GENETICS EXAM 2
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the types of mutations generally
small scale and large scale
How many bases do small scale and large scale mutations affect
small = 1-100
large = 1000+
What type of mutation is a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and what does it do
small scale mutation (most common)
switches a T for an A
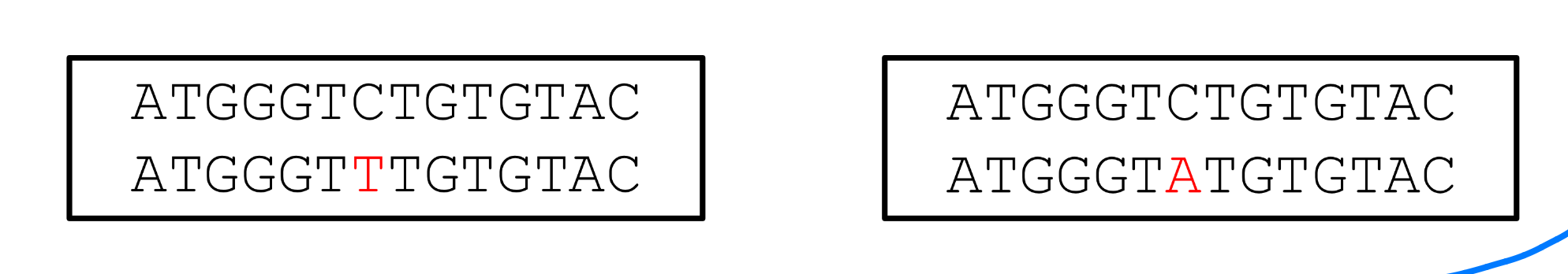
What is a transition and transversion, what is more common and why ?
transition = same type of nucleotide makes a base switch (ex. purine and purine)
