Week 5 - Respiratory System (Trachea, Branchial Tree, The Lungs and Alveoli)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
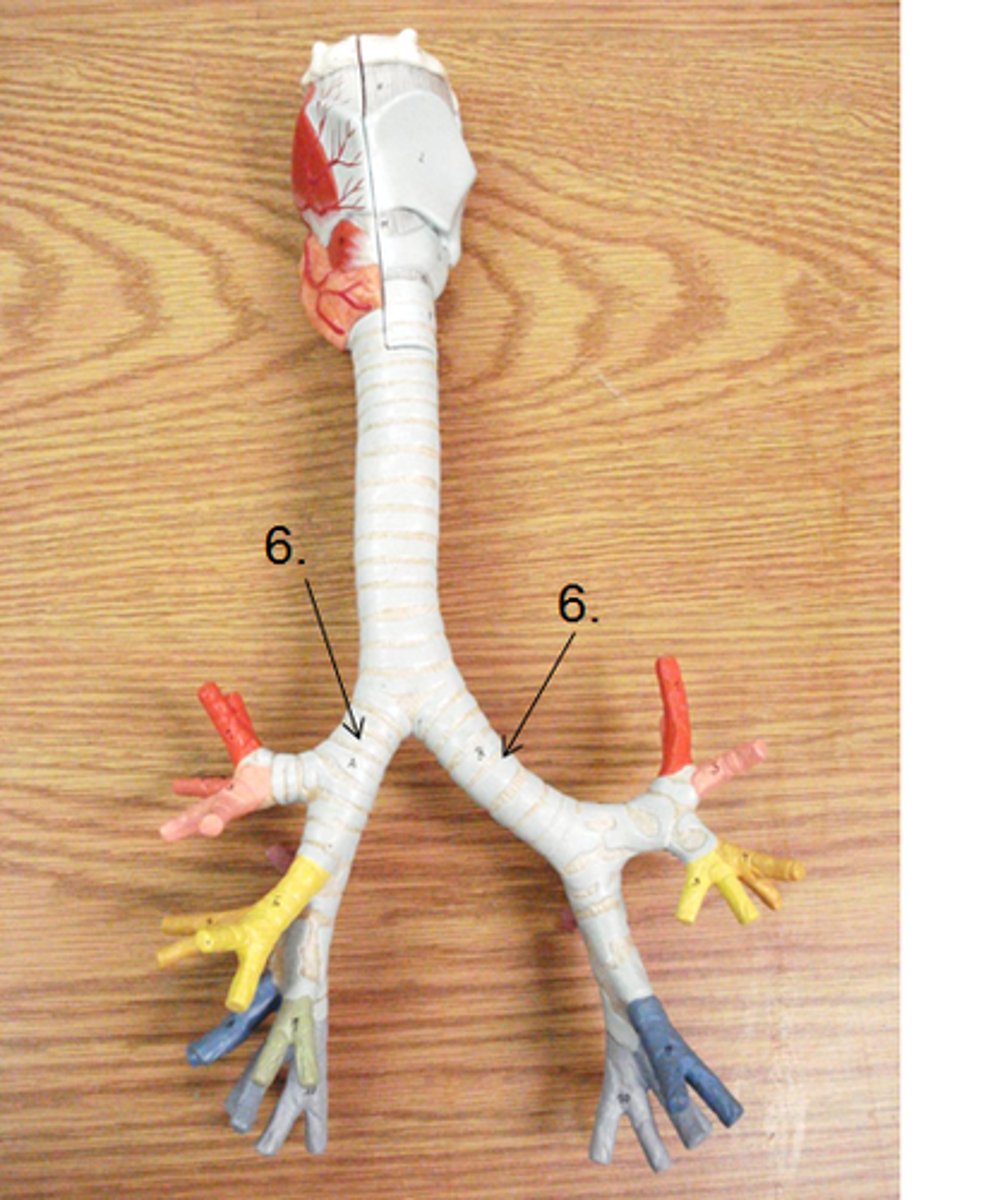
trachea
tube composed of cartilaginous rings and supporting tissue that connects the lung bronchi and the larynx; provides a route for air to enter and exit the lung
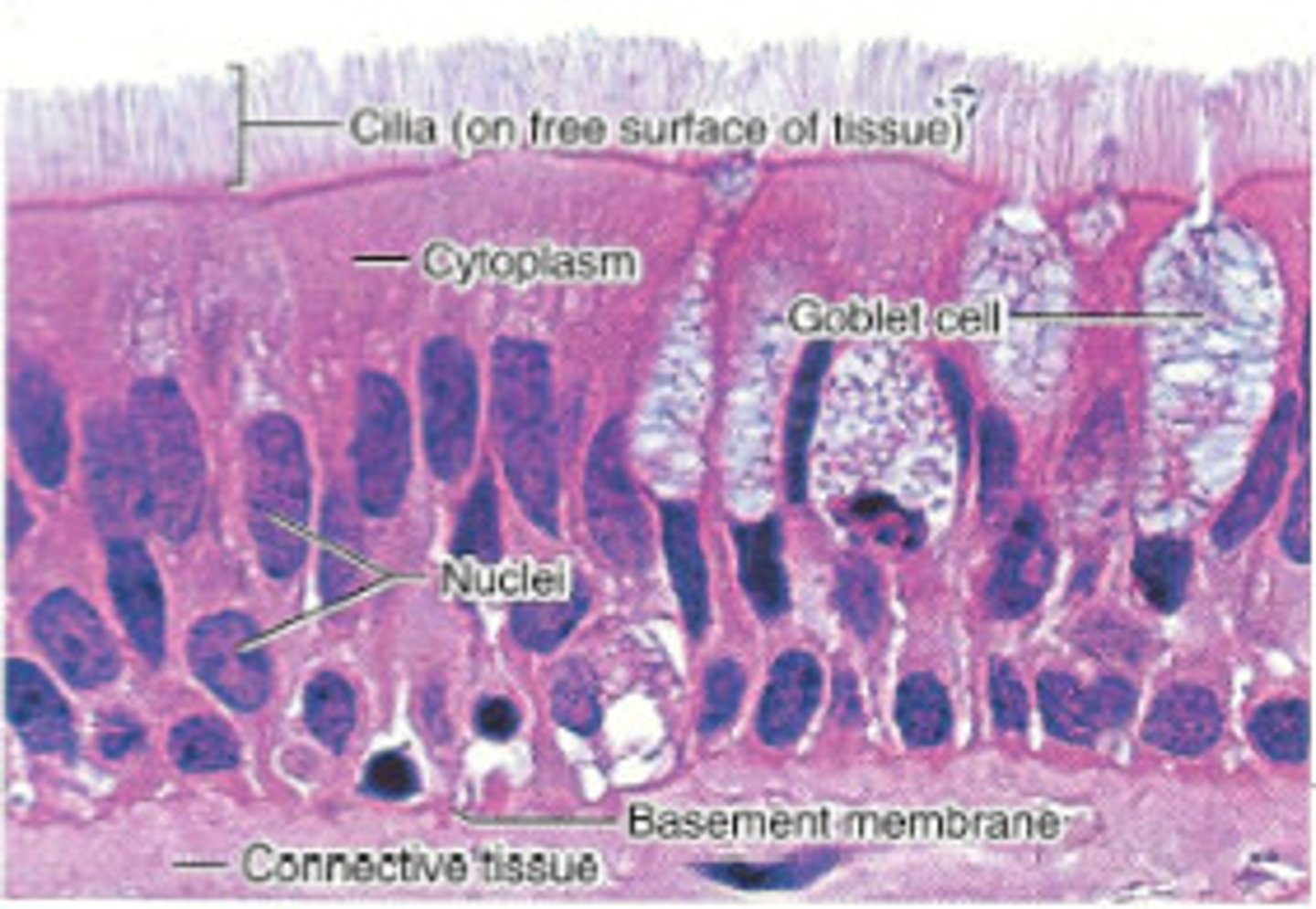
respiratory epithelium
ciliated lining of much of the conducting zone that is specialised to remove debris and pathogens, and produce mucus
