Wall and Roof Framing Terminology
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Construction Technologies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
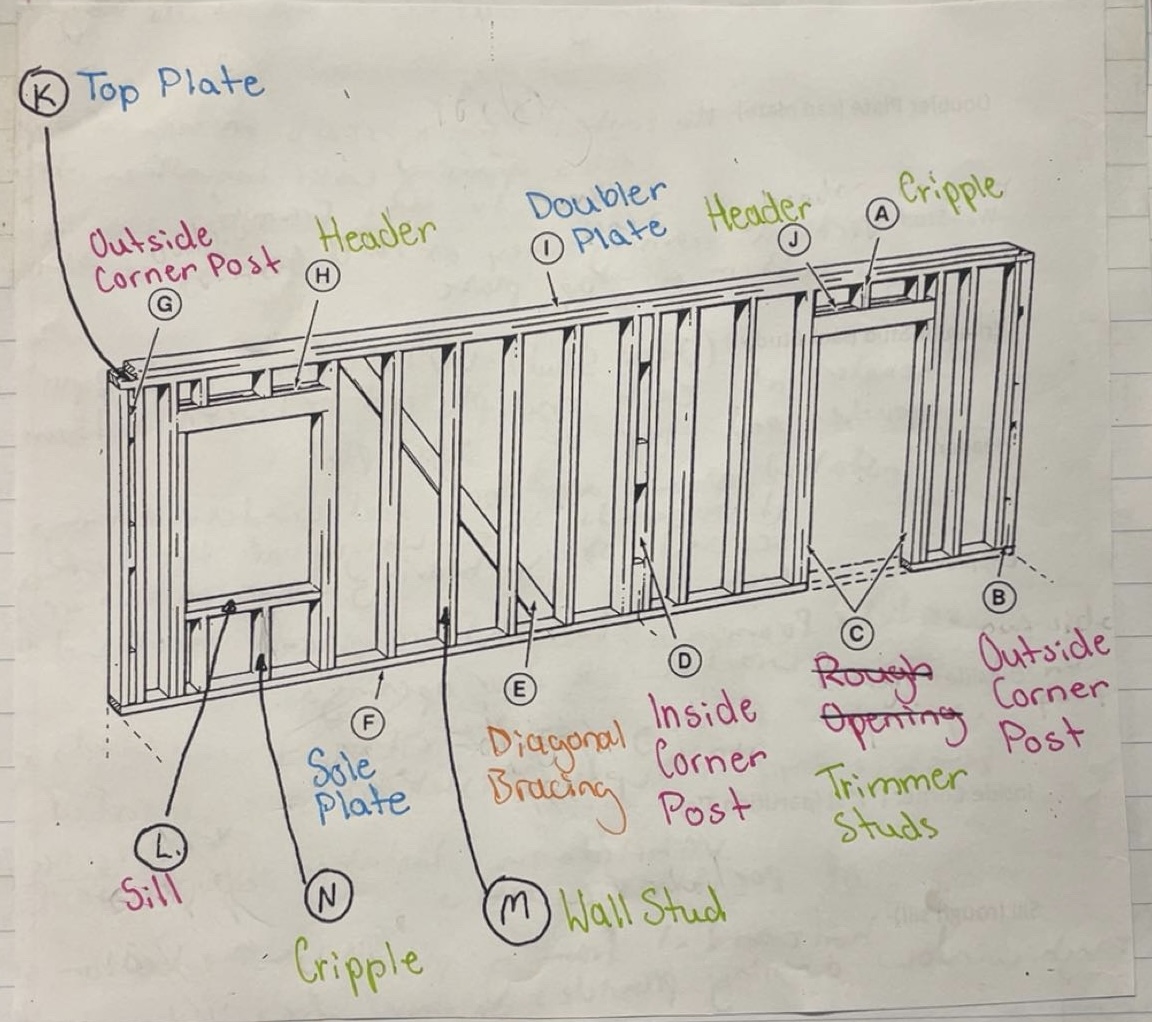
Sole Plate
Horizontal framing that rests on top of the subfloor and holds bottoms of all studs together
