Human Anatomy - Chapter 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
1
New cards
What is tissue?
a group of cells that have a common embryonic origin and function together to carry out specialized activities
2
New cards
What is histology?
the study of tissues
3
New cards
What are the four basic types of tissues?
epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous
4
New cards
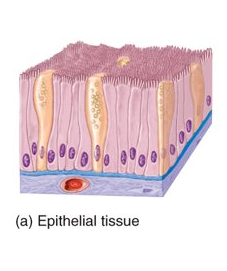
What is epithelial tissue?
covers body surfaces, lines hollow organs, body cavities and ducts, forms glands
5
New cards
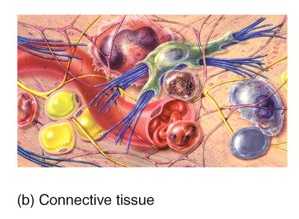
What is connective tissue?
protects and supports the body and its organs, binds organs together, stores energy reserved as fat, provides immunity
6
New cards
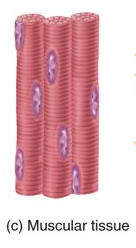
What is muscle tissue?
responsible for movement and generation of force
7
New cards
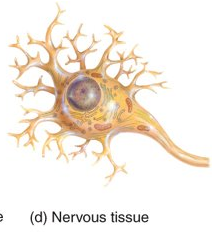
What is nervous tissue?
initiates and transmits action potentials that help coordinate body activities
8
New cards
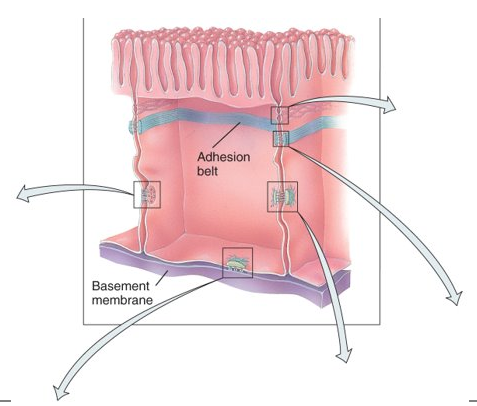
What is a cell junction and what do they do?
point of contact between adjacent plasma membrane: form fluid-tight seals between cells, anchor cells together or to extracellular material, or act as channels which allow ions and molecules to pass from cell to cell within a tissue
9
New cards
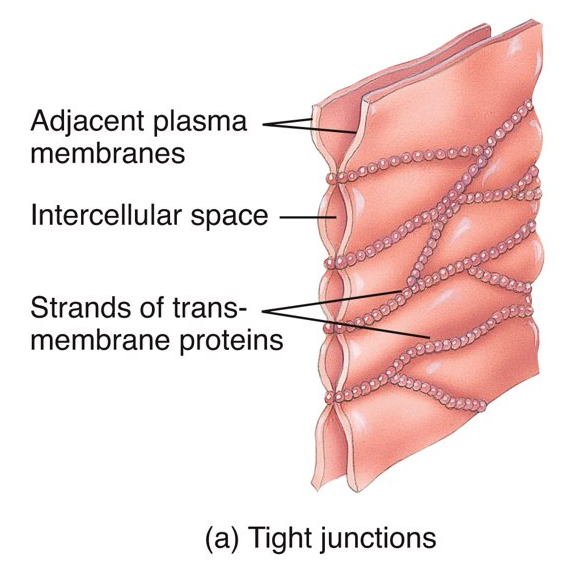
What is a tight junction, where can you find it, and what does it do?
transmembrane proteins fuse together adjacent cells; located in epithelial tissue in the stomach, intestines, and urinary bladder; inhibits the passage of substances between cells
10
New cards
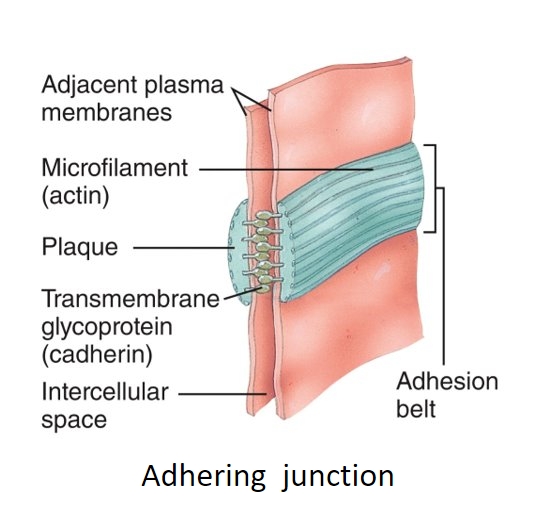
What is an adhering junction, where can you find it, and what does it do?
