17.2 Federal Deficits and the National Debt Using Fiscal Policy to Fight Recession Unemployment and Inflation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Federal debt is the ______ of annual budget deficits and surpluses? Select the correct response to fill in the blank.
Select the correct answer below:
sum
difference
product
quotient
sum
Federal debt is the sum of annual budget deficits and surpluses. Annual deficits do not always mean that the debt/GDP ratio is rising. During the 1960s and 1970s, the government often ran small deficits, but since the debt was growing more slowly than the economy, the debt/GDP ratio was declining over this time. In the 2008–2009 recession, the debt/GDP ratio rose sharply.
What happens to aggregate demand during expansionary fiscal policy?
Select the correct answer below:
it shifts inward
it shifts outward
it remains the same
it shifts both inward and outward
it shifts outward
Graphically, we see that fiscal policy, whether through changes in spending or taxes, shifts the aggregate demand outward in the case of expansionary fiscal policy and inward in the case of contractionary fiscal policy.
Express what happens to the aggregate demand curve when the government decides to cut business taxes.
Cutting business taxes, and therefore increasing after-tax profits, is a form of expansionary fiscal policy. Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
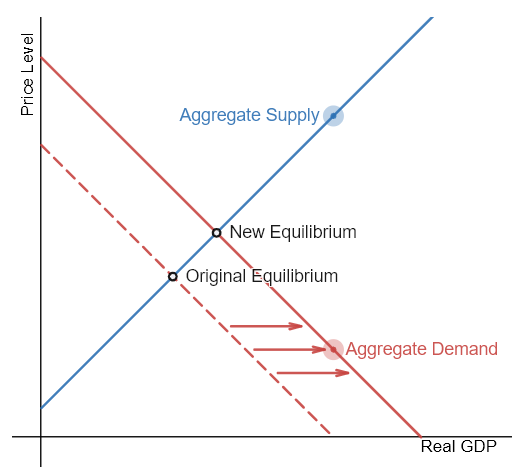
The economy is booming, and the government wants to make it grow even faster. Show what happens when expansionary fiscal policy is applied.
Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the AD curve rightward, raising the price level as well as real GDP in equilibrium.
Illustrate what happens to the aggregate demand curve when the government decides to reduce its spending.
AD to left
When the government decides to reduce its spending, it is exercising contractionary fiscal policy. This type of policy reduces upward pressure on the price level, and thus decreases aggregate demand.
By adjusting the aggregate demand curve, show how the equilibrium point is affected by contractionary fiscal policy.
AD to left
Contractionary fiscal policy reduces the overall spending in the economy, which reduces aggregate demand. This reduces both the real GDP and the price level in equilibrium.
Up until which decade did the debt/GDP ratio reveal a fairly clear pattern of federal borrowing?
Select the correct answer below:
1960s
1970s
1980s
1990s
1970s
Until the 1970s, the debt/GDP ratio revealed a fairly clear pattern of federal borrowing. The government ran up large deficits and raised the debt/GDP ratio in World War II, but from the 1950s to the 1970s the government ran either surpluses or relatively small deficits, and so the debt/GDP ratio drifted down.
Which of the following would be an example of contractionary fiscal policy?
Select the correct answer below:
increasing government spending
increasing taxes
printing new money
increasing government investment
increasing taxes
The government may increase taxes which will reduce spending by consumers and/or businesses in the economy. This will have a contractionary effect on the economy.
By moving the aggregate demand curve, show how increased government spending impacts the economy.
Increased government spending is a form of expansionary fiscal policy, which increases levels of output and shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
Illustrate only what happens to the aggregate demand curve after the government increases after-tax profits by cutting business taxes.
Raising after-tax profits via cutting business taxes is a form of expansionary policy. This increases investment spending, and thus shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
Show what happens in this economy when the government reduces after-tax profits by raising business taxes.
AD shift left
If business taxes are raised, business spending will decrease. This is a case of contractionary fiscal policy. As a result, aggregate demand decreases and the new equilibrium is at a lower price level and a lower real GDP.
Show what happens in the economy when the government decreases its spending.
AD shift left
If government spending is decreased, this indicate a contractionary fiscal policy, which lowers aggregate demand and establishes a new equilibrium at lower price level and a lower real GDP.
Illustrate what happens only to the aggregate demand curve when the federal government raises federal grants to state and local governments.
AD shift right
By raising federal grants to state and local governments, the federal government is employing expansionary fiscal policy. The government is increasing spending, and thus aggregate demand increases as well.
Illustrate what happens to the aggregate demand curve when the government increases its purchases.
AD shift right
By increasing its purchases, the government is employing expansionary fiscal policy, which causes aggregate demand to rise.