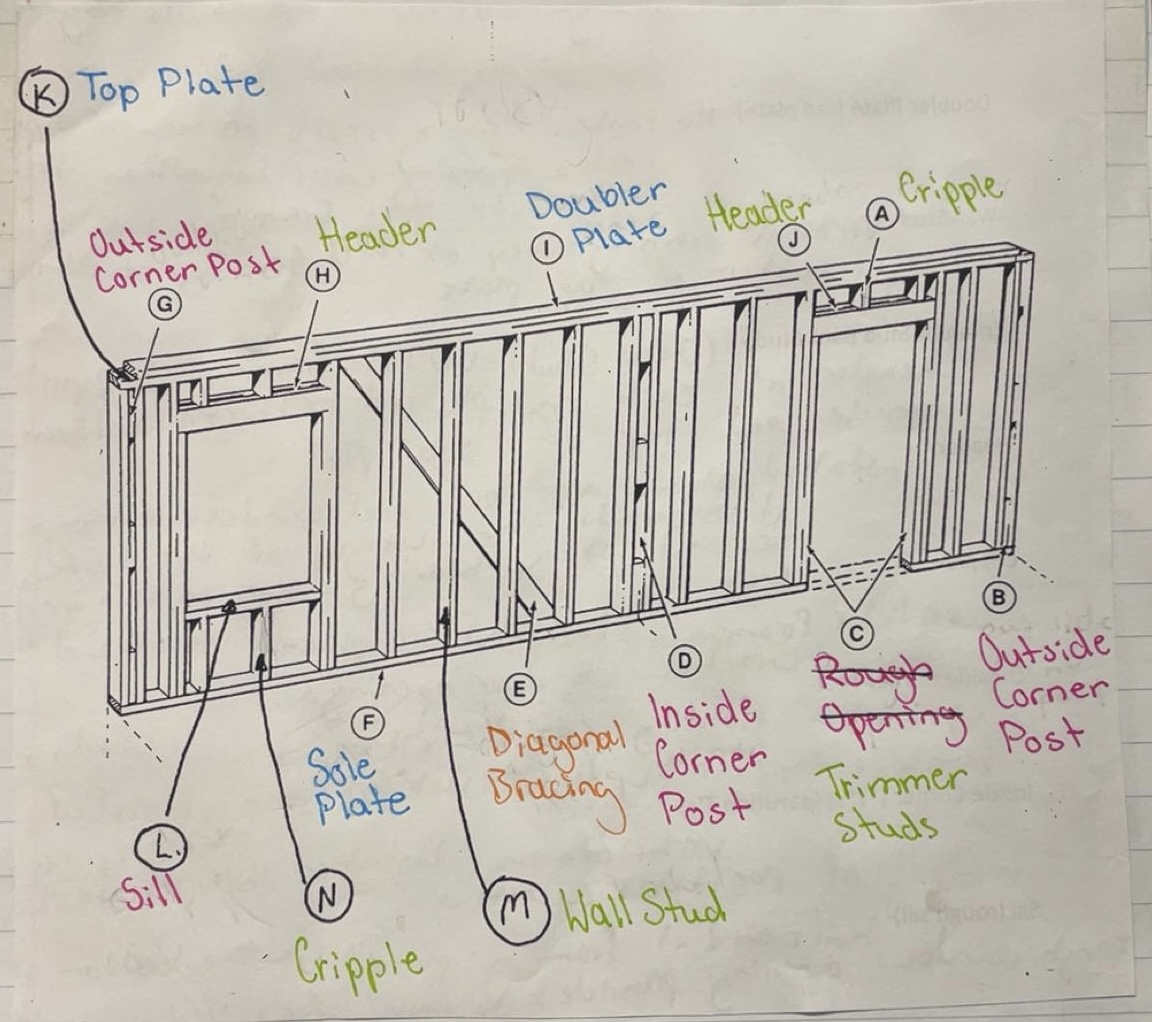
Top Plate
Horizontal framing that holds top of all studs together
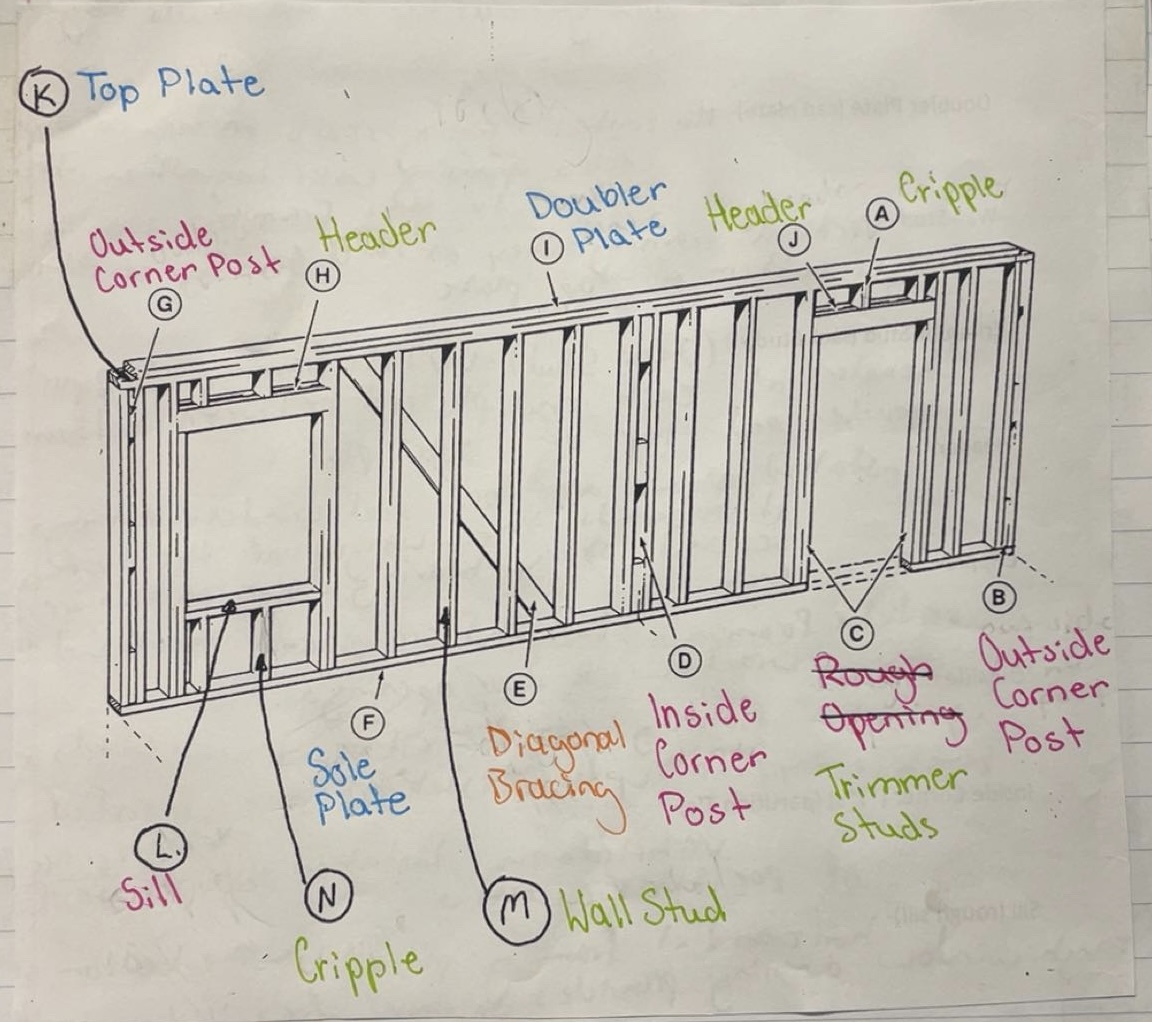
Doubler Plate (Cap Plate)
Horizontal framing that rests on top of the top plate. Locks opposing walls together. Trusses and rafters fasten to this framing

Wall Stud
