The Gastrointestinal System
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 309
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
the digestive system comprises organs concerned with processing food and water by:
ingestion
mechanical reduction
chemical digestion
absorption
elimination of unabsorbed residues
another word for digestive tract
alimentary tract
the digestive system begins from the _____ and ends at the _____
mouth; anus
list the additional organs that interact and contribute to the digestive system through various tracts and ducts
salivary glands
pancreas
liver and gall bladder
list the major components of the digestive tract in proper sequence
oral cavity
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
functions of the oral cavity
prehension
mastication
insalivation
what does the size of the entrance into the oral cavity depend on?
an animal’s diet and feeding habits
what animal has smaller oral cavity openings?
herbivores — suffice for stationary food like grass and leaves
lips are also known as the …
labia
function of lips is highly dependent on what?
the species due to differences in diet and feeding habits
describe the size of the labia in different domestic animals
carnivores — reduced in size and less likely to get snagged in the dental arcade
horses, sheep, goats — highly tactile
cattle and swine — stiff and less mobile
what are the different tissue layers of the lips?
skin
oral mucosa
another name for cheeks
buccae
the inner lining of the cheek
buccal mucosa
the buccal mucosa may have a different appearance between …
species
describe the buccae of carnivores and ruminants
carnivores — smooth and delicate
ruminants — thick with large pointed papillae
how is the hard palate in ruminants unique?
it has a rostrally positioned dental pad
dental pad
a tough but cushion-like pad positioned where the upper incisors would be located (lacking in ruminants)
(true/false) there is a distinct demarcation between the hard and soft palate
false
the soft palate is lined with _____ ______ ventrally and _______ ______ dorsally
oral mucosa; respiratory mucosa
tongue
a highly muscular organ capable for both vigorous and precise movements
what movements do the tongue aid in?
prehension
lapping water
grooming
manipulating food
location of the tongue
occupies the greater part of the oral cavity and extends into the pharynx
attached to the floor of the oral cavity by a ventral fold of mucosa
what is the name of the fold of mucosa that attaches the tongue to the floor of the oral cavity?
frenulum
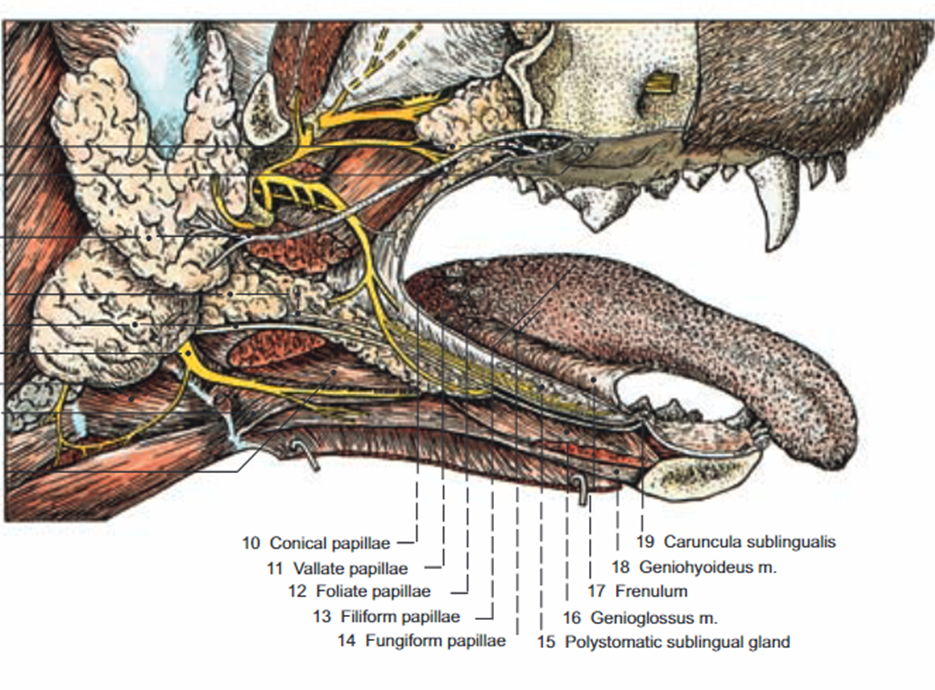
much of the surface of the tongue is covered with __________
papillae of various types
papillae
small nipple-like projections that assist with sense of taste
function of salivary glands
responsible for producing and releasing saliva into the oral cavity
list the main types of salivary glands
parotid salivary gland
mandibular sg
sublingual sg
zygomatic sg
function of saliva
serves to keep the mouth moist and facilitate mastication of food
once properly masticated, the food mixes with saliva to form a lubricated _______ and can be swallowed more easily
bolus
how is the temporomandibular joint formed?