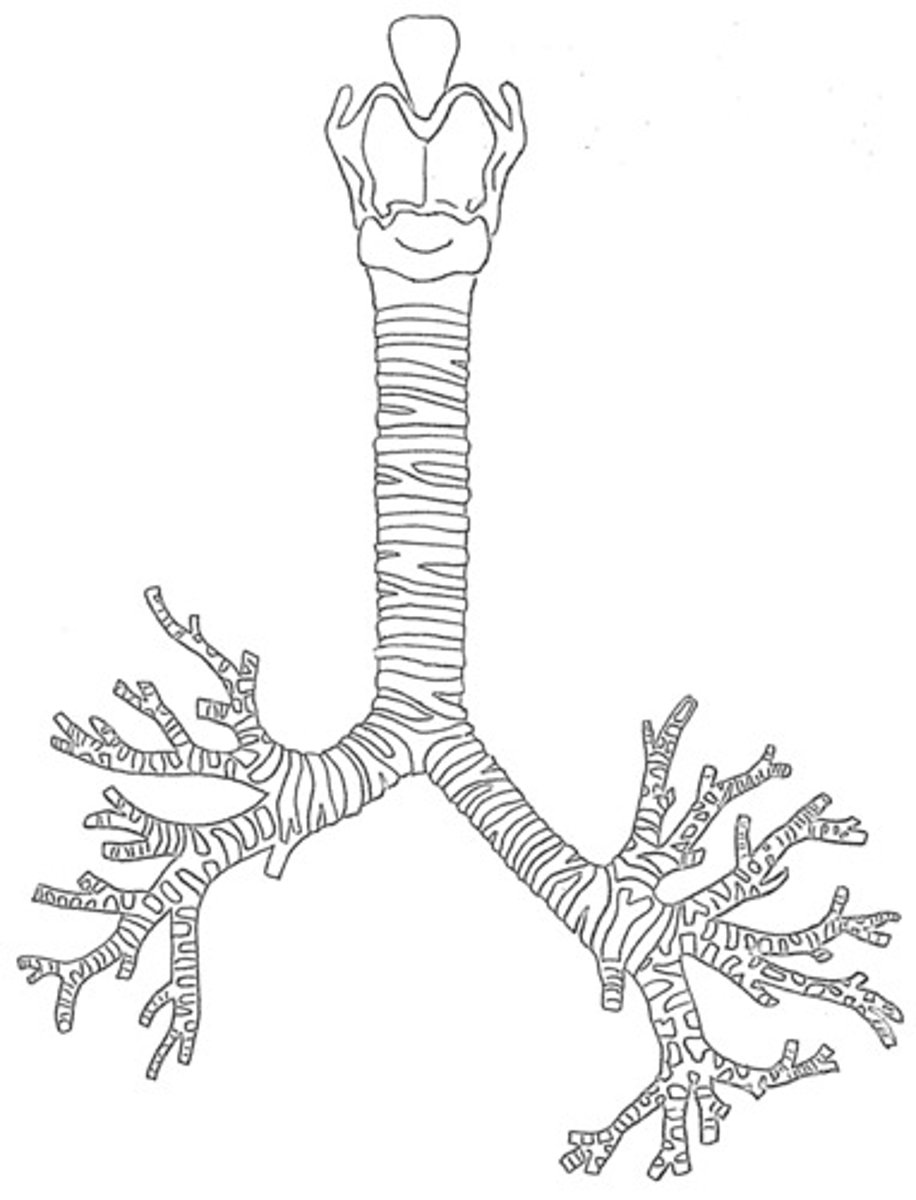
bronchial tree
collective name for the multiple branches of the bronchi and bronchioles of the respiratory system
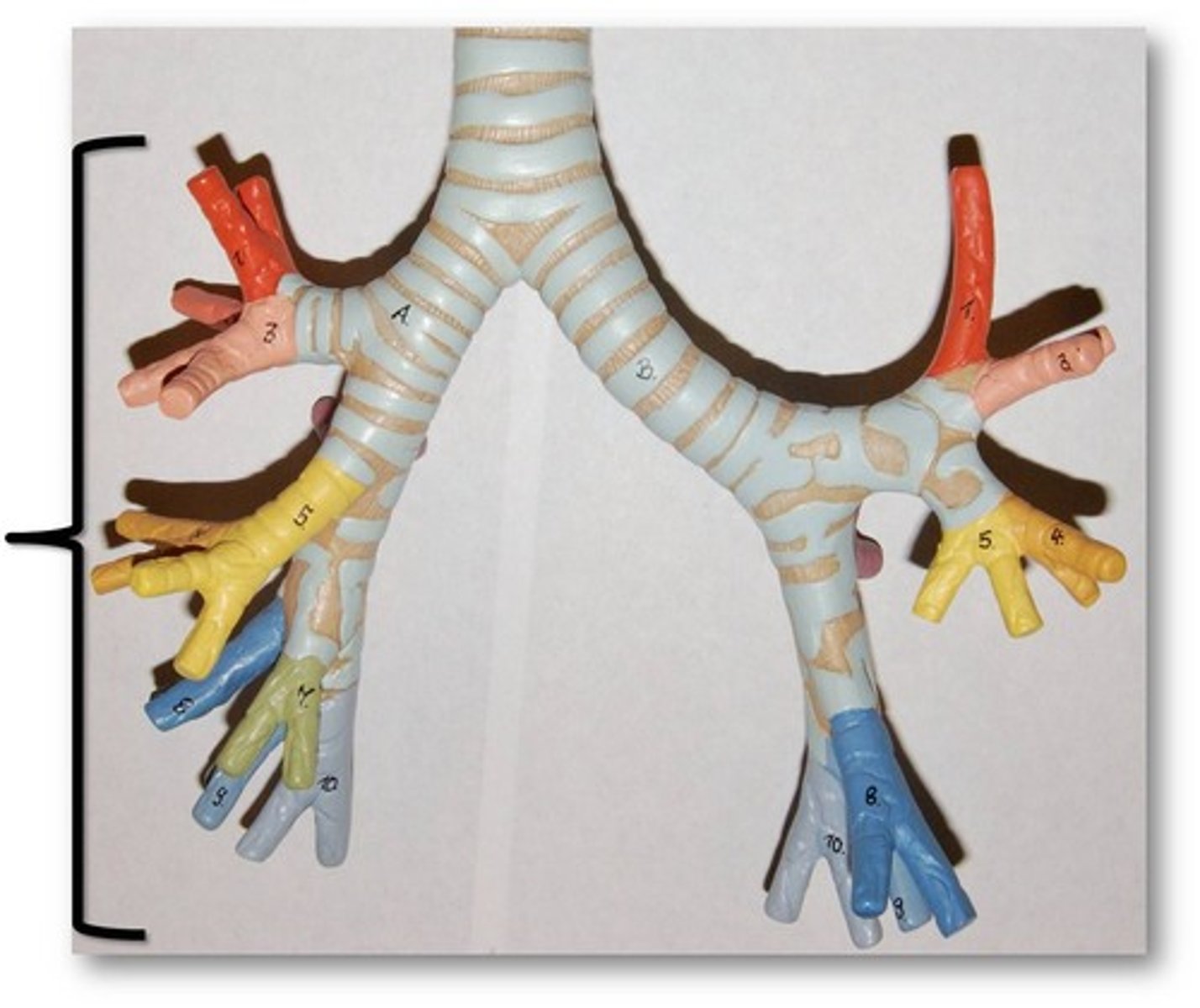
bronchus
tube connected to the trachea that branches into many subsidiaries and provides a passageway for air to enter and leave the lungs
primary bronchi
The first branches of the trachea. There are two primary bronchi, one for each lung.
