Quiz- 3.2 ( Heart Sounds and Blood Analysis)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Which Biopac measurement would allow you to measure the amplitude (loudness) of a heart sound?
P-P
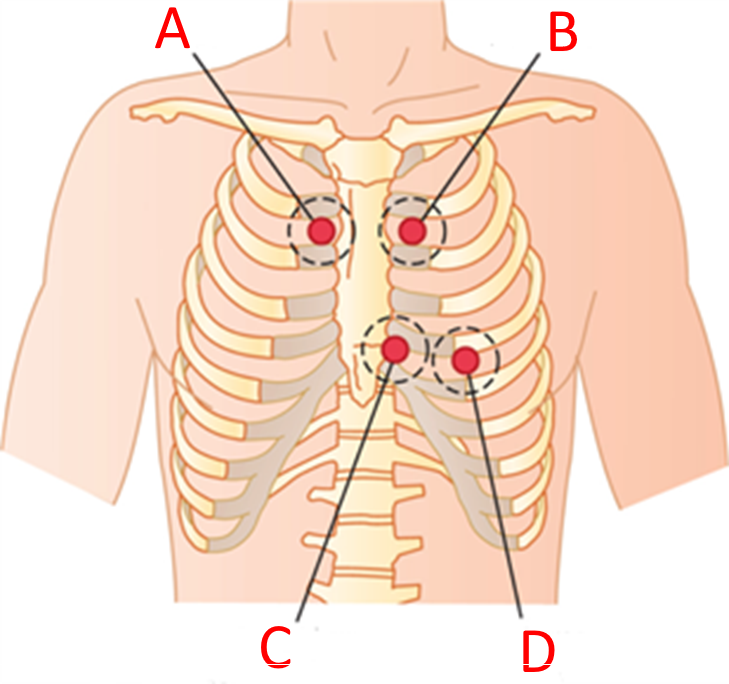
At which of the following locations would you listen if you suspected your patient had tricuspid valve stenosis?
C
Which time interval most closely corresponds to ventricular systole?
S1 --> S2 (the time between the first heart sound and the second heart sound
Which time intervals decrease significantly when a person is engaged in strenuous physical activity?
S2 --> S1 (the time between the second heart sound of one cardiac cycle and the first heart sound of the next cardiac cycle)
R --> R (the time between the peak of the R-wave of one cardiac cycle and the peak of the R-wave of the next cardiac cycle)
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may be elevated (increased) in all of the following conditions except:
angina pectoris (chest pain without heart attack)
Which of the following statements about erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is false?
To measure ESR, Ca2+ must be added to the blood so that it will clot in the narrow sedimentation tubes.
What is the term for the condition in which a heart valve thickens and the heart works to push blood through a smaller than normal space?
stenosis
In some cases, when the baroreceptor reflex is triggered by decreased blood pressure, it can also cause increased ventilation (i.e. more rapid and / or deeper breaths). What are some possible advantages of increased ventilation when blood pressure is low?
The amount of oxygen in the blood could be increased and the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood could be decreased.
The respiratory pump will help return blood to the heart more rapidly.
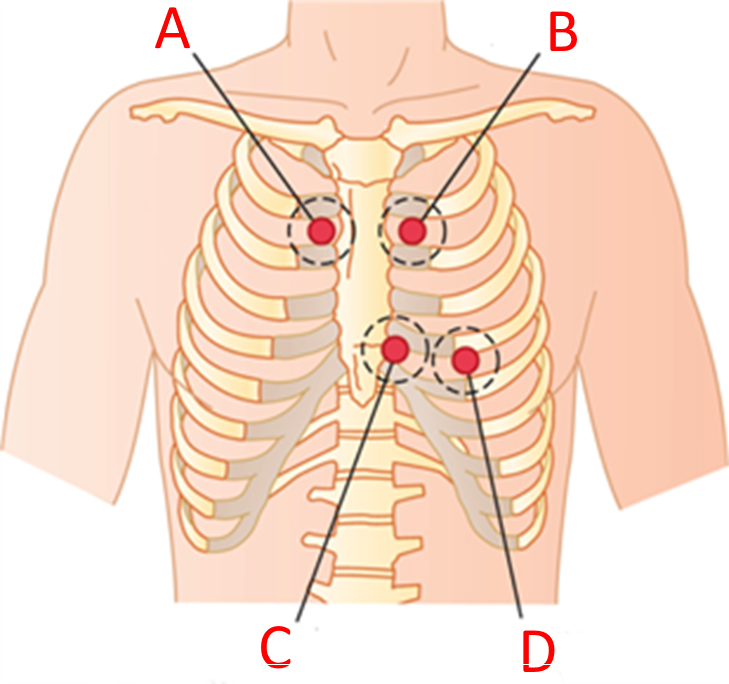
Assume you place the bell of your stethoscope at location A and hear the sound of the turbulent blood flow between "dub" of one heartbeat and the "lub" of the next heartbeat (i.e. you hear turbulent blood flow between S2 and S1 of the next cardiac cycle ).
What valve defect is mostly like to have caused this heart murmur?
aortic valve insufficency
Starting just before a person exhales, select the correct order of events that occur as "respiratory pump" helps move blood back to the heart through the abdominal cavity against gravity:
1. When a person exhales, the abdominal cavity expands and the thoracic cavity is compressed
2. Blood pressure in the IVC ( in the abdominal cavity) is decreased
3. Blood flows (past valves) from the lower limbs pelvic cavity into IVC in the abdominal cavity.
4. When a person inhales, the thoracic cavity expands and the abdominal cavity is compressed.
5. Blood pressure in the IVC v (in the abdominal cavity) is increased.
6. Blood flows (past valves) from the IVC in the abdominal cavity into the right atrium.