a dense layer of proteins (plaque); epithelial tissue; anchor cells together (help epithelial surfaces resist separation during various contractile activities)
11
New cards
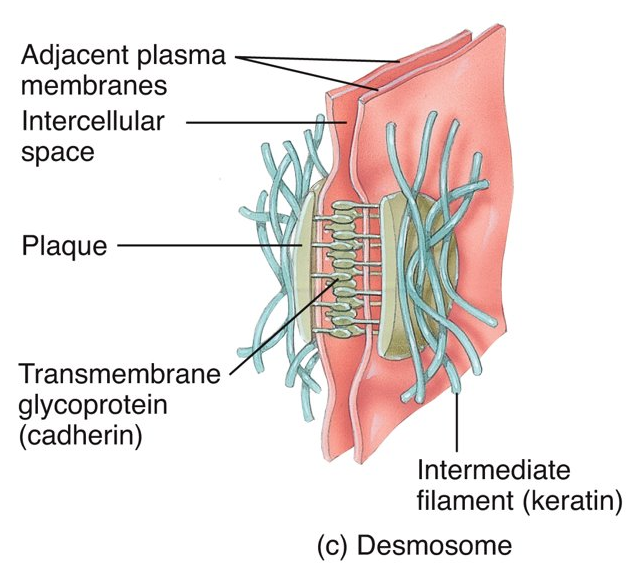
What is a desmosome, where can you find it, and what does it do?
plaque and have transmembrane glycoproteins (cadherins); epidermal cells and cardiac muscle; contributes to stability of cells and tissue (prevent epidermal cells from separating under tension and cardiac muscle cells from pulling apart during contraction)
12
New cards
What is a hemidesmosome, where can you find it, and what does it do?
same as desmosomes however it anchors cells to the basement membrane
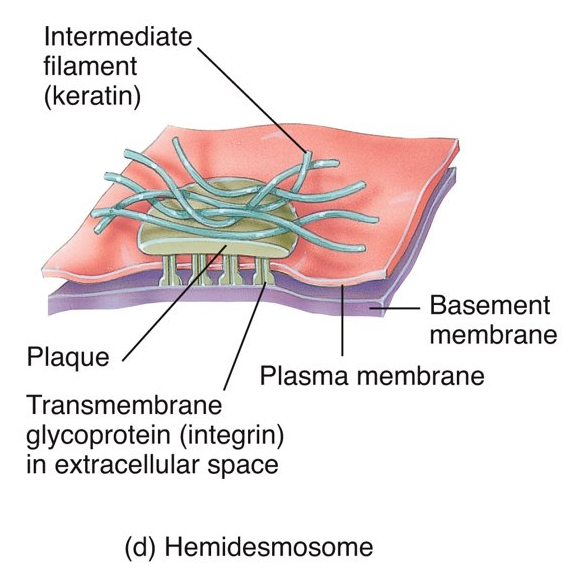
13
New cards
What is a gap junction, where can you find it, and what does it do?
connexins (transmembrane protein channels); anywhere that requires large area nervous control; enable nerve or muscle impulses to spread rapidly among cells
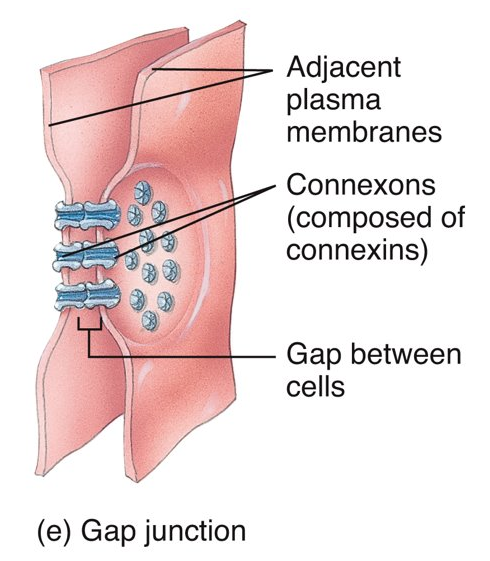
14
New cards
What is the major structural differences between epithelial and connective tissue?