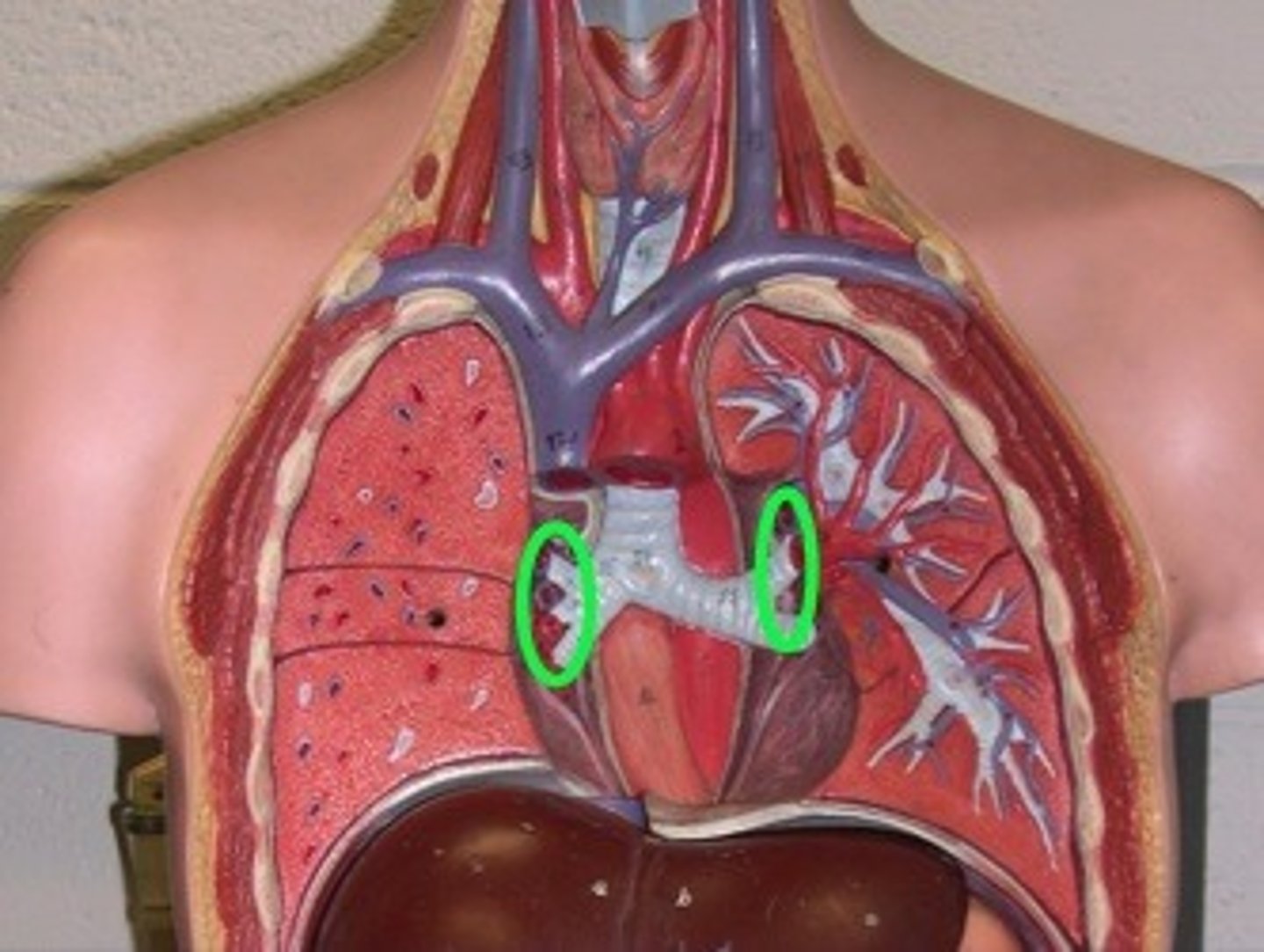
hilum
concave structure on the mediastinal surface of the lungs where blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves, and a bronchus enter the lung
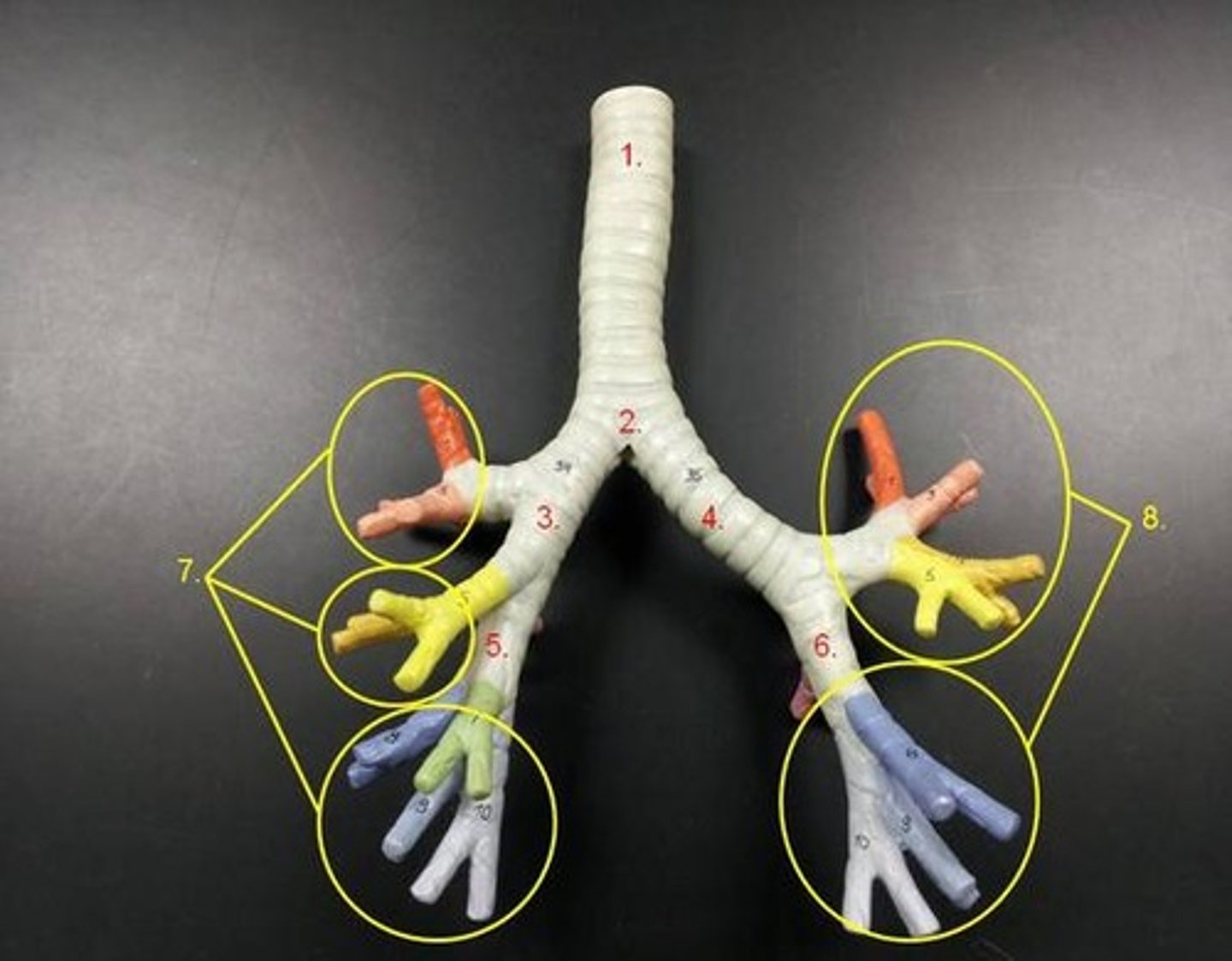
secondary bronchi
The primary bronchi split into these smaller tubes within the lungs
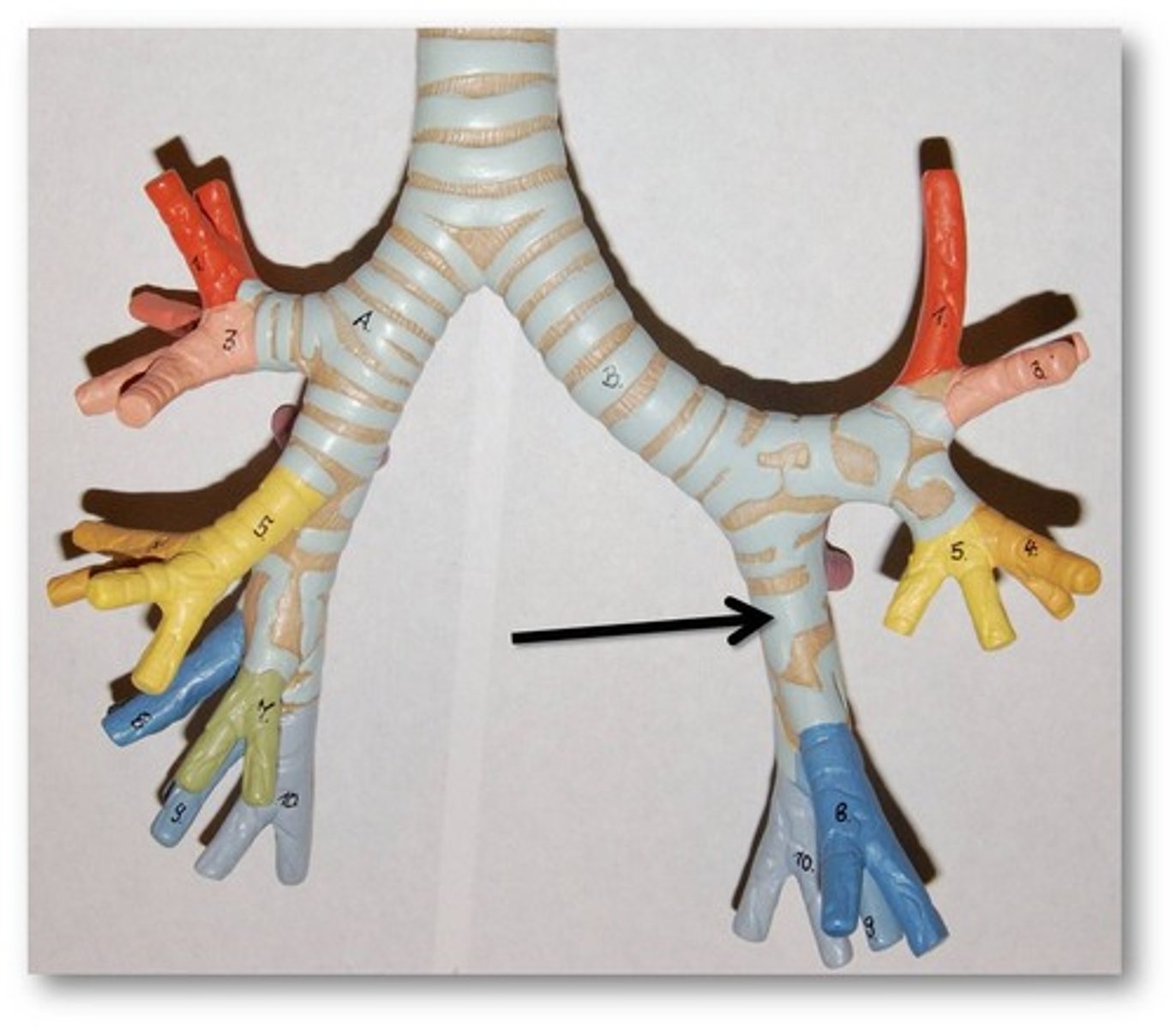
tertiary bronchi
branches of the secondary bronchi that divide into bronchioles; also called segmental bronchi