Vertical framing that extends from the top of sole plate to the bottom of top plate

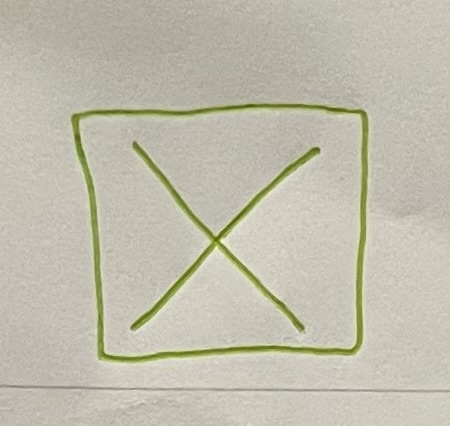
Trimmer Stud (Jack Stud)
Vertical framing that supports header at each end and is placed between bottom of header and top of sole plate
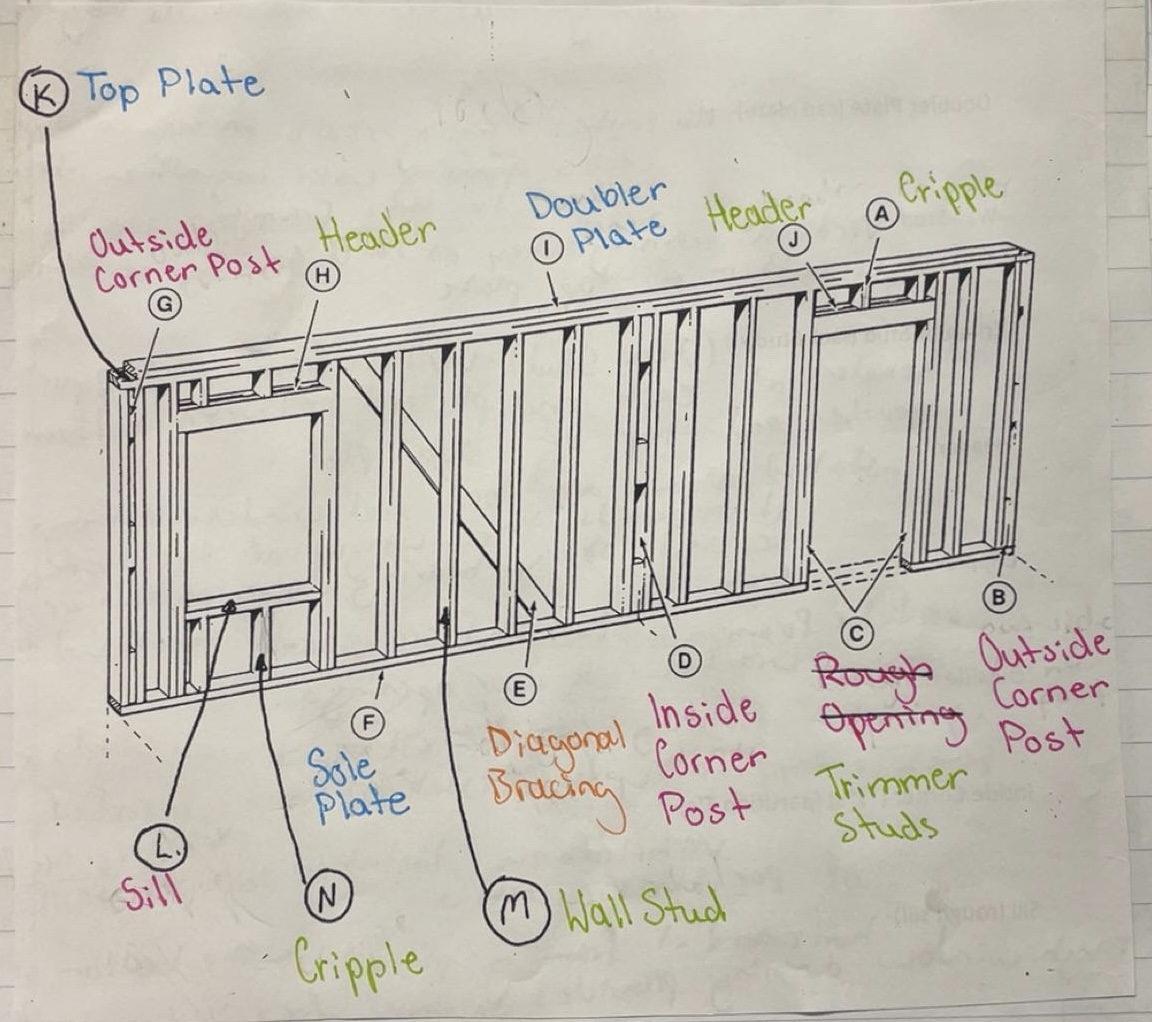
Header