epithelial tissue:
many cells are tightly packed together with little or no extracellular matrix
epithelial tissue has no blood vessels
almost always form surface layers and are not covered by another tissue
connective tissue:
a large amount of extracellular material separates cells
have significant networks of blood vessels
many cells are tightly packed together with little or no extracellular matrix
epithelial tissue has no blood vessels
almost always form surface layers and are not covered by another tissue
connective tissue:
a large amount of extracellular material separates cells
have significant networks of blood vessels
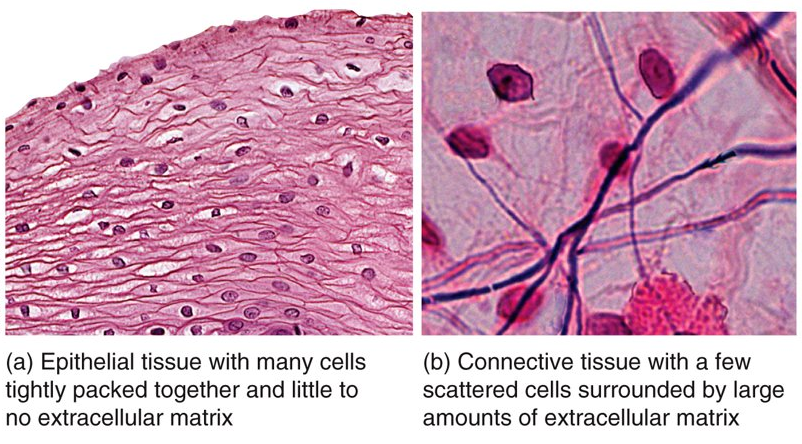
15
New cards
What is the difference between epithelial and epidermis?
epithelial:
one or more layers of cells which forms the covering of most internal and external surfaces of the body.
epidermis:
top layer of skin
one or more layers of cells which forms the covering of most internal and external surfaces of the body.
epidermis:
top layer of skin
16
New cards
What some features of epithelial tissue?
cells arranged in densely packed sheets, many cell junctions, avascular, attaches to basement membrane, apical surface, mitosis
17
New cards
What is the basement membrane?
a thin, two-layered membrane consisting of the basal lamina (closer to epithelial) and reticular lamina (closer to underlying connective)
18
New cards
What are the four types of shapes of epithelial tissue?
squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube-like), columnar (rectangular), and transitional (variable)
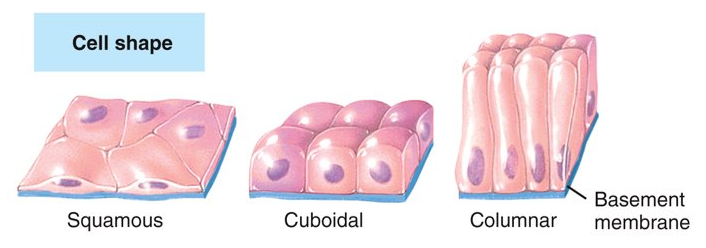
19
New cards
What is simple squamous?
single layer of flat, scale-like cells; best for diffusion and filtration (lungs and kidneys), found in parts that are subject to little wear and tear (endothelium lines the heart and blood vessels, mesothelium lines the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities)
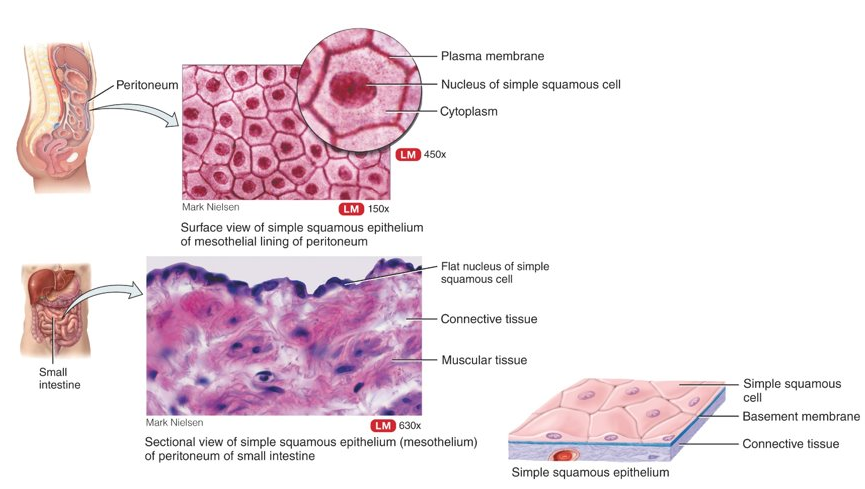
20
New cards
What is simple cuboidal?