terminal bronchiole
branch of bronchi that are 1 mm or less in diameter and terminate at alveolar sacs
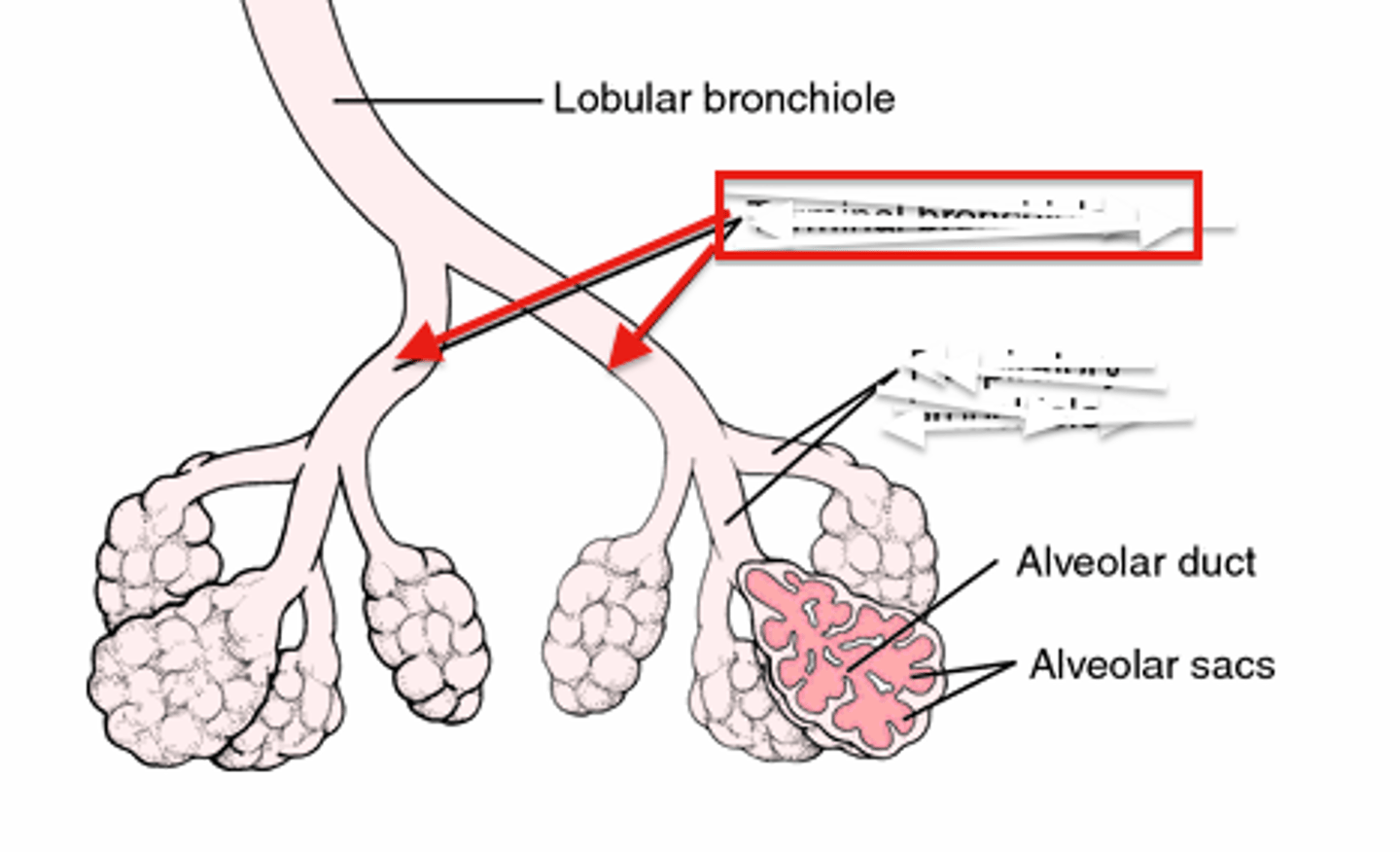
respiratory bronchiole
branches of the terminal bronchioles that subdivide into several alveolar ducts
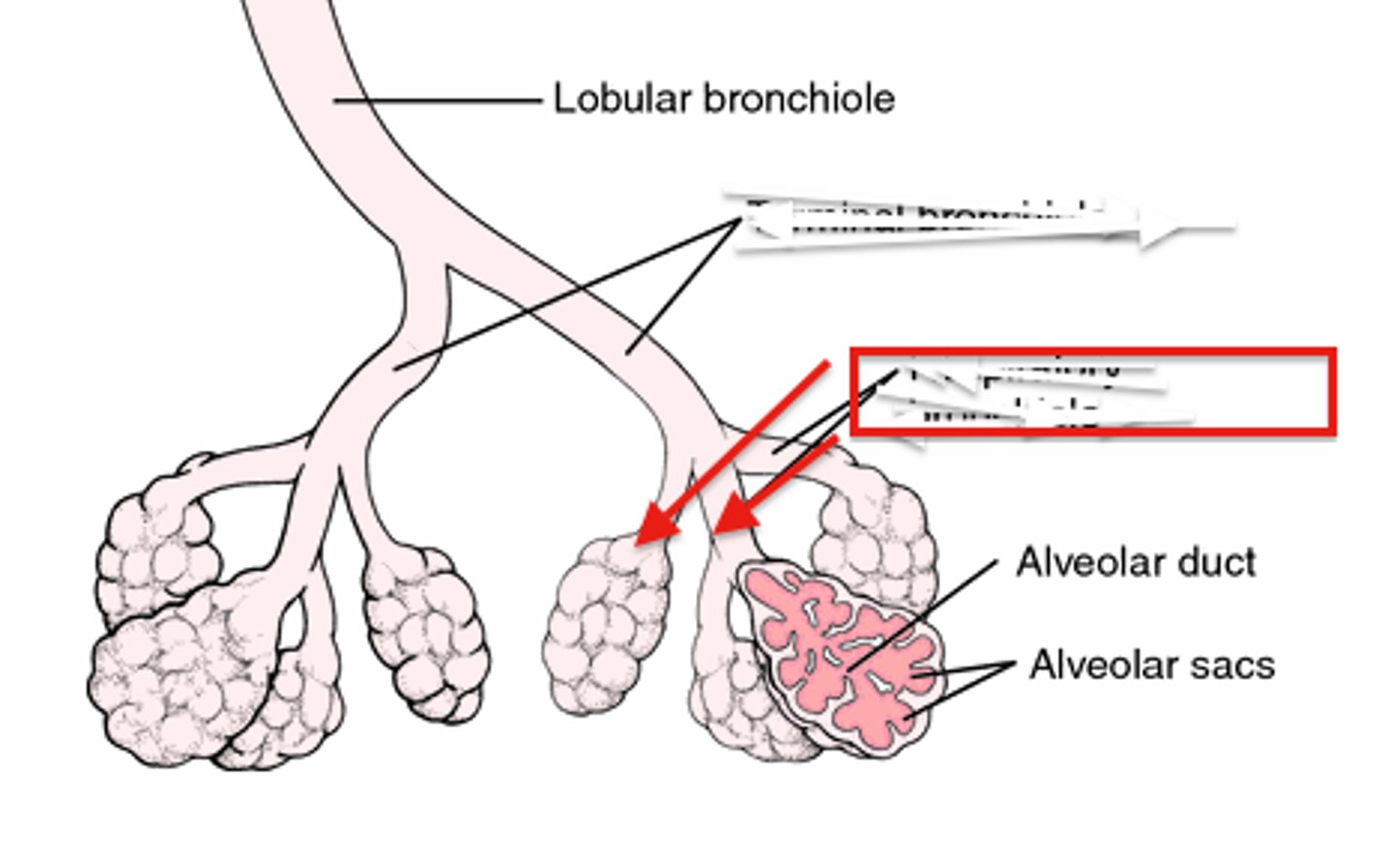
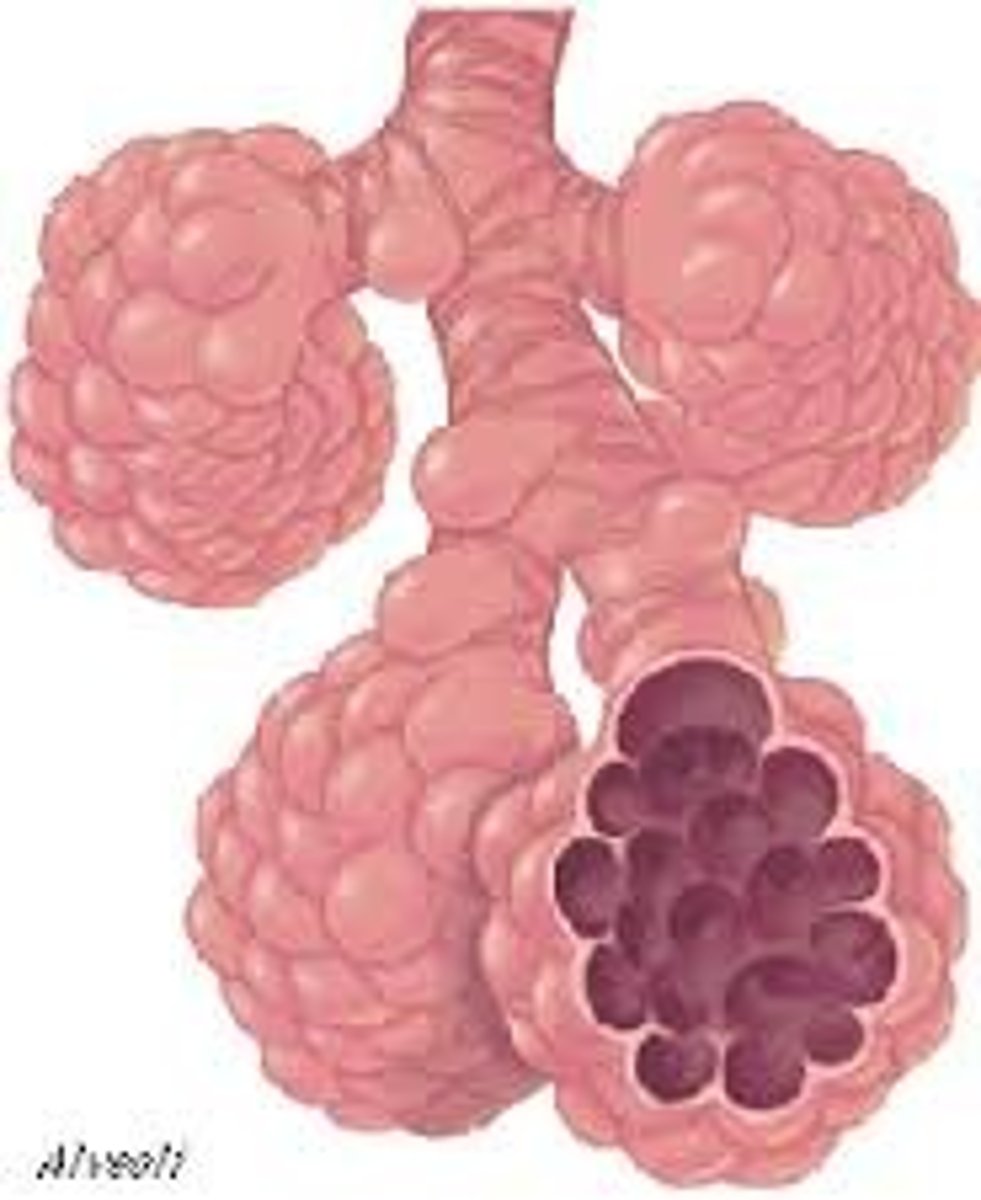
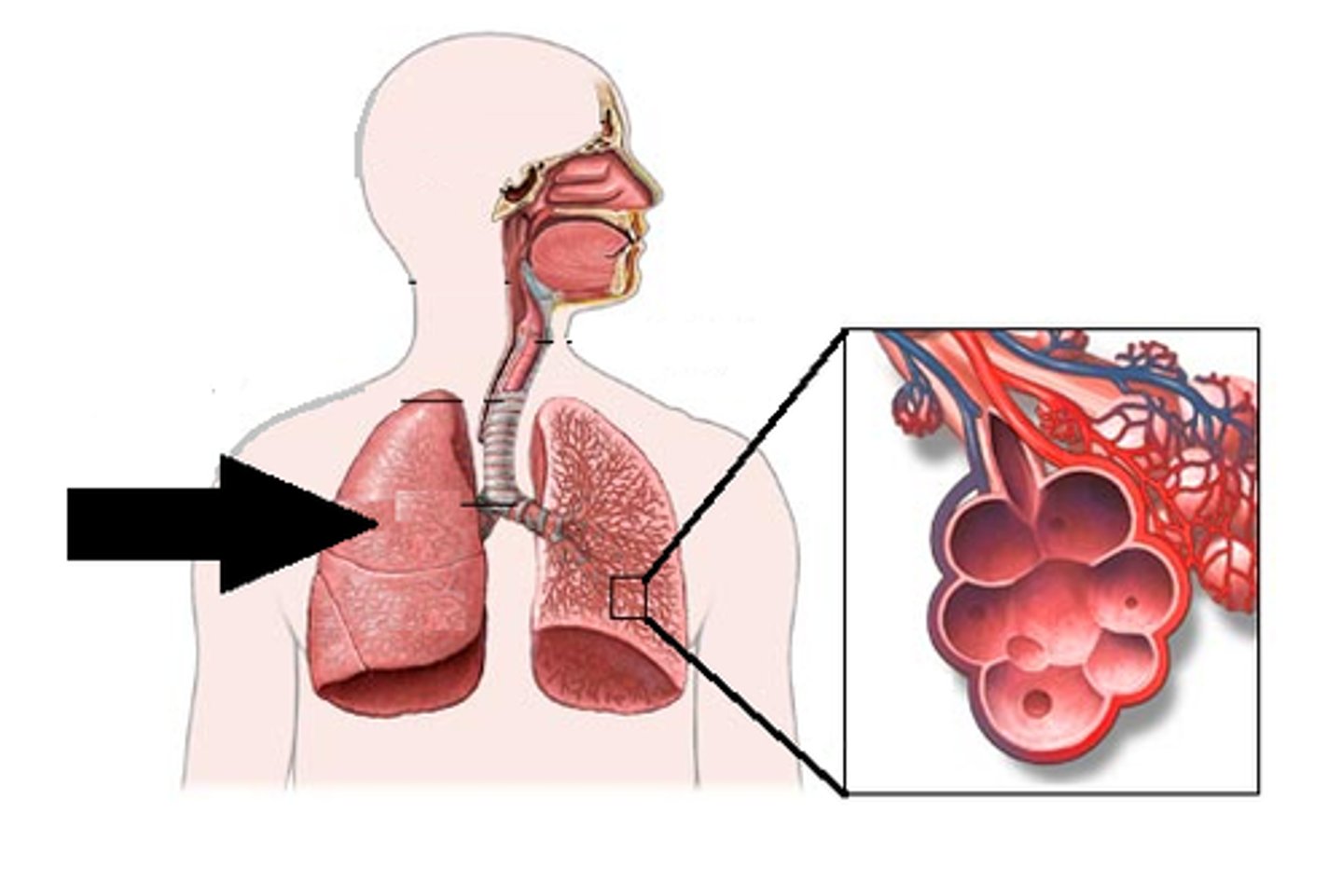
alveous
small, grape-like sac that performs gas exchange in the lungs
lung
