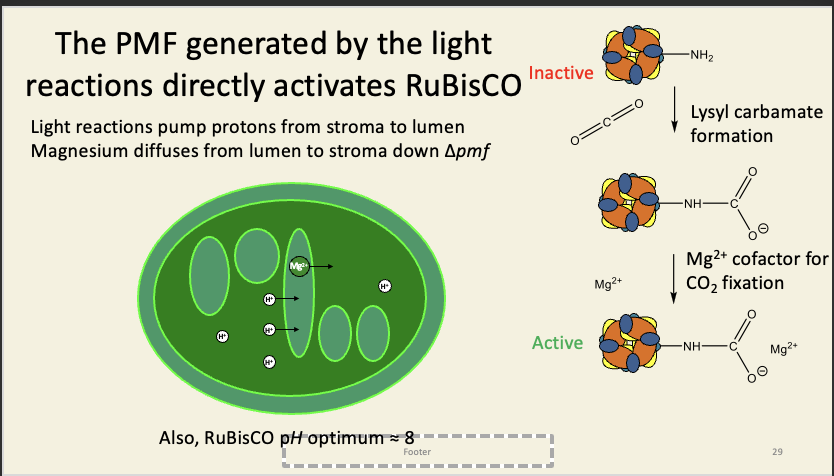

The sugar-phosphates (which actually include RuBP itself!) binds the same lysine that the magnesiums bind to, i.e. the sugar-phosphates compete with the activating Mg2+.