transversion = different nucleotide types make a base switch (ex. purine x pyrimadine)
transitions are more common since you are using bases from the same nucleotide family
Purine: A → G, G → A
Pyrimidine: A → T, T → A
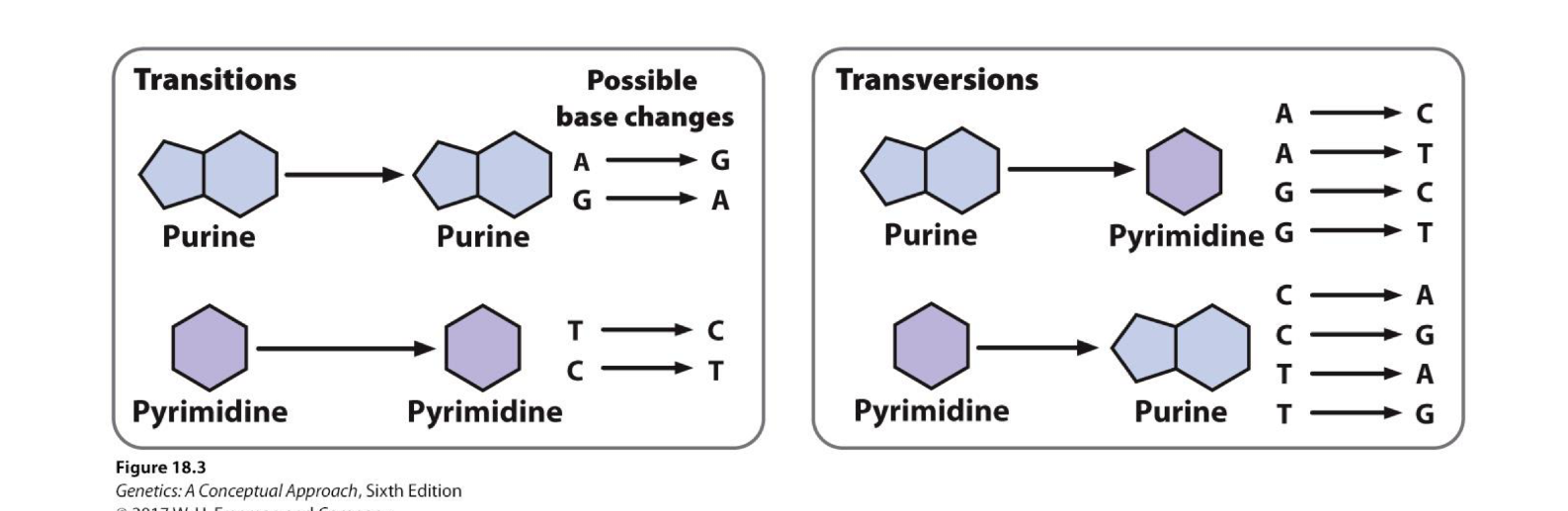
How many genomes do SNP’s account for if humans have 6 million genomes
about 3-5 million, or 0.1%
Why we are so identical
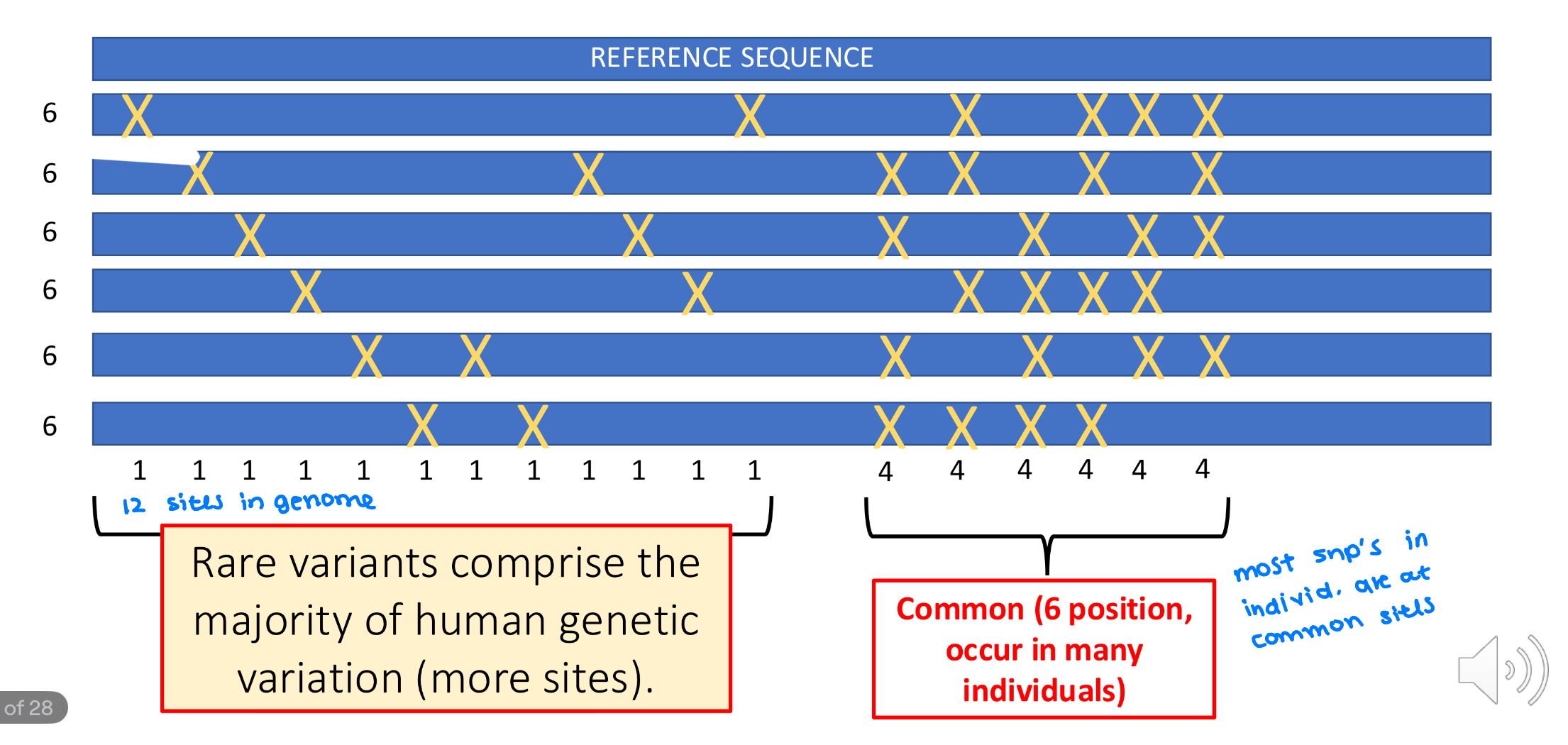
In this SNP comparison, which are the rare mutations and which are the common
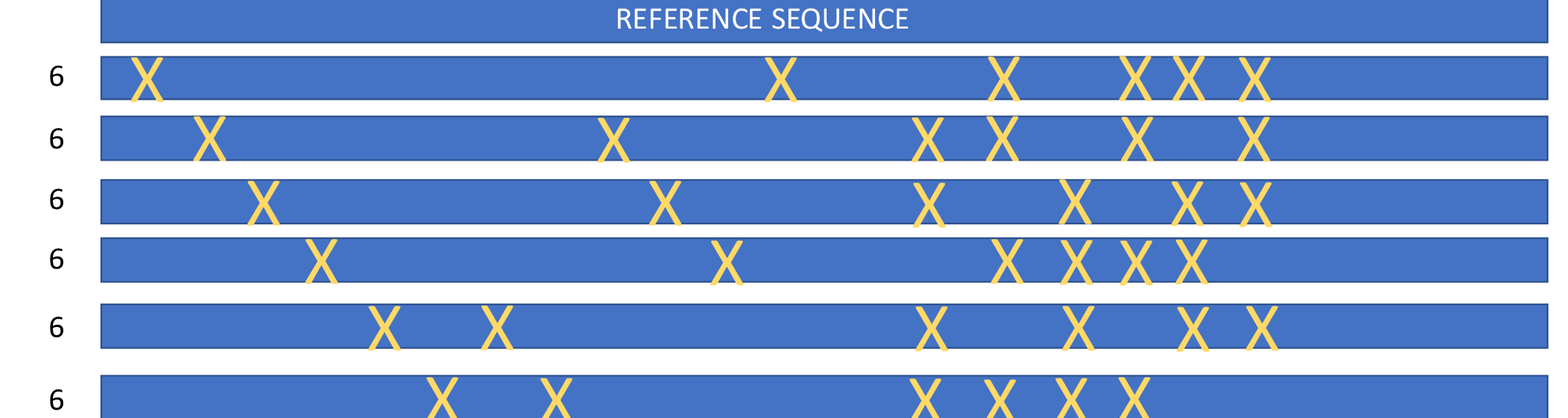
Why?
the 12 X’s to the left are the rare and 6 X’s to the right are common
