Human AP Final Exam Review CH.9
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Where is skeletal muscle located?
Attached to bones or skin (e.g., facial muscles).
Where is cardiac muscle located?
In the walls of the heart.
Where is smooth muscle found?
In walls of hollow organs (except heart), eye muscles, airways, and large arteries.
Describe skeletal muscle cells.
Long, cylindrical, multinucleate, with striations.
Describe cardiac muscle cells.
Branching chains, uni- or binucleate, with striations.
Describe smooth muscle cells.
Spindle-shaped, uninucleate, no striations.
Is skeletal muscle voluntary or involuntary?
Voluntary (except for some like the diaphragm).
Is cardiac muscle voluntary or involuntary?
Involuntary (controlled by the heart's pacemaker and nervous system).
Is smooth muscle voluntary or involuntary?
Involuntary.
What is excitability in muscle tissue?
The ability to respond to stimuli (like neurotransmitters).
What is contractility in muscles?
The ability to shorten forcefully when stimulated.
What is extensibility in muscle tissue?
The ability to stretch without being damaged.
What is elasticity in muscle tissue?
The ability to return to original length after stretching.
What are four functions of muscular tissue?
Movement, posture, stabilize joints, generate heat.
What neurons stimulate skeletal muscle?
Somatic motor neurons.
What connective tissue wraps the whole muscle?
Epimysium.
What wraps bundles of muscle fibers (fascicles)?
Perimysium.
What wraps individual muscle fibers?
Endomysium.
What is fascia?
Dense connective tissue that surrounds muscles, under the skin.
What is a tendon?
A cord that connects muscle to bone.
What is aponeurosis?
A broad, flat tendon.
What is the origin of a muscle?
The fixed starting point of the muscle.
What is the insertion of a muscle?
The moving end of the muscle during contraction.
What is sarcolemma?
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
What is sarcoplasm?
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber, contains glycogen and myoglobin.
What are T-tubules?
Tunnels that carry action potentials into the muscle fiber.
What does the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) do?
Stores calcium ions; releases them to trigger contraction.
What are myofibrils?
Rod-like elements in muscle fibers made of sarcomeres.
What is a sarcomere?
The smallest contractile unit of a muscle fiber, from Z disc to Z disc.
What proteins make up thick and thin filaments?
Myosin (thick) and actin (thin).
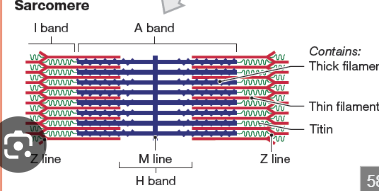
What is the A band in a sarcomere?
Dark band where actin and myosin overlap.
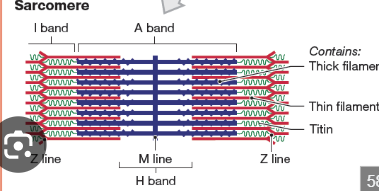
What is the I band in a sarcomere?
Light band with only actin.
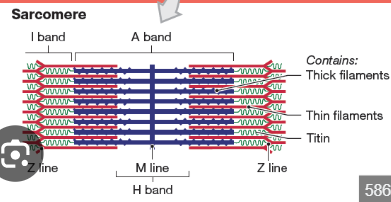
What is the H zone in a sarcomere?
Area with only myosin.
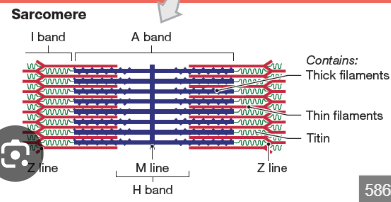
What is the M line?
The center line of the sarcomere, holds myosin in place.
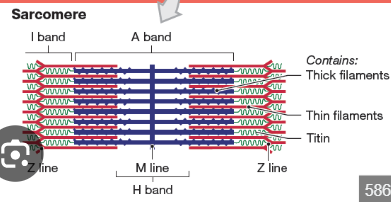
What is the Z disc?
Boundary of each sarcomere, connects actin filaments.