Midterm - Medieval Architecture 412
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
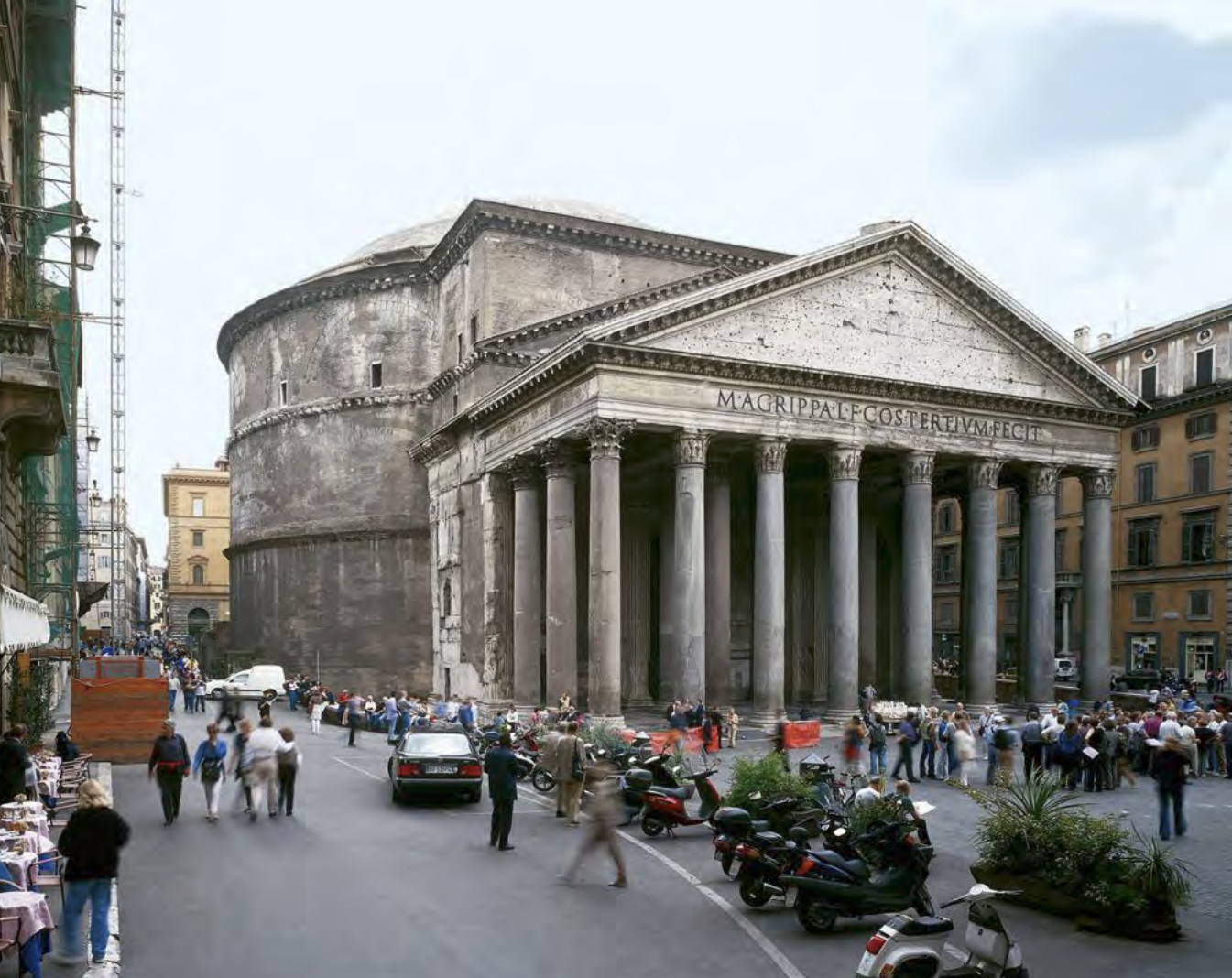

Dedicated to all gods, signified Romans wanting to bring order (imperial authority) to gods/cosmos/new and foreign societies
Pantheon | Imperial Roman
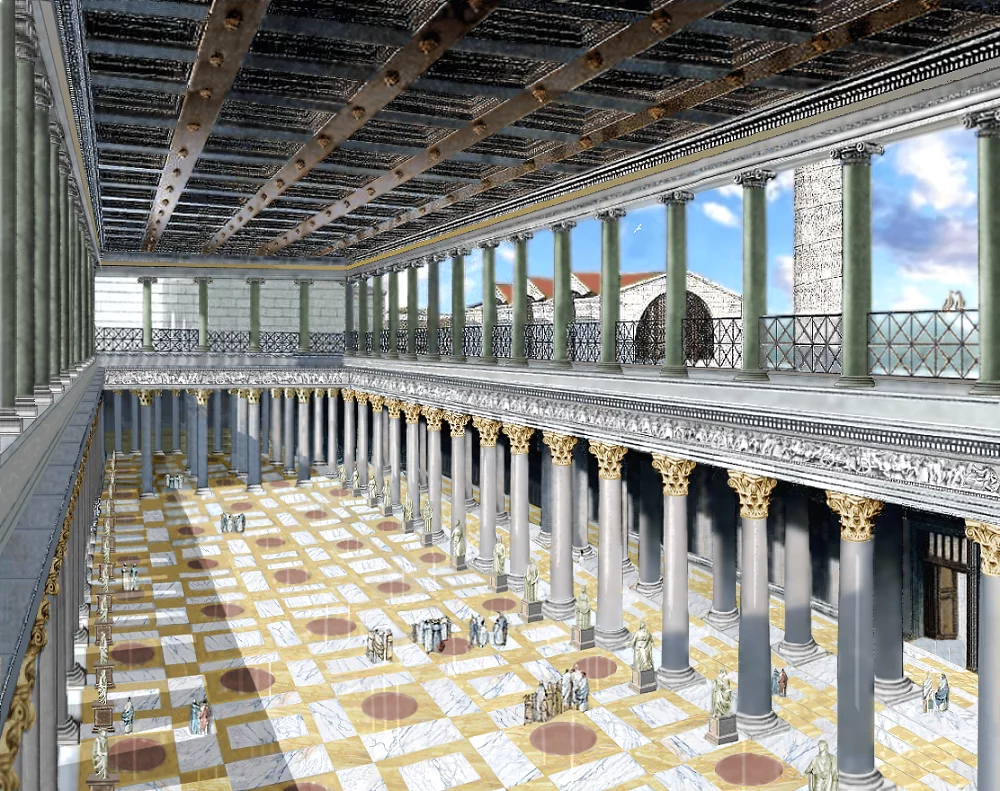

Ancient Roman civic building, located in the Forum of Trajan
Basilica Ulpia | Imperial Roman
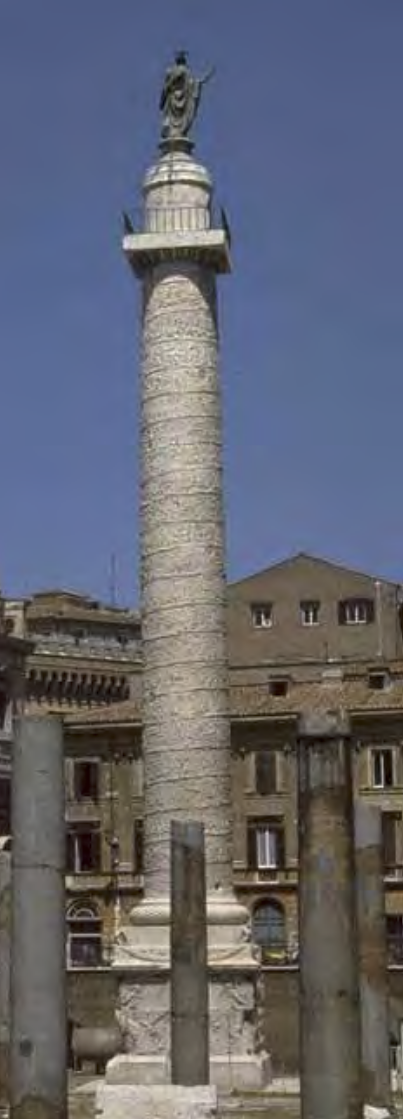


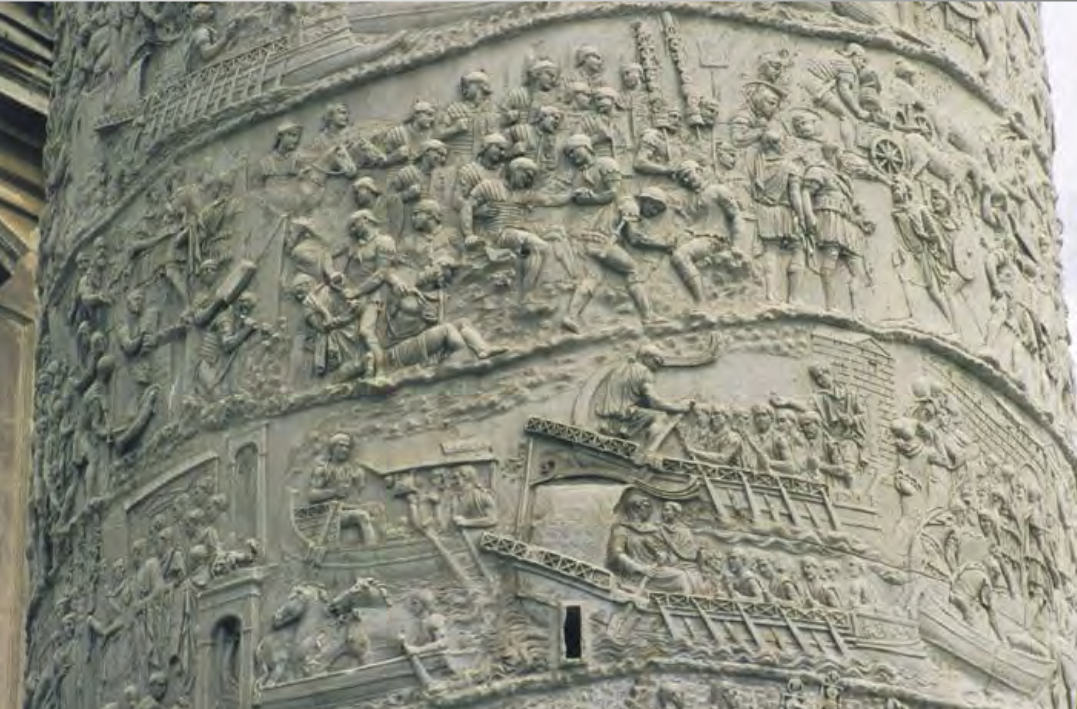
Commemorative monument with spiral registers depicting Trajan’s army and victories
Column of Trajan | Imperial Roman