organ of the respiratory system that performs gas exchange
lobes
smaller units that compose each lung
fissure
separates lobes in each lung
horizontal fissure
separates the superior and middle lobes of the right lung
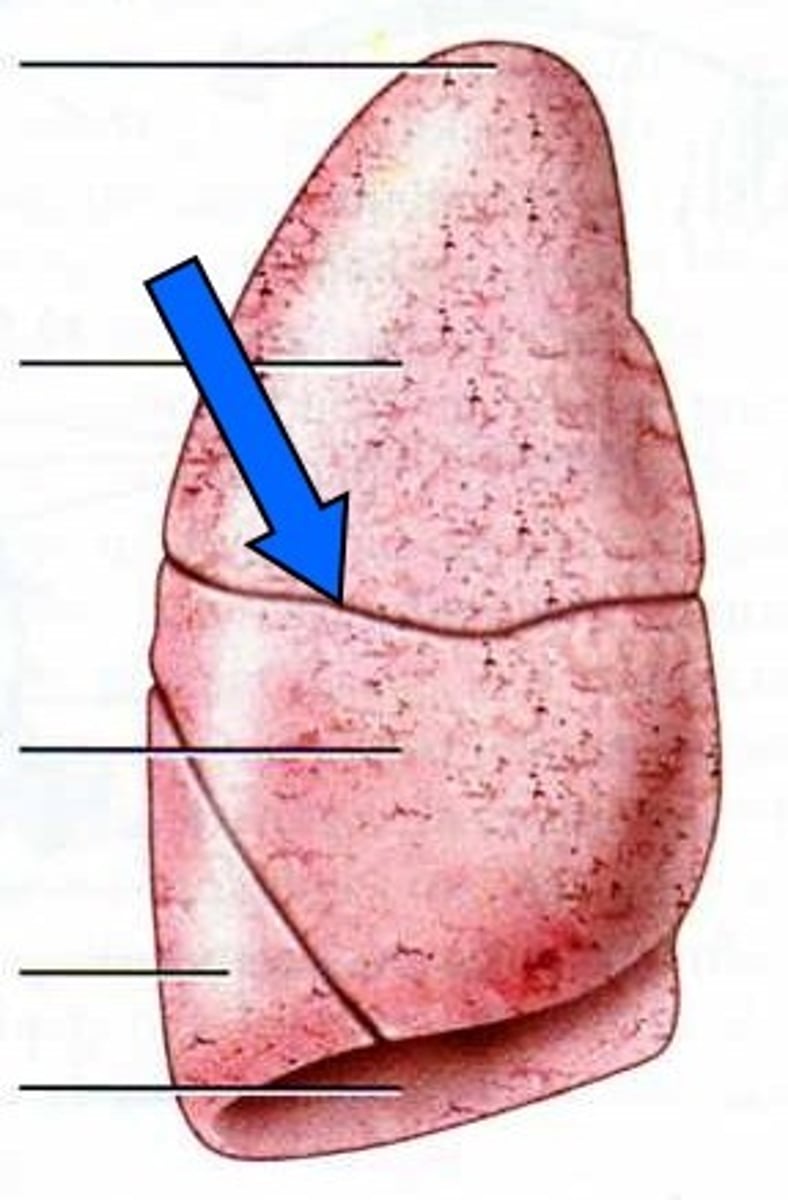
right oblique fissure
separates the right middle and inferior lobes
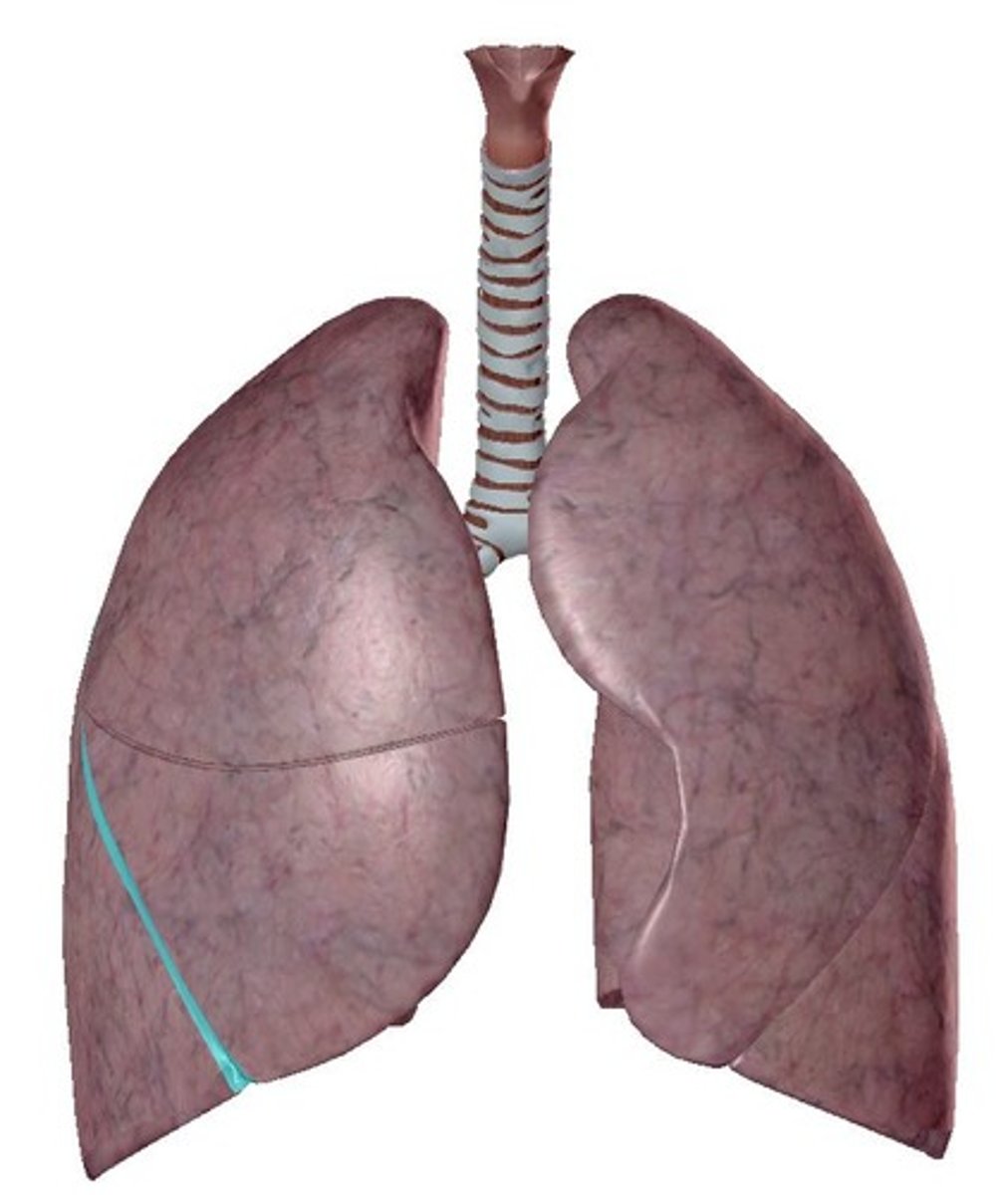
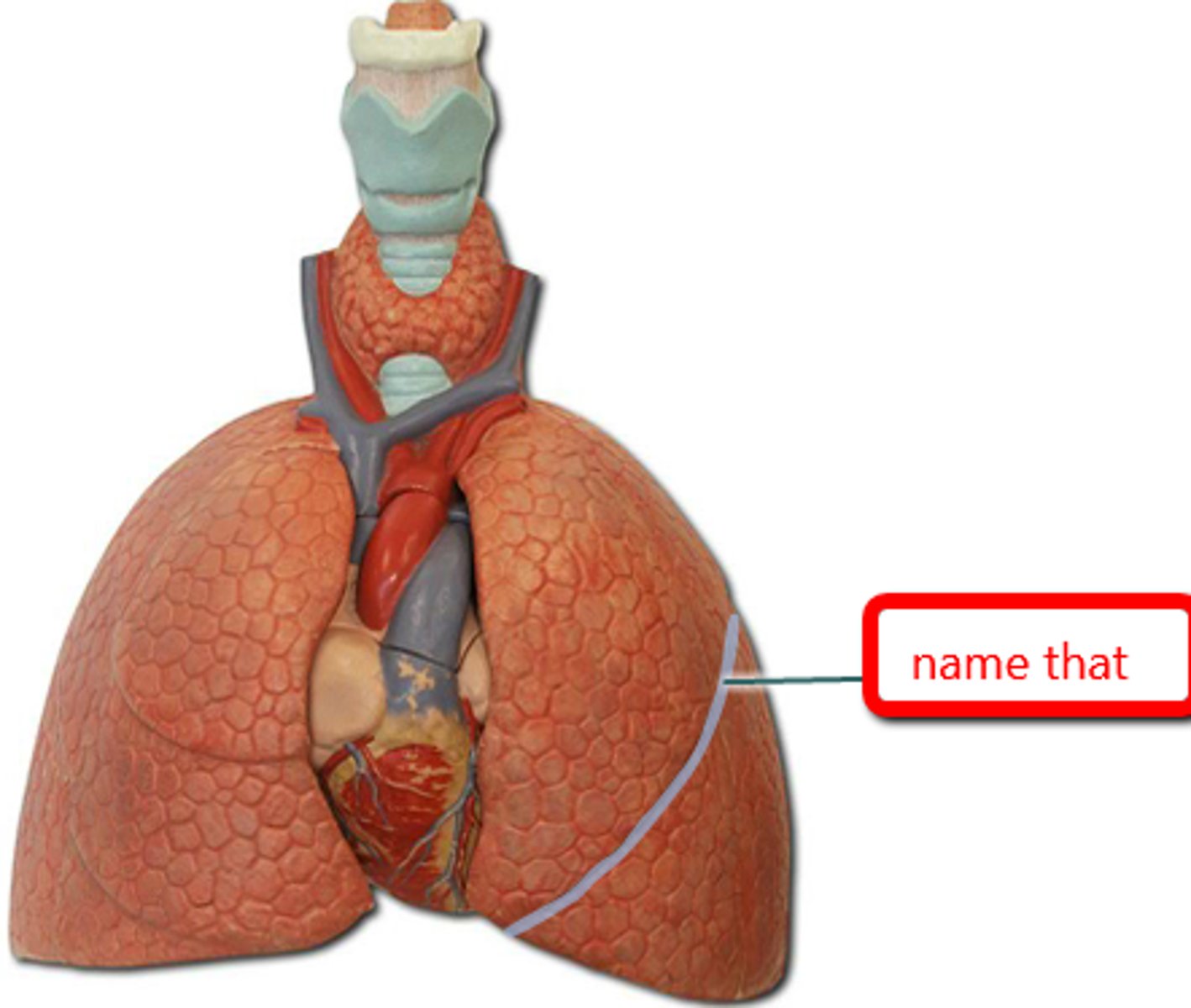
left oblique fissure
separates the superior and inferior lobes of the left lung