rare mutations are more recently found in time not affecting a large population
common mutations have been around in the population for awhile

What type of mutations comprise of majority of human genetic variation
rare variants because there are more sites spread across the genome compared to common variants were there are less positions at more common site
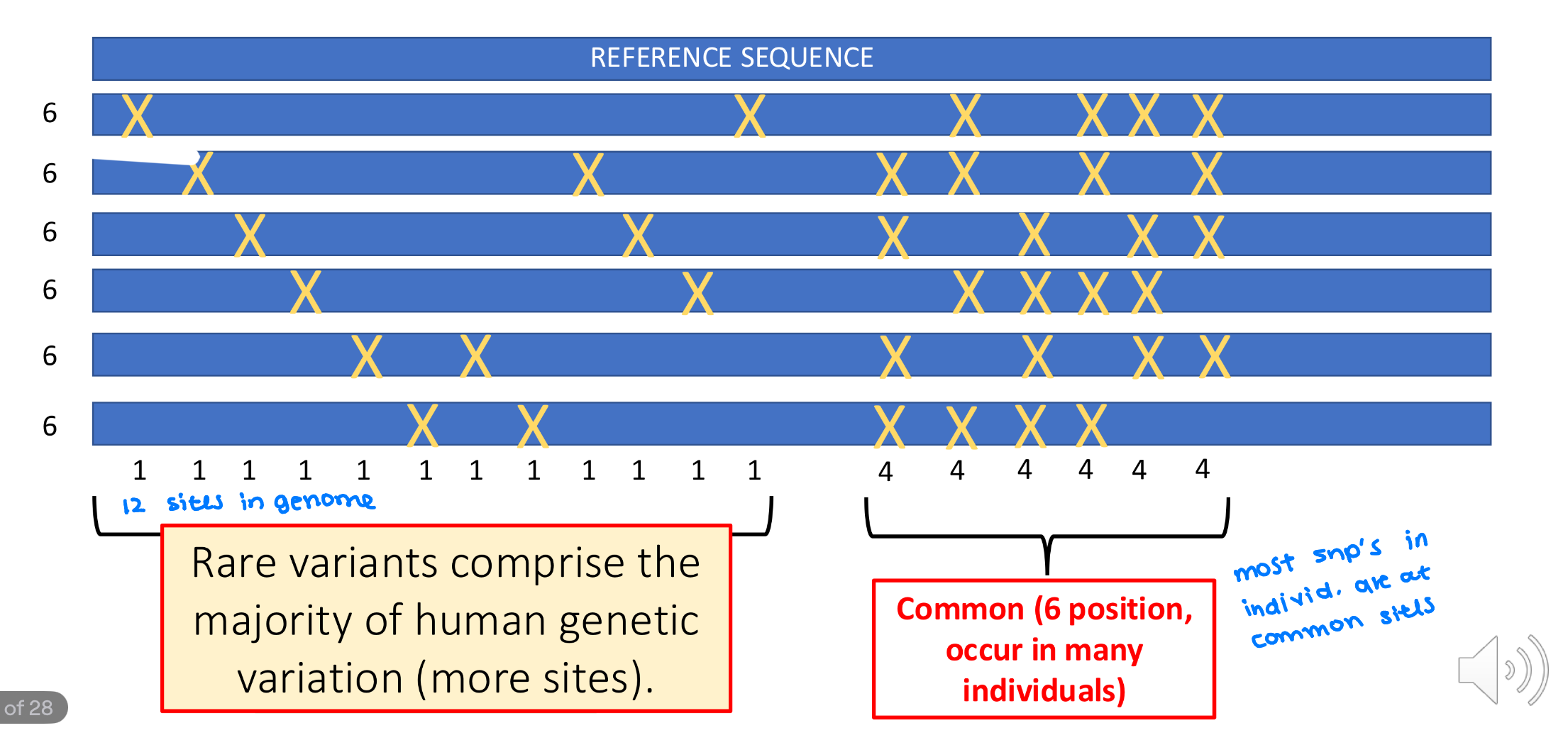
Where is most of the variation in an INDIVIDUAL genome found
at the common sites
What are SNP’s function
unsure
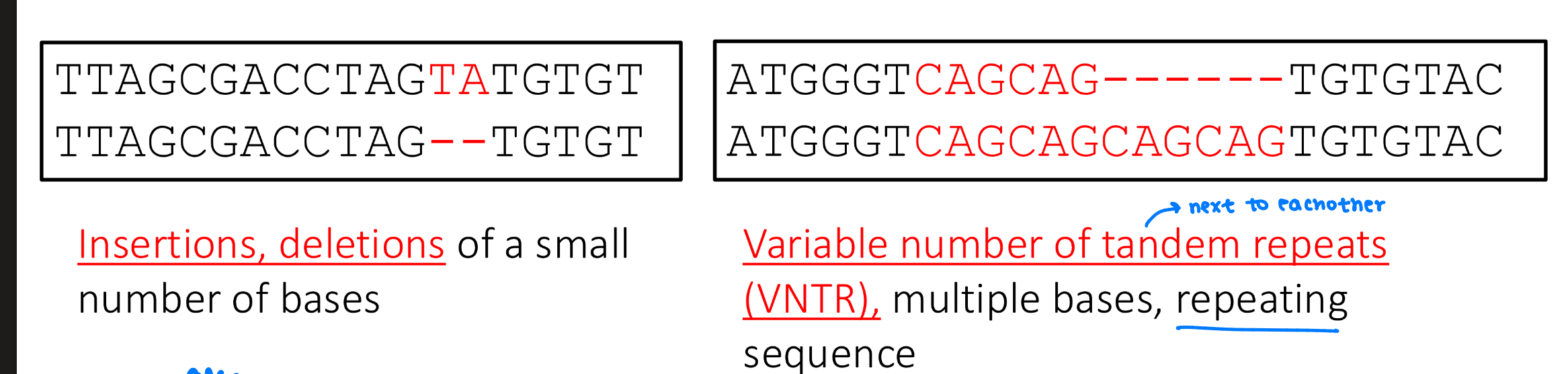