Installed above all door and window openings. It supports the weight of the roof and/or second story bearing down on this section of wall

Cripple
Vertical framing - studs that are placed above or below door and window openings
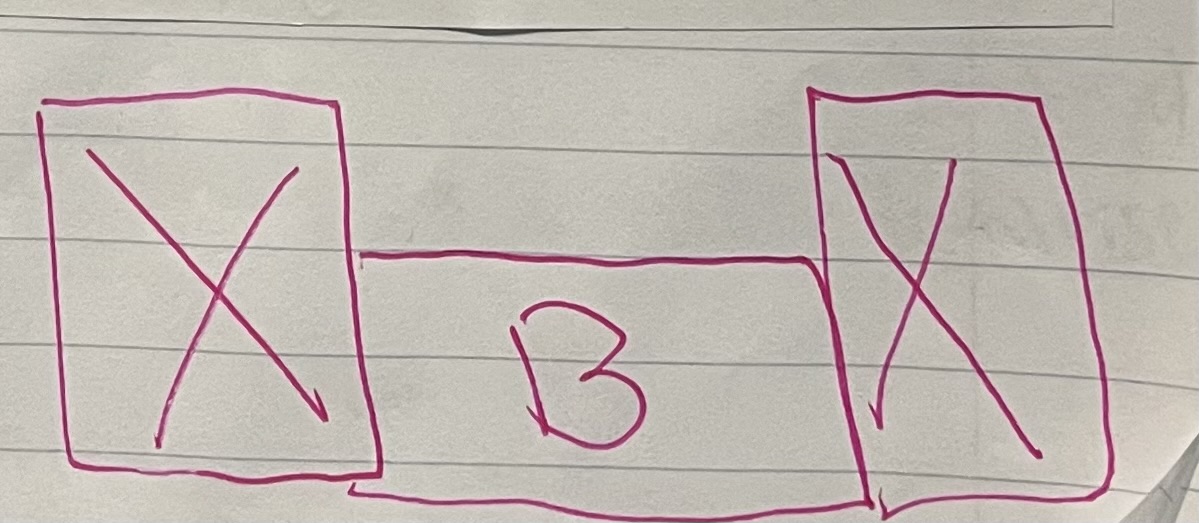
Outside Corner Post
Vertical framing composed of 2 wall studs and 3 blocks typically 16’ installed at each end of exterior walls