single layer of cube cells; performs the functions of secretion and absorption in ovaries, kidney tubules, and thyroid
21
New cards
What is simple columnar?
single layer of rectangular cells; non-ciliated: contain microvilli to increase surface area and rate of absorption in GI tract, ciliated: help move fluids or particles along a surface in bronchioles and fallopian tubes
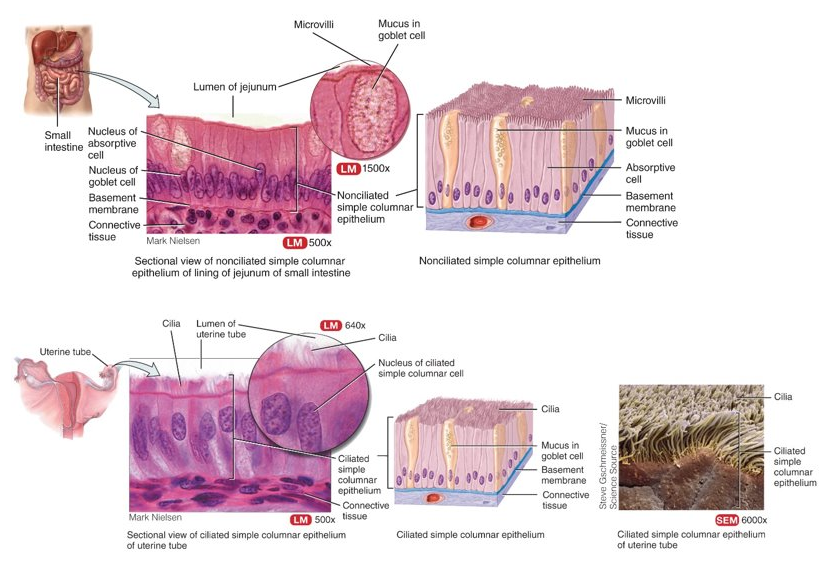
22
New cards
What is pseudostratified columnar?
one layer but gives the appearance of many; all cells attached to basement membrane but some don't reach apical surface, non-ciliated: male urethra and epididymis, ciliated: upper respiratory tract
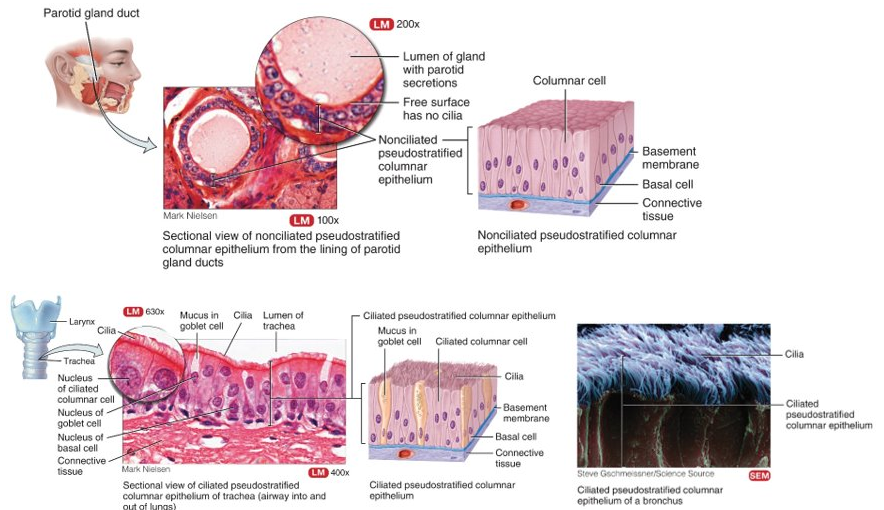
23
New cards
What is stratified squamous?