What are the types of small scale mutations
insertions/deletions - of small # of bases
variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) - repeating sequences of multiple bases
What causes small scale mutations
spontaneous
environmental factors (chemical, UV light, radiation)
What are the specific types of spontaneous small scale mutation examples
altered base pairing
tri-nucleotide repeats causing slippage
deamination
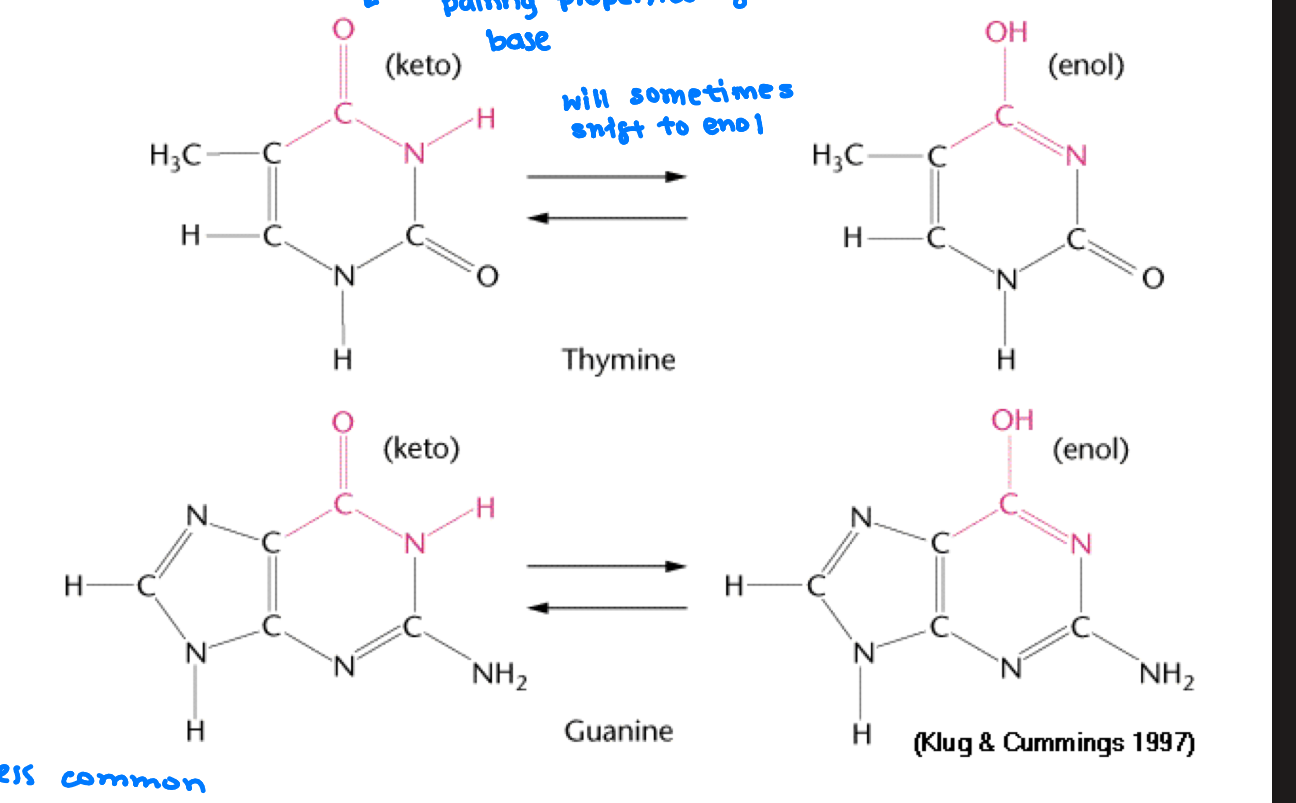
Explain how altered base pairing causes mutations
G will pair w/ T instead of C
A will pair with C instead of T