Second largest Roman public baths, used hypocausts (under floor heating systems)
Baths of Caracalla | Imperial Roman
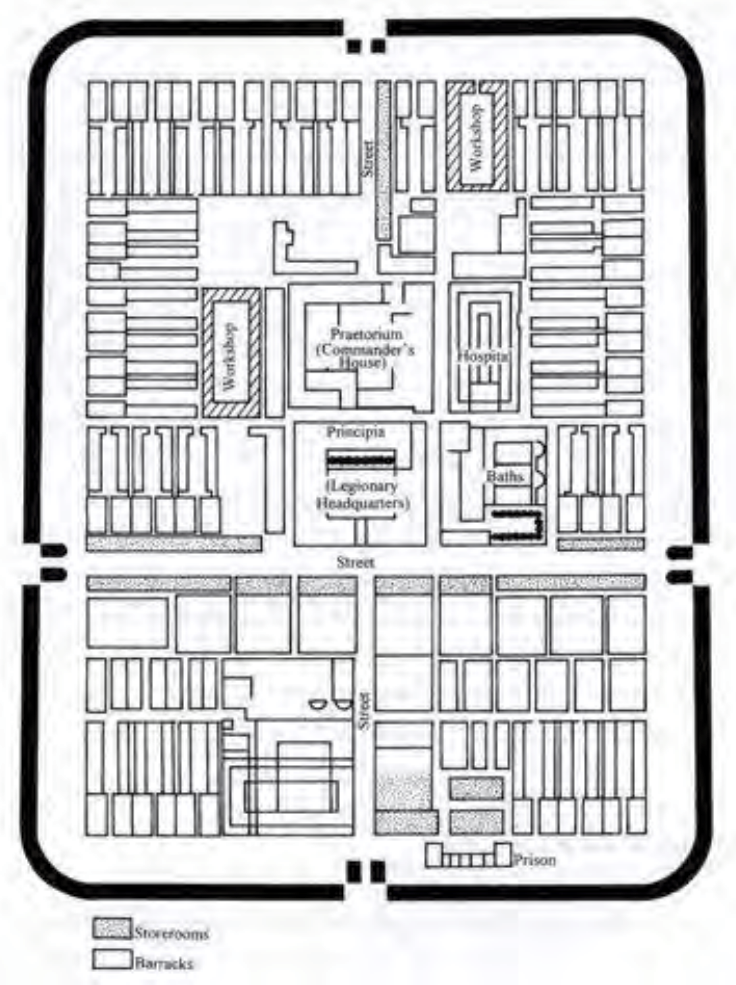
Typical Roman military camp, featuring cardo (ns) and decumanus (ew)
Castrum
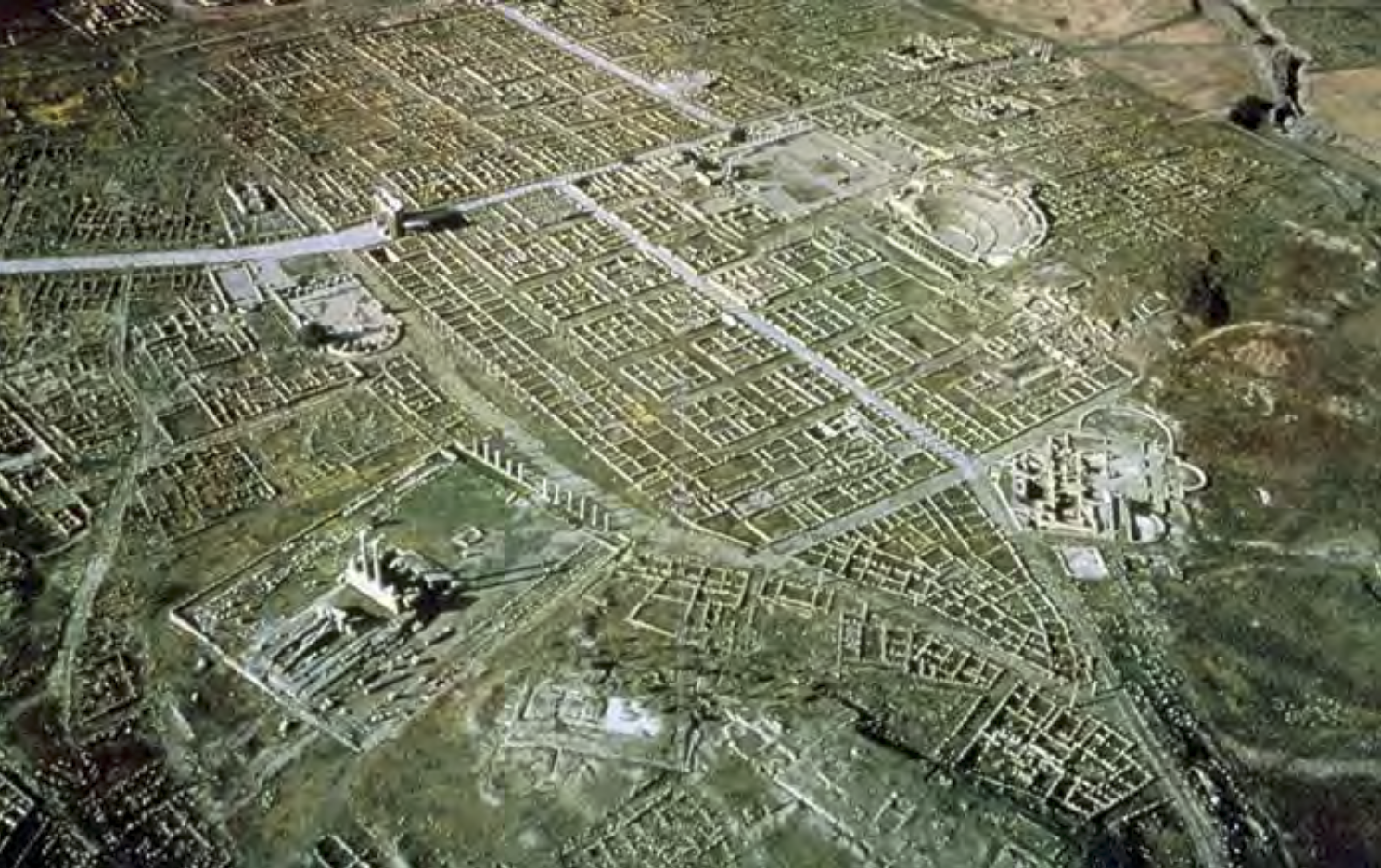

Walled, provincial Imperial Roman “kit” city. Where Arch of Trajan is located.
City of Thamugadi/Timgad | Imperial Roman
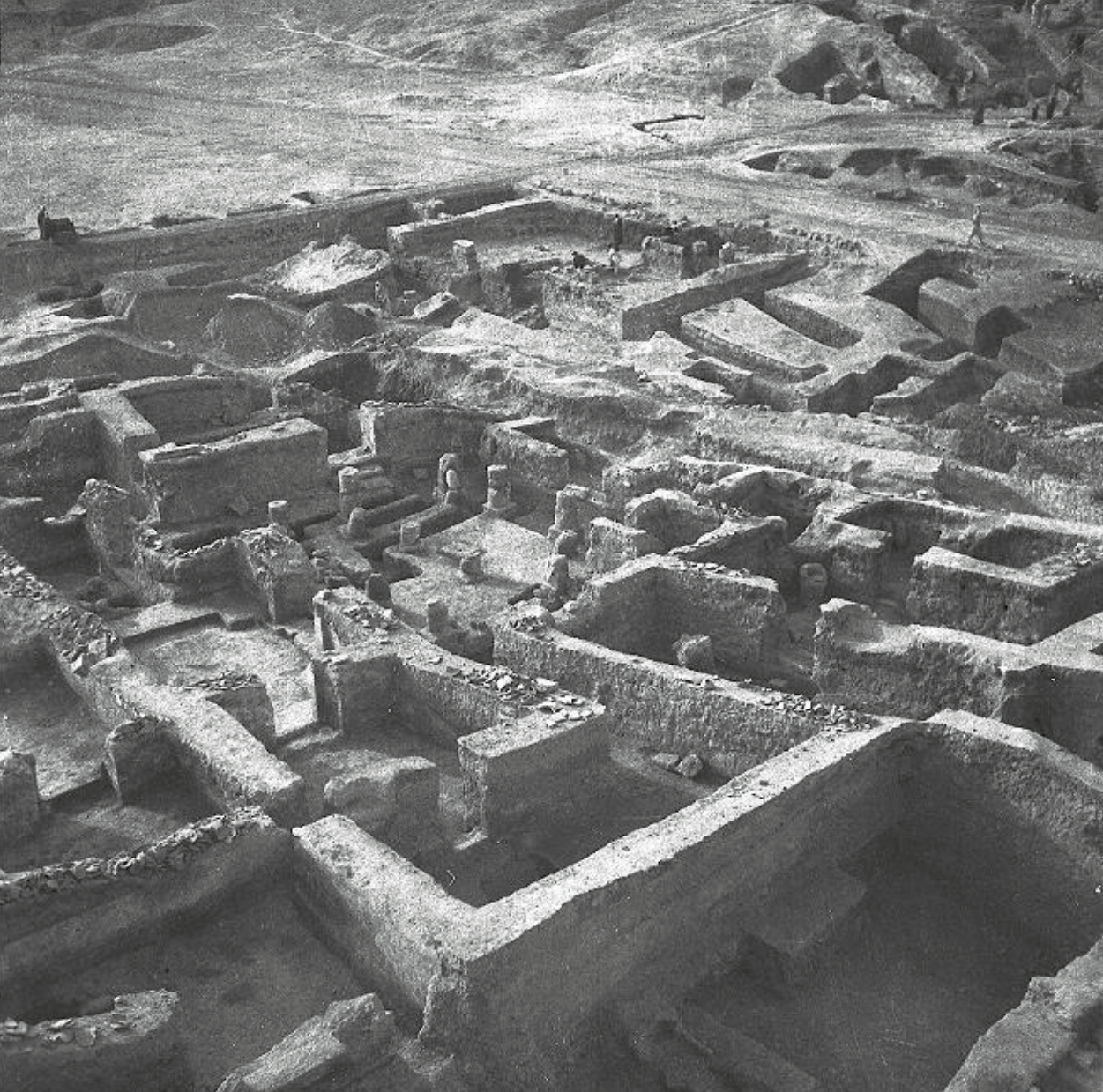


Multi-religion/cultural town, Eastern border of the Roman Empire. Well preserved, provided insight into outskirt towns and how Roman culture interacted w bordering cultures (example of syncretism)
City of Dura Europos | Late Antique/Roman
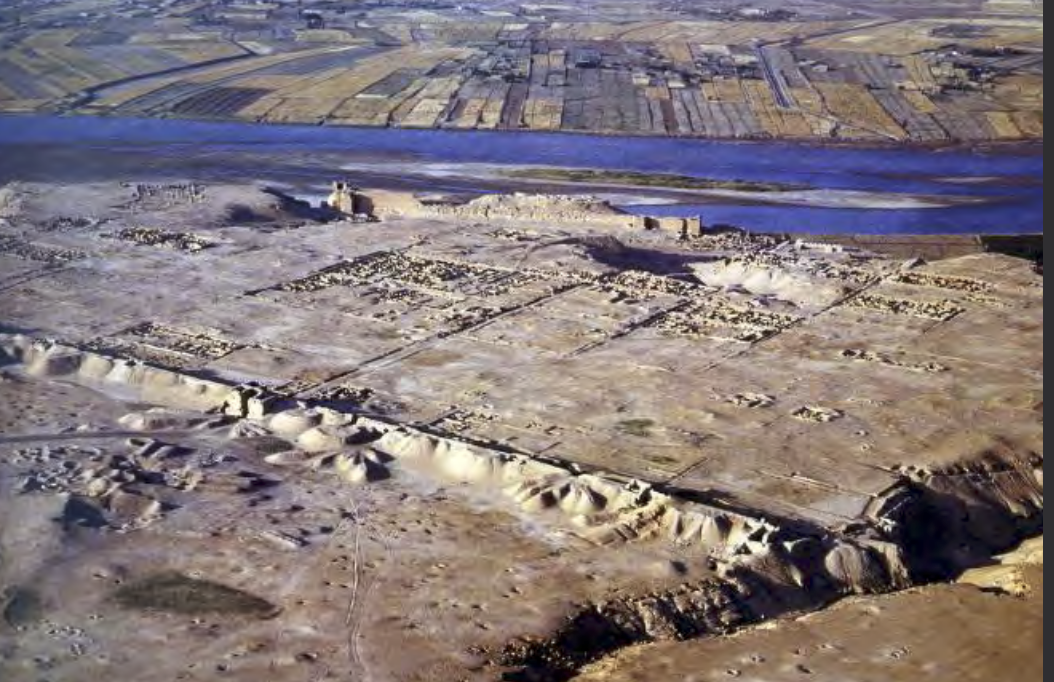
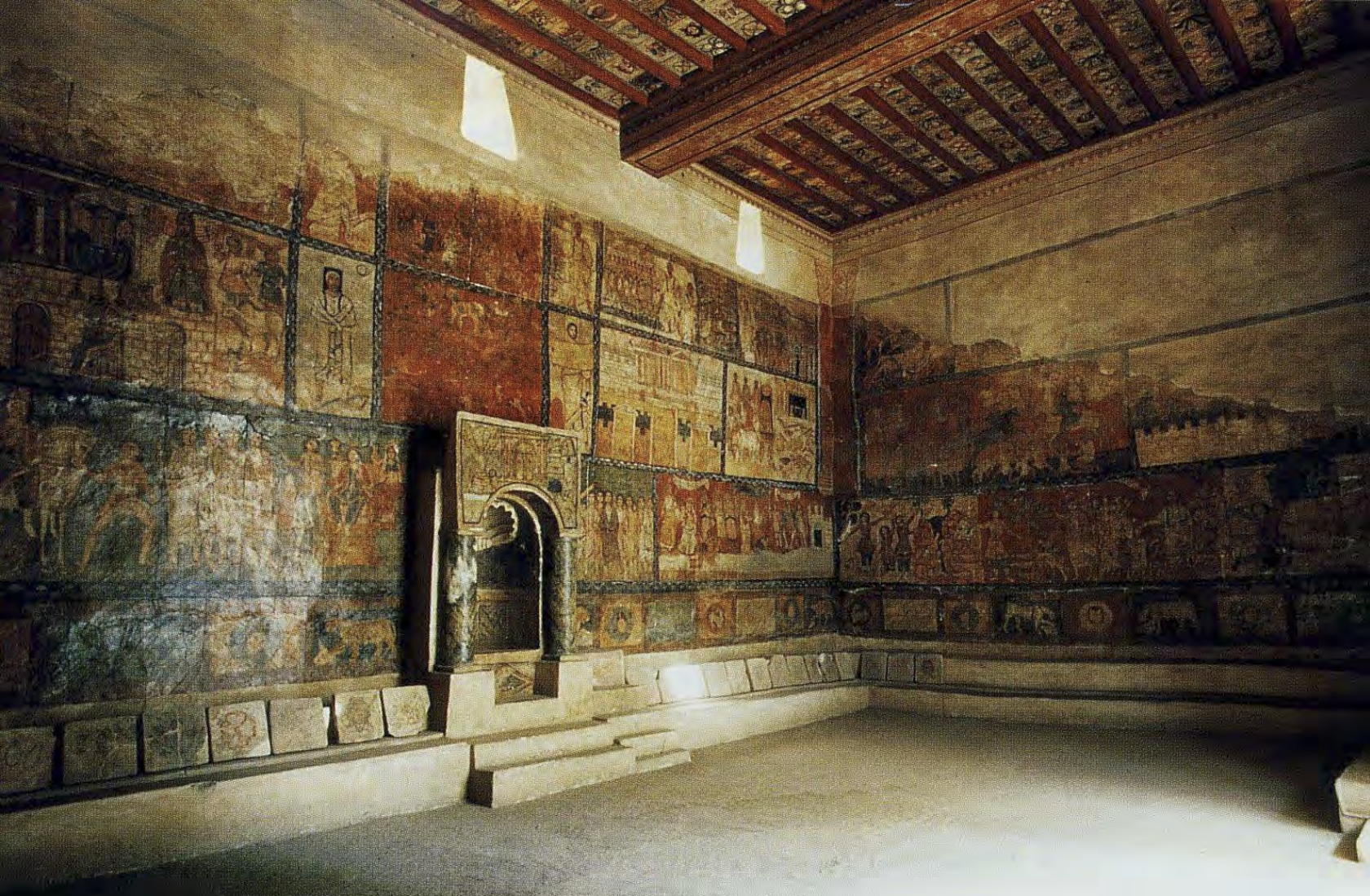