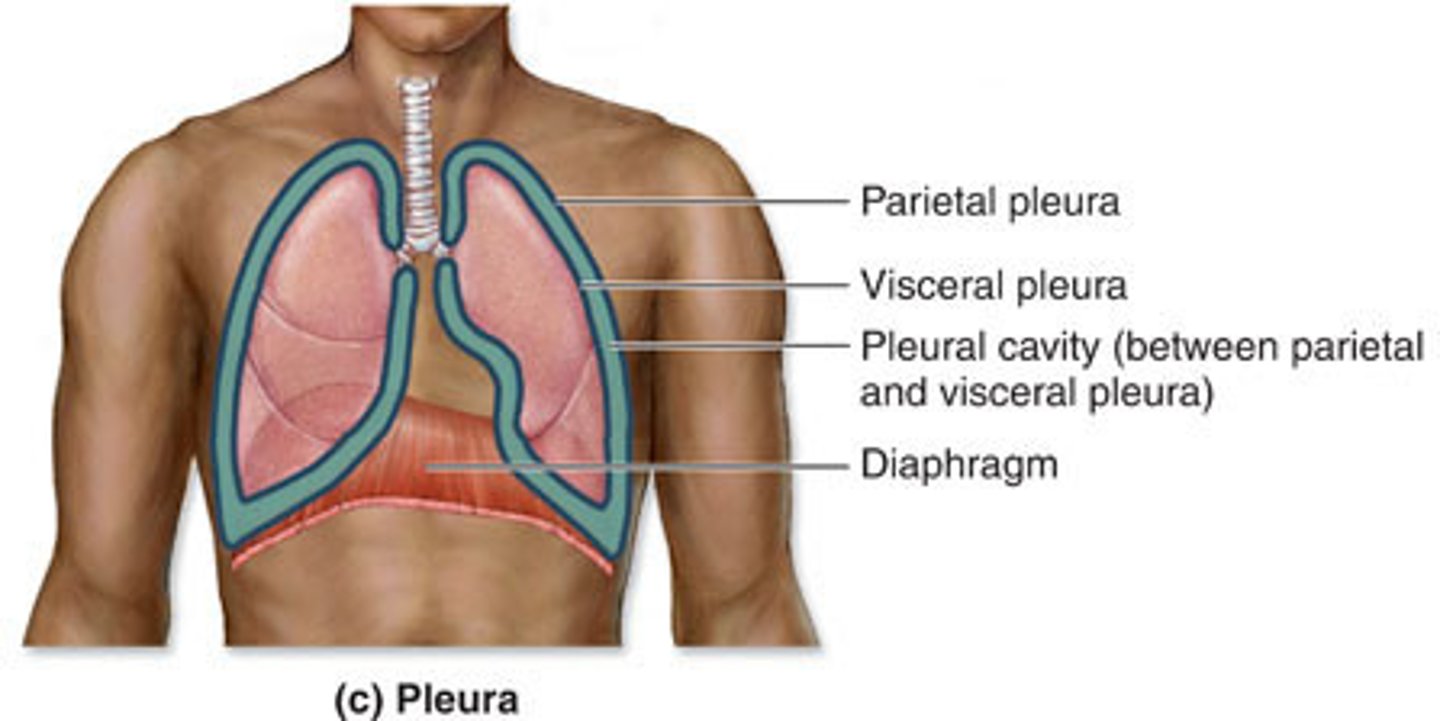
pleurae
thin, double-layered serosal membrane that divides thoracic cavity into two pleural compartments and mediastinum
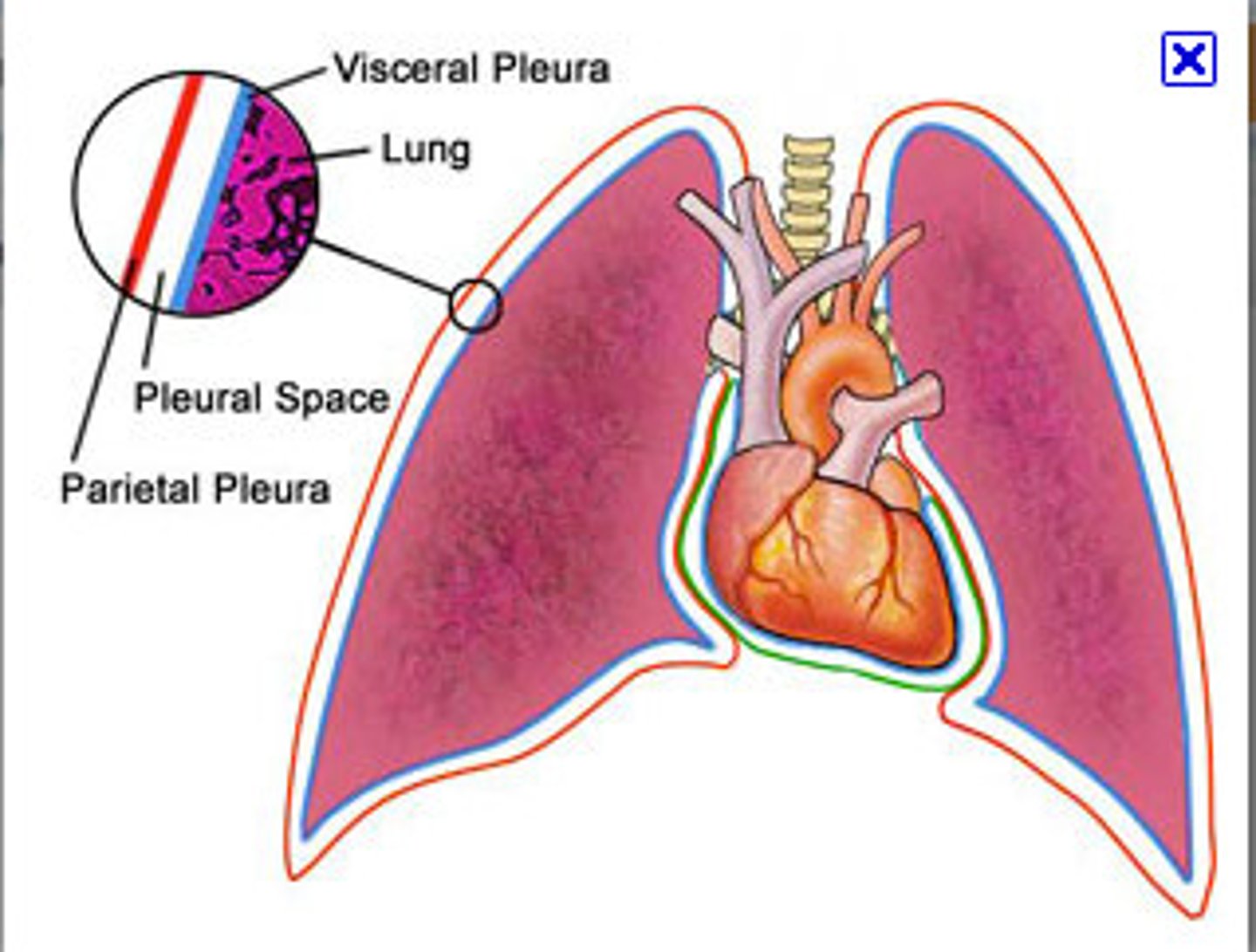
parietal pleura
outermost layer of the pleura that connects to the thoracic wall, mediastinum, and diaphragm
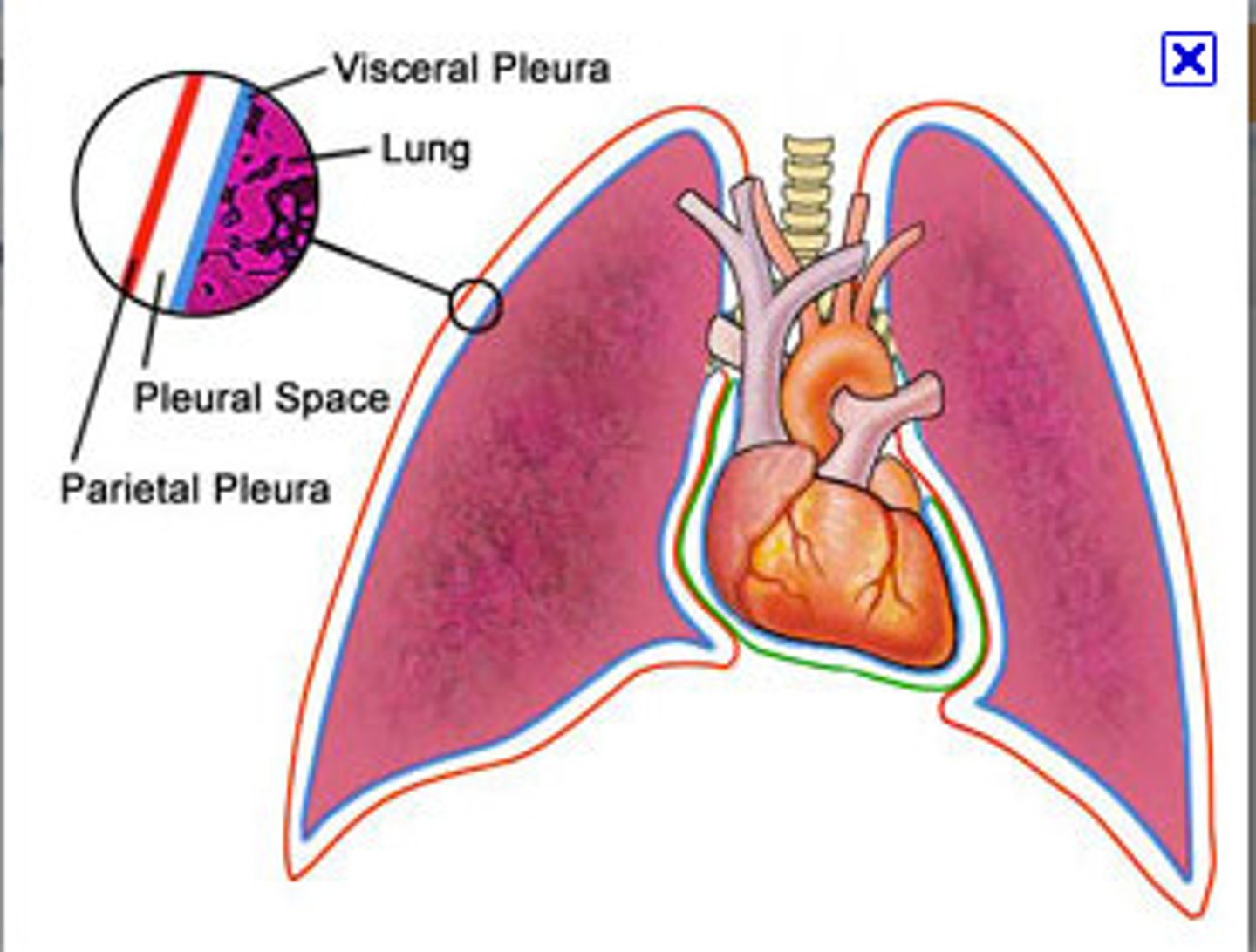
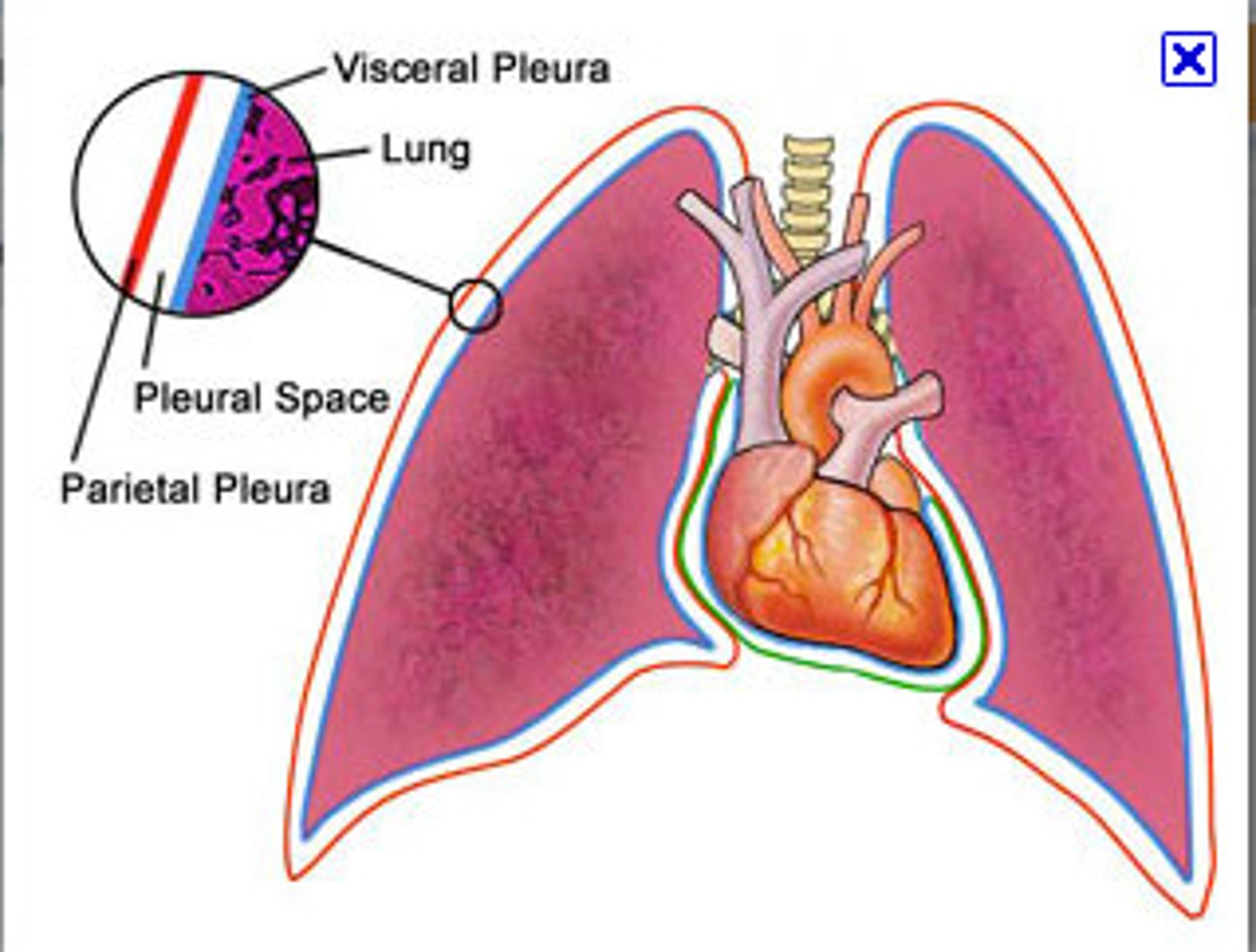
pleural cavity
space between the visceral and parietal pleurae
pleural fluid