If G or T is in enol form it will pair with eachother
If A or C is in imino form it will mispair with each other
Explain how tri-nucleotide repeats causes mutations (and what are the common sequences)
CAG, CGG, GAA
expanded trinucleotide repeats get confused by the polymerase adding complimentary bases during DNA replication
it will add bases to these repeats and sometimes the new nucleotides will slip out causing the polymerase to go and add new bases back to it (expansion)
If the template loops and the polymerase misses the sequence, new bases will not be added to the new template strand (contraction)
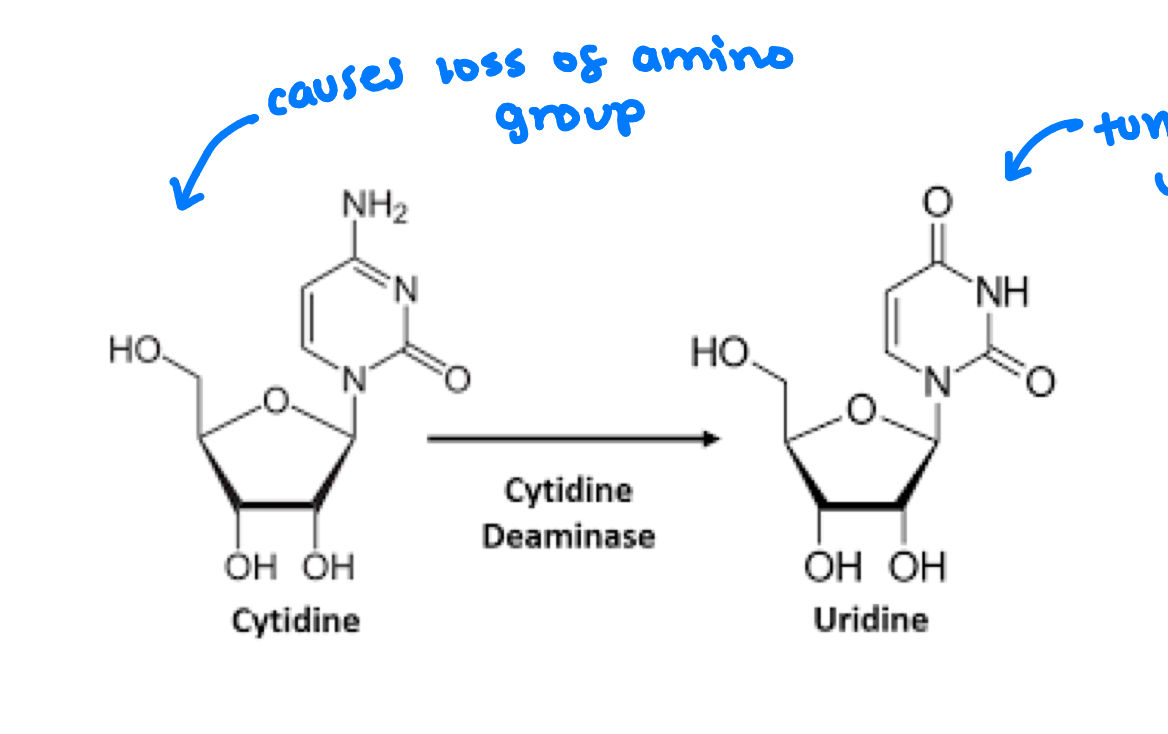
Explain deamination causes mutations
cytidine deaminase will remove an amino group from a nitrogenous base ex. cytosine causeing it to turn into uracil which will bond to adenine instead of guanine
What chemical process causes small scale mutations
alkylating agents chemically altering base structure by donating an alkyl group
causes G to pair with T
guanine exposed to EMS will add an alkyl group to oxygen chemically messing up the structure and bonding it to T
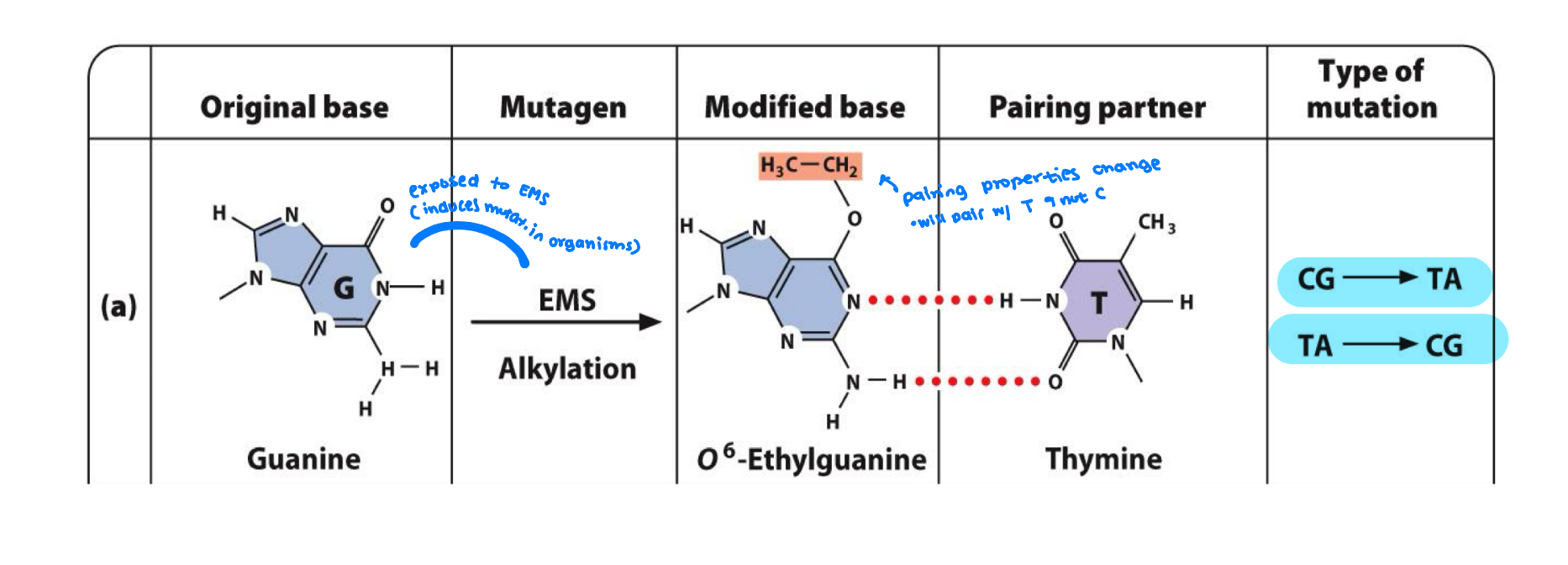
How does UV light cause small scale mutations