Religious buildings, such as these, share art styles and decor which reveals the multiculure and multilanguage community where this building is located
Synagogue at Dura Europos | Late Antique/Roman
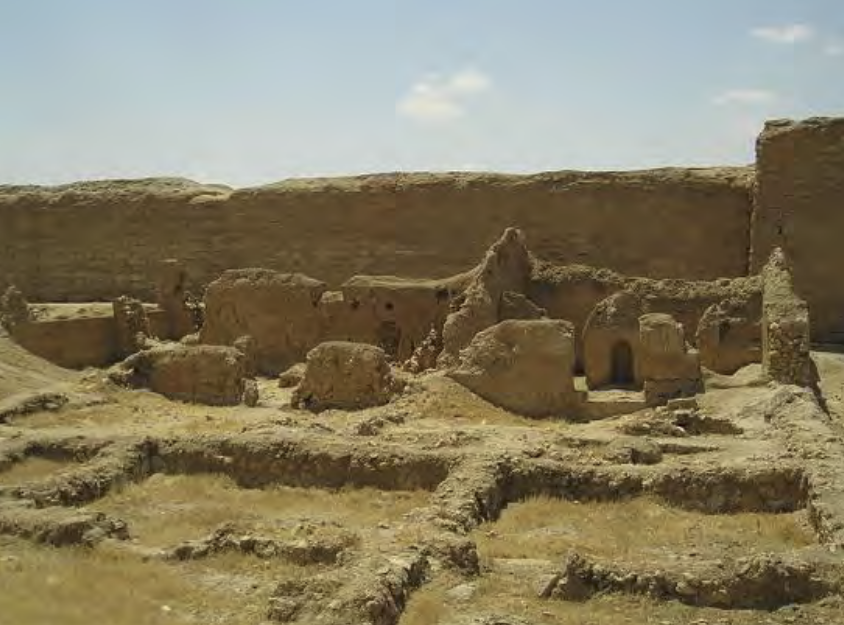
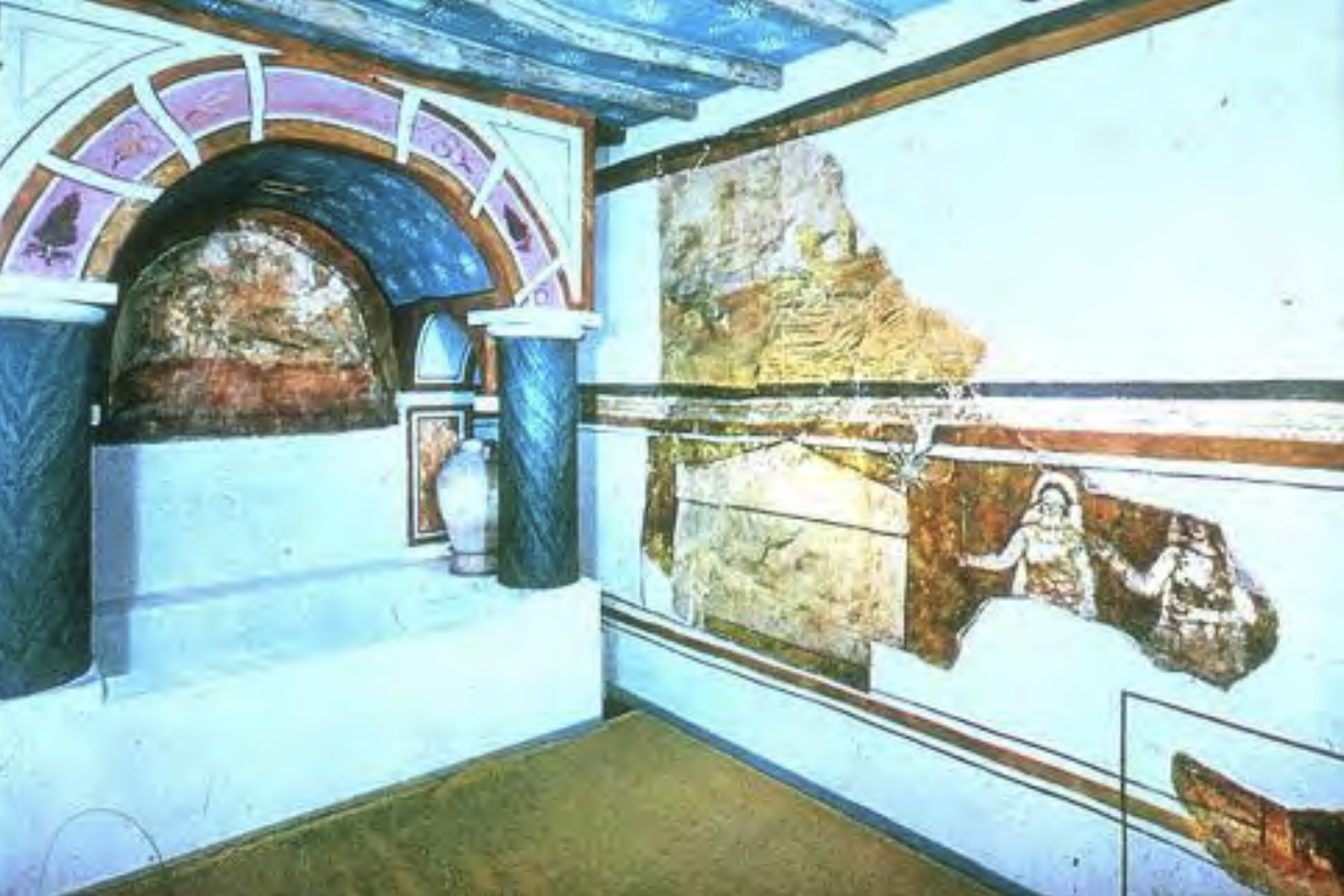


Early Christian space for worship, teaching, and baptism.
Domus Ecclesiae/House-Church | Late Antique/Roman
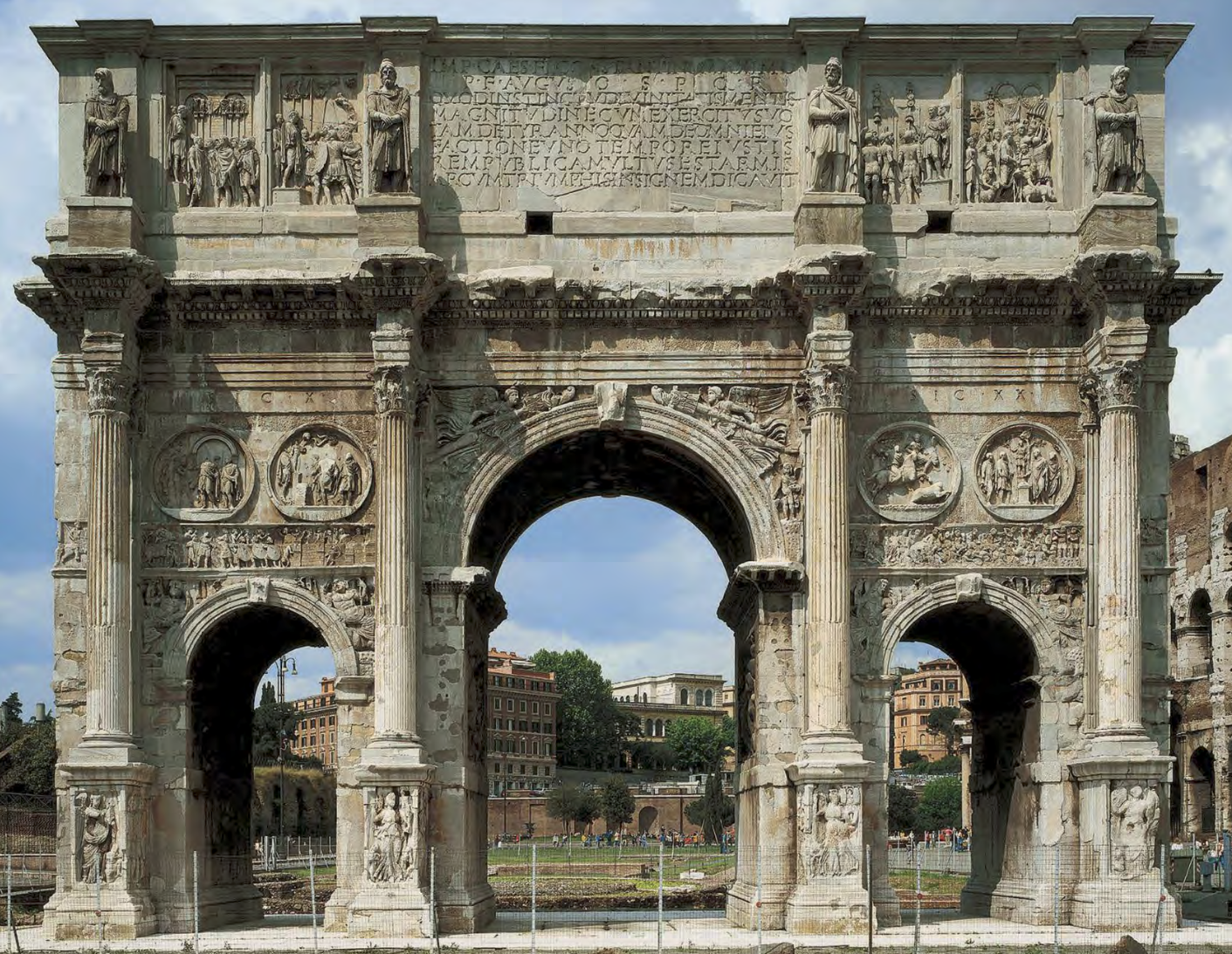


Arch placed in relation to procession pathway, colossal scultpture of Sol, and Meta Sudans fountain. Uses spolia to preserve monuments and legitimize this person as emperor.
Arch of Constantine | Constantinian
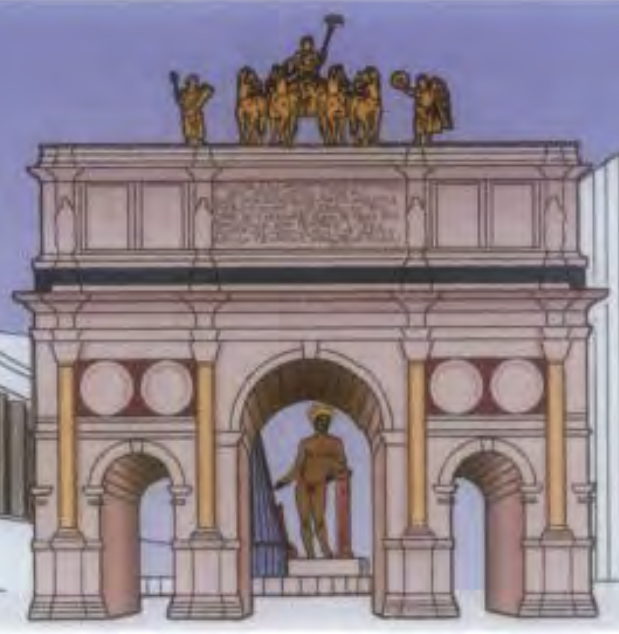