substance that acts as a lubricant for the visceral and parietal layers of the pleura during the movement of breathing
visceral pleura
innermost layer of the pleura that is superficial to the lungs and extends into the lung fissures
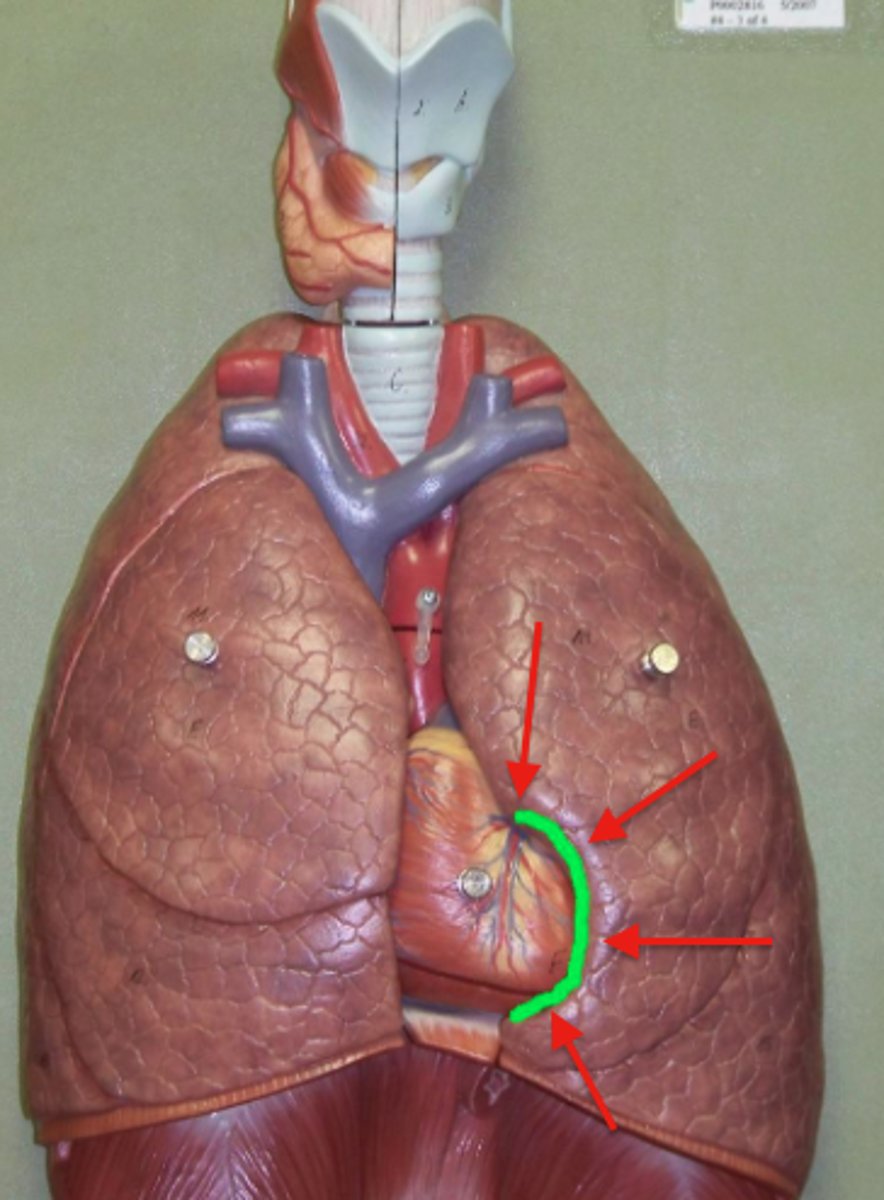
lingula
a tongue-like extension of the left superior lobe projects anteriorly over the heart

cardiac notch
a concave space on the left lung in which the heart lies
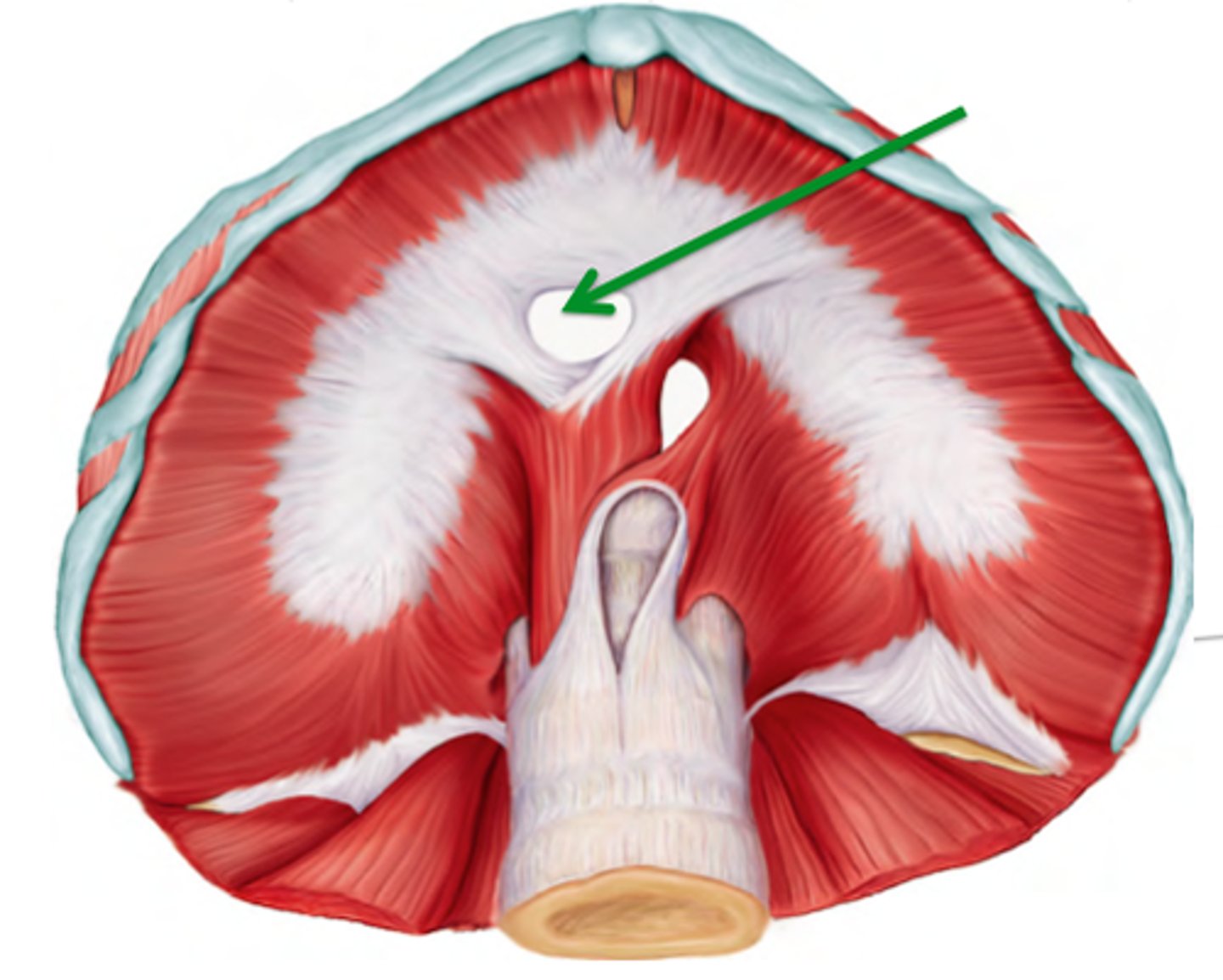