when DNA is exposed to UV light it induces thymine dimers (covalently linked T’s next to each other)
causes distortions of DNA structure and errors during DNA replication (body able to reverse it though)
How does ionizing radiation induce small scale mutations
both strands or single strand of DNA breaks causing loss of a base structure
How many mutations do your parents contribute to the next generation
30
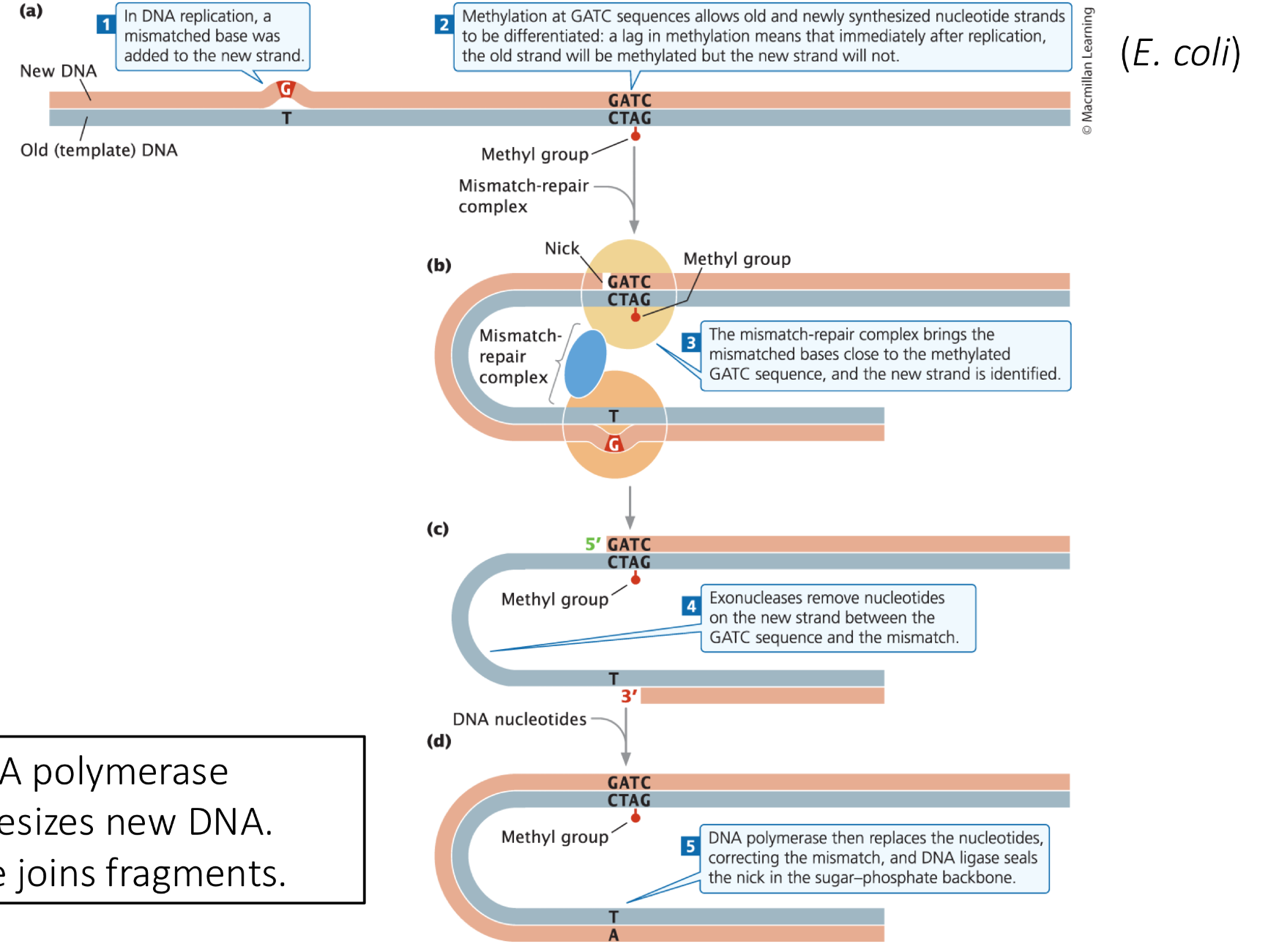
What is a mismatch repair
mismatched pair is identified
the original strand is identified