![<p>Civic (law court) basilica begun by [X], [Y] continued building after his defeat of [X]. </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/49435fab-6f2e-4415-bf50-a0f81139271e.png)
Civic (law court) basilica begun by [X], [Y] continued building after his defeat of [X].
Basilica of Maxentius/Constantine (Basilica Nova) | Constantinian
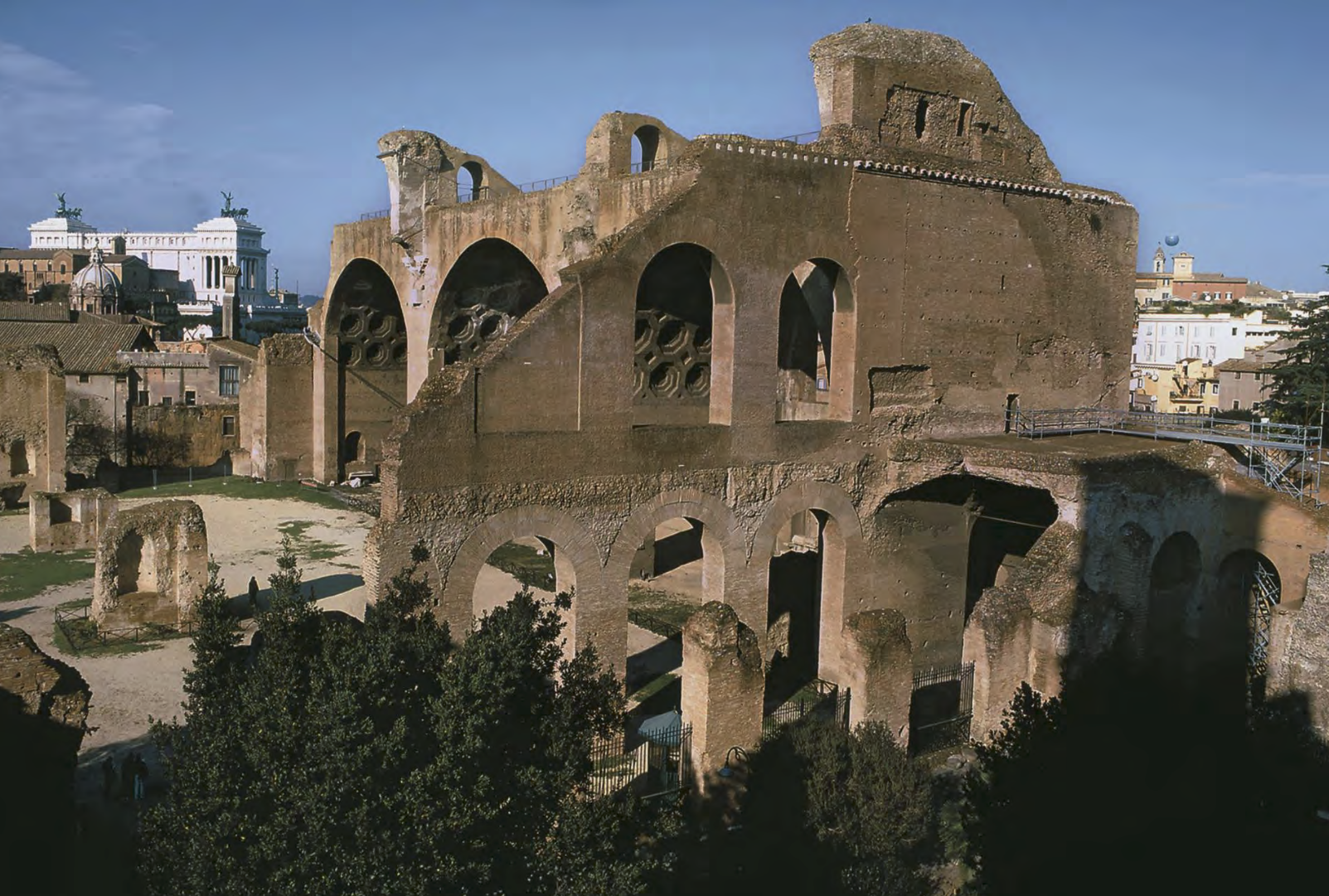

![<p>Where tomb of St. [X] lies, holy place of importance, basilica built over shrine by Constantine so Christians could have a proper place of worship. Located on Vatican Hill.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/19660300-eef0-4934-b6c7-1749a1dc6196.png)
Where tomb of St. [X] lies, holy place of importance, basilica built over shrine by Constantine so Christians could have a proper place of worship. Located on Vatican Hill.
Old St. Peter’s Basilica | Constantinian
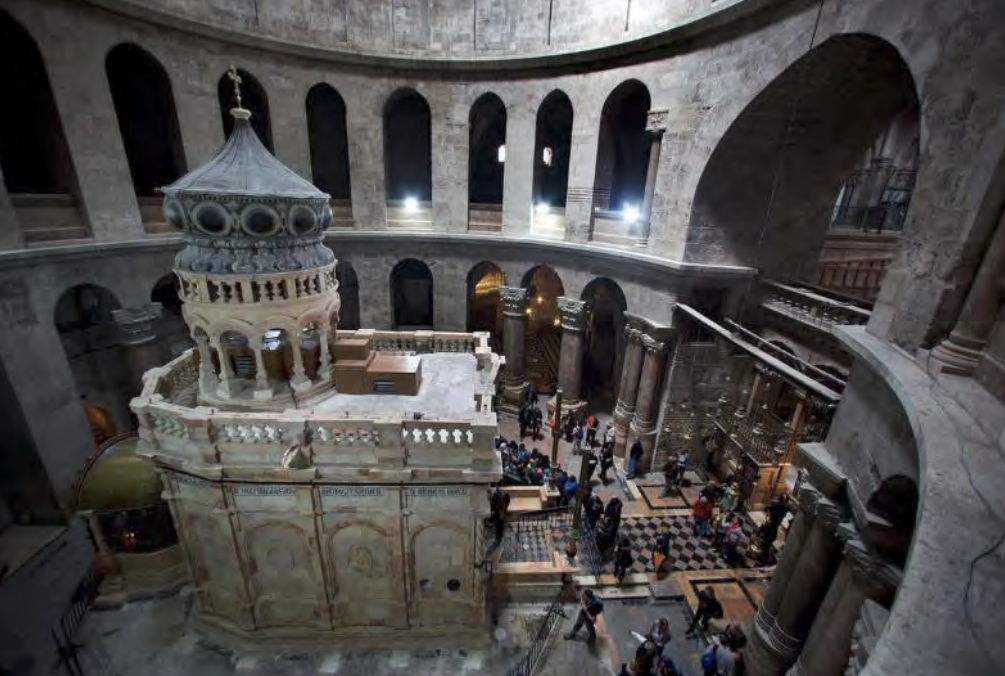
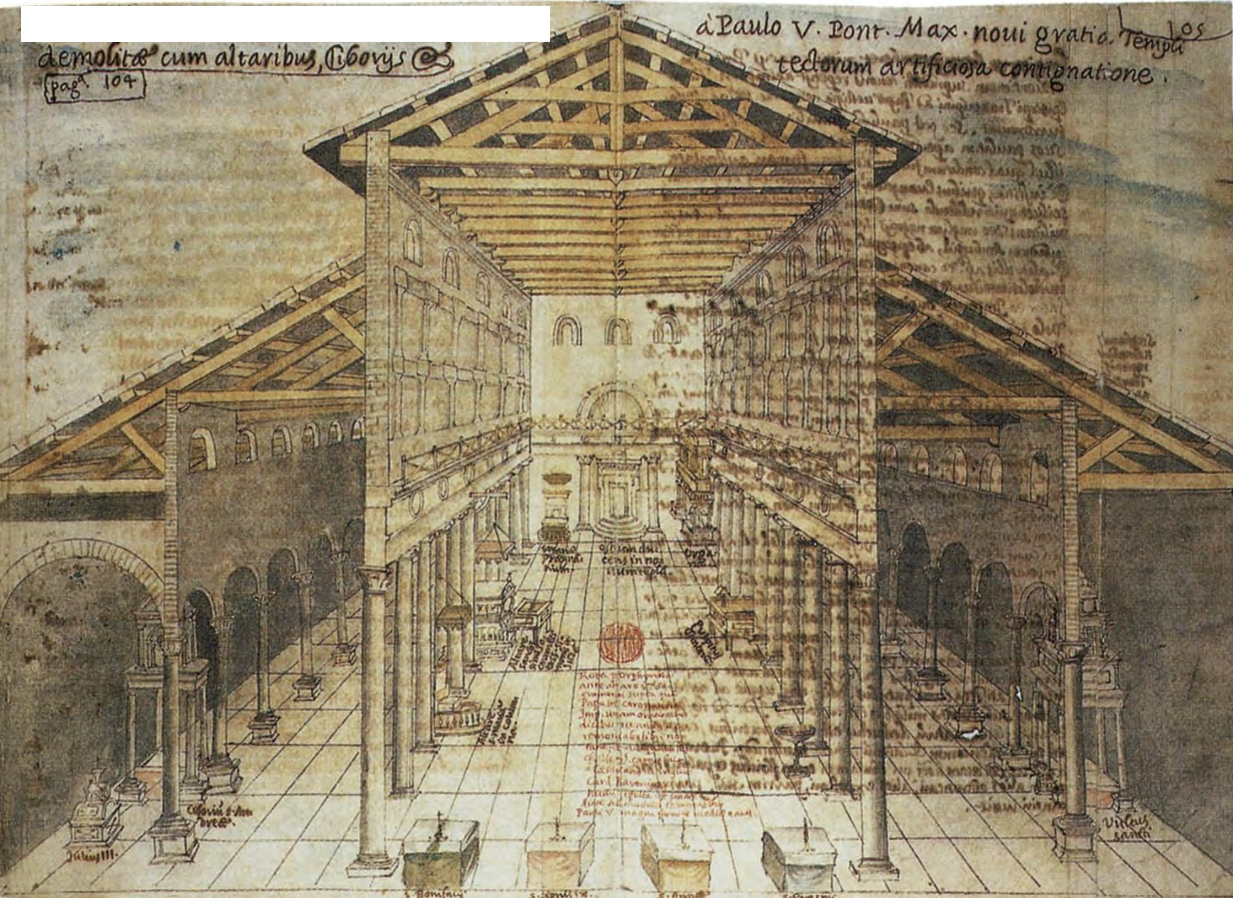

Martyrium, aedicule inside the Rotunda of Anastasis (Resuurection) houses tomb of Christ. Features centralized martyrium with centralized basilica built by Constantine. The MOST important pilgrimage site.
Church of the Holy Sepulcher | Constantinian
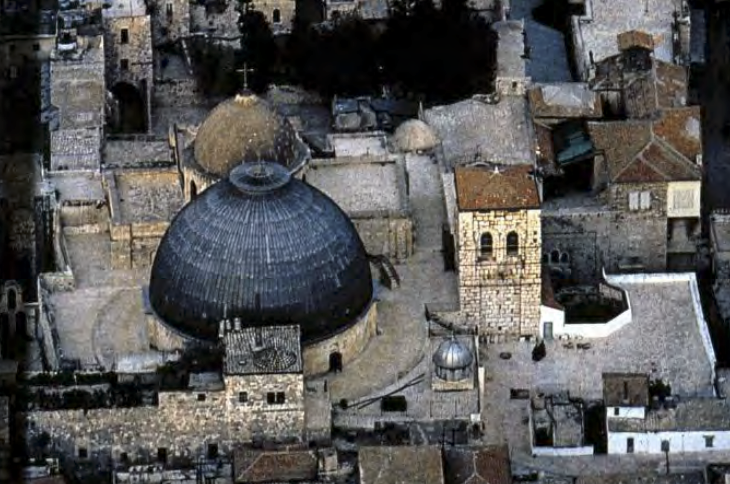