formed by joining the condylar process of the mandible and the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
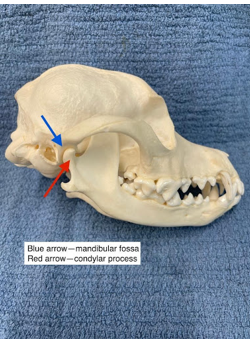
function of the temporomandibular joint
promotes the articulation for opening and closing the mouth
mandibular symphysis
the joint that connects the left and right mandible
complete fusion in many species
little to no movement
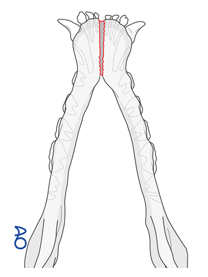
muscles of mastication are muscles that serve to open or close the jaw. list these muscles
temporalis m.
masseter m.
digastricus m.
pharynx
a passage that lies behind the mouth and continues into the esophagus
what parts is the pharynx divided into?
oral
nasal
laryngeal
oropharynx
the region between the soft palate and back of the tongue; essentially the “bottom” of the throat
nasopharynx
the dorsal compartment of the pharynx or the “top” of the throat
laryngopharynx
the largest and most caudal region of the pharynx; dorsal to the larynx
esophagus
conveys the food from the oral cavity (more specifically the pharynx) to the stomach
the esophagus passes along the ______ side of the neck relative to the trachea
left
the structure that the esophagus passes through in the diaphragm
esophageal hiatus
the outer layer of the esophagus in the cervical region is called __________, but is replaced by _________ in the thorax and abdomen
adventitia; serosa
in the pharyngeal region of the esophagus there is skeletal muscle, it begins to transition to smooth muscle in the _________
thoracic region
location of abdominal cavity
portion of the trunk that lies caudal to the diaphragm
begins at the diaphragm and extends pelvic region, and is the largest cavity of the body
what is the most cranial portion of the abdominal cavity called and where is it located?
called the Intrathoracic abdominal cavity
is surrounded and protected within the region of the caudal ribs and costochondral cartilages
list the structures that the abdominal cavity contains
stomach
small and large intestine
liver
pancreas
spleen
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder
uterus and ovaries
adrenal glands
blood vessels, nerves
lymph nodes and vessels
peritoneum
thin layer of tissue that lines the abdominal cavity and its contents
parietal peritoneum
the layer of peritoneum that lines the abdominal wall
visceral peritoneum
the layer of peritoneum that lines the abdominal organs
the peritoneal layer
provides a smooth surface within the abdominal cavity and its organs (lessening the chance for adhesions)
releases a small amount of fluid that lubricates the contents of the abdomen
peritonitis
the inflammation of the peritoneal cavity
describe greater omentum
thin delicate sheet of weblike translucent material
what is the weblike material seen when you open the abdomen from the ventral aspect?
greater omentum
greater omentum originates from the ______ ________ of the stomach and blankets the visceral organs from direct contact with the ventral abdominal wall
greater curvature
function of greater omentum
a protective tool in the abdomen; primarily functioning to contain and isolate infections by wrapping around areas of inflammation or injury
the _________ is one of the first compartments where digestion takes place after ingestion
stomach
gastric emptying from the stomach can take up how much time?
as soon as 30 minutes and may take up to 10 hours to completely empty?
what is the convex aspect of the stomach serosal surface called? the concave aspect?