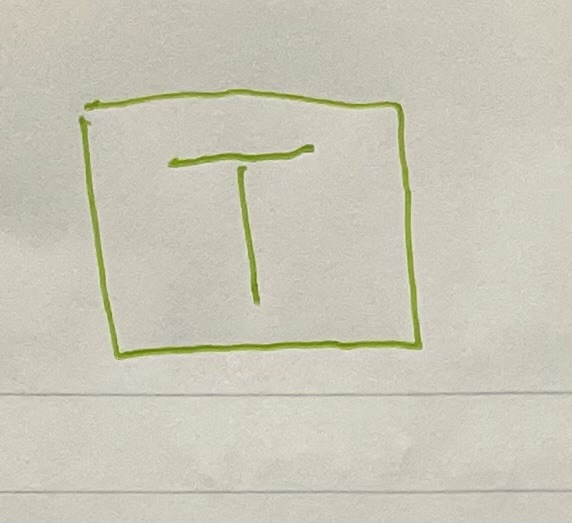
Inside Corner Post (“T”s) (Partition T’s)
Vertical framing installed at intersections of partition walls
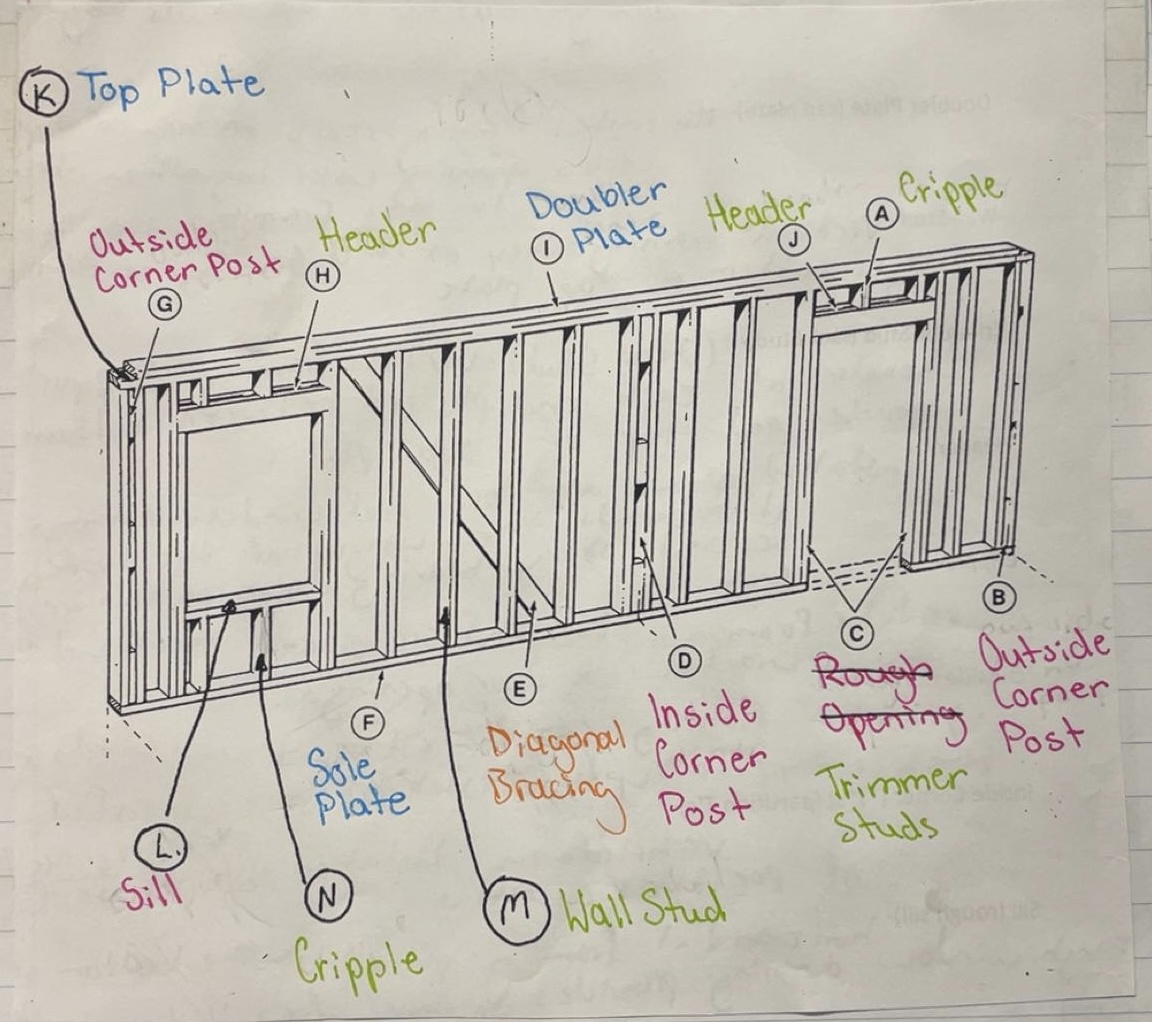
Sill (Rough Sill)
Horizontal framing placed at the bottom of the rough window opening, provides support for window unit
Rough Opening
The allowance made for framing in doors and windows.
Doors Width of Opening
Measured between trimmer studs and height of opening is measured between top of subfloor and bottom of header
Windows Width of Opening
Measured between trimmer studs and height is measured between bottom of header and top of sill.