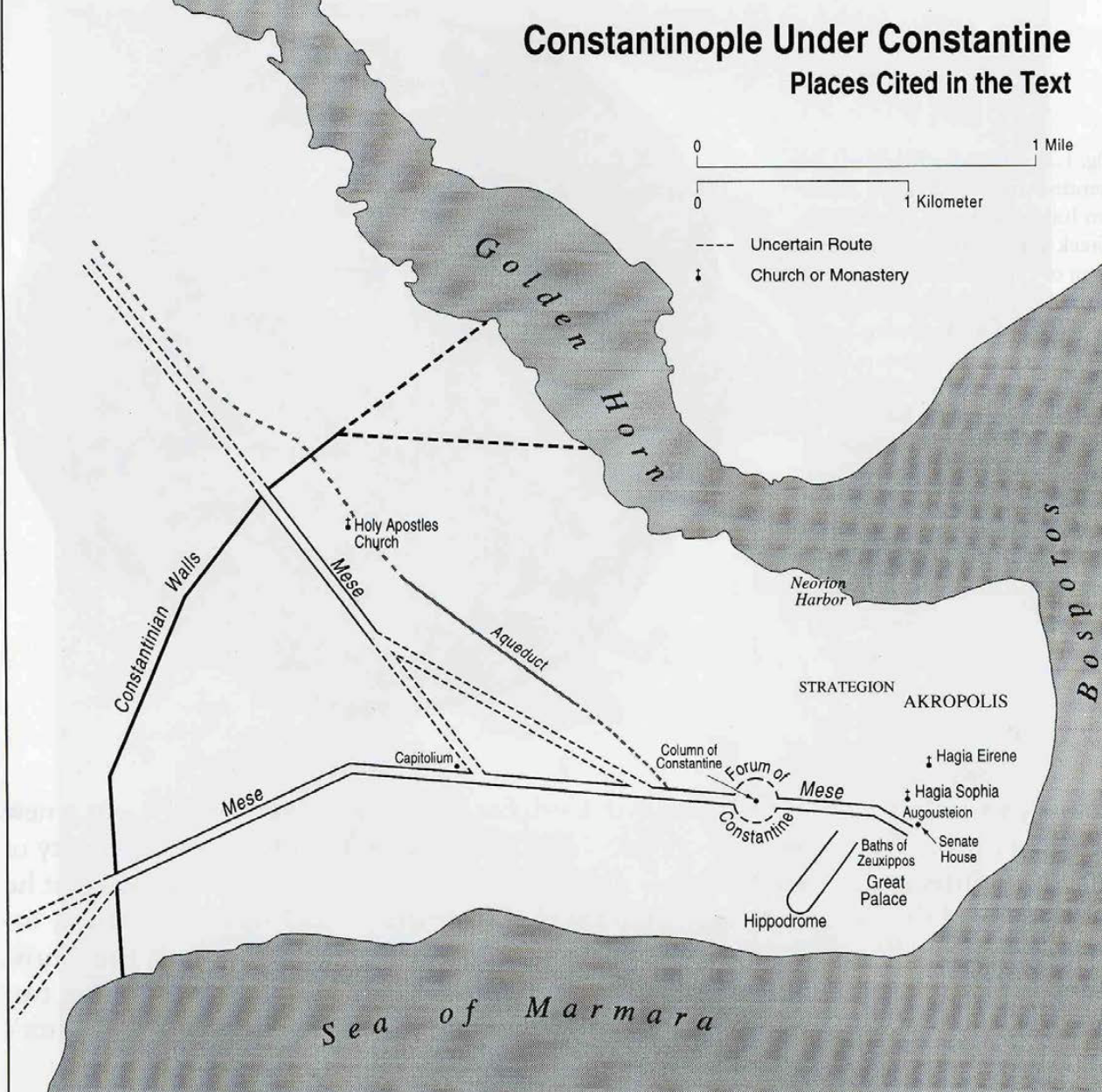
uses political topography: city at edge of Europe and Asia, easy to defend - surrounded by water on 3 sides, access to trade routes. Basileia = Imperial Palace, Sacerdotium = Hagia Sophia, Senate = Augustaion Forum (balance)
Plan of Constantinople | Early Byzantine
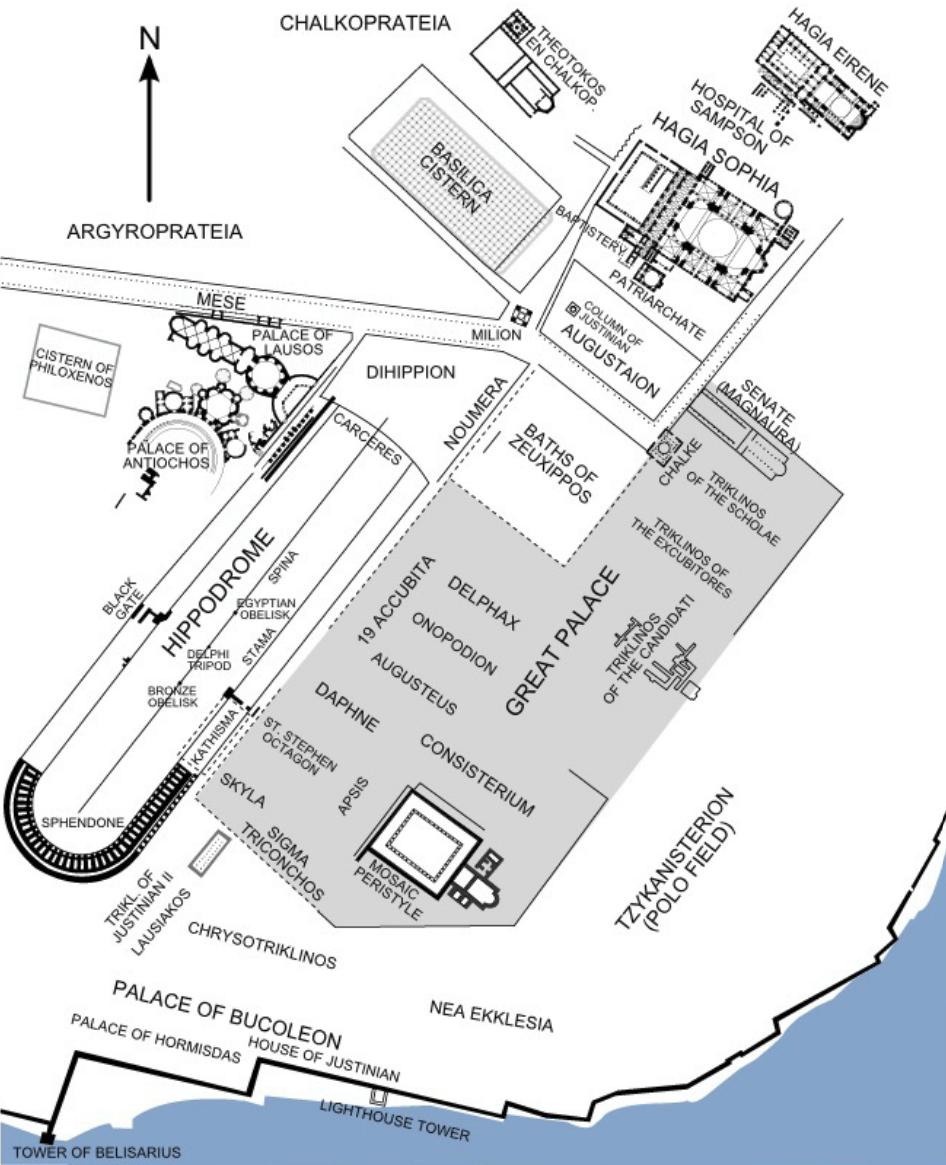
Identify the red dots
Hagia Sophia (ecclesiastic power), Augustaion Forum (senate, balance), Great Palace (secular power), Column of Constantine (arrow, celebrating Const. expansion of Byzantium), Hippodrome (secular power, sports arena, community and entertainment, as well as place for Emperor to present to public) | Early Byzantine
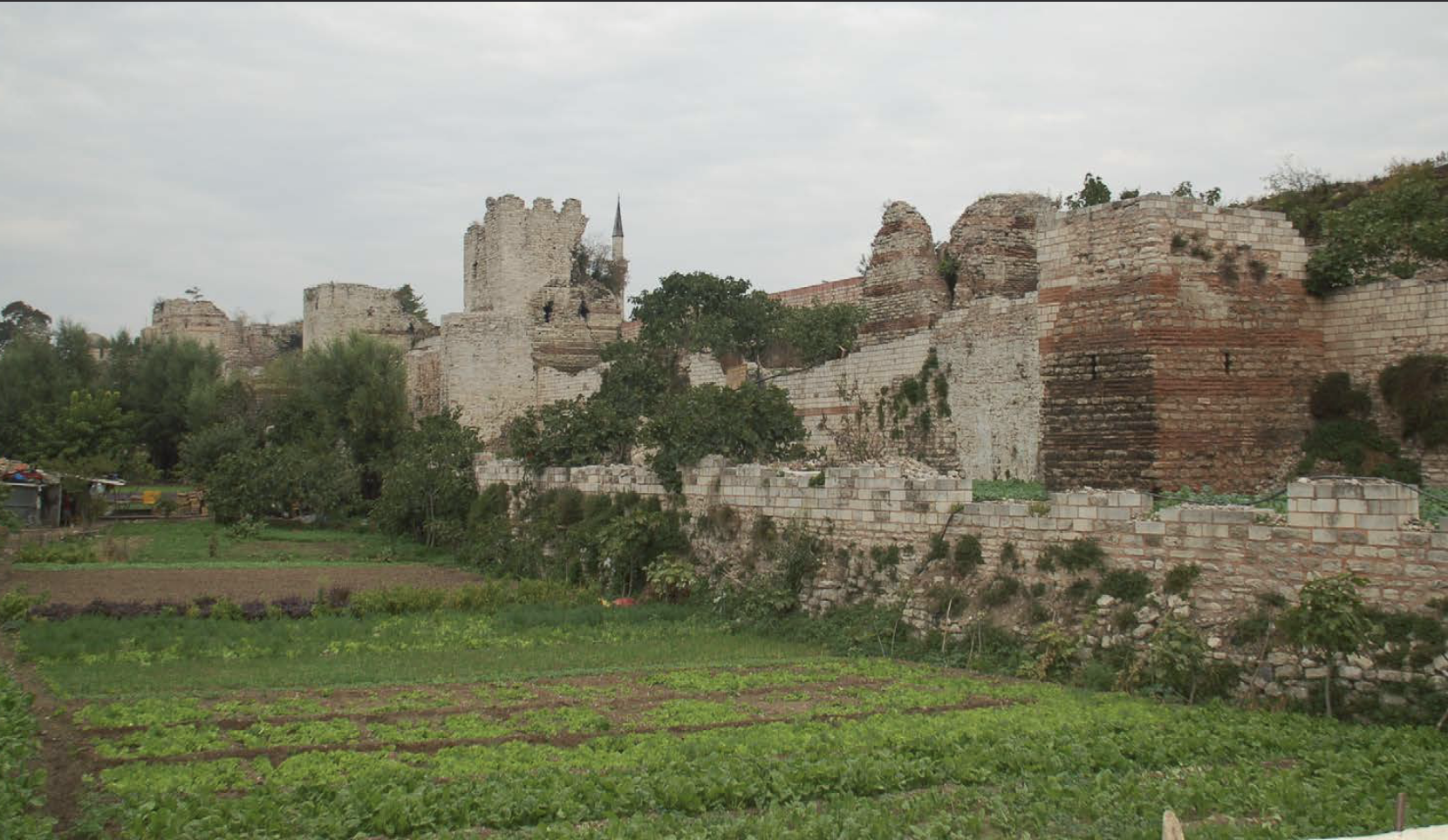

Protected Constantinople for 1000+ years, outer area consisted of market gardens where families could grow food to sell
Land Walls of Theodosius II | Early Byzantine
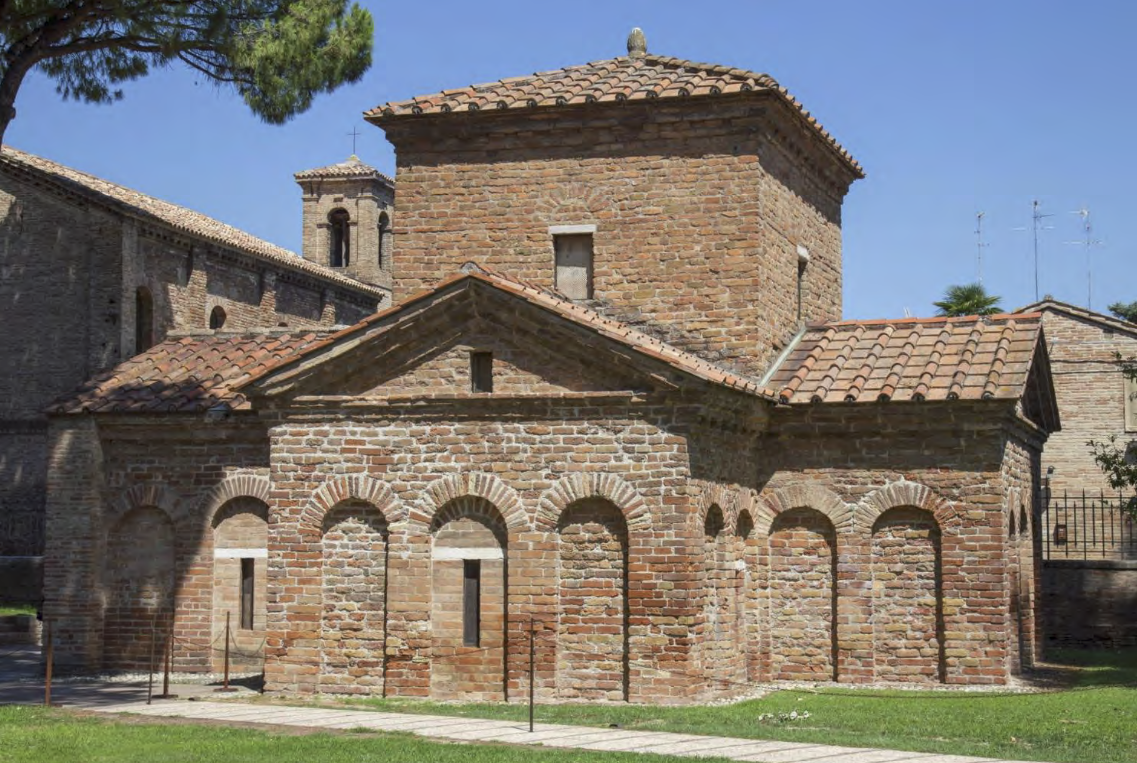