top layer of cells is flat, deeper layer of cells vary in shape from cuboidal to columnar; non-keratinized: mouth and esophagus, keratinized (very water-resistant protein): superficial layer of skin
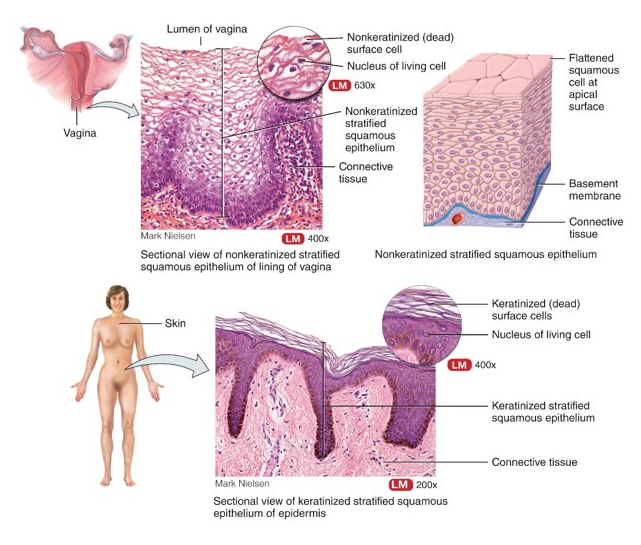
24
New cards
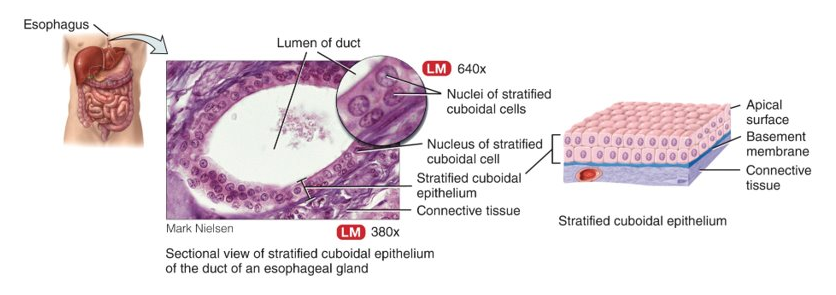
What is stratified cubodial?
two or more layers of cuboidal cells; makes things, adult sweat glands
25
New cards
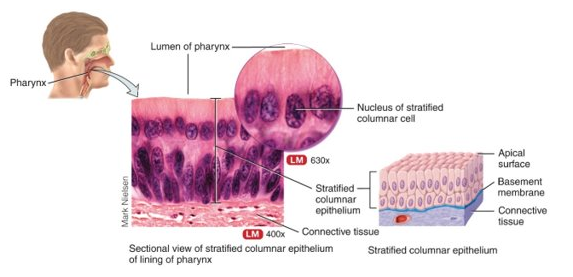
What is stratified columnar?
only top layer is columnar; conjunctiva of eye, part of urethra
26
New cards
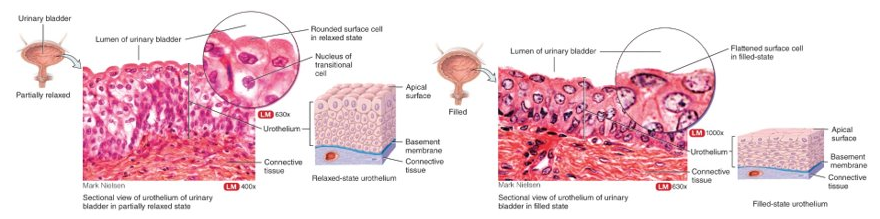
What is transitional or urothelium?
several layers of cells that all vary in shape; capable of stretching and permits distention of an organ, lines most of urinary tract
27
New cards
What is a gland?
a single cell or mass of epithelial cells adapted for secretion
28
New cards
What is an endocrine gland, location, and function?
ductless; secretory product (hormones) enter the extracellular fluid and diffuse into the blood; pituitary glands in brain, pineal gland in brain, thyroid, etc.; regulate many metabolic and physiological activities
29
New cards
What is an exocrine gland, location, and function?
secrete products into ducts that empty at the surface of covering and lining epithelium or directly onto a free surface (skin or lumen of stomach); sweat, oil, digestive gland; produce substances such as sweat to help lower body temp, oil, earwax, saliva, or digestive enzymes
30
New cards
What is the most abundant tissue?