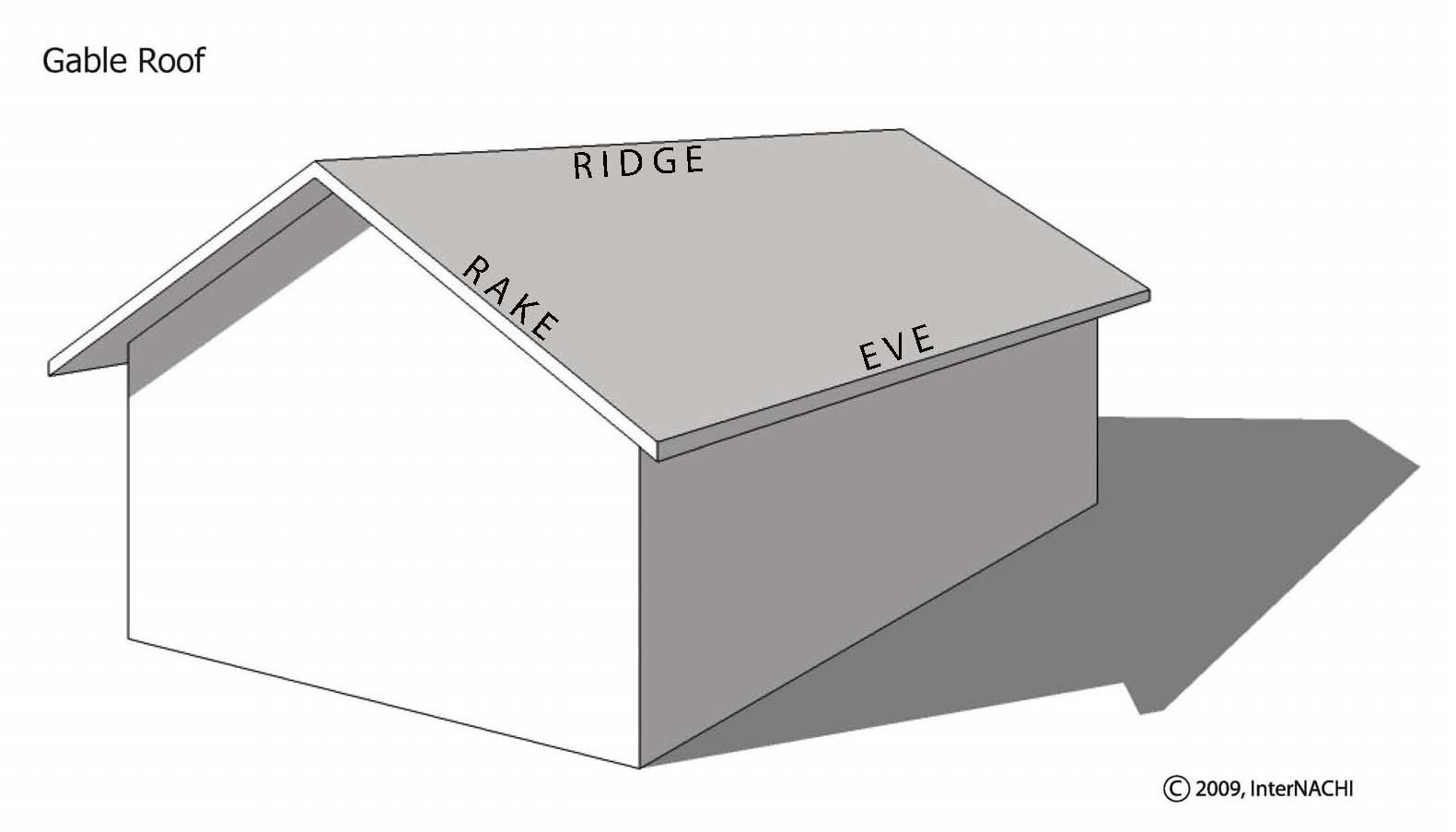
Gable Roof
2 Sloping sides
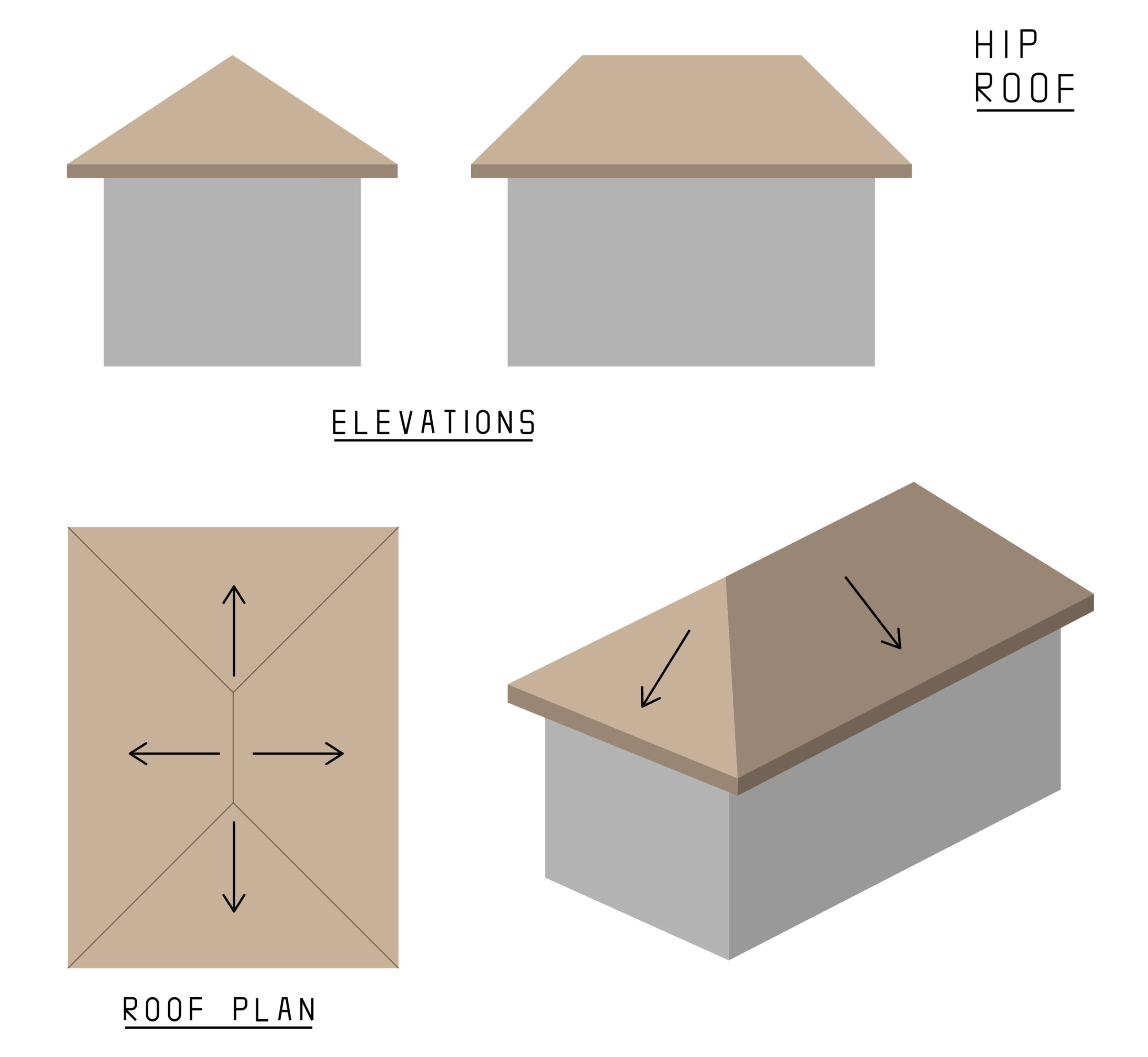
Hip Roof
4 Sloping sides
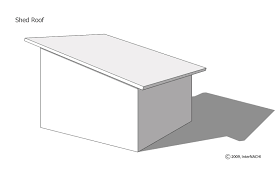
Shed Roof
1 Sloping side
Total Span
The overall width of the building
Total Run
1/2 the distance of the span
Total Rise
Distance from top of the plate to top of the ridge
Unit Rise
the # of inches on a roof rise for every feet of run
Unit Run
12’’ (based on a Gable Roof)
Allowable Span
The distance from the ridge to wall plate
Deadload
Weight of material used to construct roof
Liveload
Temporary loads that a roof must be able to support during construction process, also weather.
Pitch
the slope of the roof
Gable Roof
Common Rafter
Ridge Board
Gable Studs
Common Rafters
Extend from top of wall plate to the ridge board
Ridge Board
Placed at peak of the roof, it providing nailing surface for tops of all common rafters
Gable Studs
Vertical Stud that provides nailing for sheathing at Gable ends
Theoretical length
Length of rafter from park to heel plumb (outer wall plates)
Actual length
minus 1/2 the thickness of the ridge board
Common Rafter (3 Plumb Cuts)
Ridge plumb cut
Heel plumb cut
Tail plumb cut
Birds Mouth
The notch created by the intersection of the heel plumb cut and the seat cut.
Seat Cut
Should equal the width of you top plate
Stand
Referring to the amount of lumber that should remain above your birds mouth