Cross plan (cubes attached to cubes), tomb of Galla Placidia, daughter of Emperor Theodosius I, cross shape is iconastic depiction of Christ
Mausoleum of Galla Placidia | Early Byzantine
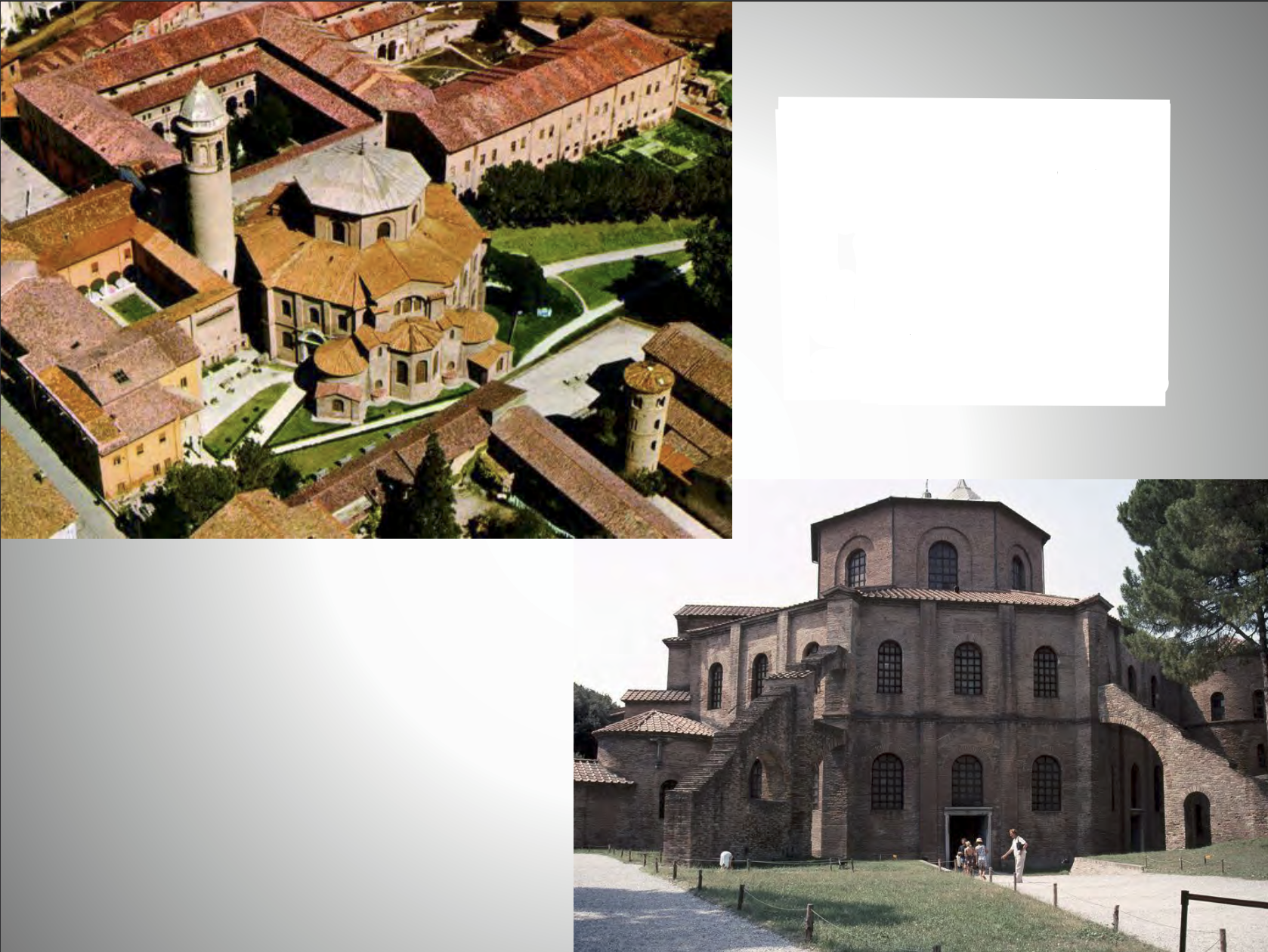

double shell octagon plan, attached to the palace of the Bishop of Ravenna
San Vitale | Justinianic
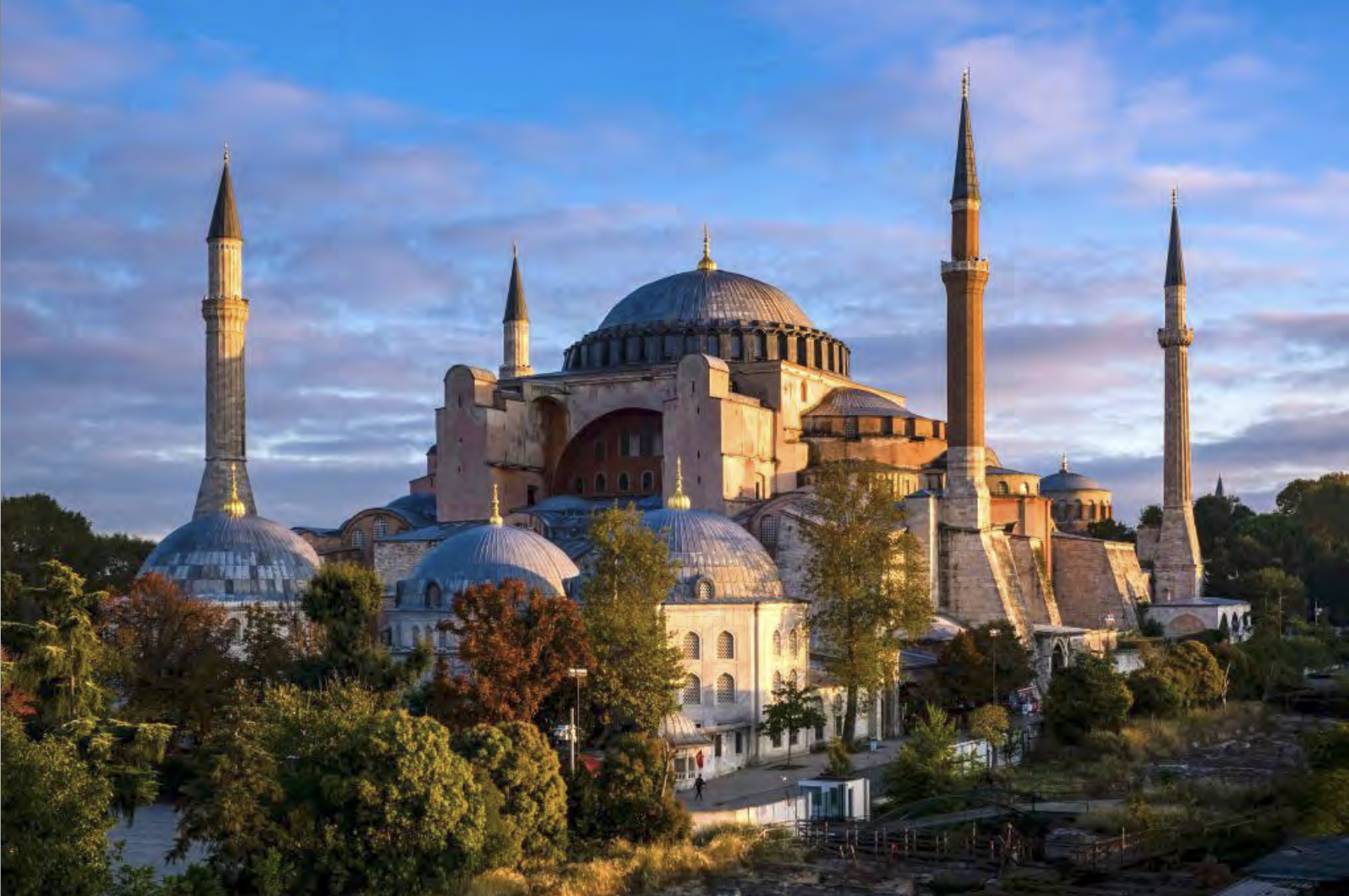

Ecclesiastic power of Byz. Empire and Constantinople, Justininian builds cathedral unlike any other to reestablish his power - both longitudinal (narthex, long nave, apse, nave 2x wide as aisles) and centralized (piers create squared spaces, dome over naos creates focal point)
Hagia Sophia | Justinianic
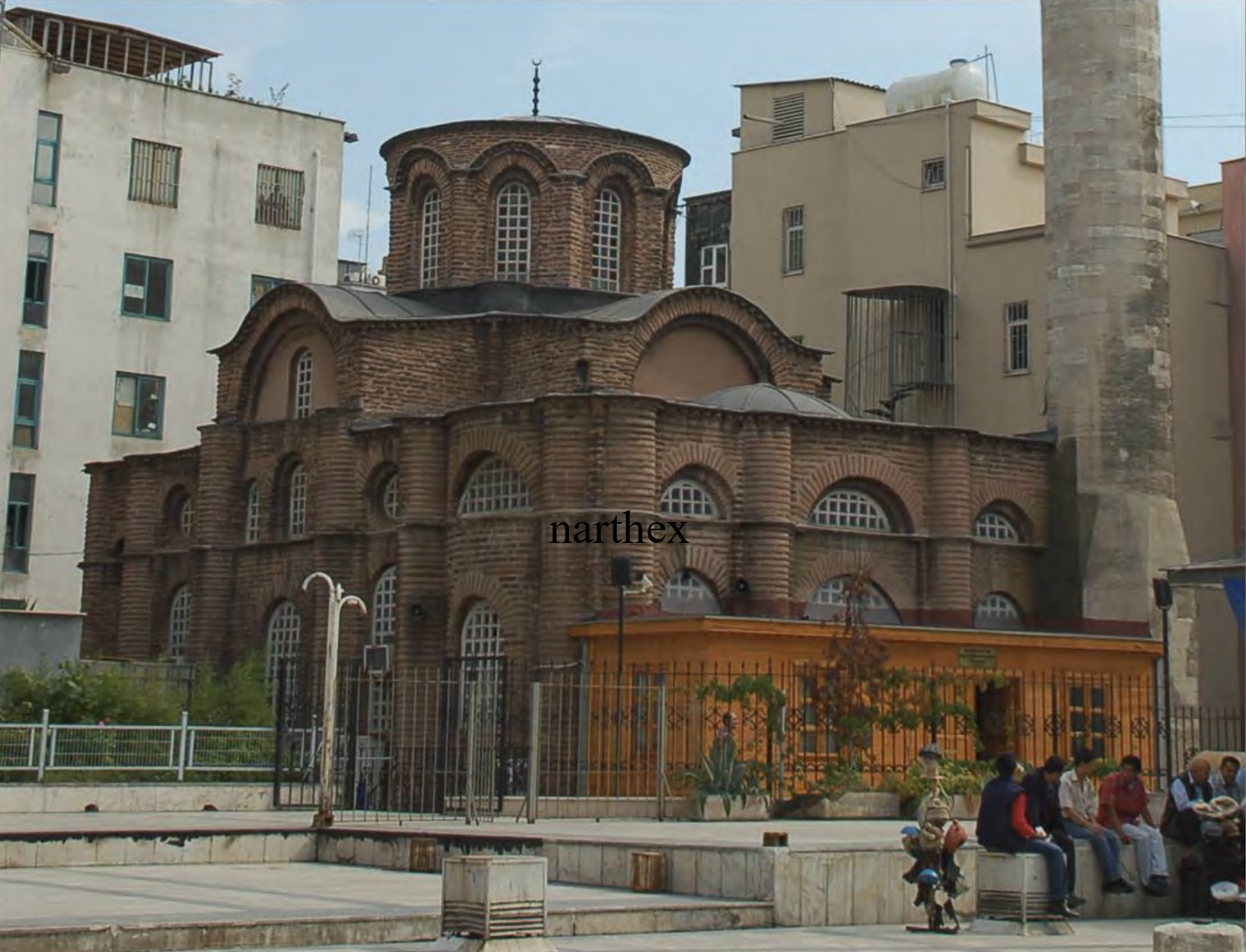