convex — greater curvature
concave — lesser curvature
what are the 3 regions of the stomach?
cardiac part
fundus
pyloric part
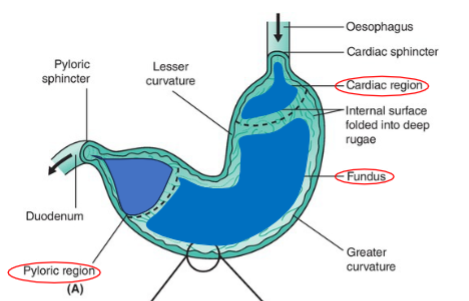
what is the first portion of the stomach that is situated nearest to the esophagus?
cardiac part
what is just to the left and dorsal of the cardia of the stomach? (dome shaped region)
fundus
the body of the stomach is the large middle portion that extends from the fundus to the ________ ________, which then leads to a narrower Pyloric Canal which communicates with the Duodenum
pyloric part
where is a common location of gastric foreign body obstructions?
pyloric part of stomach
define gastrotomy
making a surgical incision in the stomach
what is the name of the procedure done to remove a gastric foreign body?
gastrotomy
where is the incision for a gastrotomy made?
in the least vascular portion of the stomach between the greater and lesser curvatures
the entire mucosal surface of the stomach is lined with characteristic gastric folds called…
rugae
gastric acid and mucous are secreted from the rugae of the stomach. what is their function?
to facilitate the initial phase of digestion before moving into the small intestine
within the stomach mucosa are the ________ _______, consisting of three types of cells responsible for the gastric secretions
gastric pits
what are the three cells responsible for gastric secretions?
goblet cells
chief cells
parietal cells
goblet cells
found in all parts of the stomach
secrete mucus to lubricate the food and protect the stomach wall from damage by digestive enzymes
chief cells
found within the fundus
secrete pepsinogen, the precursor to the active enzyme pepsin
pepsin breaks down proteins to peptides
parietal cells
found within the fundus
secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl); creates an acid pH which enables pepsin to work effectively
where does the intestine begin and end
begins at the pylorus and ends at the anus
where is the primary site of nutrient absorption?
small intestine
where are water and electrolytes absorbed?
large intestine
duodenum
relatively short in length and somewhat fixed in position near the mesentery region
the jejunum and ileum are less closely fixed in place and the coils of the intestines are carried by the ________
mesentery
(true/false) there is a sharp, identifiable boundary between the jejunum and ileum
false
what are the layers of the small intestine? (outer to inner)
serosa
muscularis
submucosa
mucosa
the mucosal lining of the small intestines are lined with _________, which greatly increase the absorption surface area
microvilli
what is the structure that separates the small intestine and large intestine?
cecum
there are anatomical differences of the large intestine between different ___________
species
what are the 3 regions of the large intestine?
cecum, colon, and rectum
what are the parts of the colon?
ascending
transverse
descending
they are divided by flexures
what is the most dorsal structure of the pelvic viscera that lies above the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and urethra?
rectum
in many species (including horses and pigs), the outer muscle layer of the large intestine is mainly concentrated in a number of bands called _______
Teniae
function of teniae
on shortening, the pucker the gut so that a linear series of sacculation’s (haustra) are produced
are teniae present in dogs and cats?
no
the anal canal is a short passage that is constricted at the __________ __________
rectoanal junction
many glands are present in the anal region (both in the anal tissue and skin issues). the dog and cat possess two sacs called…
anal sacs
location of anal sacs
about the size of a hazelnut and located ventrolateral to the anus between the internal and external anal sphincters
the anal sac secretes an odorous fluid that drains through a single duct to the opening at the _____________ __________
mucocutaneous junction
how do anal sacs empty?
they are compressed during defecation
where are anal sacs commonly found?
in carnivores and more; most notorious in skunk
anal sacculitis
inflammation of the anal sac
what main vessels provide blood to the intestines?
cranial and caudal mesenteric arteries
what is the most cranial part of the abdomen, immediately behind the diaphragm?
liver
function of liver
produces bile
metabolism of protein, carbohydrates and fat