the mismatch pair complex identifies the region with mutation
the exonuclease removes newly replicated nucleotides
the DNA polymerase will then synthesize new DNA and ligase will join the fragments
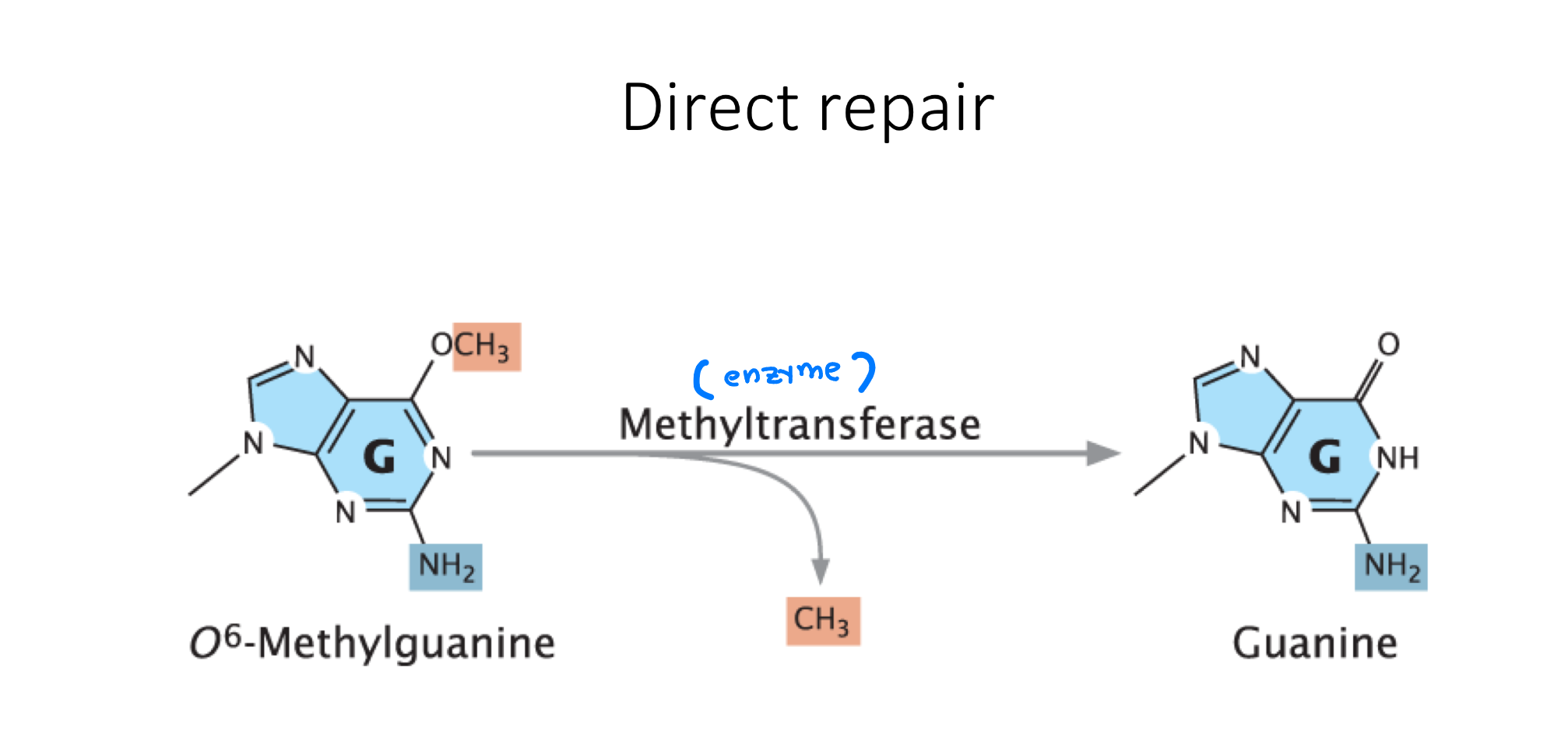
What is a direct repair and how common is it
an enzyme repairs the molecule
What is a base excision repair
deaminated C or other types of damaged bases are recognized by diff. DNA glycosylases
DNA glycosylases will remove base from the DNA
the endonuclease will remove the ribose sugar
the DNA polymerase will add a new nucleotide and ligase will join the nucleotides