private church for wealthy individuals in imperial family, centralized plan, vaulted, domed, masons playing with brick mortaring (recessed brickwork)
Myrelaion | Middle Byzantine
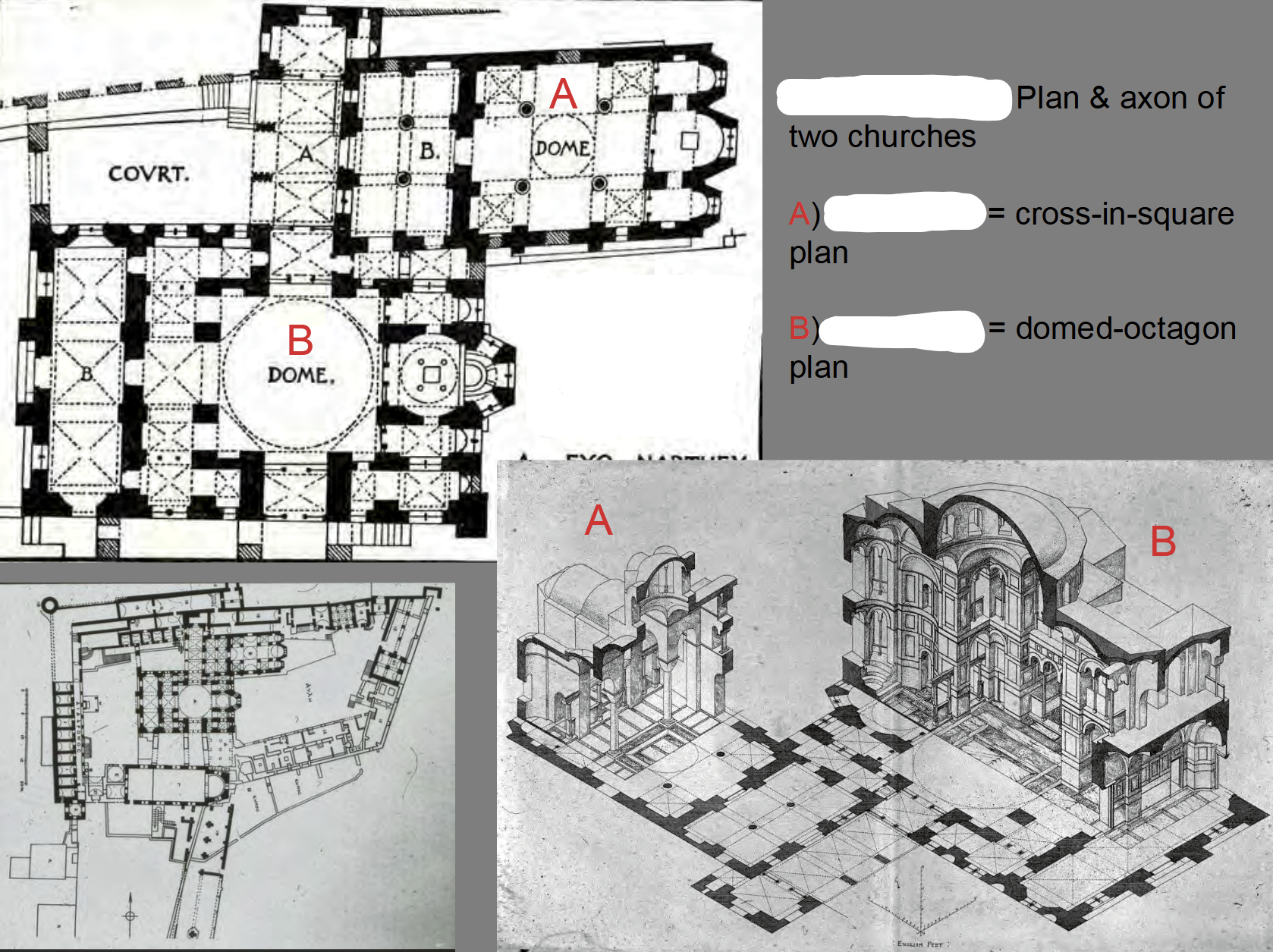
Built as thanks to God for victory in battles, A. Domed Cross-in-Square (old church), B. Domed Octagon Plan (new church)
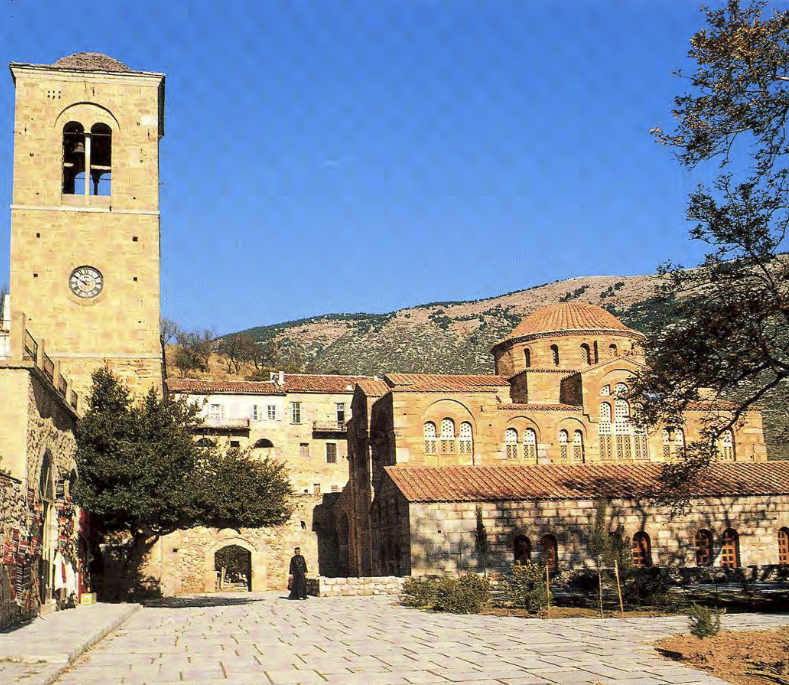
Hosios Loukas Monastery, A. Theotokos B. Katholikon | Middle Byzantine
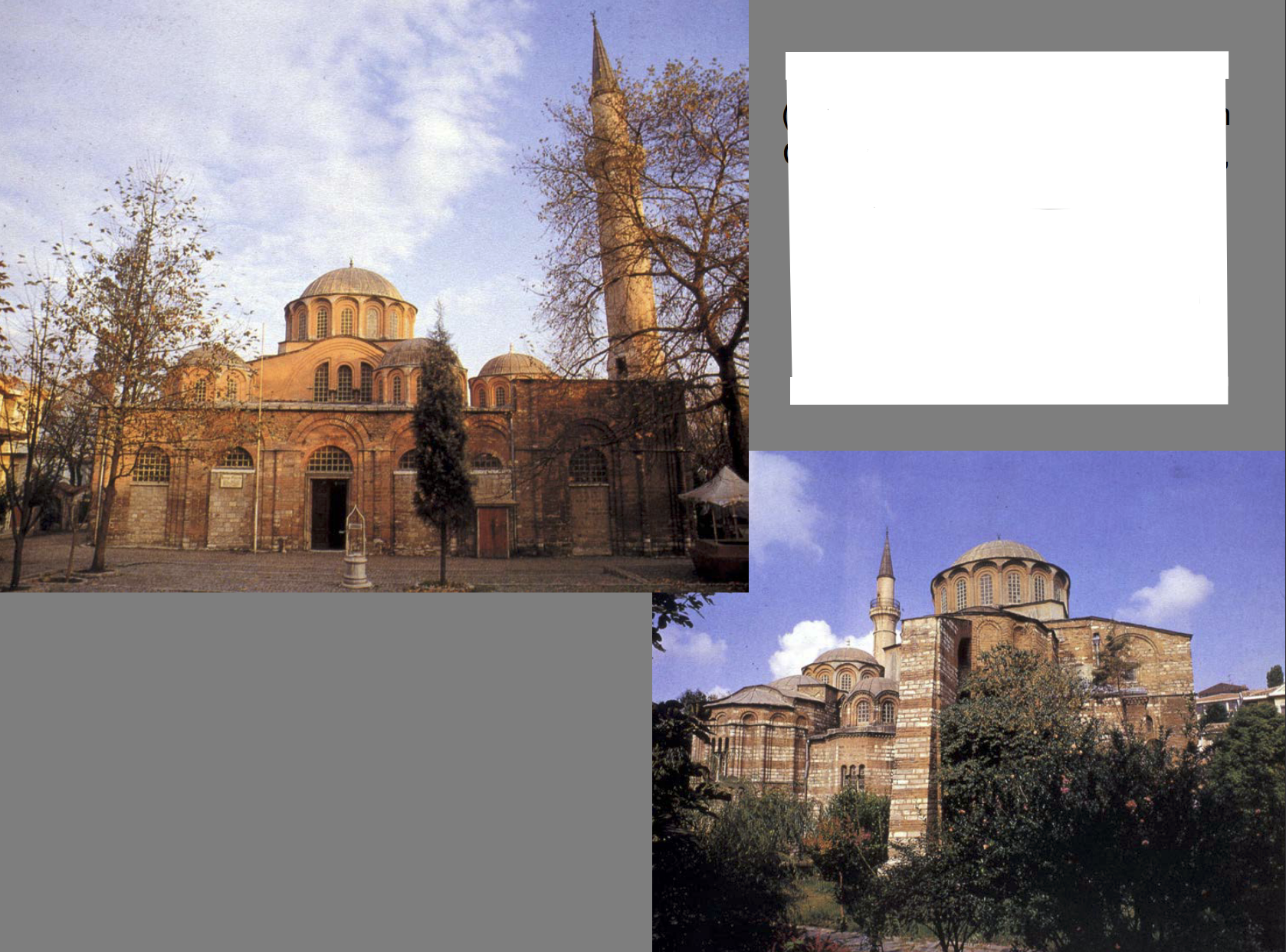


Domed Octagon Plan (plans include a Middle Byzantine Church, no tripartite apse), situated by fertile fields (fertility = Mary, mother of Christ), Theodore Metochites rebuilds and renovates - adds extra narthex, adds paraklession (private side chapels), decorated with frescos in palaiologan style (flowey, three-dimensional, back to natural/classic depiction)
Chora Monastery/Kariye Camii | Late Byzantine
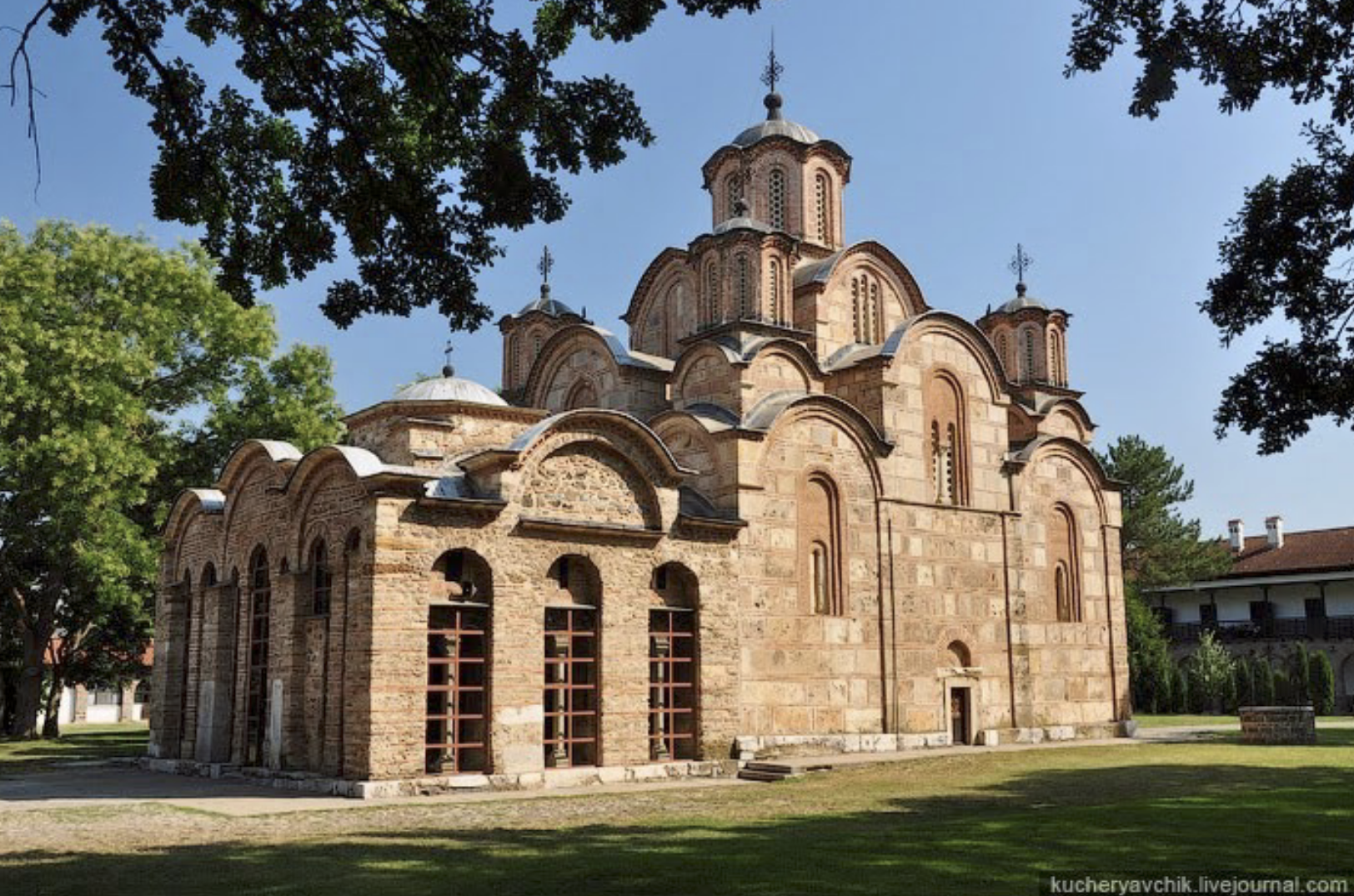