connective
31
New cards
What are the two basic elements of connective tissue?
cells and extracellular matrix
32
New cards
What are some general features of connective?
does not occur on free surfaces, is highly vascularized, and has nerve supply (except tendons and cartilage)
33
New cards
What is a fibroblast?
secretes fibres and ground substance
34
New cards
What is a macrophage?
develop from monocytes and are phagocytic
35
New cards
What is a plasmocyte?
develop into B lymphocytes/B cells

36
New cards
What is a mast cell?
produce histamine
37
New cards
What is a adipocyte?
store energy in the form of fat
38
New cards
What is a leukocyte?
white blood cell
39
New cards
What is extracellular matrix?
fibers and ground substance

40
New cards
What are collagen fibres?
collagen; very tough and resistant to stretch, allow some flexibility; found in bone, cartilage, tendons, and ligament

41
New cards
What are elastic fibres?
elastin; provide strength and stretch; found in skin, blood vessels, and lungs

42
New cards
What are reticular fibres?
collagen and glycoprotein; provide support in walls of blood vessels and form a strong, supporting network; fat cells, nerve fibres, and skeletal and smooth muscle fibres

43
New cards
What is loose connective?
fibres are loosely arranged between cells
44
New cards
What is dense connective?
fibres are thicker and more densely packed, but have fewer cells than loose connective tissue (tendon)
45
New cards
What is elastic connective?
strong and can recoil back to its original shape after being stretched
46
New cards
What is cartilage?
dense network of collagen fibers and elastic fibers firmly embedded in chondroitin sulfate
47
New cards
What is bone?
a matrix containing mineral salts and collagenous fibers and cells called osteocytes
48
New cards
What is blood?
has a liquid extracellular matrix called blood plasma and formed elements
49
New cards
What are the three types of cartilage?
hyaline, fibrous, and elastic
50
New cards
What is hyaline cartilage, location, and function?
resilient gel are ground substance, bluish-white, shiny, prominent chondrocytes in cartilage lacunae surrounded by perichondrium (except joints, growth plates, where bone lengthen); end of long bones, anterior end of ribs, nose, larynx, etc.; smooth surface for movement at joints, flexibility, and support
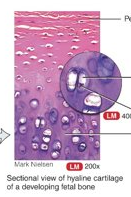
51
New cards
What is fibrous cartilage, location, and function?
chondrocytes among thick bundles of collagen fibres within extracellular matrix, no perichondrium; pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs, menisci, etc.; support and joining structures together
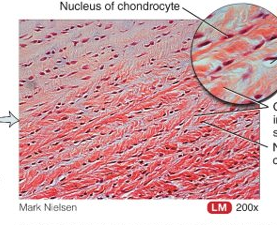
52
New cards
What is elastic cartilage, location, and function?
chondrocytes in a threadlike network of elastic fibres within extracellular matrix, perichondrium; epiglottis, auricle, eustachian; provides strength and elasticity, maintains shape
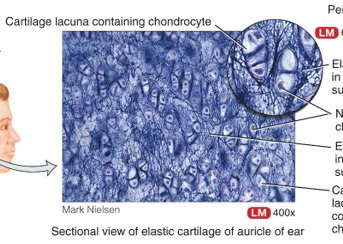
53
New cards
What is the most abundant cartilage?
hyaline
54
New cards
What is the weakest cartilage?
hyaline
55
New cards
What is the strongest cartilage?
fibrous
56
New cards
What is a membrane?
flat sheet of pliable tissue that covers or lines a part of the body
57
New cards
What are the two types of membranes?
epithelial and synovial
58
New cards
What are the three types of epithelial?
mucous, serous, and cutaneous
59
New cards
What is the mucous membrane?
lines cavities that open to the exterior (ex. GI tract); important aspect of the body’s defense mechanisms, acting as a barrier to pathogens; connective tissue layer called lamina propria
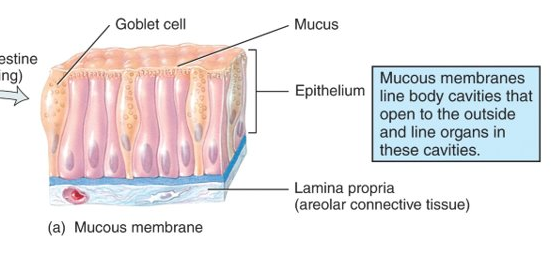
60
New cards
What is the serous membrane?