caval foramen
carries the inferior vena cava from the abdomen to the thorax to empty blood into the right atrium of the heart
Oesophageal hiatus
allows the oesophagus to enter the abdomen to empty food into the stomach
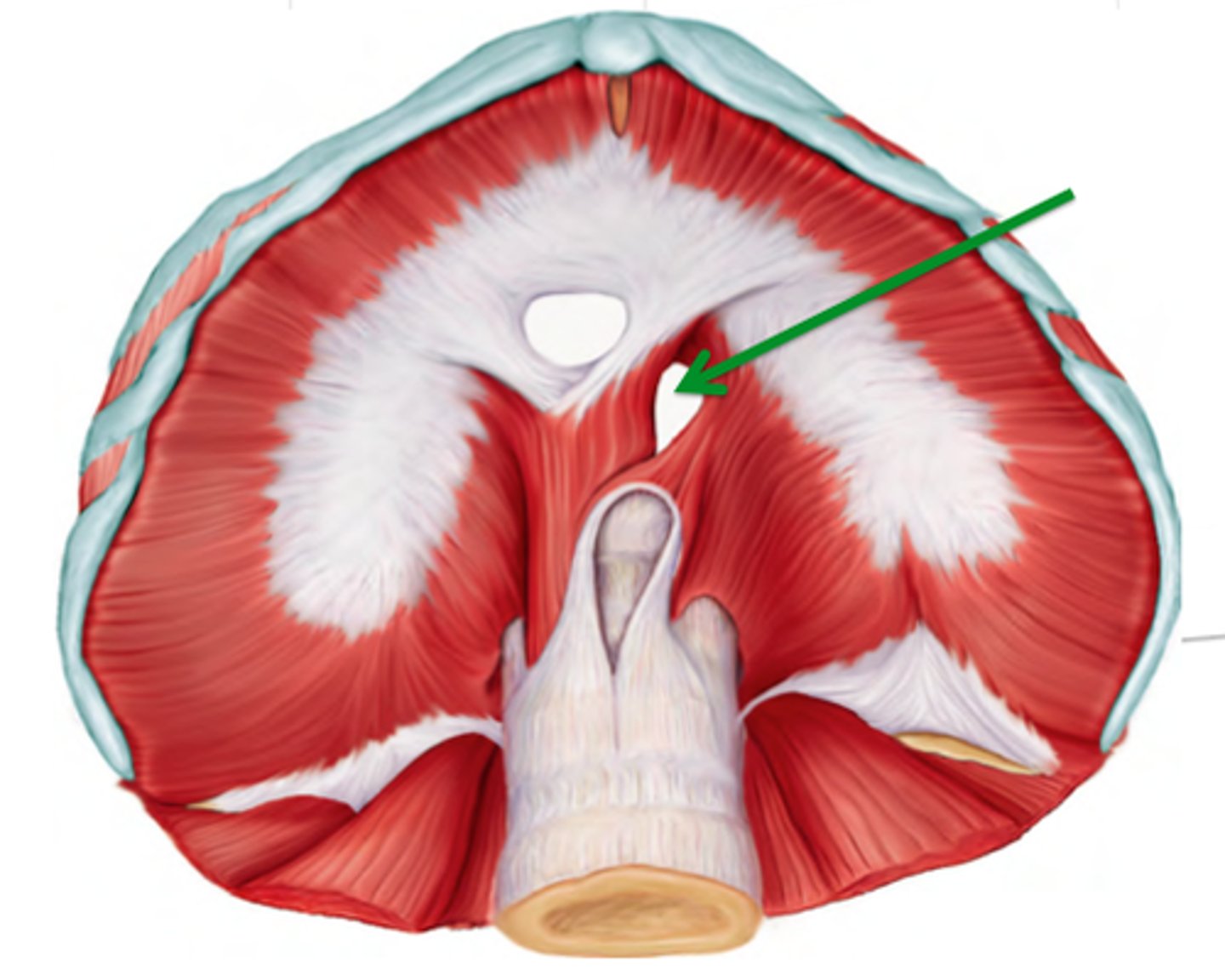
aortic hiatus
opening in diaphragm for the aorta to pass from the heart to the abdomen
Type I alveolar cells
simple squamous cells where gas exchange occurs
Type II alveolar cells
secrete surfactant