Example of how Byzantine was influencing neighboring regions, Domed Cross-in-Square Plan, cloissone brickwork, using Middle Byzantine plan with added paraklession (private side chapels), highly decorated niches, layers of arching (taller proportions), making statement that says “I am the Emperor of Serbia in the same way as the Emperor of Byzantine”
Church of the Gracanica Monastery | Late Byzantine
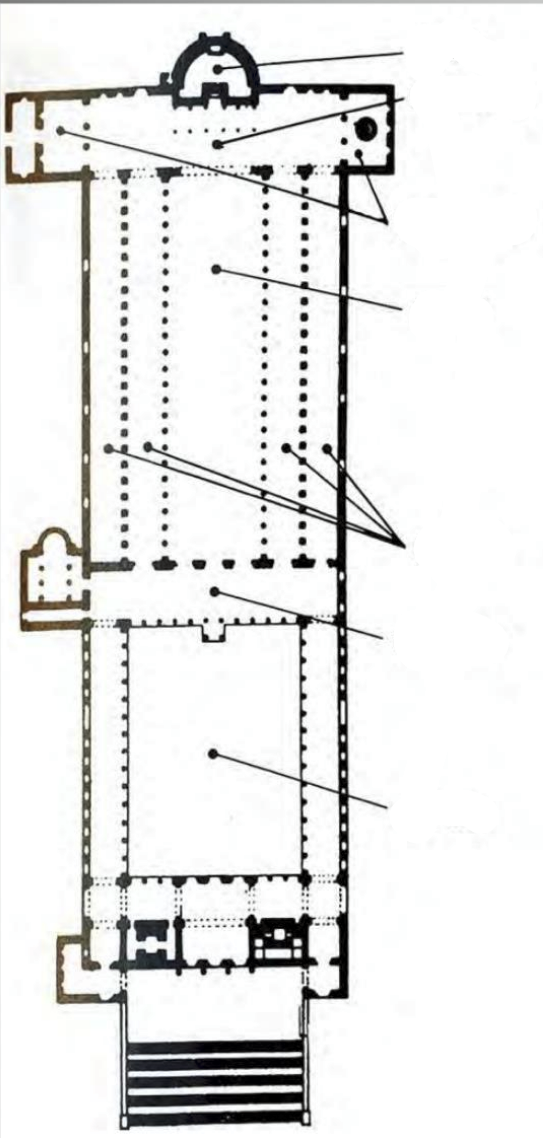
Label top to bottom
Apse, Crossing, Transepts, Nave, Aisles, Narthex, Atrium
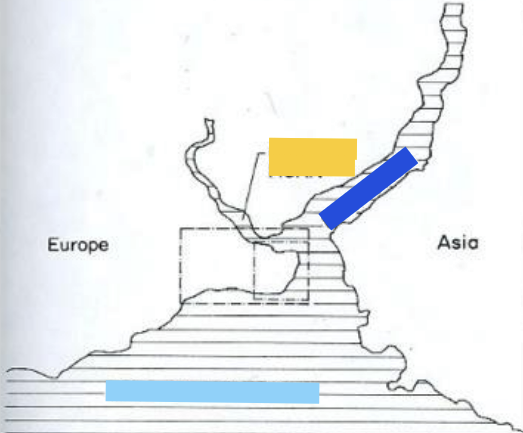
Label yellow, blue, teal
Yellow = Golden Horn
Blue = Bosphorus
Teal = Sea of Marmara
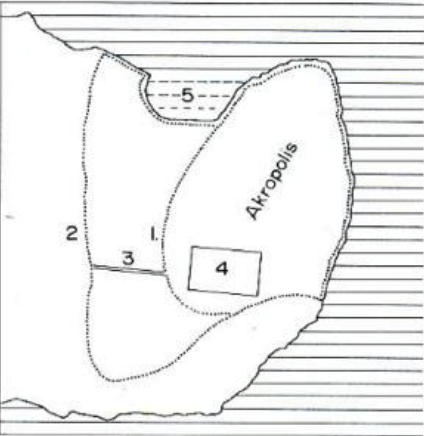
Label order of growth 1-3
Akropolos with Greek colony named Byzantion
2nd Cent. CE Roman city
Constantinian, then Early Byz. city with two lands walls in 4th + 5th Cent.
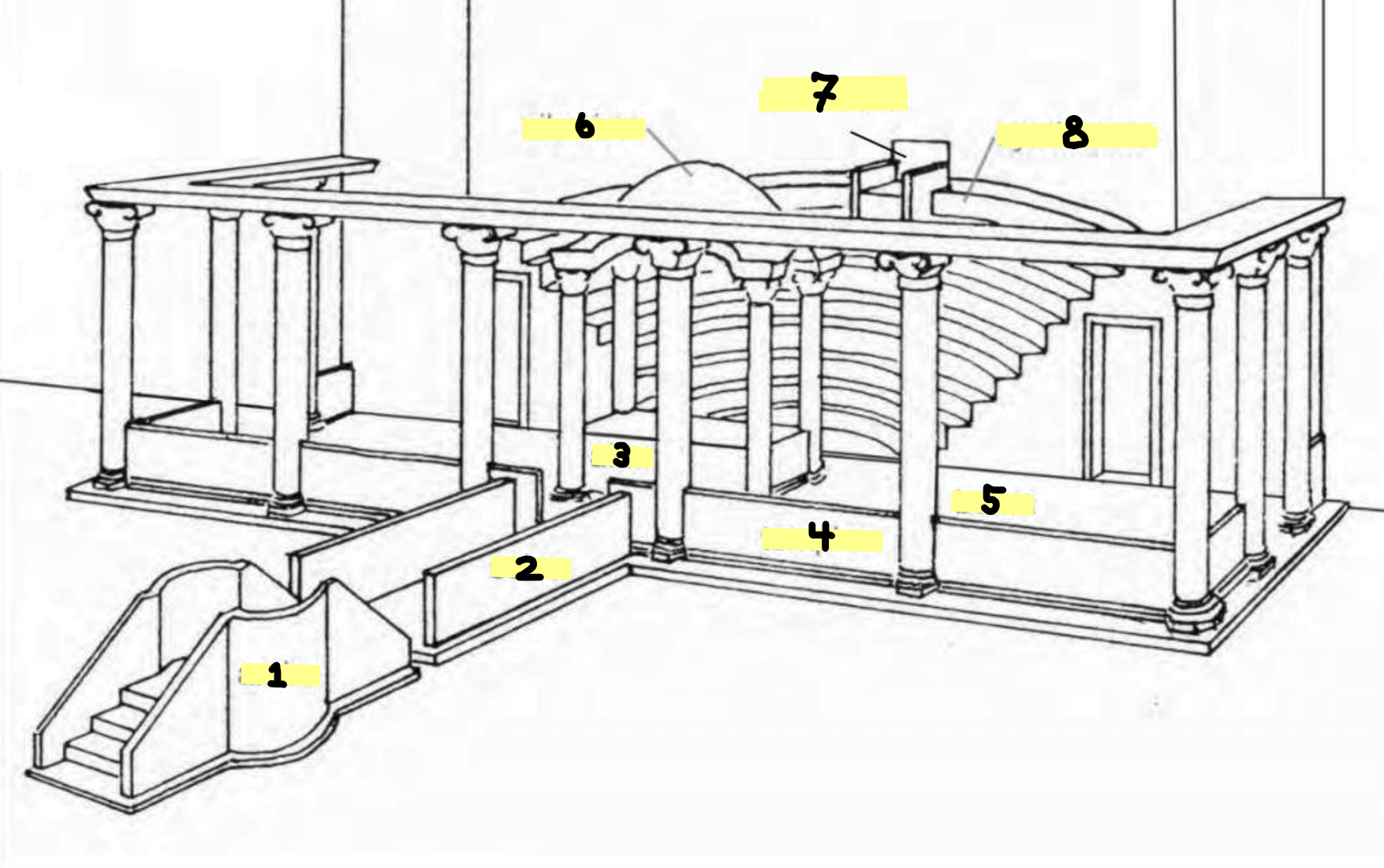
Label 1-8
ambo
solea
altar
templon
bema
ciborium
kathedra
synthronon

Label the parts (left to right, top to bottom)
Narthex, Naos, prothesis, kyrios/main apse, diakonikon
Joggled Voussoirs
offset layers of brick, way of ruler establishing own identity while still establishing unity with the Roman Empire

Temple
Building for the Roman state religion (pagan, polytheistic)
Polytheism
belief/worship of more than one god
Monotheism
belief/worship in only one god
Forum
Centre of day-to-day life in Rome; commerce, politics, religion, law, and public meetings/events happened here
Basilica
Colonnaded hall with a longitudinal axis, usually with an apse on at least one side (multi-function building)
Centralized Planning
having walls equidistant from a center point (features: piers create squared spaces, dome over naos that creates focal point)
Longitudinal Planning
having a single, axial focus and line of the plan (features: narthex, long nave leading to apse, nave 2x as wide as aisles)
Apse
Vaulted semi-circular termination of a building
Coffer
Decorative, patterned indentation in the surface of a ceiling or arch
Oculus
Circular opening in a dome (or wall)
Revetment
decorative facing (stone/stucco/marble/etc) that covers a surface constructed of a less decorative material (brick/concrete/etc)
Hypocaust
under-floor heating system
Insula
A tenement/apartment block, mixed use building (restaurants, shops, communal kitchens and latrines, with apartments on upper floors)
Cardo
Main north-south street that meets at center with decumanus, buildings designed around these streets
Decumanus
Main east-west street that meets at center with cardo, buildings designed around these streets
Castrum
Roman military camp. Rectangular plan with cardo (main north-south street) and decumanus (main east-west street) that meet at center
Peristyle House
Residence organized around an open courtyard or garden surrounded by a colonnade, with rooms stemming off; can have several interior courtyards
Syncretic/Syncretism
Combination or coexistence of characteristics of multiple cultures within one broader society or group
Mystery Cult
Religions in which participation is reserved for those who have learned the beliefs and undergone initiation ceremony
Domus Ecclesiae
“house-church”, Early Christian space for worship, teaching and baptism
Chi Rho
monogram for Christ (it is the first two letters in Greek: Χριστος); often combined with the
cross. It is an aniconic representation of Christ, as the cross was.
Spolia
reused materials (marbles, sculpture, fresco, etc), taken for victory or economic purposes
Clerestory
area of nave wall extending above the side aisles
Catechumen
those pledged to the Church, but not yet fully initiated (i.e. not yet baptized)
Martyrium
shrine, place of remembrance for an event or life of a (holy) person
Ambulatory
Semicircular/polygonal circulation spaces enclosing an apse of straight ended sanctuary
Tessera
small, cubic pieces of cut stone or glass used to make up mosaics
Relic/Reliquary
physical remain of a holy person. Place or event (bone fragment, piece of a
shroud, earth from a holy site); the box made to contain such relics
Mausoleum
monumental burial space
Sepulcher
burial place
Anastasis
Greek, meaning “resurrection”; the term for the resurrection of Jesus Christ at the site
of his tomb in Jerusalem, one of the events of the Passion of Christ
Mese
the main, processional boulevard that led from Constantinople’s gate to the heart of the imperial quarter
Sphendone
the semi-circular end of a hippodrome; the massive supporting structure at the Constantinople hippodrome
Spina
the elevated plinth (“spine”) that ran down the center of the hippodrome
Obelisk
tall, four-sided monument with a pyramidal top made in ancient Egypt (one stood
in the hippodrome on a newly carved base)
Kathisma
imperial box at the hippodrome, which connected directly to the imperial Great
Palace
Bostan
market garden at the edge of the land wall of Theodosius
Aqueduct
infrastructure to transport water; typically arched stone/brick construction with a covered channel at its top
Palace Chapel
A chapel associated with a residence (esp. that of an emperor) and generally designated for private use by its owner or occupants
Double Shell Octagon
a building whose outer walls and interior space are created with two concentric octagons.
Pendentive
Concave sections of a sphere, resting on arch (not flat walls) used to transition from a rectilinear base to a rounded form (a dome)
Basket Capital
a capital of the Byzantine style with interlaced bands like those of a basket
Chancel Barrier/Templon
a barrier separating the nave from the sanctuary near the altar.
Theotokos
(‘bearer of God’); epithet of the Virgin Mary as the mother of God domed cross-in-square plan
Recessed Brick
Brickwork where some bricks sit further back than others
Cloisonné Brick
brickwork with a mix of stone and brick
Dentilation
Type of molding, small rectangular/tooth-like cube used in a repeated series as decoration
Pseudo-Kufic
style of decoration that imitates the Arabic script, especially Kufic (can indicate victory over Islamic states, admiration for the decor style, or indicates a belonging to a larger culture of design)
Iconostasis
Icon-filled chancel barrier between the nave and bema
Katholikon
The major church building of a monastery, corresponding to a conventual church in Western Christianity.
Naos
main worship space between narthex and sanctuary, implies a centrally planned space
Kyrios Apse
The main apse
Prothesis
Left/North apse, where communion is prepped and eucharist is stored (preparation area)
Diakonikon
Right/South apse, housed liturgical garments and sacred texts (treasury/storage)
Sanctoral
having to do with saints or the holy
Pantokrator
“all-seeing” or “all-powerful” or “all-embracing”: bust image of Christ depicted as stern protector of the faithful; holds bible in left arm, right hand is raised in a speaking gesture (seen in domes of churches, but also icon and manuscript paintings
Selective Narrative
Mathews’ term for the set of images in the Middle Byzantine church that focuses on Christ’s (human) life and especially his body to emphasize the post-Iconoclastic, Orthodox position that Christ was both divine and human in nature
Palaiologan
period of a Late Byzantine imperial dynasty (the Palailogos family), that connotes the last, late flowering of Byzantine culture and art
Parekklesion
side chappel
Arcosolia
niches covered by arches, often used as spaces for burial sarcophagi
Anastasis
resurrection (specifically refers to Christ’s resurrection, and the ‘Harrowing of Hell’ Christ bringing people put of Hell with him at the Resurrection
Roman Kit
Provided unity, affirmed power, met needs of the people, defined inside vs outside,
Remember parts with MCBBEFT - Market, Commemorative monument, Basilica, Baths, Entertainment, Temple