lines a body cavity that does not open directly to the exterior and covers the organs that lie within the cavity (ex. pleura); consist of parietal and visceral
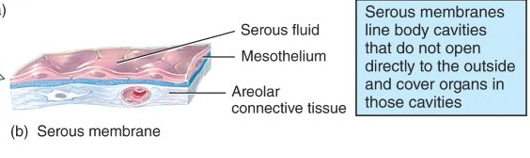
61
New cards
What is the cutaneous membrane?
cover the outside of the body (ex. skin); the epidermis consists of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and the dermis consists of areolar and dense irregular connective tissues
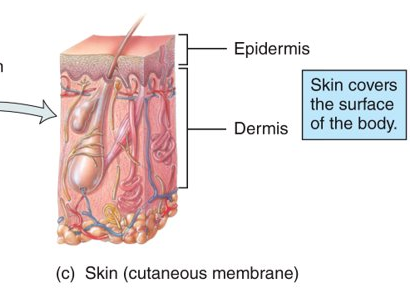
62
New cards
What is the synovial membrane?
line joint cavities, bursae, and tendon sheaths and do not contain epithelium, also secrete synovial fluid
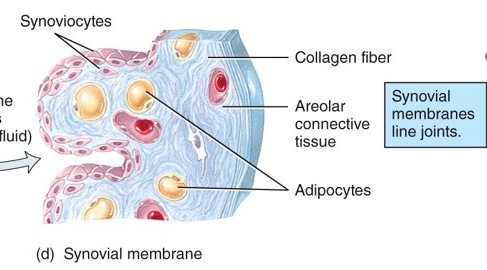
63
New cards
What is muscle tissue?
fibres that provide, motion, posture, and heat
64
New cards
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
65
New cards
What is skeletal muscle?
voluntary control; long, striated fibres
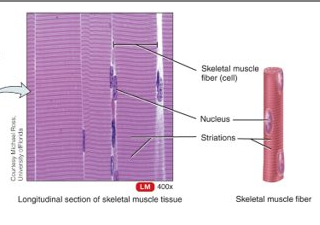
66
New cards
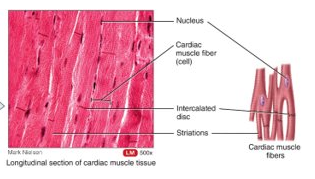
What is cardiac muscle?
involuntary control; branched, striated fibres
67
New cards
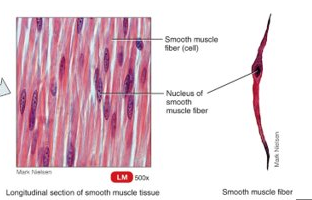
What is smooth muscle?
usually involuntary; non-striated fibres
68
New cards
What are the two types of cells in nervous tissue?
neurons and neuroglia
69
New cards
What do neurons consist of?
a cell body, dendrites, and axons
70
New cards
What is a neuron?
sensitive to stimuli, convert stimuli into nerve impulses, and conduct nerve impulses to other neurons, muscle fibers, or glands
71
New cards
What is a neuroglia?
protect and support neurons; sites of tumours of the nervous system
72
New cards
What are two types of excitable cells?
neurons and muscle fibres; respond to neurotransmitters
73
New cards
What is electrical excitability?
the ability to respond to certain stimuli by producing electrical signals which travel along the plasma membrane due to the presence of specific voltage-gated channels
74
New cards
How does each type of tissue respond to tissue repair?
epithelial: replaced by division of stem cells or undifferentiated cells
connective: bone has a continuous capacity to renewal while cartilage replenishes cells less readily
muscle: poor capacity for renewal
nervous: limited to no repair
connective: bone has a continuous capacity to renewal while cartilage replenishes cells less readily
muscle: poor capacity for renewal
nervous: limited to no repair
75
New cards
What is fibrosis?
process of scar formation
76
New cards
What is granulation tissue?
actively growing connective tissue formed over extensive injuries
77
New cards
How do disorders effect epithelial tissue?
specific to individual organs
78
New cards
How do disorders effect connective tissue?
autoimmune in nature